Module 4: Section 1: structure of skeletal muscle
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
what does striated mean
a pattern of ongoing groves in parallel fashion
what is striated
skeletal muscles
what neurotransmitter innervates the muscle at the neurotransmitter
acetylcholine
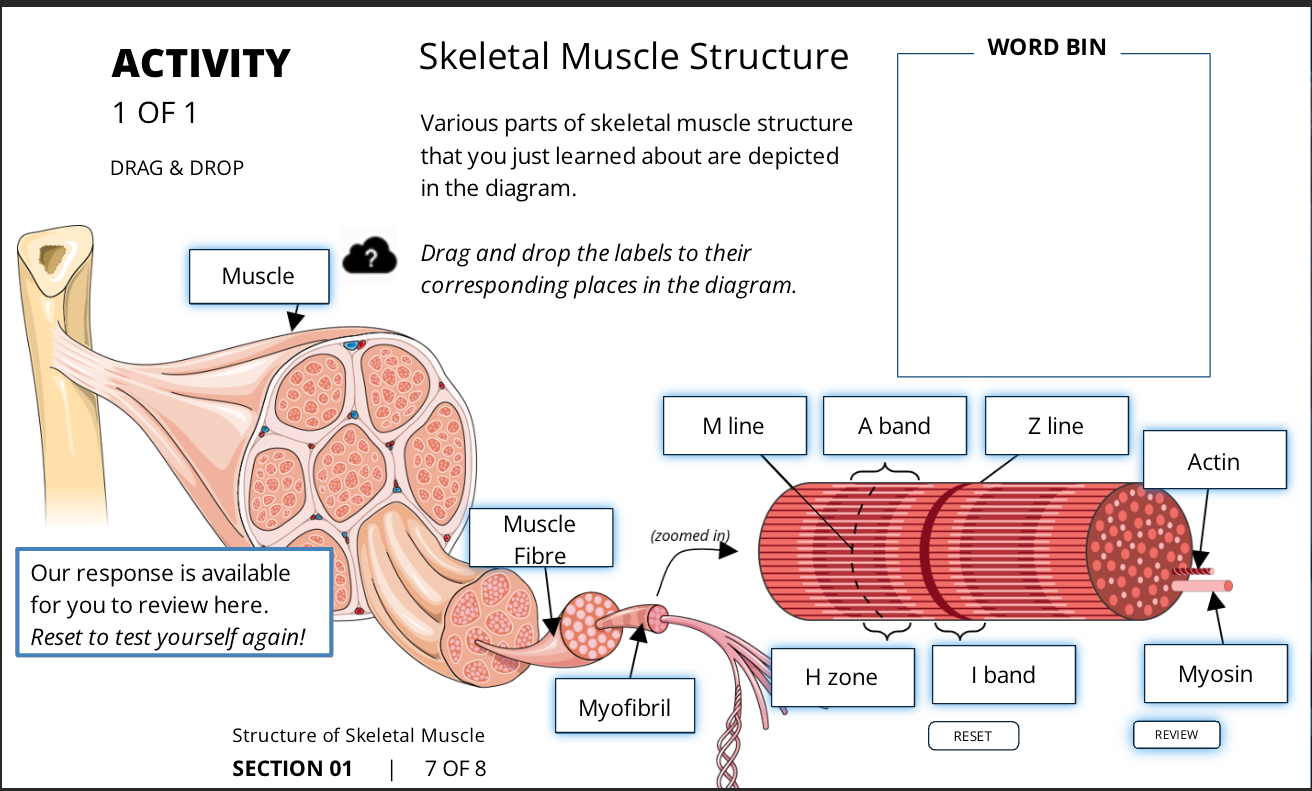
what is the fourth level of skeletal muscles
myofibrils
what is a myofibril
highly organized cytoskeletal pattern of thick and thin filaments (myosin and actin), displays a pattern of light and dark bands (makes the striated look)
what type of filament is myosin
thick
what type of filament is actin
thin
what is the second level of skeletal muscles
muscle fibre
what is a muscle fibre
fibres that run parallel to each other and are surrounded by connective tissues. A single muscle cell
what is special about muscle fibres
they have a very large number of mitochondria
what is the first level of skeletal muscles
muscle
what is a whole skeletal muscle
individual muscle fibres together that run the whole length of the mucle
what is a muscle fibre divided into
myofibrils
what is another name for A bands
dark bands
what are a bands made out of
stacked think and thin filaments that are aligned parallel to each other
how are the borders of a bands defined
by the length of the thick filaments
what is different about the middle of an a band
it is slightly lighter due to the thin filaments not making it this far from the ends
what is the lighter part of the a band called
the H zone
what is another name for an I band
light bands
what are I bands made up of
the part of the thin filaments that do not extend into the A band
what is the middle of the I band and its vertical line called
Z line
what is the H zone
the slightly lighter part of the A band
what does the H zone do
connect the thick filaments, myosin, together and hold them in a stack, only holds the heavy chains part of it
what is myosin made out of
2 heavy chains and 2 light chains
what is the M line
the proteins that hold the thick filaments together in a stacks, where the heavy chains are
what is the Z line
the vertical line found in the middle of the I band
how do Z lines help determine sacromres
the distance between each line is one whole sacromere
what is a sacromere
the functional unit of a skeletal muscle
what is the width of a relaxed sacromere
2.5 micrometers
what happens when a muscle is growing
the length of a sarcomere is growing via adding new sacromeres onto the ends
where are cross-bridges found
where in a A band that the thick and thin filaments overlap
what are cross-bridges
the connection formed when mobile myosin heads bind to actin molecules in muscles
what is myosin
a motor protein that uses ATP to move along actin filaments
what is myosin made out of
two polymers made by two molecules of monomers (two subunits), each subunit looks like a golf club
what happens when the dimers come together (with myosin)
the “shaft” of the golf club wrap around each other
what do the heads of myosin contain
a myosin ATPase site
what are thin filaments made out of
actin, tropomyosin, troponin
*main structural component is 2 actin filaments
what are actin filaments
individual spherical action molecules that come together to made a double helix
what is tropomyosin
a thin, double helix protein that is end-to-end with the actin helix.
what does tropomyosin act as
a regulatory protein that covers the active binding sites, stops interactions between actin and myosin
what is troponin
a regulatory protein complex made via 3 polypeptides
what do the 3 polypeptides do in troponin
1 binds to tropomyosin, 1 binds to actin, 1 binds to calcium
how to remember parts of the skeletal muscle structure