exam 2 pbsi 340
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
What are the basic properties of S-S relations?
They include potential outcomes and examples such as conditioned emotional responses, eyeblink conditioning, autoshaping, and conditioned taste aversion.
What is conditioned emotional response (CER)?
A learned emotional reaction to a previously neutral stimulus.
What is the process of eyeblink conditioning?
A learning process where a neutral stimulus (CS) is paired with an unconditioned stimulus (US) to elicit a reflexive eyeblink response.
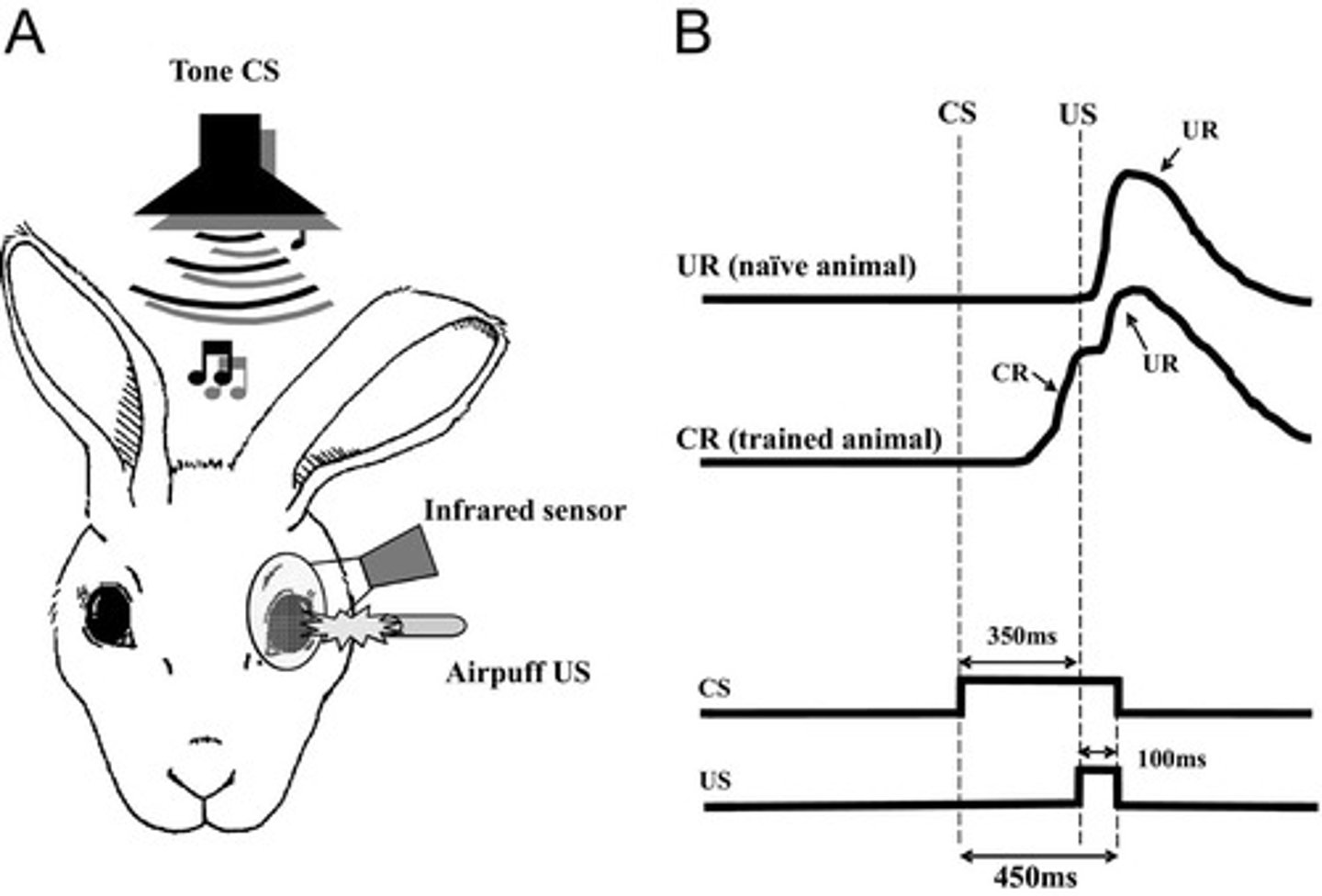
What is autoshaping?
A conditioning process where an organism learns to associate a key-light (CS) with a food reward (US), leading to a key-pecking response (CR).
What is conditioned taste aversion?
A learned aversion to a specific taste that occurs after it is paired with illness (US).
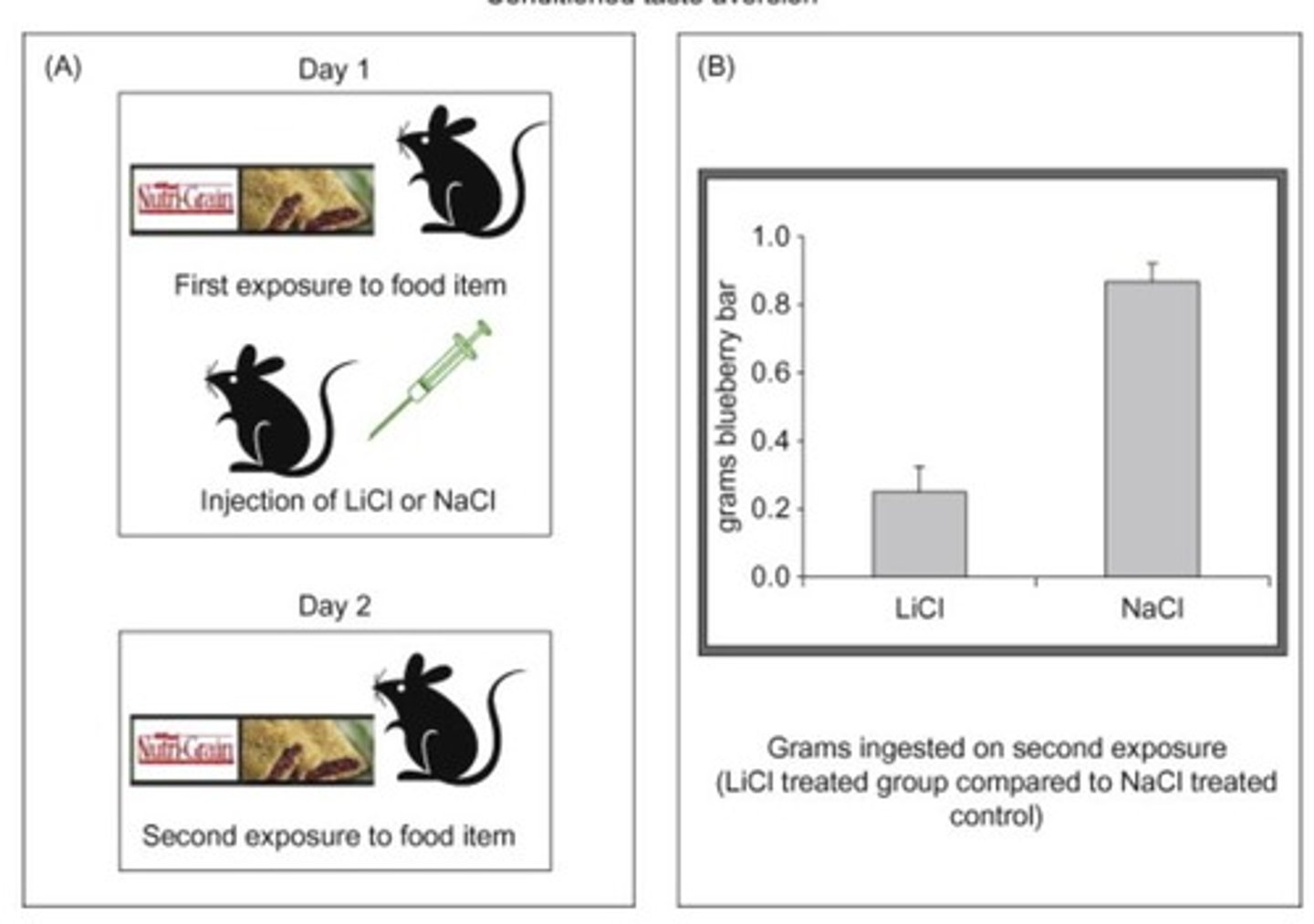
What is the significance of Little Albert's experiment?
It demonstrated conditioned fear responses through the pairing of a white rat (CS) with a loud noise (US), leading to generalization of fear to similar stimuli.
What is the McCullough effect?
A phenomenon where exposure to colored bars (CS) alters the perception of colors (US) in a subsequent test.
What are the formal properties of S-S relations?
They include criteria for inference, such as direct and indirect conditioning, and biological constraints.
What is differential conditioning?
A method of conditioning that involves presenting different stimuli to observe varying responses.
What is conditioned suppression?
A decrease in behavior due to the presence of a conditioned stimulus (CS) that predicts an aversive unconditioned stimulus (US).
What is the role of the omission control procedure?
It assesses the control of a master stimulus over the occurrence of a US, contrasting with yoked control where the US is uncontrollable.
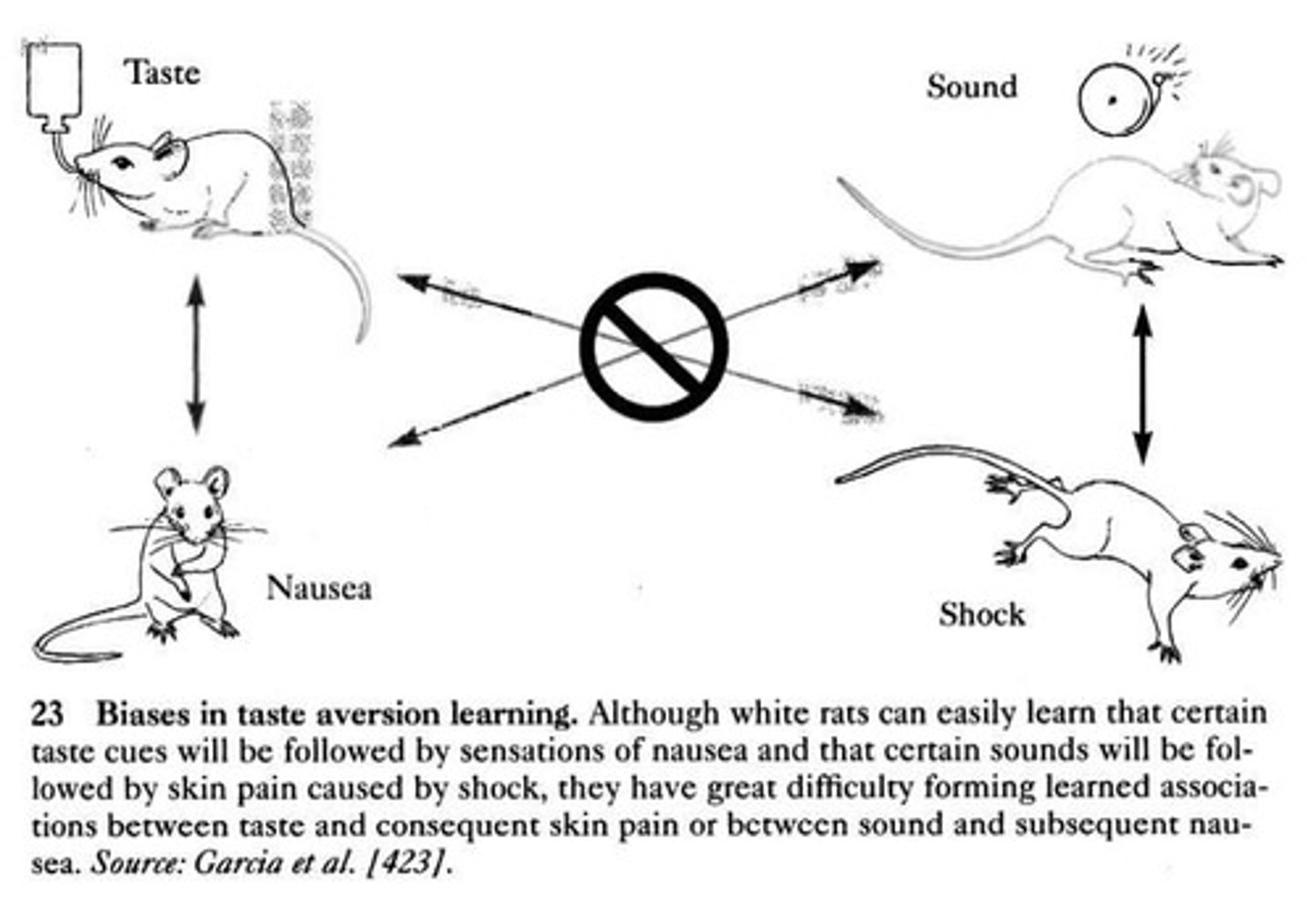
What is the significance of biological constraints in conditioning?
They limit the types of associations that can be learned, as shown in Garcia's experiments with taste aversion and radiation.
What is the summation test in conditioned inhibition?
A test that evaluates whether a conditioned inhibitor (AX-) can suppress the response to a conditioned excitor (A+).
What is the retardation test in conditioned inhibition?
A test that assesses whether a previously conditioned inhibitor can be conditioned to elicit a response after being paired with an unconditioned stimulus.
What is the difference between first-order and second-order conditioning?
First-order conditioning involves direct pairing of a CS with a US, while second-order conditioning pairs a new CS with an already conditioned CS.
What does the attentional account of learning propose?
1) That the organism has a limited attentional capacity.
2) That a CS must be attended to for learning to occur.
What is overshadowing in conditioning?
A phenomenon where a more salient stimulus overshadows the learning of a less salient stimulus when both are presented together.
What is blocking in conditioning?
A situation where prior conditioning to one stimulus prevents the conditioning of a second stimulus when both are presented together.
What are the temporal relations in conditioning?
They refer to the timing of the presentation of stimuli, including delayed, trace, simultaneous, and backward conditioning.
What is the role of the R-O relation in learning?
It examines whether the relationship between responses (R) and outcomes (O) affects the learning process.
What is the significance of the Garcia experiment?
It demonstrated that certain associations, such as taste and illness, are more readily learned due to biological constraints.
What is the role of neural plasticity in behavioral modification?
Neural plasticity allows for lasting changes in behavior based on an organism's experiential history.
What is the difference between S-S and S-R learning?
S-S learning involves the association between stimuli, while S-R learning involves the association between stimuli and responses.
What is the significance of the context in place conditioning?
The context (CS) can influence the conditioned response when paired with an unconditioned stimulus (US) like a drug.
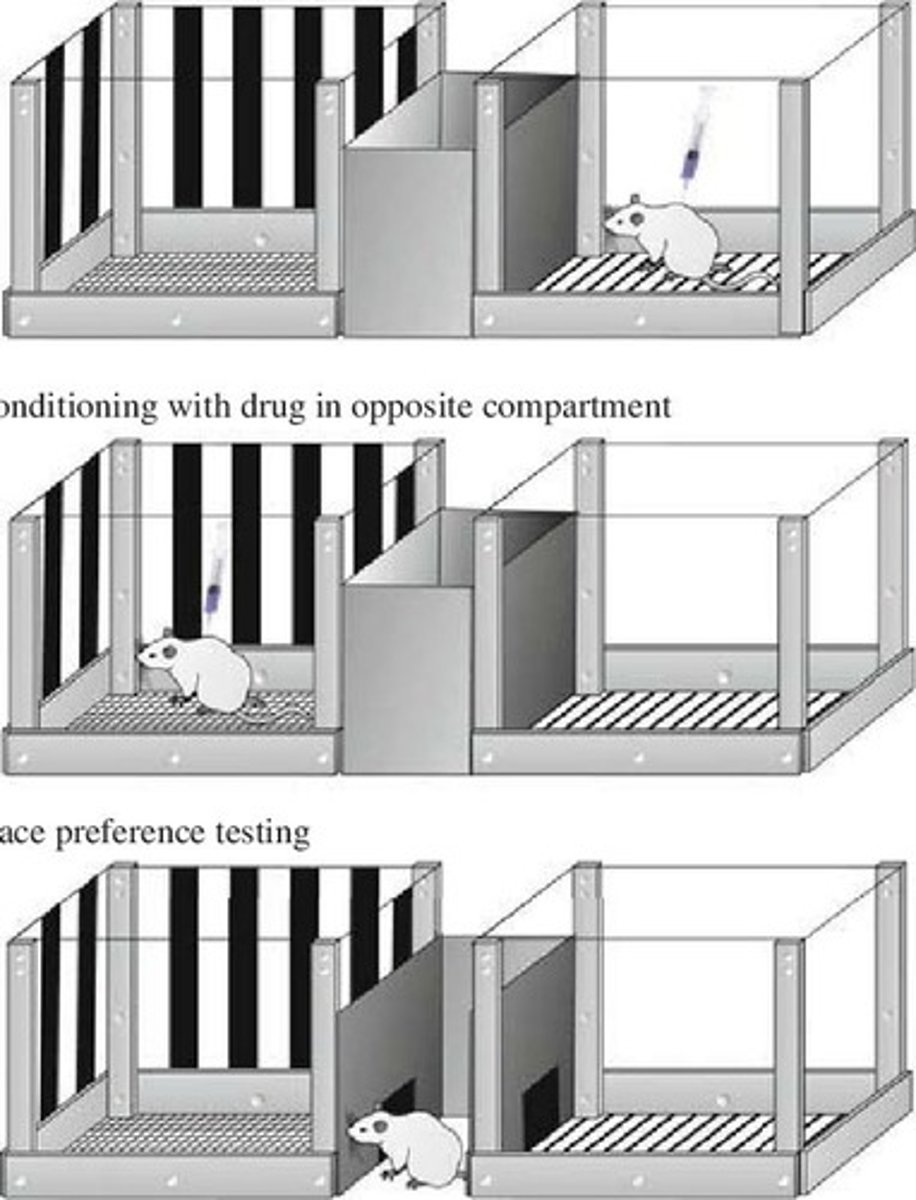
What is the concept of conditioned inhibition?
It refers to the training that engages a state opposing conditioned excitation, leading to a decrease in response.
What does p(shock | CS) > p(shock | no CS) indicate?
Conditioned excitation
What does p(shock | CS) < p(shock | no CS) indicate?
Conditioned inhibition
What is the Rescorla-Wagner model primarily used to explain?
Pavlovian conditioning processes such as acquisition, blocking, and extinction
What does λ (lambda) represent in the Rescorla-Wagner model?
The asymptote of conditioning that the unconditioned stimulus (US) can support
What is the relationship between λ and the magnitude of the US?
λ is proportional to the US magnitude
What does V represent in the Rescorla-Wagner model?
The strength of the conditioned stimulus (CS) to unconditioned stimulus (US) association
What is VT in the context of the Rescorla-Wagner model?
Net associative strength; the degree to which the US is expected, calculated as VT = V1 + V2 + ... + VN
What does (λ - VT) measure in the Rescorla-Wagner model?
The discrepancy between what the organism experienced and expected, indicating 'surprise' in learning
What does a greater discrepancy (λ - VT) imply?
A greater surprise and thus greater potential for learning
What does α (alpha) signify in the Rescorla-Wagner model?
The salience of the conditioned stimulus (CS), assumed to be between 0 and 1
What is the learning rate parameter denoted by β (beta) in the Rescorla-Wagner model?
A parameter that influences the rate of learning, also assumed to be between 0 and 1
What does ∆V represent in the Rescorla-Wagner model?
The change in associative strength on a particular learning trial
What is the formula for change in associative strength for a particular CS (A)?
∆VA = αA β (λ - VT)
What is the effect of blocking in Pavlovian conditioning?
Prior conditioning of one CS (A) prevents the learning of a second CS (X) when both are presented together
What is overshadowing in Pavlovian conditioning?
When a more salient CS (B) inhibits the learning of a less salient CS (Y) during conditioning
What happens during extinction in Pavlovian conditioning?
The conditioned response decreases when the CS is presented without the US
What is conditioned inhibition?
A process where a CS (X) predicts the absence of a US, leading to a decrease in the strength of the CS association
What is the US pre-exposure effect?
Prior exposure to the US alone impedes learning about a new CS
What is the significance of the overexpectation effect?
When two CSs (A and X) are trained to asymptote, additional training with both can lead to a decrease in their individual associative strengths
What is the outcome of the Rescorla-Wagner model during acquisition training?
The strength of the CS association increases as the organism learns to expect the US
What does the term 'net associative strength' (VT) refer to?
The total strength of all CSs presented together, influencing the expectation of the US
What does a decrement in associative strength indicate?
A reduction in the strength of the CS association, often due to extinction or conditioned inhibition
What is the role of salience (α) in the Rescorla-Wagner model?
It affects how quickly a CS can become associated with a US based on its prominence
What does the term 'trials' refer to in the context of Pavlovian conditioning?
The repeated presentations of the CS and US during the conditioning process
How does the Rescorla-Wagner model predict learning outcomes?
By calculating the discrepancy between expected and actual outcomes, guiding the adjustment of associative strengths
What is the significance of the learning rate parameter (β) in conditioning?
It determines how quickly the organism adjusts its expectations based on new experiences
What does the term 'A+' signify in Pavlovian conditioning?
A CS that is consistently paired with a US during training
What does the term 'A-' signify in Pavlovian conditioning?
A CS that is presented without the US, leading to extinction of the conditioned response
What is the effect of AX+ training in phase II on the values of A and X?
It results in a decrement in strength.
What does VT represent in the context of conditioning?
VT represents the total value, calculated as VA + VX.
What is the formula for the change in VX during training?
∆VX = ⍺Xß (𝛌 - VT).
What is the significance of Ca++ in Pavlovian conditioning in Aplysia?
Ca++ fosters the conversion of ATP to cAMP by adenylate cyclase.
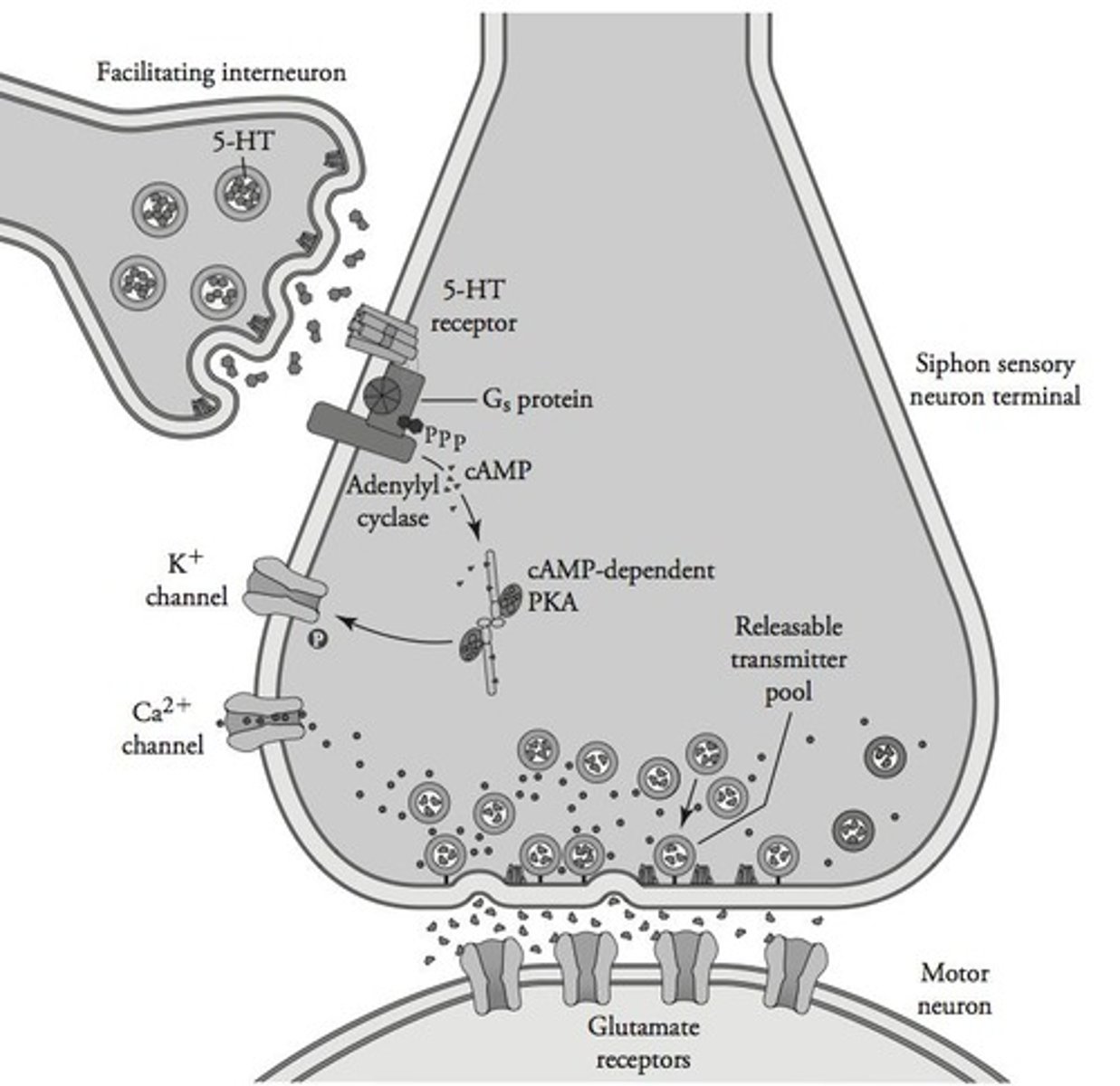
What role does engaging the sensory neuron prior to shock play in Aplysia conditioning?
It allows Ca++ to enter the cell, enhancing the conditioning process.
What is the essential neural circuit for delayed conditioning in the eyeblink paradigm?
It lies within the brainstem and cerebellum.
What are the methods used to study the cerebellum in conditioned eyeblink responses?
Methods include electrolytic and neurochemical lesions, temporary lesions, genetic lesions, and optogenetics.
What is the function of the inferior olive in the neural pathways for eyeblink conditioning?
It is part of the teaching pathway that contributes to the conditioned response.
What is the role of the amygdala in emotion and fear responses?
It is involved in processing fear and includes US and CS pathways.
What is the Rescorla-Wagner model's teaching signal modulation in the amygdala?
The teaching signal to the lateral amygdala is modulated by the vlPAG.
What does the term 'contingency effect' refer to in conditioning?
It refers to how the context (C) and conditioned stimulus (CS) interact to influence learning.
What are the two types of groups in the contingency effect study?
Random group (C+, CX+) and Informative group (C-, CX+).
What is the impact of blocking GABA with bicuculline in conditioning?
It eliminates the blocking effect in conditioning.
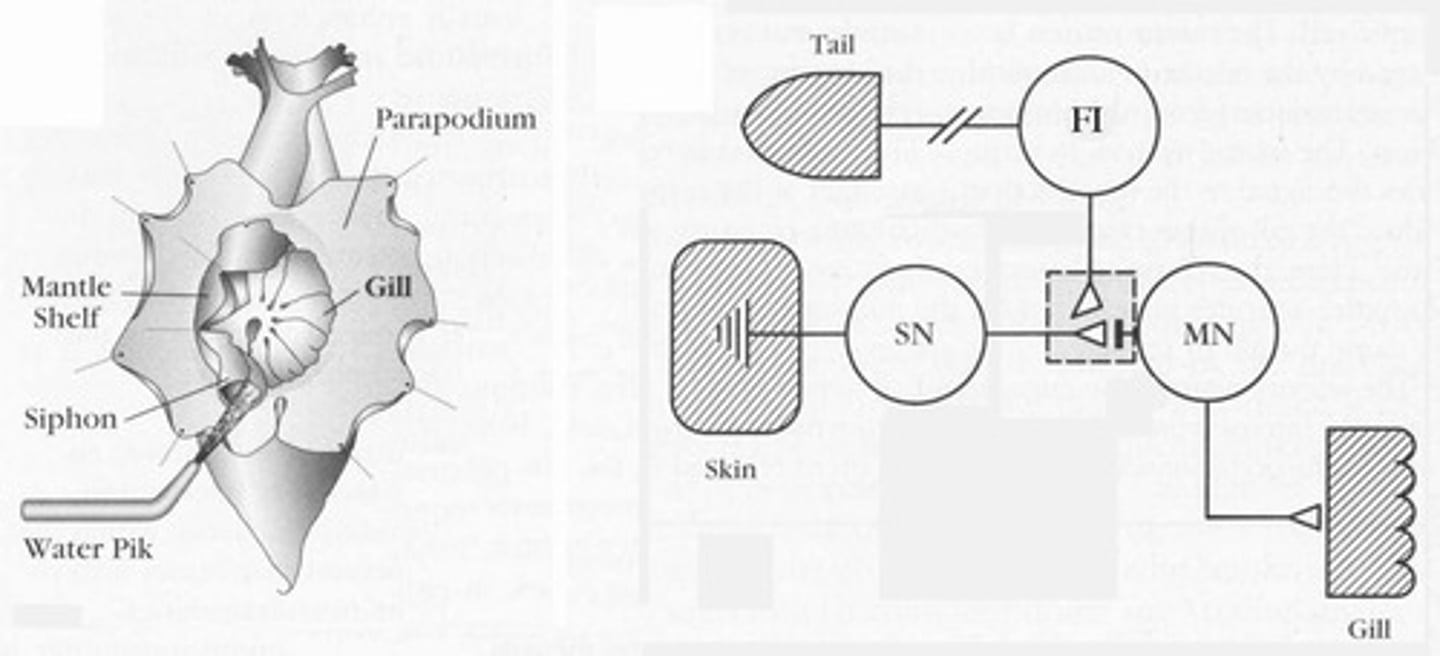
What is the significance of the magnitude of the gill withdrawal response in Aplysia?
It indicates the effectiveness of the conditioning process.
What does the term 'overexpectation' imply in the context of conditioning?
It refers to the phenomenon where the combined expectation of two conditioned stimuli exceeds the actual outcome.
What is the relationship between US pathways and CS pathways in the amygdala?
They converge within the basolateral amygdala, integrating sensory and emotional information.
What is the role of the context in the conditioning process?
The context provides a background that influences the learning and recall of conditioned responses.
What does the term 'mimicry/substitution' refer to in the activation methods of conditioning?
It refers to using electrical and neurochemical methods to replicate or substitute natural stimuli.
allodynia
touch elicits pain
pain from touch