Term 2
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all the complicated words for Term 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Define: Percipitate
A solid formed from a change in a solution, often due to a chemical reaction.
Define: Ligand
Ligands are ions or neutral molecules that bond to a central metal atom or ion. Ligands act as Lewis bases (electron pair donors), and the central atom acts as a Lewis acid (electron pair acceptor).
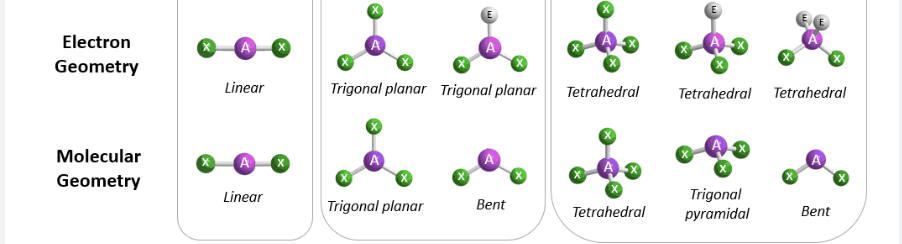
What is Electron Geometry? +its shapes
The arrangement of electron pairs around a central atom. Excludes lone pairs, BUT repulsion from lone pair(s) is taken into account in bond angles.
LINEAR, TRIGONAL PLANAR, TETRAHEDRAL
What is Molecular Geometry? +its shapes
The three-dimensional structure or arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
LINEAR, BENT, TRIGONAL PYRAMIDAL, TRIGONAL PLANAR, TETRAHEDRAL
Define: Polarity
The separation of the electric charge which leads to a molecule having a negatively charged end and a positively charged end.
What causes a molecule to be polar/non-polar?
Existence of Polar Bonds (electronegativoity)
The shape of the molecule (symmetrical can cancel out polarity)
The size of the polar portion compared to the non-polar portion.
Electronegativity
The tendency for an atom to attract electrons toward itself
Electronegativity difference (define and remember symbol)
The difference in electronegativity between two bonding atoms. It can tell us a rough measure of polarity and thus the bond type.
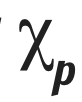
The ranges for covalent and ionic bonds (based on electronegativity difference)
0.0-0.4 Non-polar COVALENT
0.4-1.8 Polar COVALENT
>1.8 Ionic Bonding
What is a dipole moment?
The measure of the electrical polarity of a system of charges. Has a magnitude and direction.
In polar covalent bonds the more electronegative atom gets a partial negative charge 𝛅- and the less electronegative gets
partial positive charge 𝛅+
What is a net dipole moment?
The sum of vectors. Net dipole moments must be >0 for a molecule to be polar (dipole moments are always present with vectors).
Different reactions (5)
Combustion
Redox
Neutralization
Decomposition
Replacement/ Displacement/ Persipitation
Combustion
Fuel and Oxidant (O2) combust to produce CO2 and H2O (organic compounds)
Metals combust to form metal oxides
Redox
“Electrons are transferred“
Atom that loses electrons undergoes oxidation and forms a cation
Atom that gains electrons undergoes reduction and forms a anion
Neutralization
Acid and base react to form H2O and salt
Decomposition
Compounds are broken down into smaller compounds.
Replacement/ Displacement/ Precipitation
Atom/Ion get replaced for another atom/ion
Single replacement:
CuSO4 (aq) + Mg (s) → Cu (s) + MgSO4 (aq)
Double replacement:
Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + 2 KI (aq) → PbI2 (s) + 2 KNO3 (aq)
The Brønsted-Lowry Theory
A Brønsted-Lowry acid is a proton (hydrogen ion) donor
Examples of acids:
Strong acids: HCl, HNO3, H2SO4, HBr, HI, HClO4
Weak acids: All other acids, such as HCN, HF, H2S, HCOOH
A Brønsted-Lowry base is a proton (hydrogen ion) acceptor
Examples of bases:
Strong bases: The hydroxides of the Group I and Group II metals such as LiOH, NaOH, KOH etc.
Weak bases: All other bases, such as NH3, CH3NH2, C5H5N
Limiting reactant
Reactant which runs out first and thus determines the max amount of the product.
n (excess) = n(total) - n(used)
Types of yield:
Theoretical yield, Actual yield, Percentage yield
Titration
The slow addition of a known amount of a substance with a known concentration (titrant) to a known amount of another substance with an unknown concentration
Equivalence point
When the amount of titrant is equal to the amount of analyte according to the mole ratio in the balanced reaction equation.
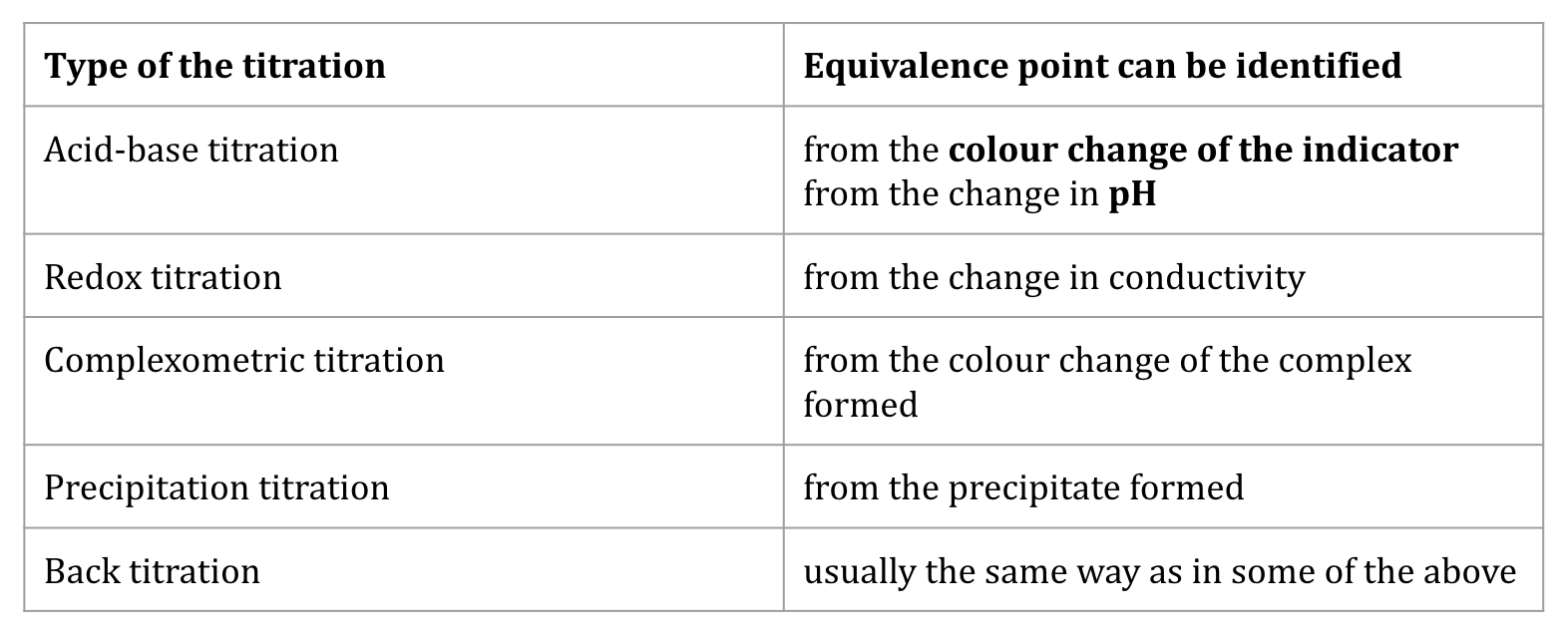
Types of Titration
Acid-Base (change in pH seen by the indicator color change)
Redox (change in conductivity)
Complexometric (color change of complex formed)
Percipitation (percipitate formed)
Back
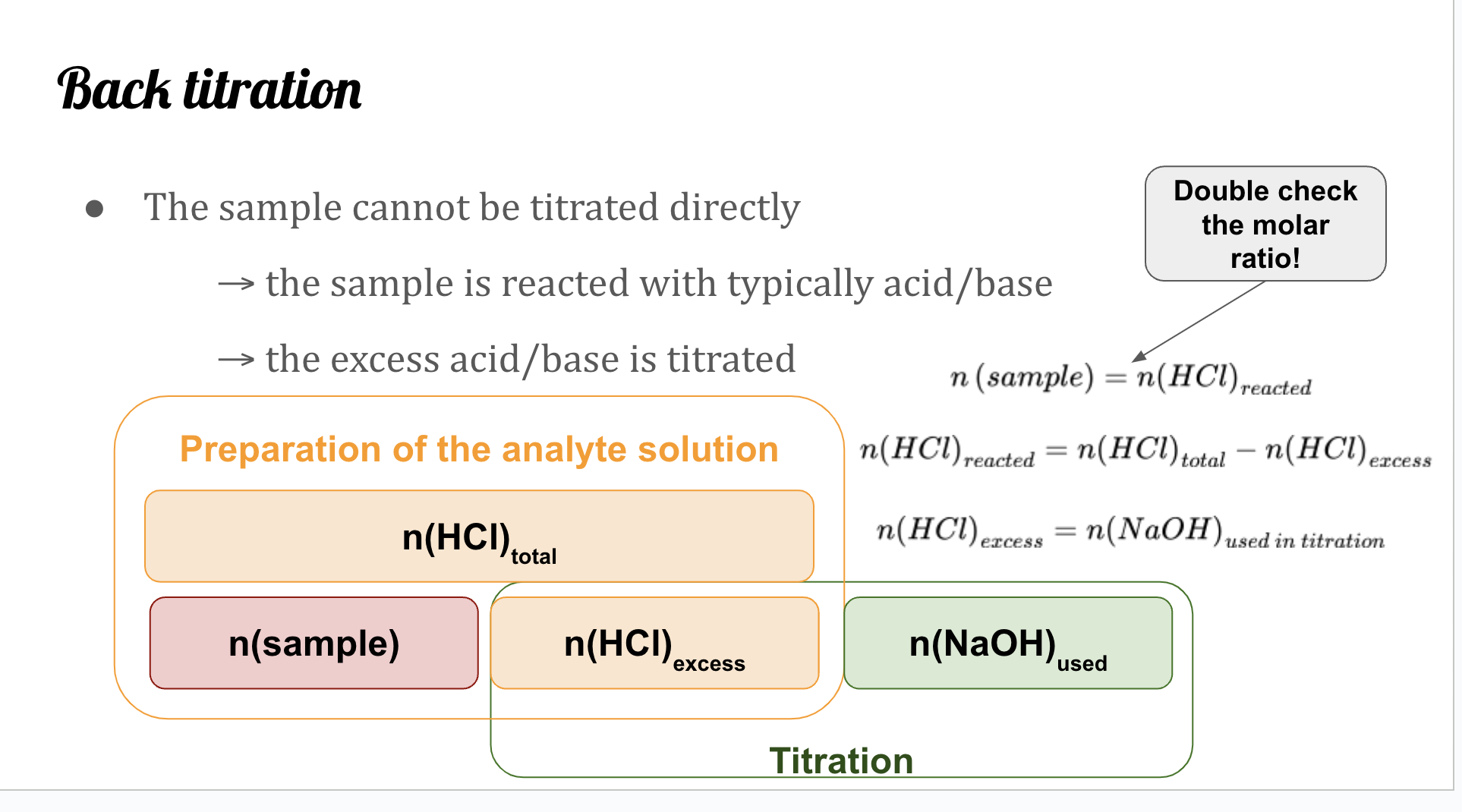
Back titration
When a sample cannot be titrated directly.
Excess acid is titrated
Green chemistry principles
Prevent!
Atom economy
Less hazardous and safer chemicals in synthesis;
Reactants, products, by-products and solventsEnergy efficiency
Renewable feedstock
Recycling of chemicals
Analysis and real-time monitoring of pollutants
Atom economy
measure of efficiency of a reaction. Based on the singular molar mass of a chosen product against the combined molar mases of all starting materials, catalysts and solvents used in the reaction:

VSEPR theory
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory components
When a molecule is formed, the outer shell electrons repel each other
The molecule takes the shape which minimises the repulsion between
electron domainsElectron domain
= the region in which electrons are
most likely to be found. Bonding pairs, lone pairs,
single, double, and triple bond represents
each one region of an electron domain.
immiscible
(of liquids) not forming a homogeneous mixture when mixed.
volatility
How readily a substance vaporizes.
The more non-polar, the more volatile because non-polar substances tend to have weaker intermolecular forces.
Metals
high m.p and b.p
solid at room temp
conductive (heat + electricity)
Shiny, Hard
High desnity
Ductile/Malleable
Metallic bonding
Strong electrostatic attraction between metal cations & delocalized elctrons
why are metals shiny:
Electrons absorb photons and then reflect them out. They absorb the light energy and emit them back out.
Why are metals malleable
The layers of atoms can slide over each other without breaking the metallic bond. This is because the delocalized electrons allow atoms to move freely.
Why are metals conductive
The delocalized electrons can carry a charge and also move around and conduct heat.
Charge density definition
Charge density is the measure of electric charge per unit volume or area in a given space, indicating how concentrated the charge is within that region.
What affects the charge density
The charge and radius of metal cations.
Ionic bonding
Formed between a metal and a non-metal. Strong electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions (+ and -).
Coordination number
The number of nearest neighboring atoms or ions surrounding a central atom in a coordination complex (AKA Lattice).
Lattice Enthalpy definition
The heat energy needed to break ionic lattice. the magnitude depends on the charges of the ions and the distance between them.
-Greater charge, greater electrostatic attraction, greater Lattice Enthalpy
-Larger radius, greater separation of charge, smaller Lattice Enthalpy
properties of Ionic molecules:
High m.p. and b.p
Solids at room temp →hard
Form crystal lattice
Dissolve in polar substances (like dissolves like)
Conducts electricity in molten or aqueous states. (electrolytes)
Low/non-volatile
Why do ionic substances condusct electrity in aqueous states?
Electrostatic attractions hold anions and cations in definite positions bin solid form while in aqueous form, ions are free to move and carry electric charges
What is a ion-dipole bond?
A type of intermolecular force that occurs between an ion and a polar molecule, where the positive or negative charge of the ion interacts with the partial charges on the polar molecule.
What is covalent bonding
The sharing of electron pair(s). It’s a strong electrostatic attraction between electrons and positively charged nuclei.
occurs in non-metals.
neutral compounds (=no charge) with covalent bonds are called molecules.
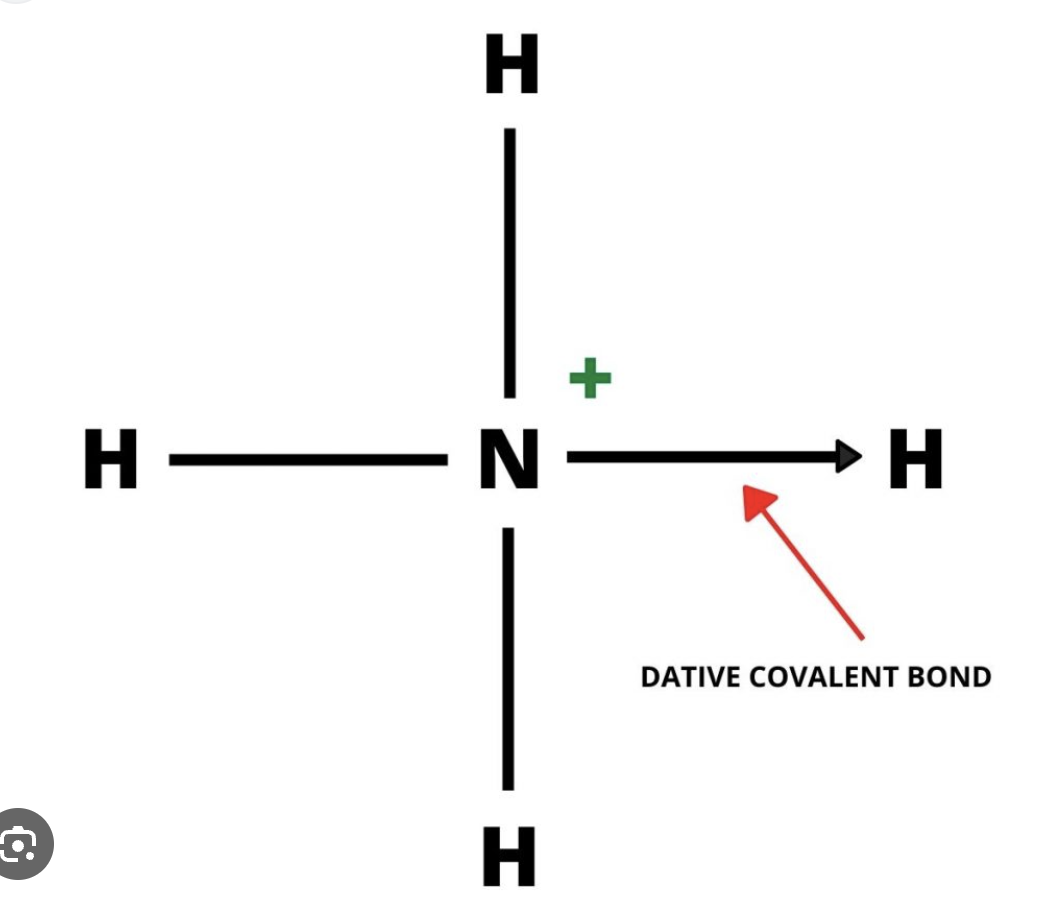
What is coordinate or diative covalent bonding
in some molecules and plyatomic ions, both electrons shared are from the same atom.
(arrow points to reciever)
properties of covalent compounds
Low m.p and b.p.
Solids, liquids, or gases at room temp
Do not conduct electricity
Dissolve in non-polar substances
What is Green chemistry?
The area of chemistry that focuses on the design of chemical products or the processes that reduce or eliminate the use or generation of hazardous substances
What is Atom economy?
Measure of the efficiency of a reaction. (M of one product compared with combined M of all starting materials, catalysts, and solvents)
Bond order
#Bonding pairs between two atoms
greater bond order=stronger bond and shorter bond length
Bond enthalpy
Amount of energy needed to break a covalent bond
Giant covalent structures
the atoms are bonded by covalent bonds in a continuous network
the entire crystal may be considered as a one giant macromolecule
→ atomic lattice
→ Much higher boiling points!