CSD200 Midterm Review
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
What is the function of the articulatory system?
Serves as filter for the phonatory source to shape the sounds of speech
Moveable articulators (Lick Monkeys Very Tender, Cheeky Pharaoh!)
Lips, mandible, velum, tongue, cheeks, pharynx
Immobile Articulators (Alvin Really Hates Painting Tables)
Alveolar ridge of maxillae, hard palate, teeth
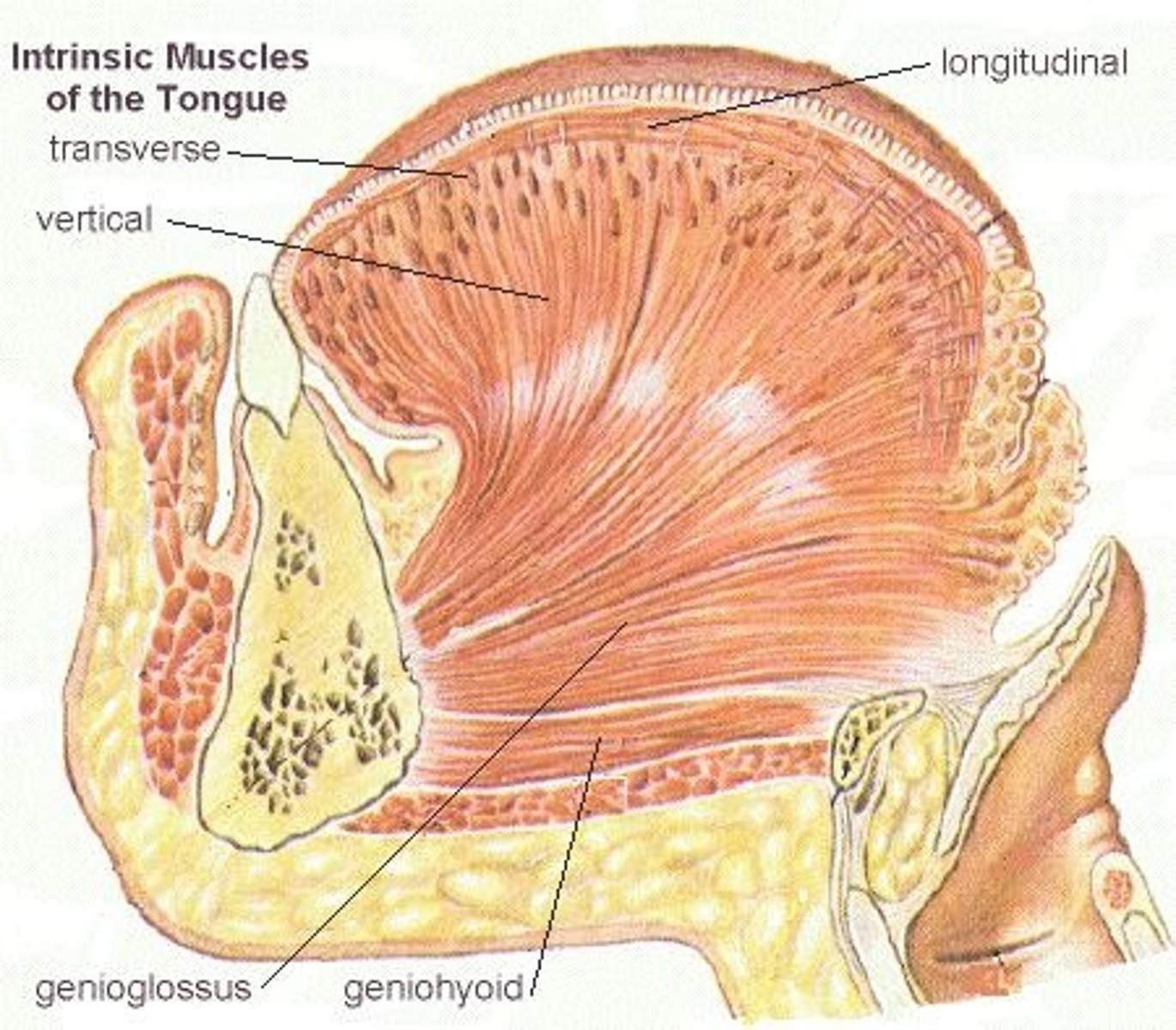
Intrinsic vs extrinsic tongue muscles
intrinsic: tongue muscles are entirely within the tongue, change its shape
extrinsic: tongue muscles attach the tongue to other structures, control position
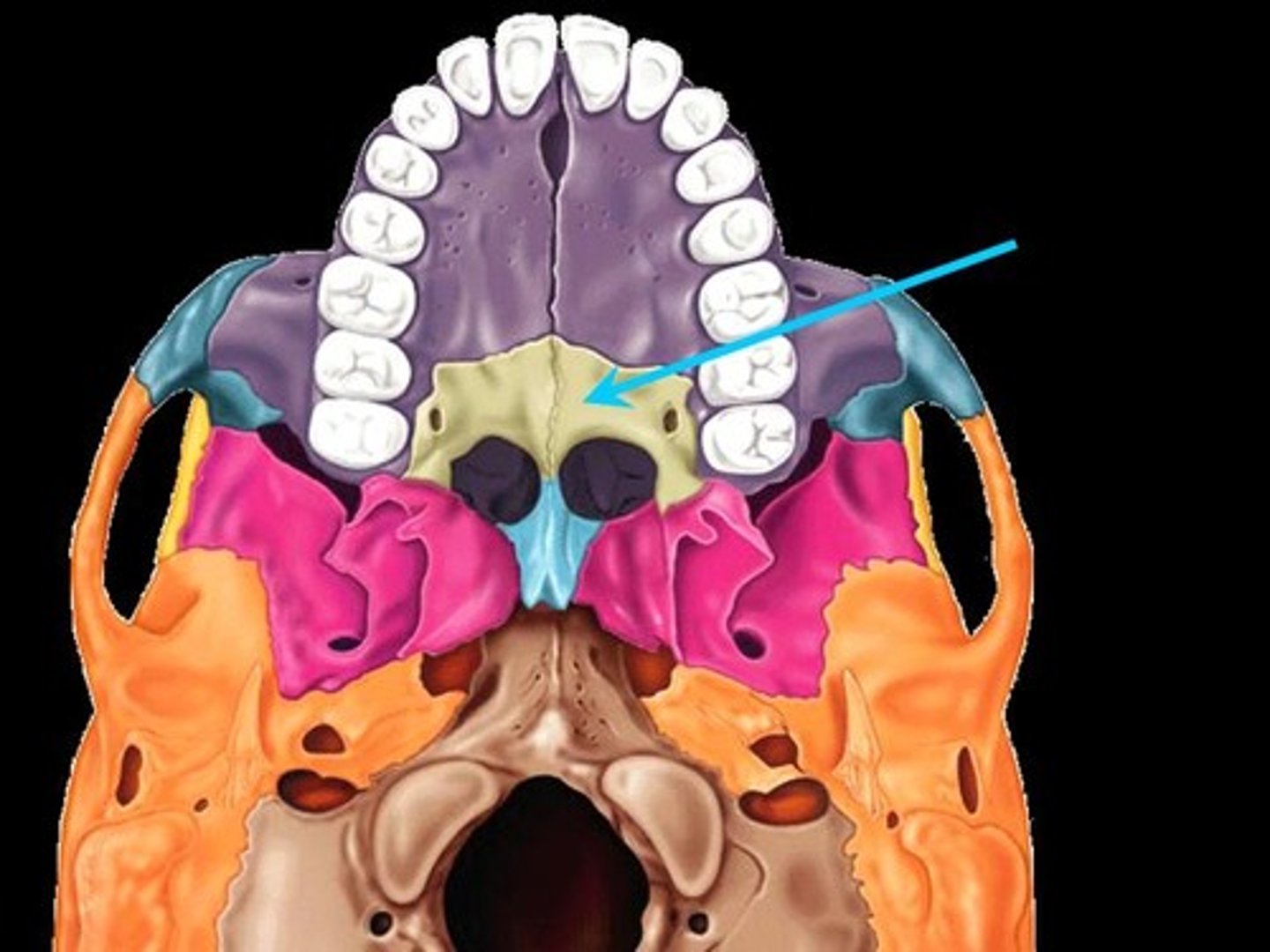
What bone makes up the hard palate
palatine bone
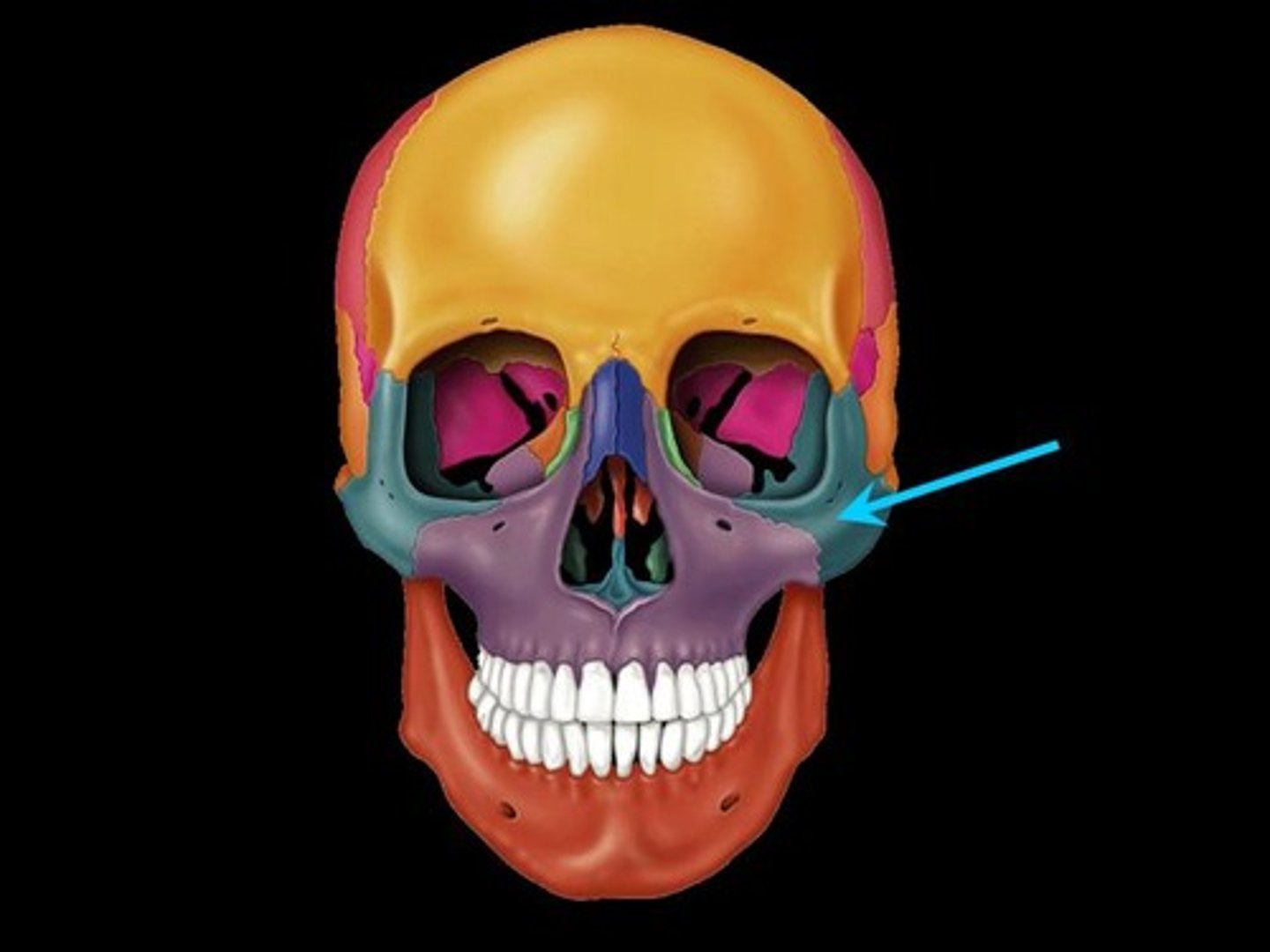
What bone makes the cheekbones
zygomatic bones
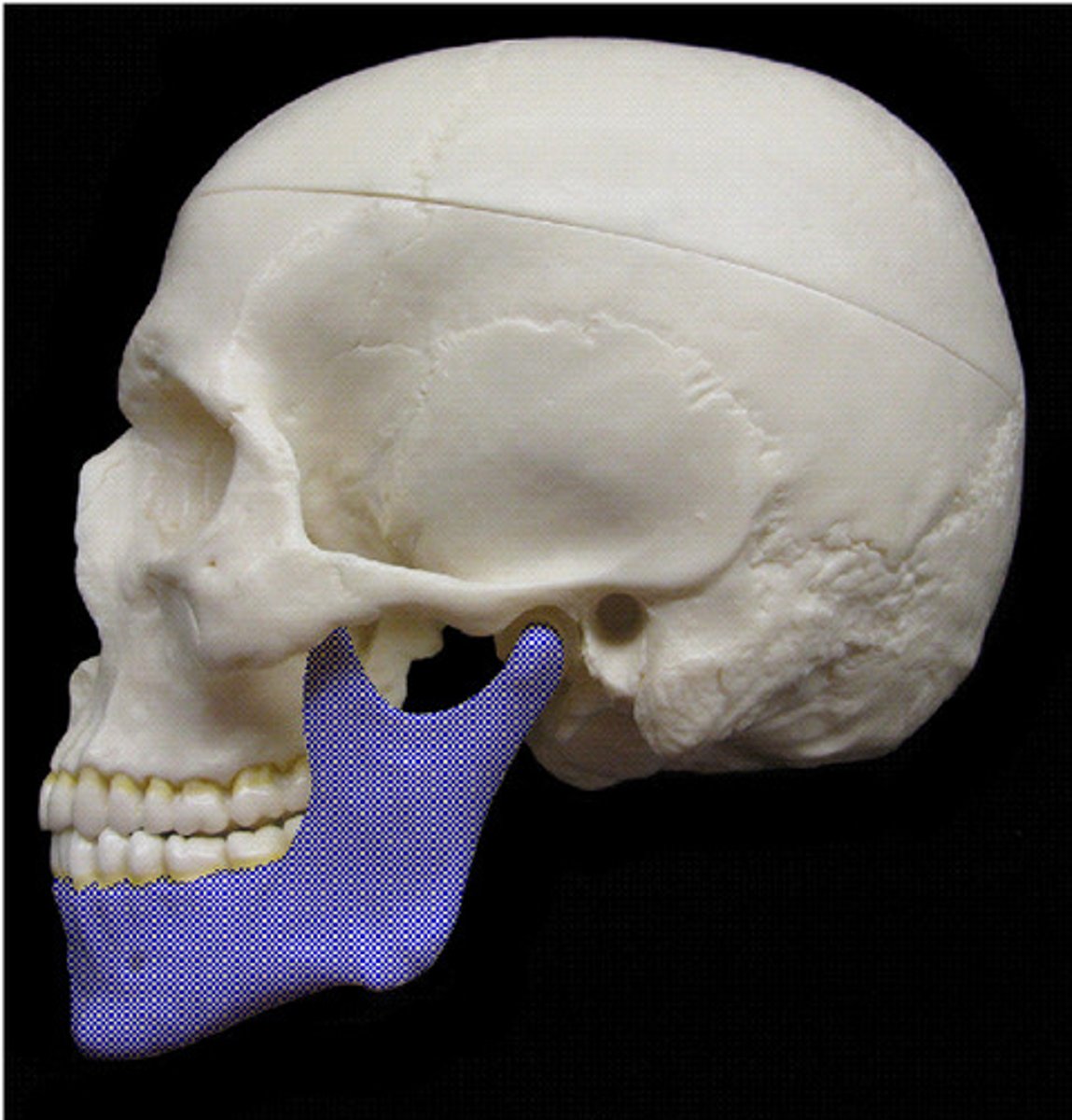
what bone makes the lower jaw
mandible
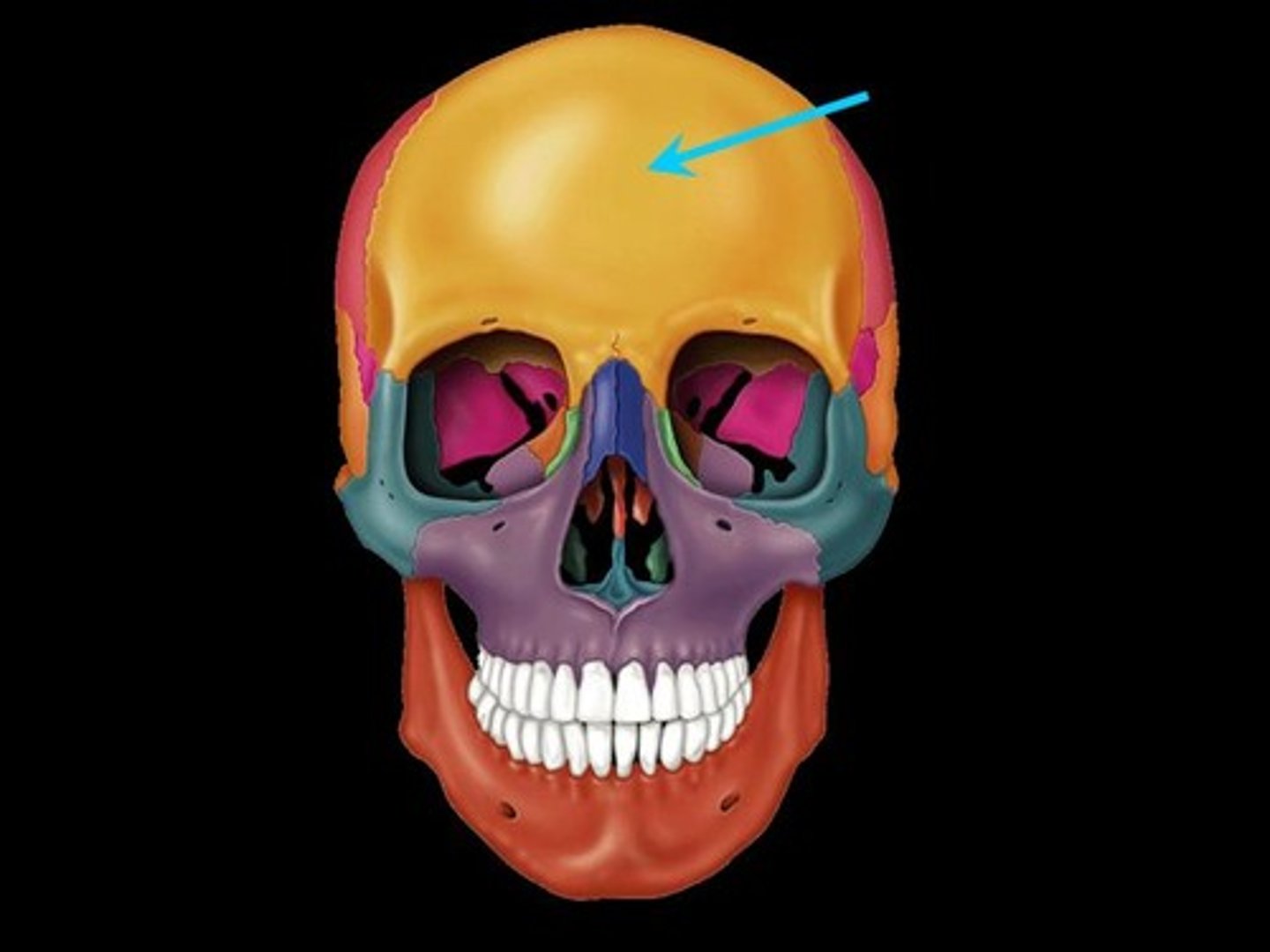
What bone makes the forehead
Frontal bone
What bone makes the lateral skull
temporal bone
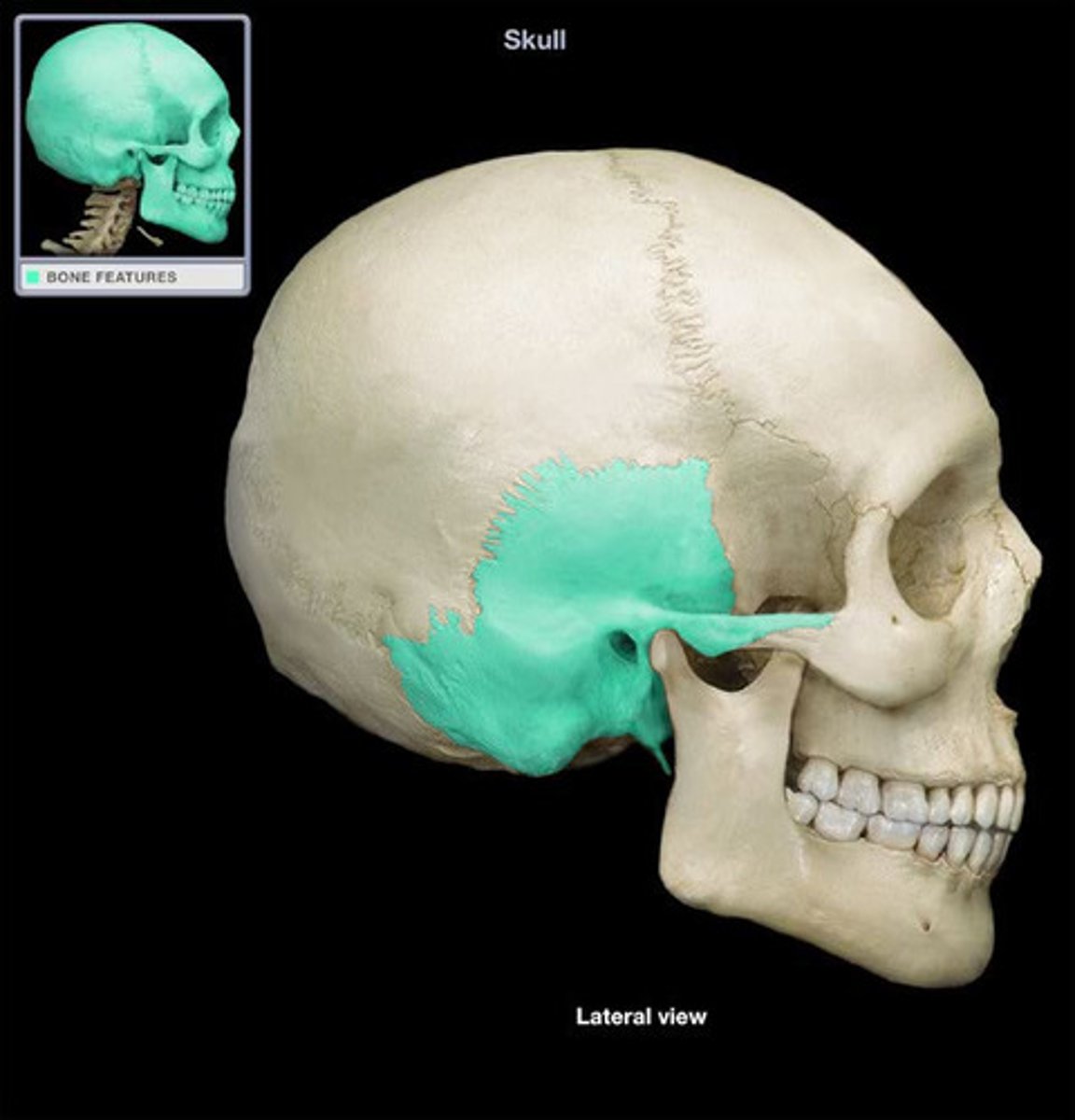
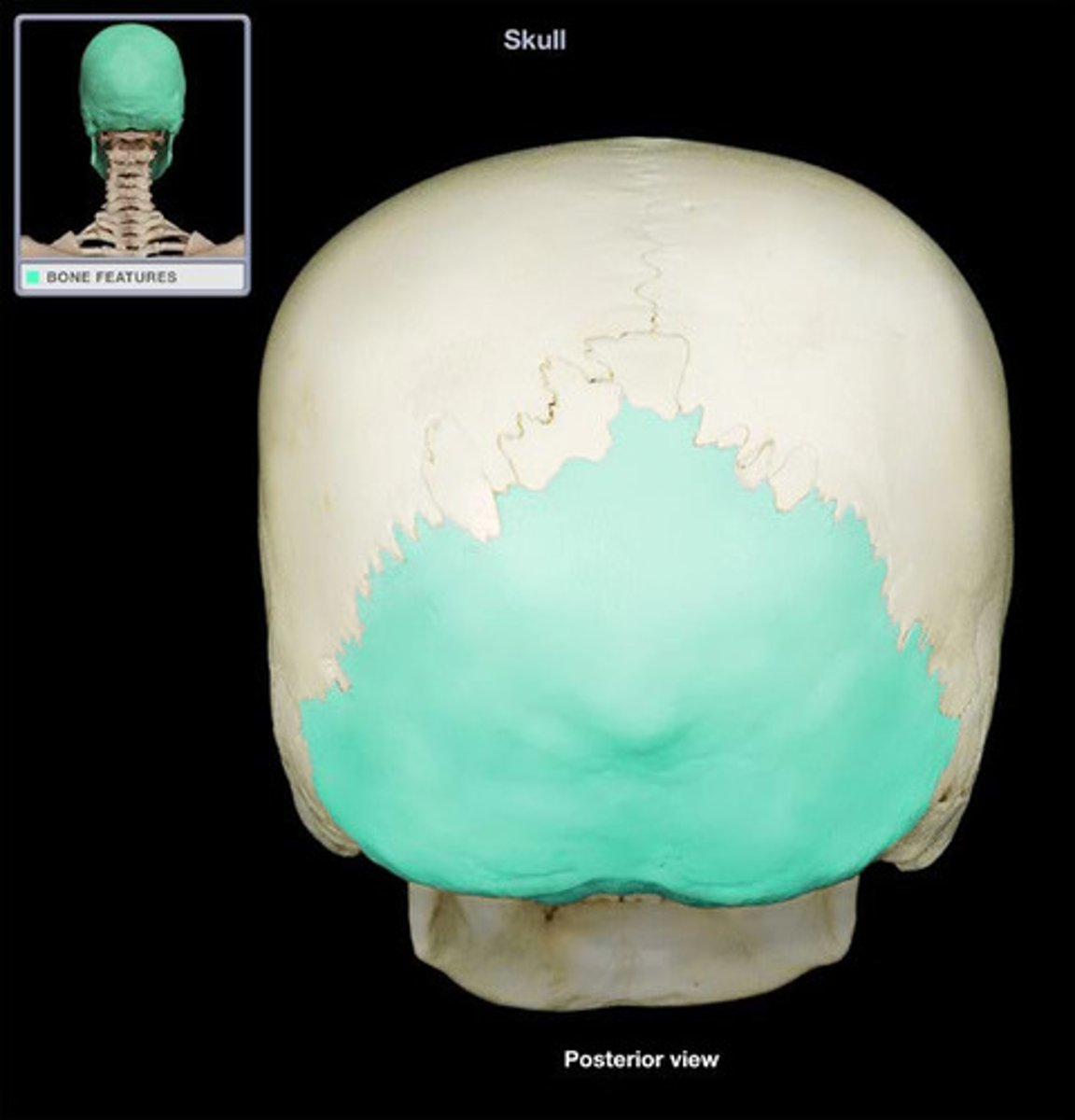
what bone makes the posterior skull
occipital bone
What are the cavities of the oral tract? (BOPN your head to the beat)
buccal, oral, pharyngeal, nasal cavity
buccinator
compresses cheek,
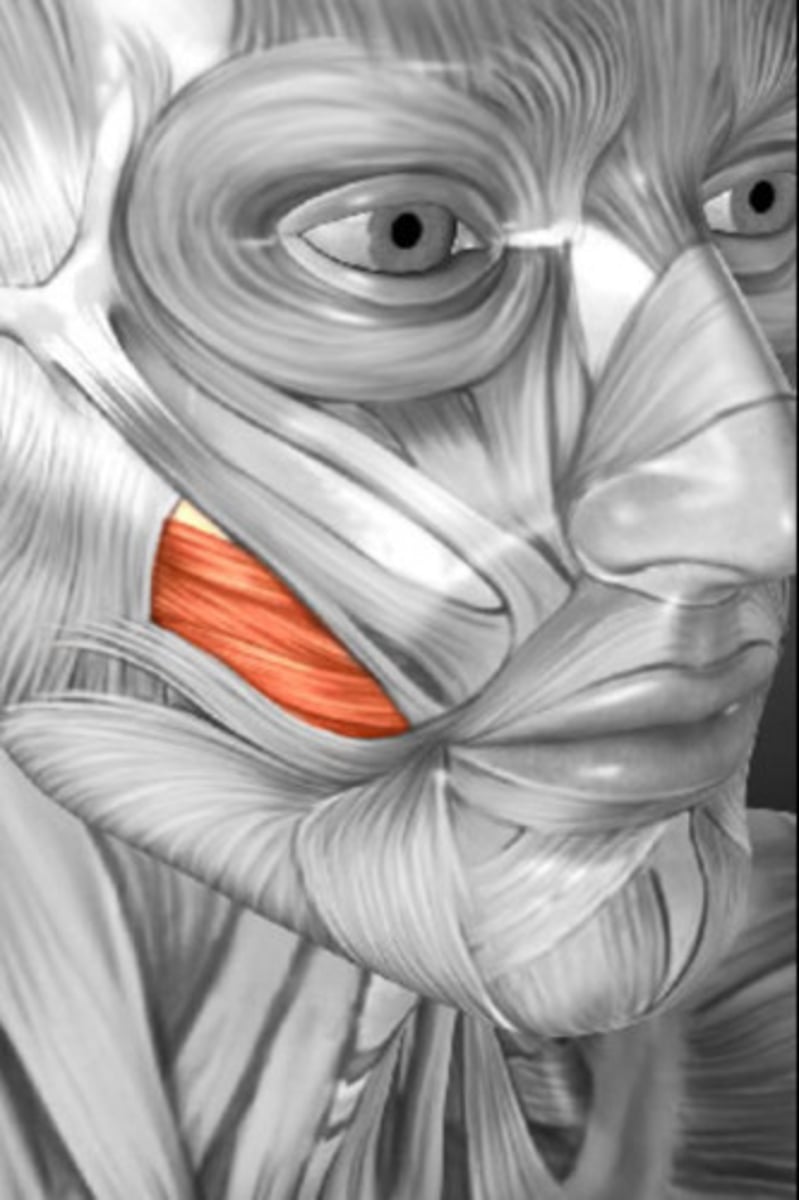
Risorius
Draws corner of mouth laterally

Mentalis
Elevates and protrudes lower lip

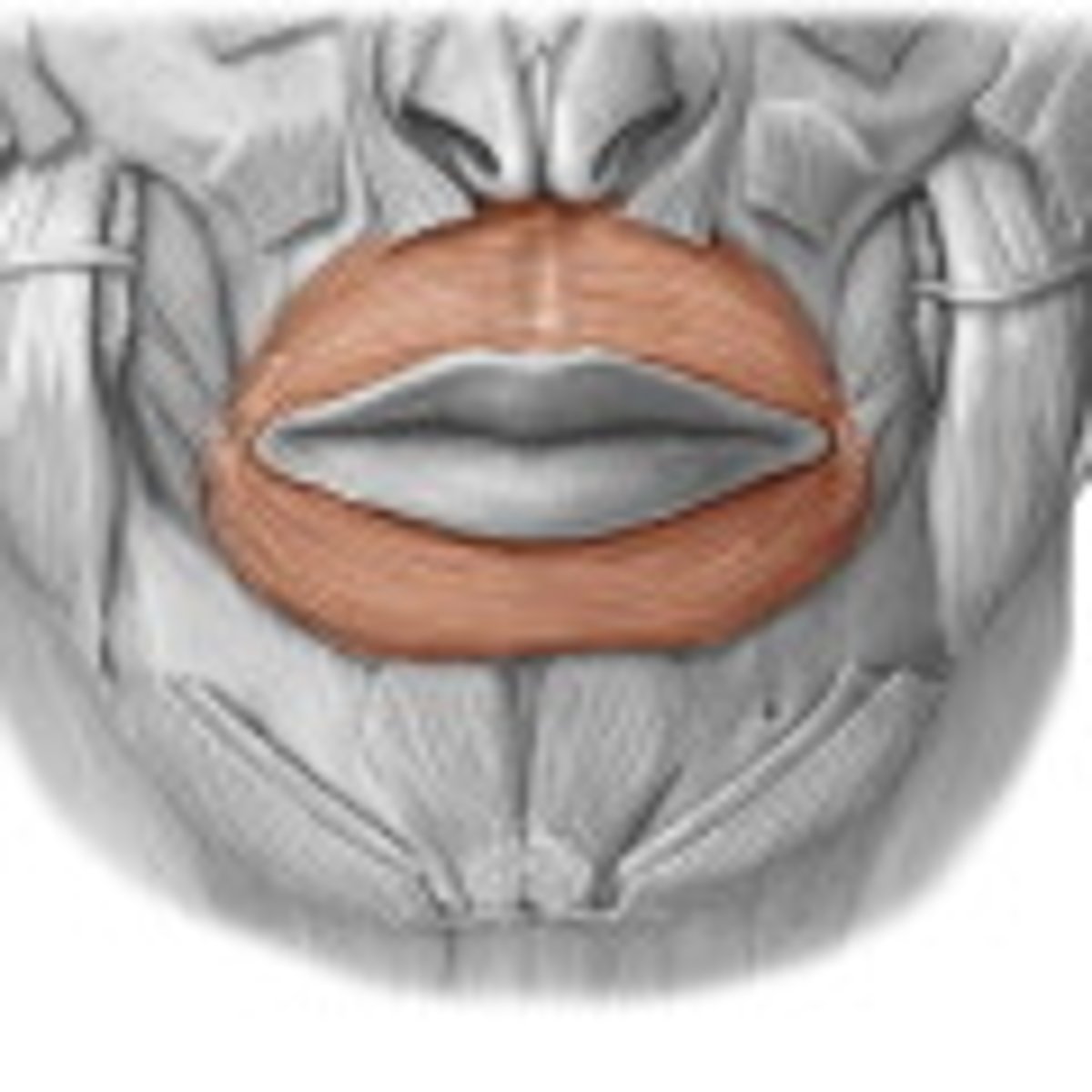
Orbicularis oris
closes and protrudes lips (kissing muscle-- ♀️ )
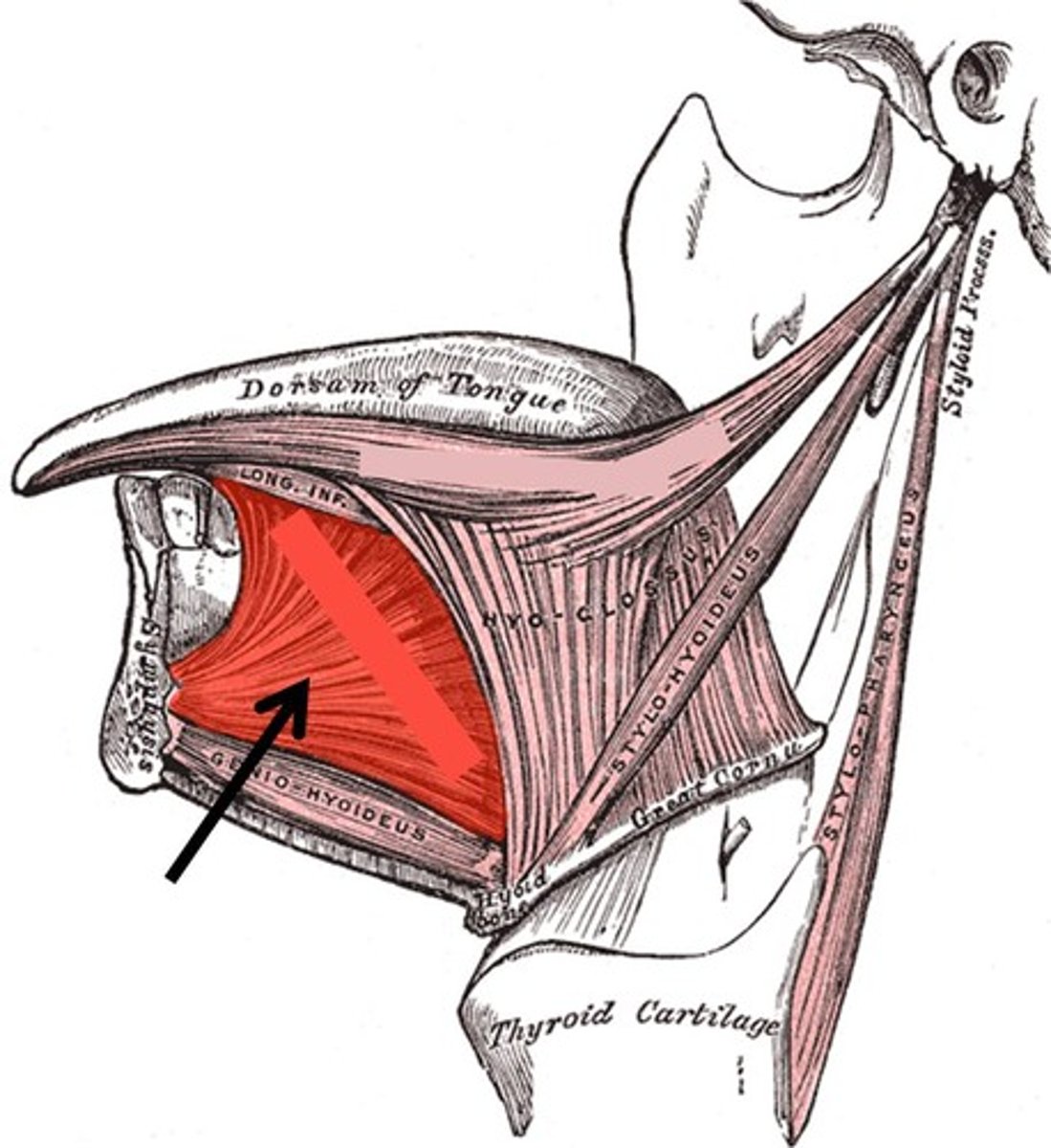
Genioglossus
depresses and protrudes tongue
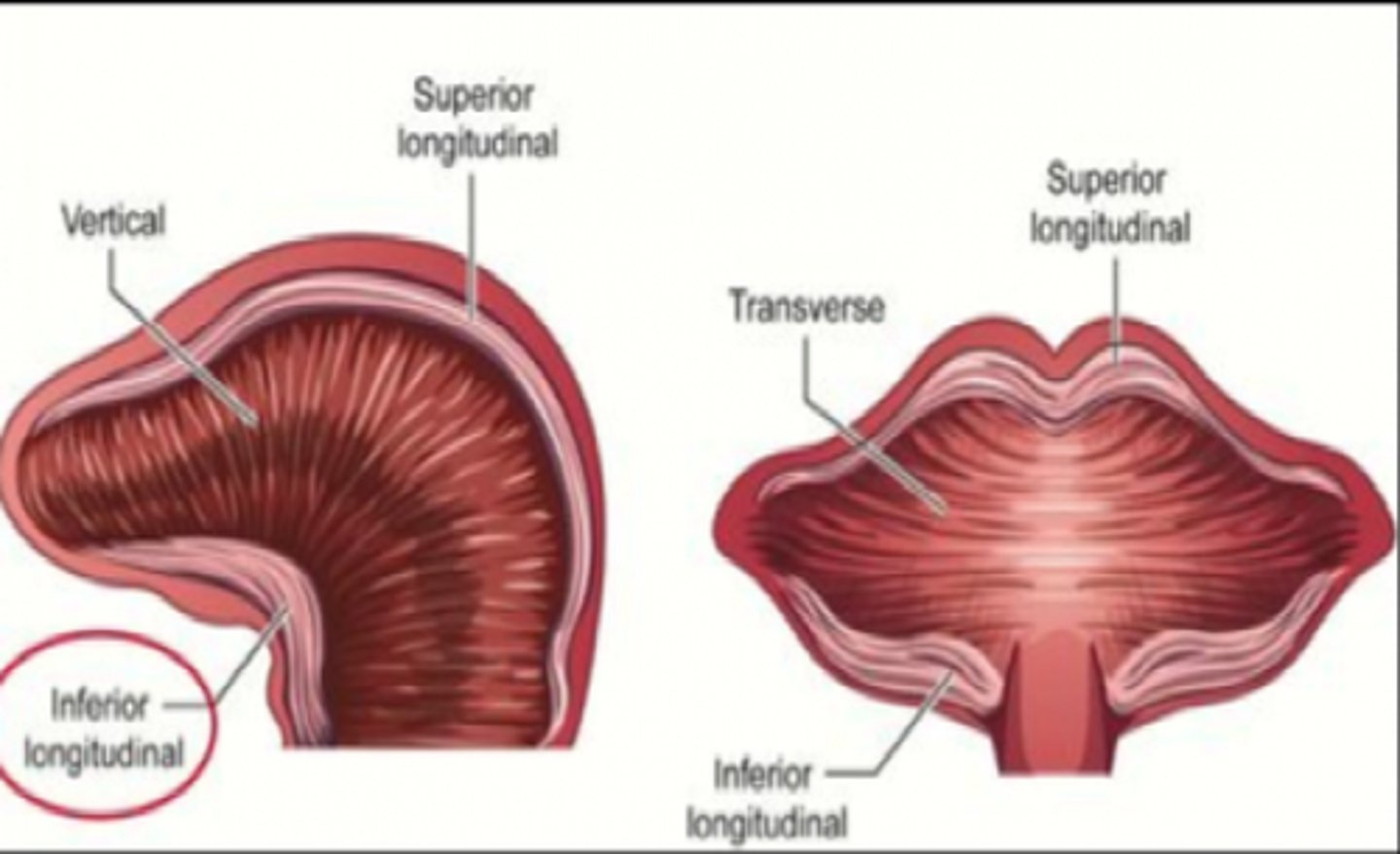
Superior longitudinal
elevates tongue tip
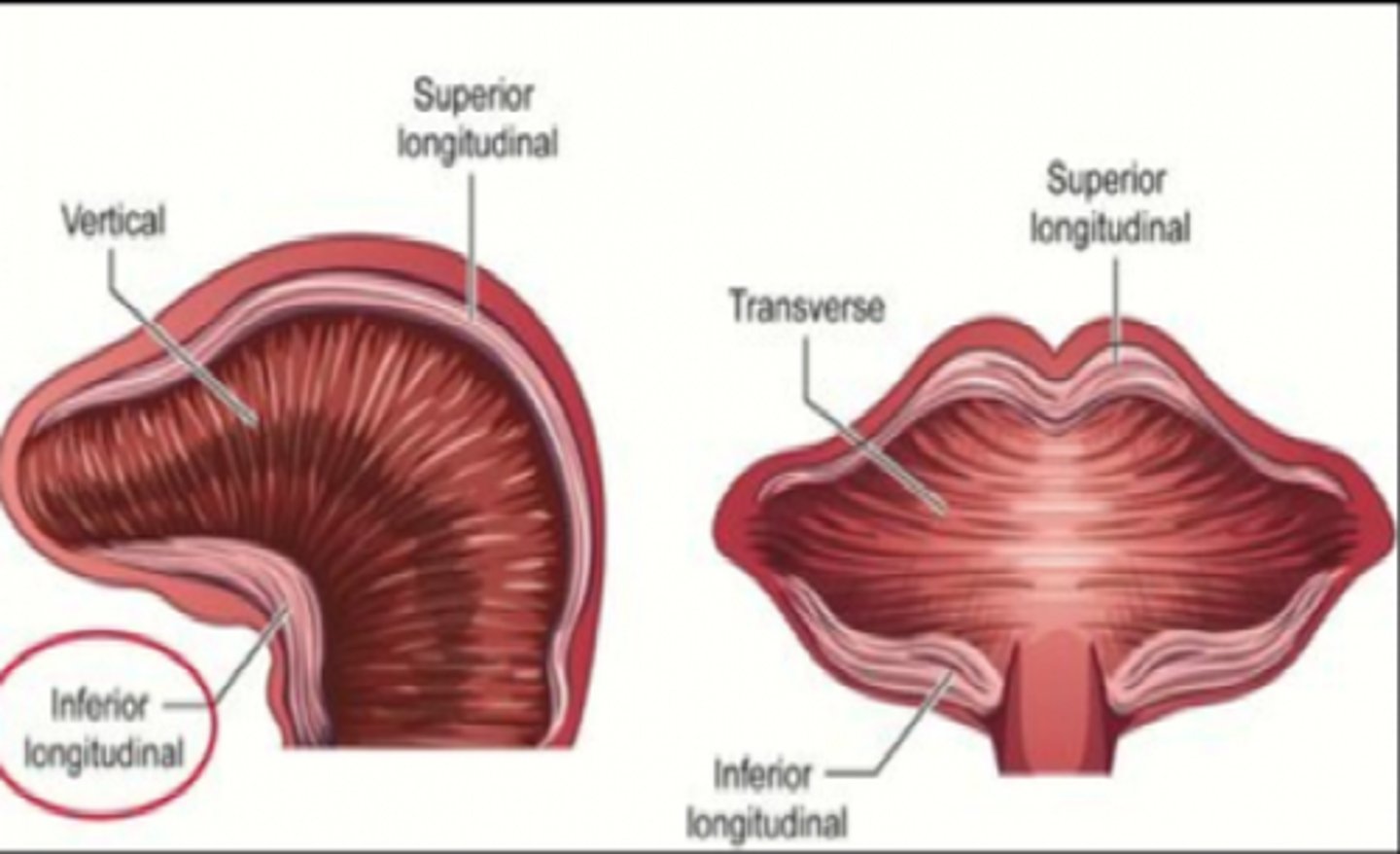
Inferior longitudinal
pulls tongue tip down
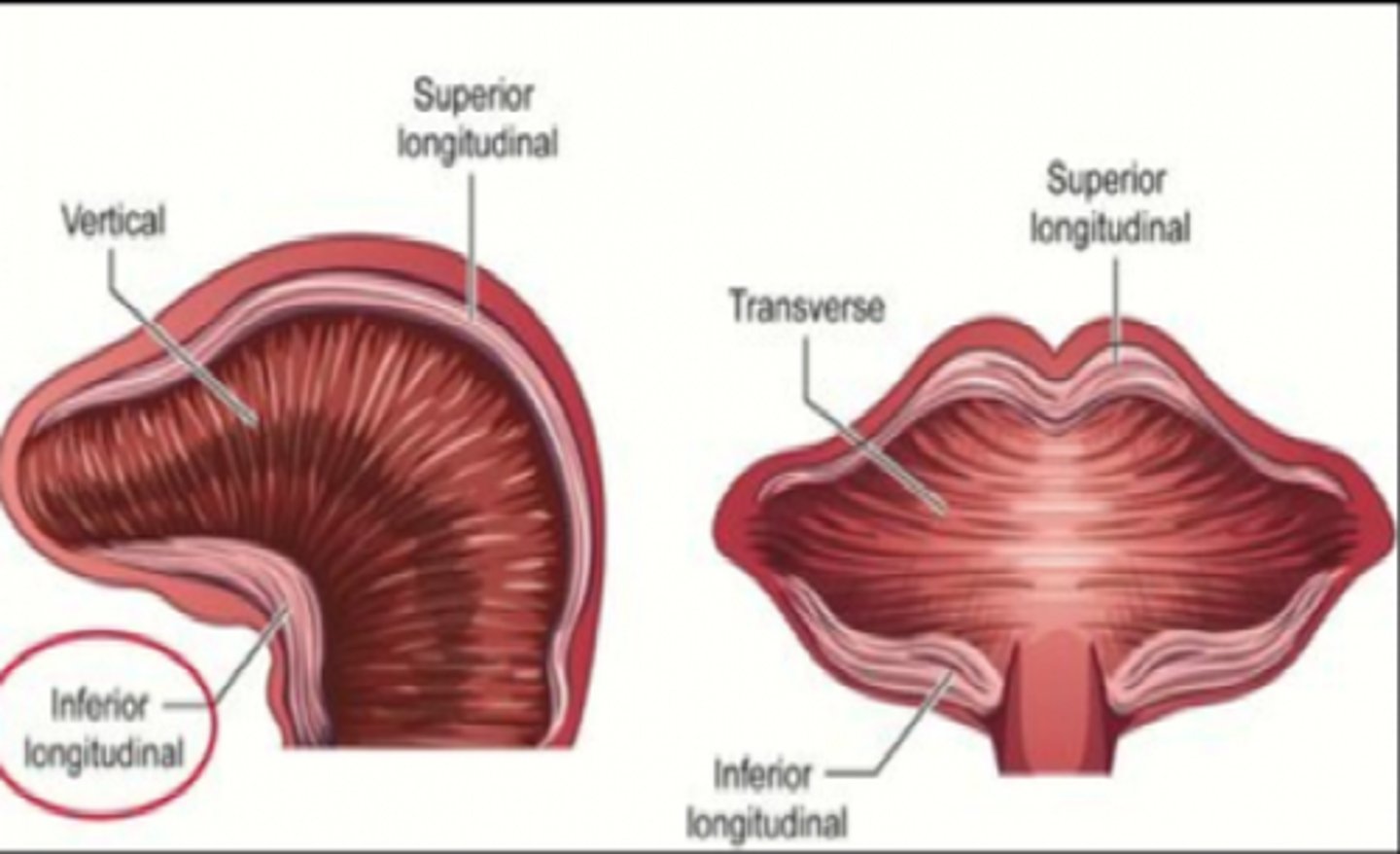
Transverse muscle
narrows and elongates tongue
Verticalis muscle
flattens and widens tongue
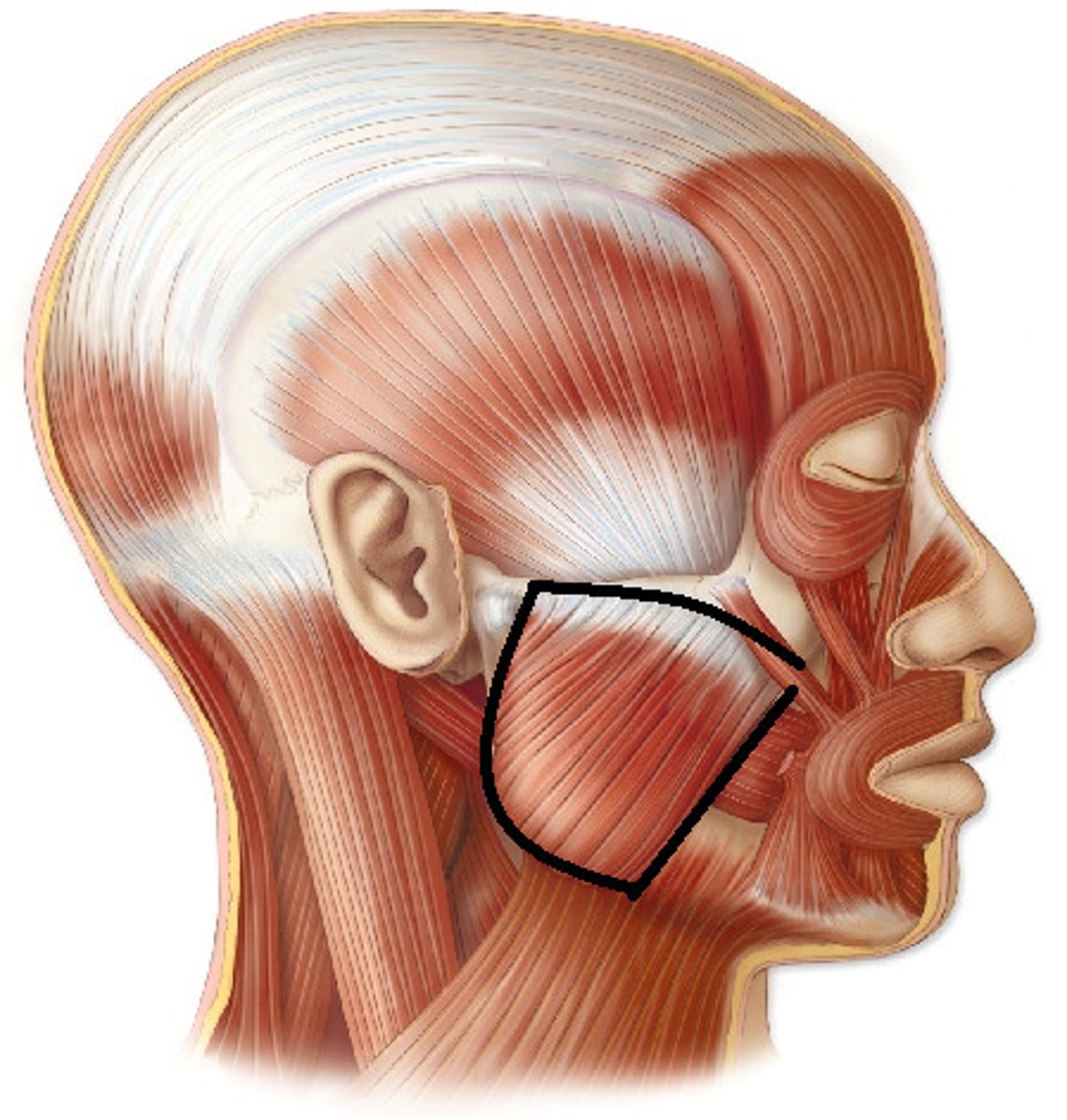
Masseter
elevates mandible (closes jaw)
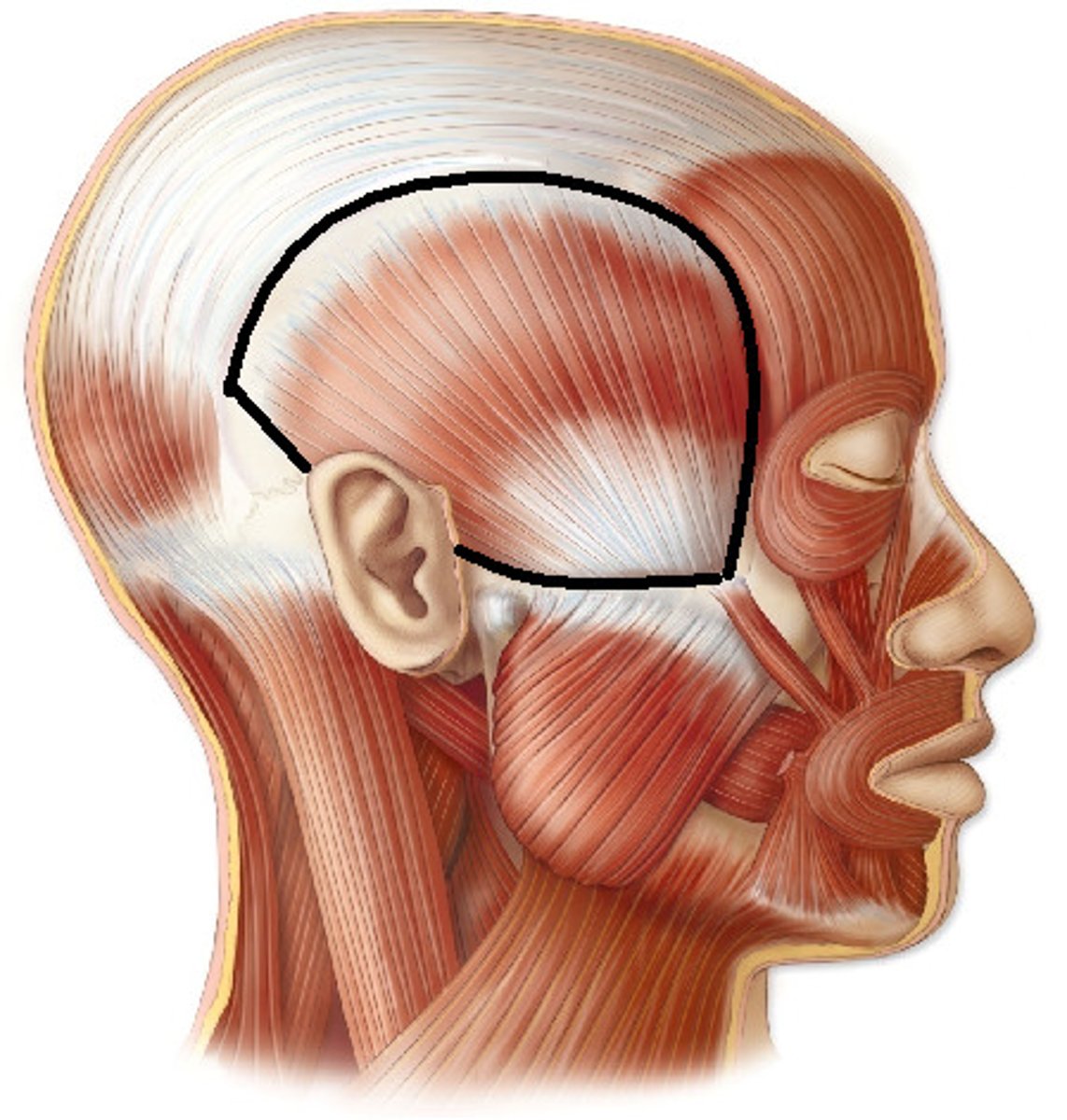
Temporalis
elevates and retracts mandible
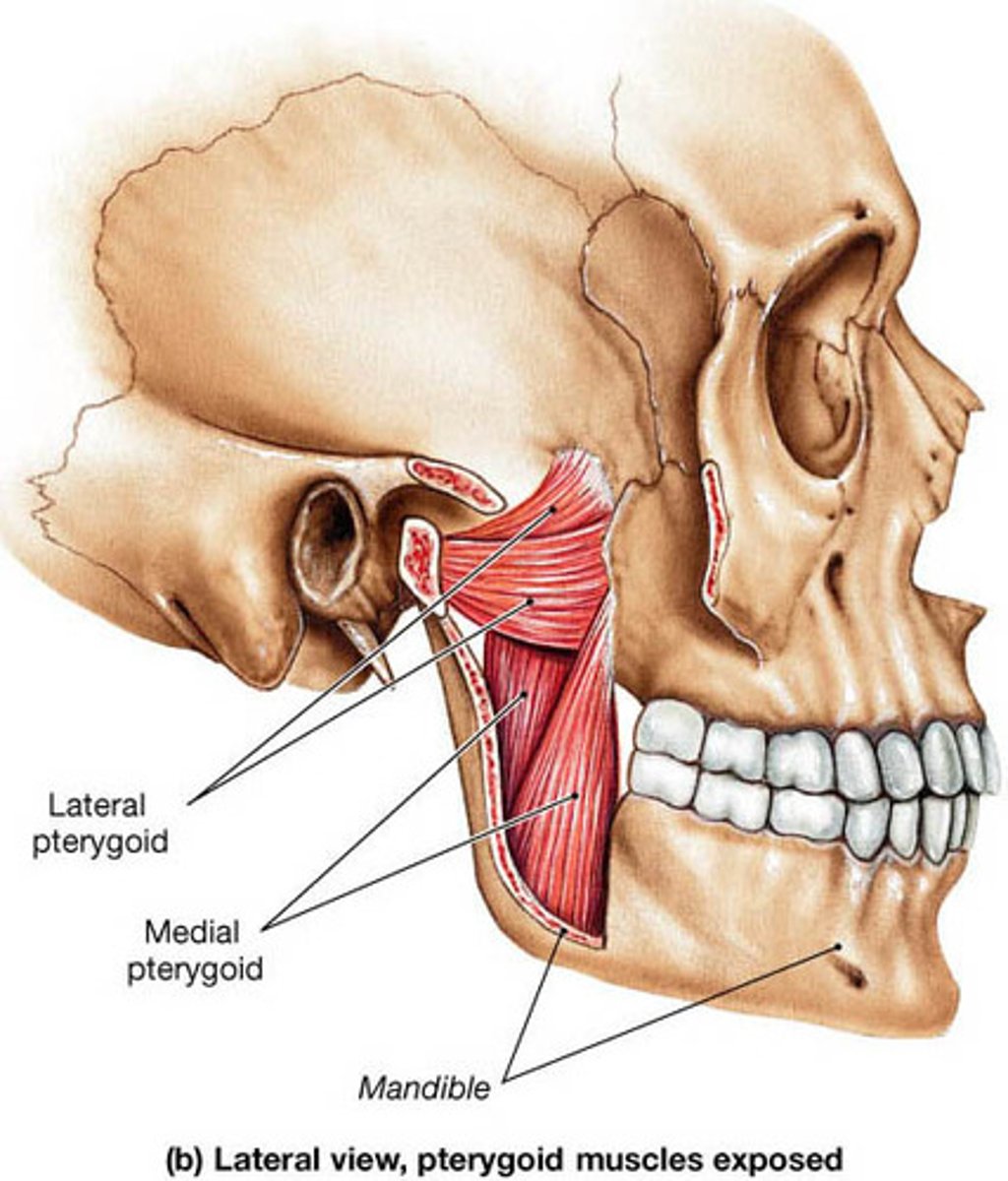
Pterygoid muscle
Winglike muscle that raises, lowers, and allows side-to-side movement of the mandible.
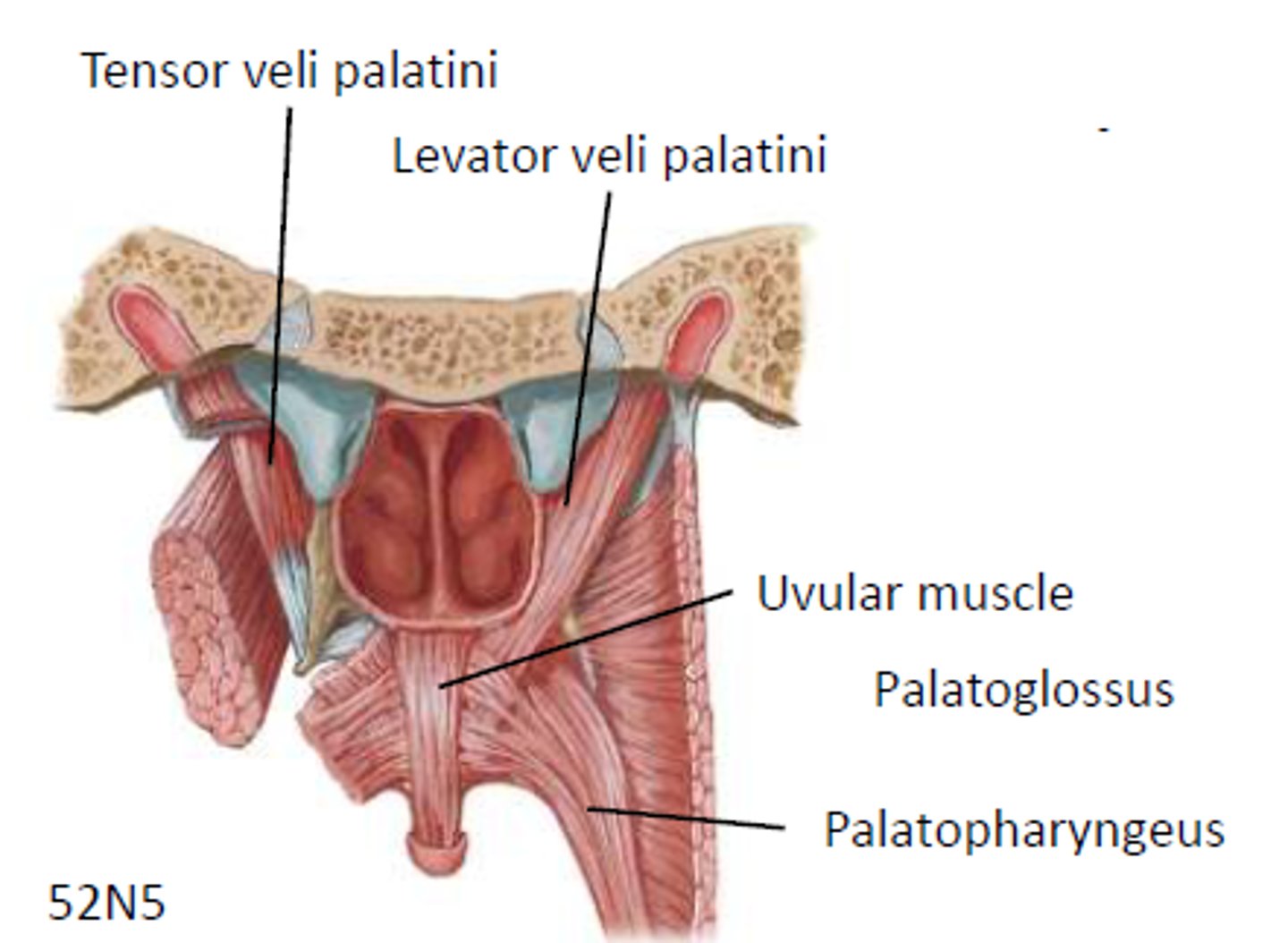
What muscle elevates the velum
levator veli palatini
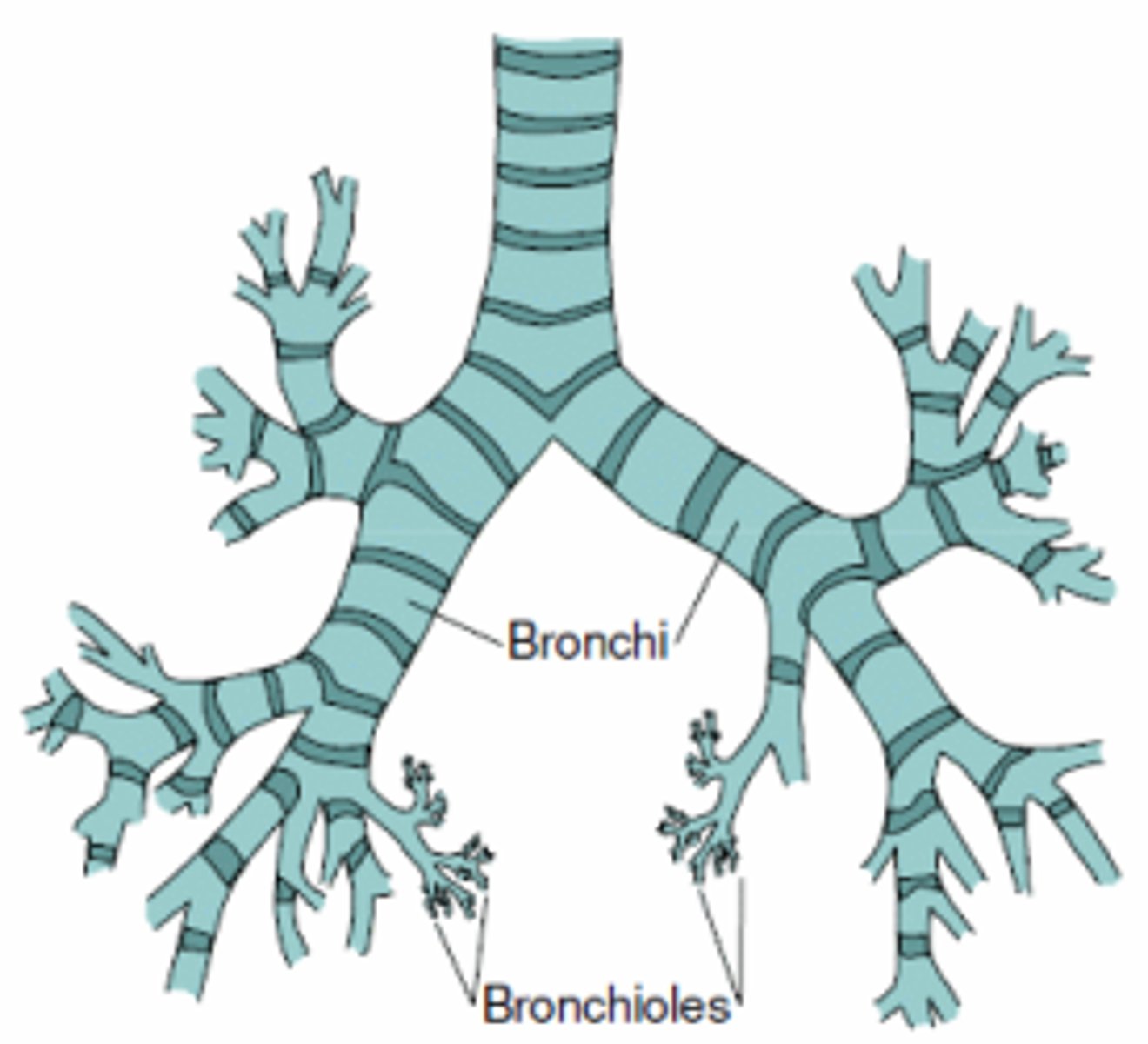
the bronchi branch out into
bronchioles
Where does the gas exchange occur
capillaries
How many pairs of ribs are there
12 pairs of ribs (7 true ribs, 3 false ribs, 2 floating ribs)
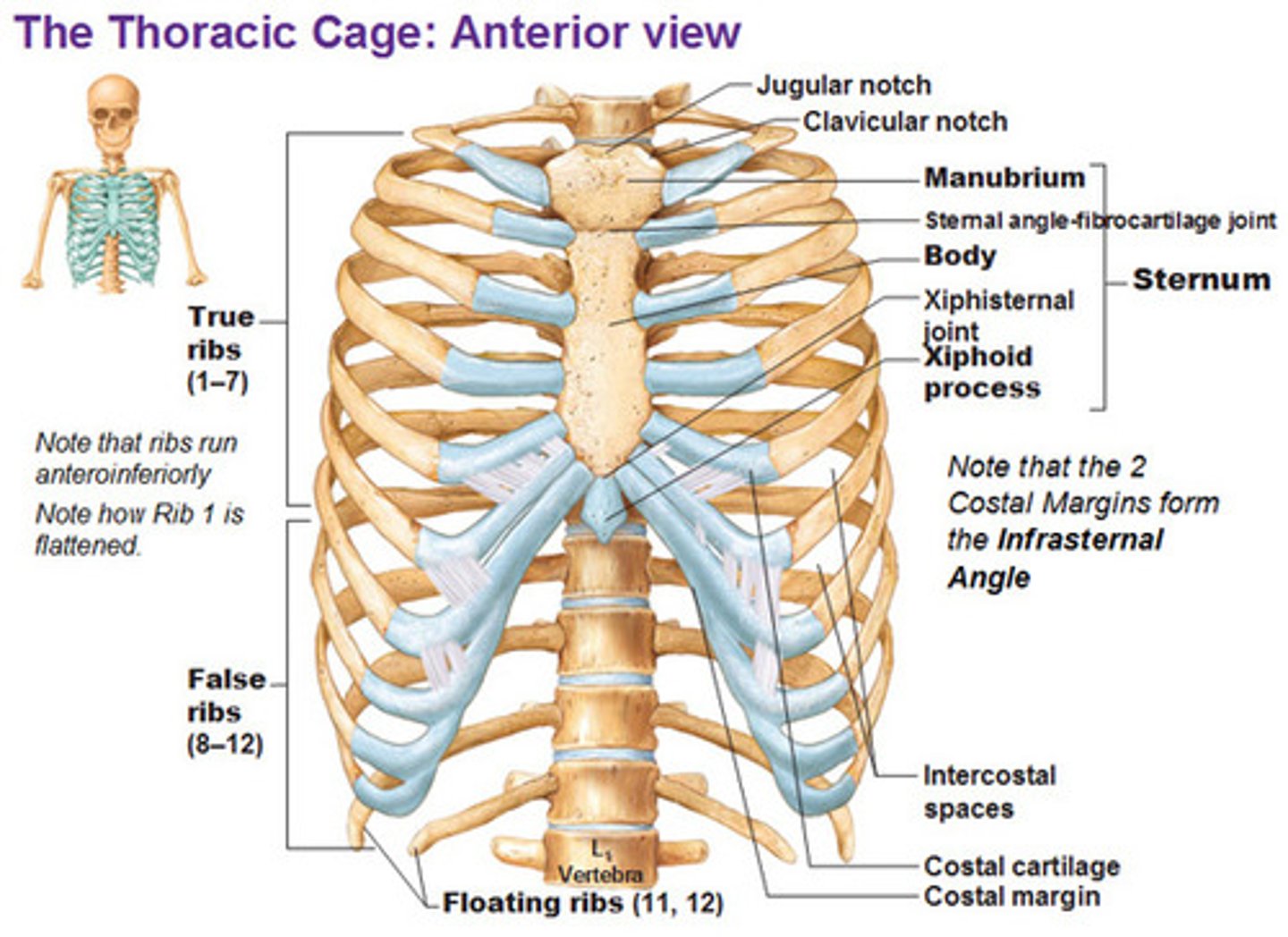
what happens when the rib cage elevates
Volume increases, pressure drops, air flows into the lungs (inhalation)
What is the diaphragm
muscle under the rib cage involved in breathing

Diaphragm descends during (Idea)
inspiration
Diaphragm elevates during
expiration
Second most important muscles to respiration
intercostals
Internal intercostals
depress ribs
External intercostals
elevates ribs
How does Boyle's law relate to breathing?
-as volume increases in a closed container, the pressure will decrease
vise versa, when the volume decreases in a closed container, the pressure will increase.
-when we change the volume of our thoracic cavity, for a moment there is a change in pressure, which will allow air to move in or out of the lungs

Types of expiration
passive and active
Sustained phonation
vocal folds held in a fixed position in the airstream - maintenance of a laryngeal posture through tonic (sustained) contraction of the musculature
What forces need to be overcome to allow for sustained phonation or speech production?
Musculature + Aerodynamic forces
*note: that comes from the slides. I have literally no idea what that means or if that'e even the right answer. Google doesn't know either. Whoops.
biological purpose of the respiratory system
Respiration + Phonation
Respiration for speech vs regular breathing
Speech:
-Abdominal wall + thoracic muscles muscles are recruited actively
-Inhale: 10%, Exhale 90%
-Rapid increase in alveolar pressure
Regular Breathing:
-Passive muscle usage
-Inhale 40%, Exhale 60%
-Alveolar pressure negative (inhalation)
Resting tidal volume
amount of air that enters the lungs during one cycle
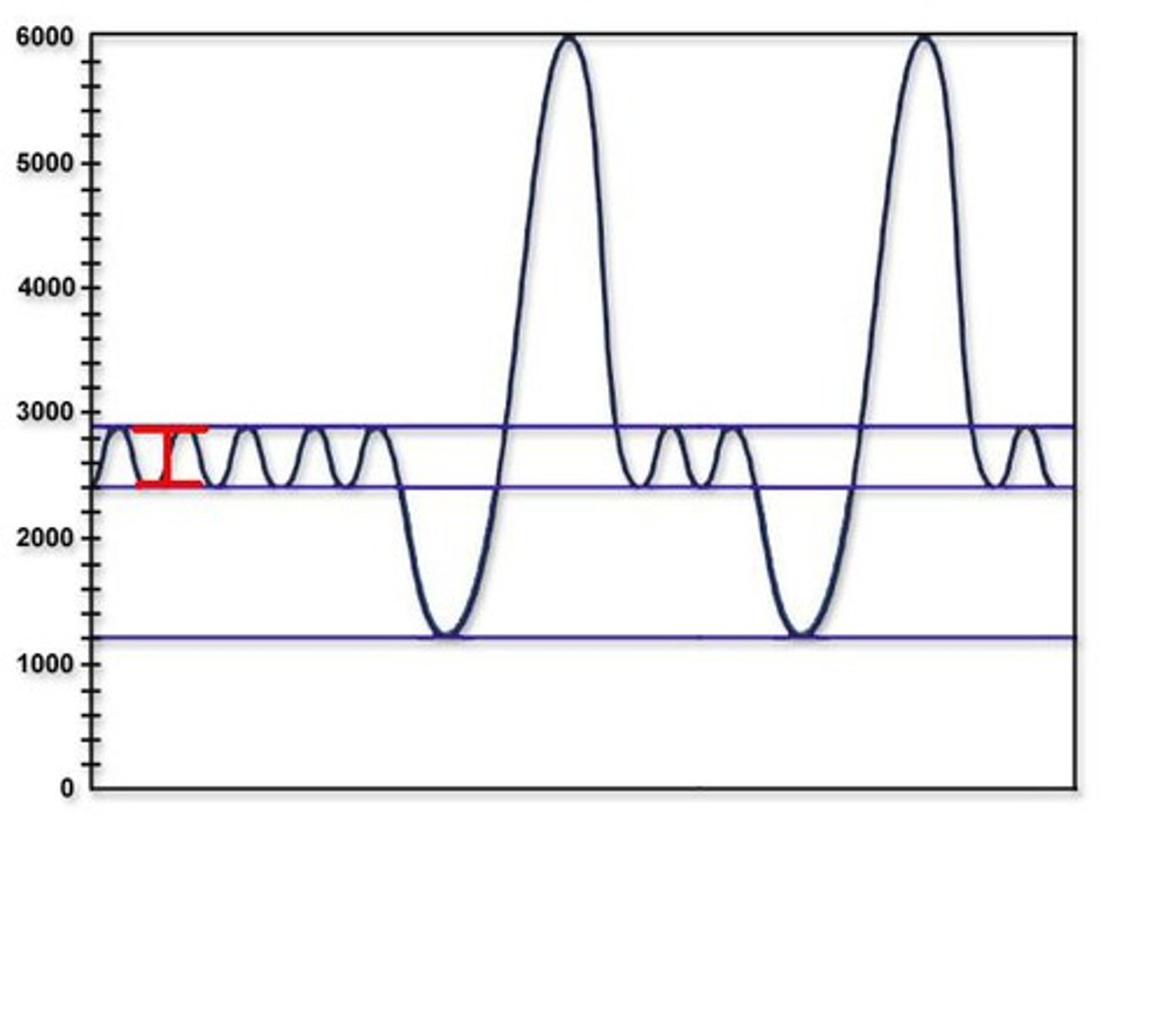
inspiratory reserve volume
Amount of air that can be forcefully inhaled after a normal tidal volume inhalation
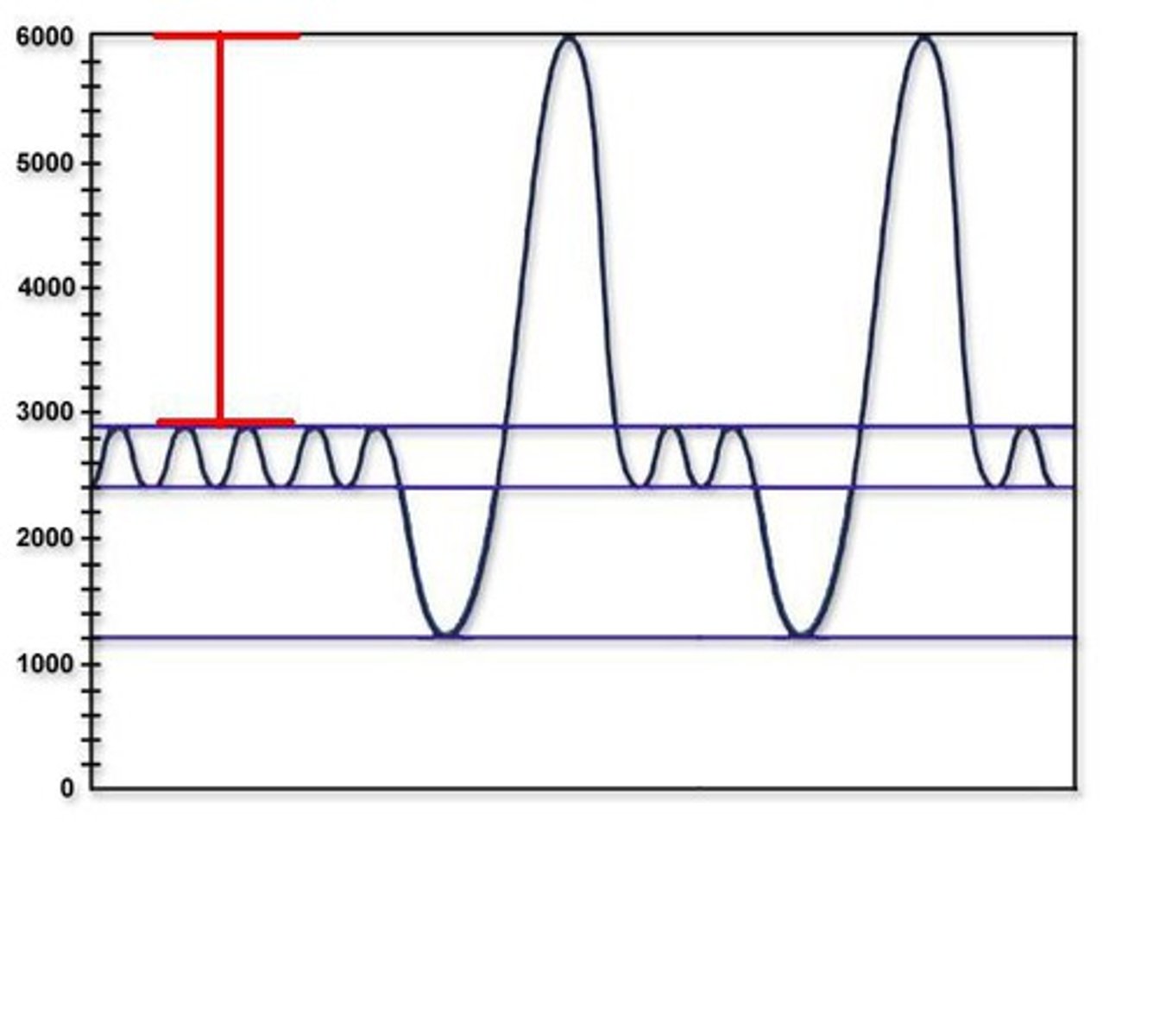
expiratory reserve volume
Amount of air that can be forcefully exhaled after a normal tidal volume exhalation
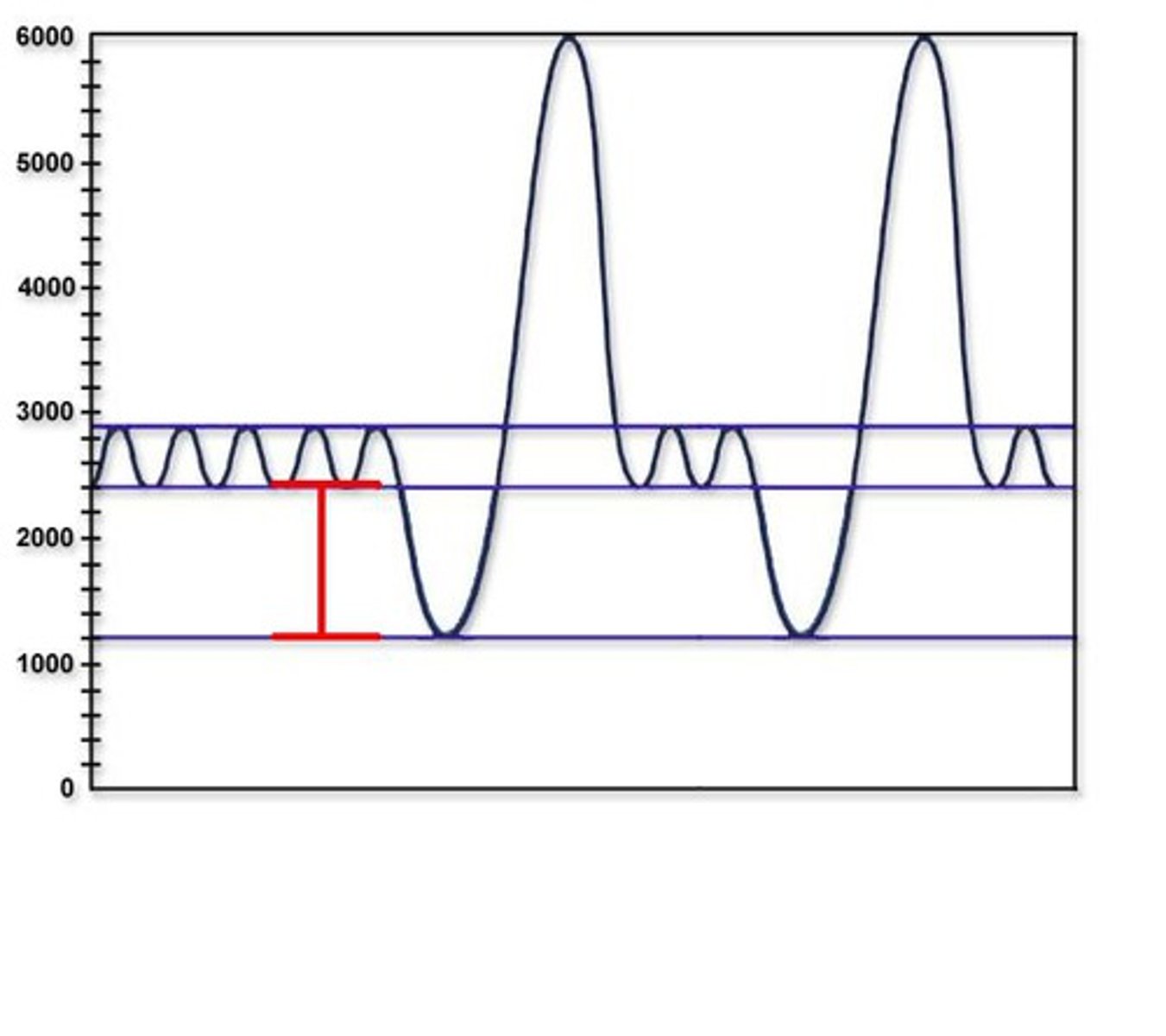
Residual Volume
Amount of air remaining in the lungs after a forced exhalation
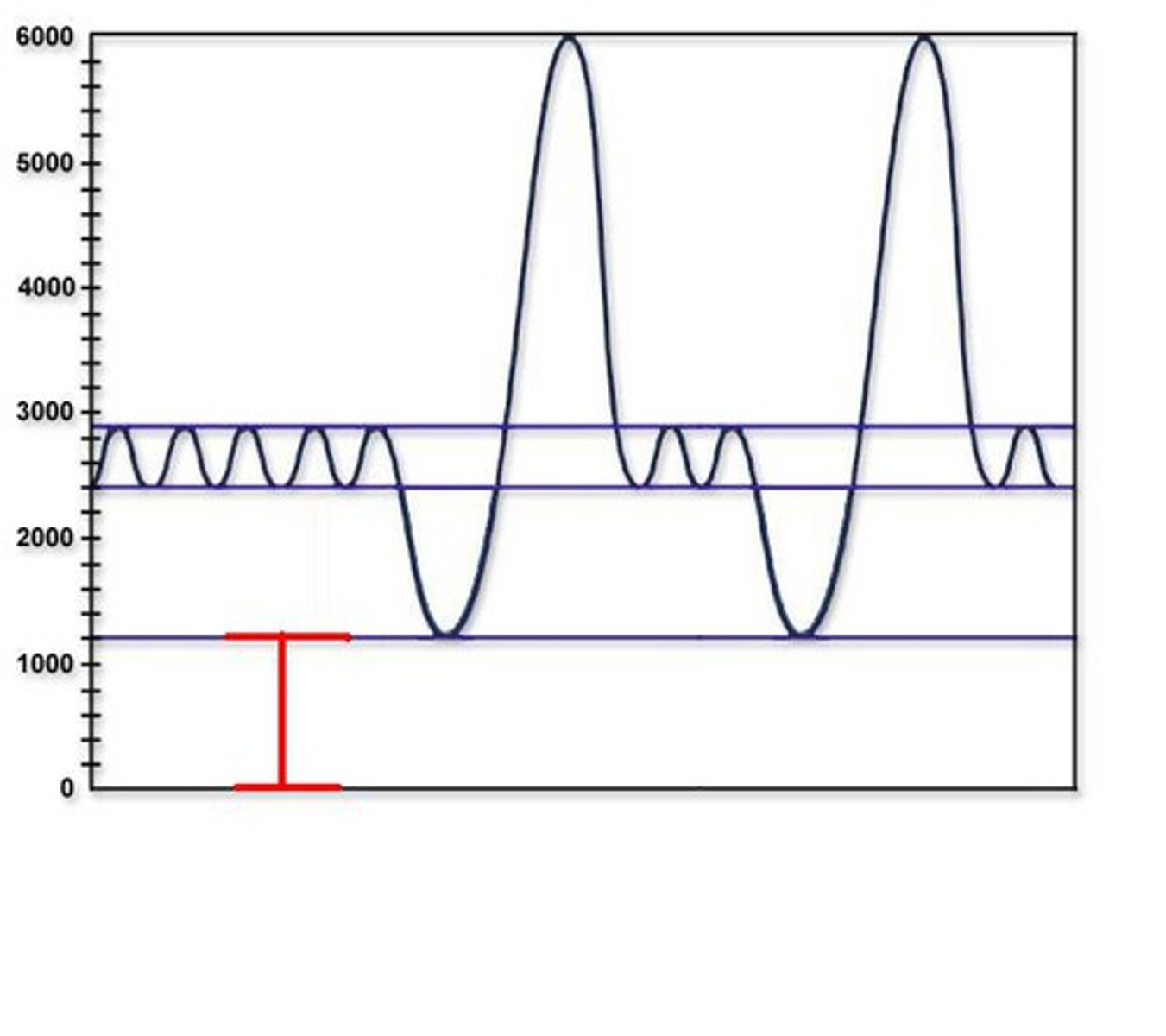
Vital capacity
The total volume of air that can be exhaled after maximal inhalation.
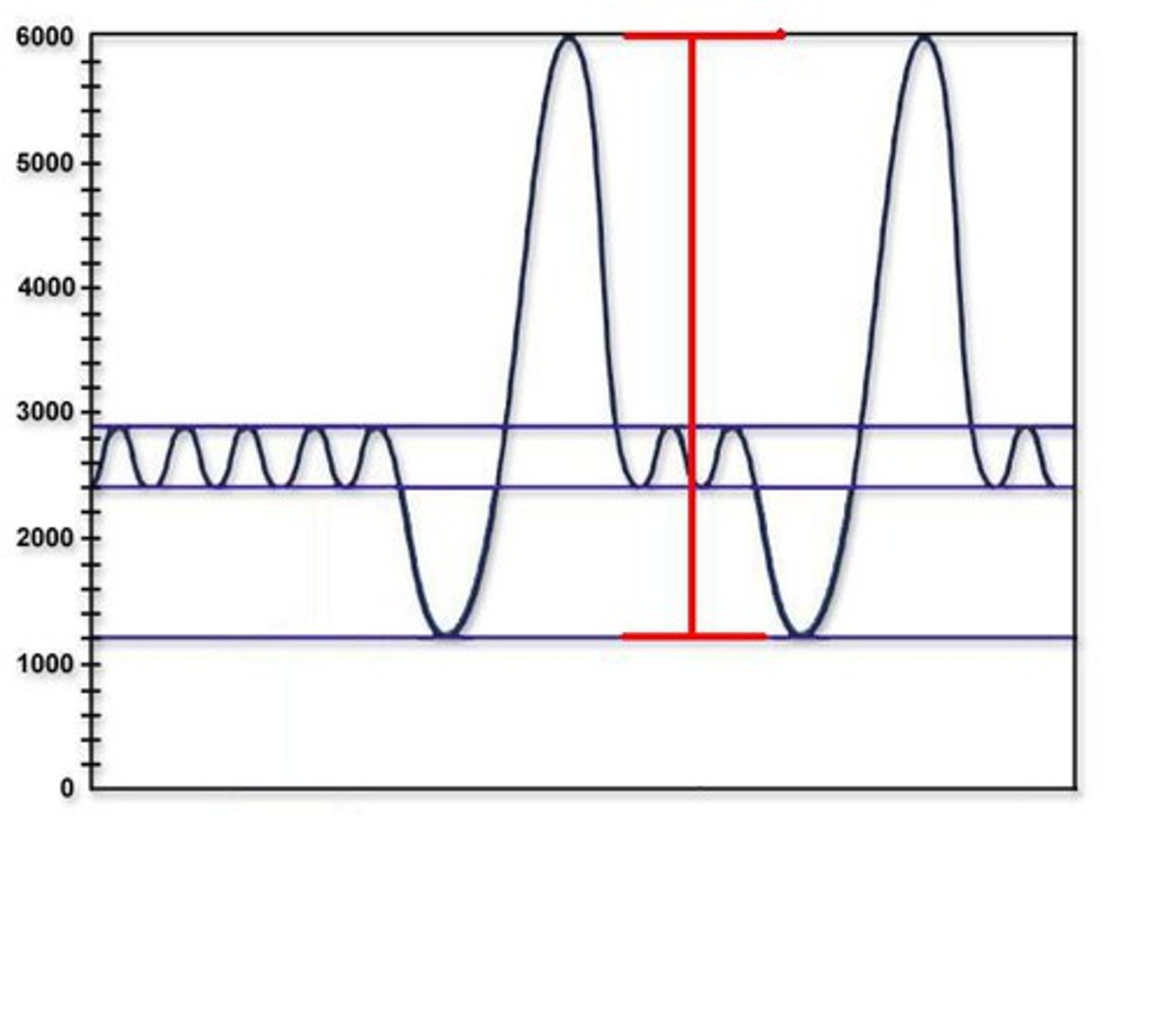
total lung capacity
vital capacity + residual volume
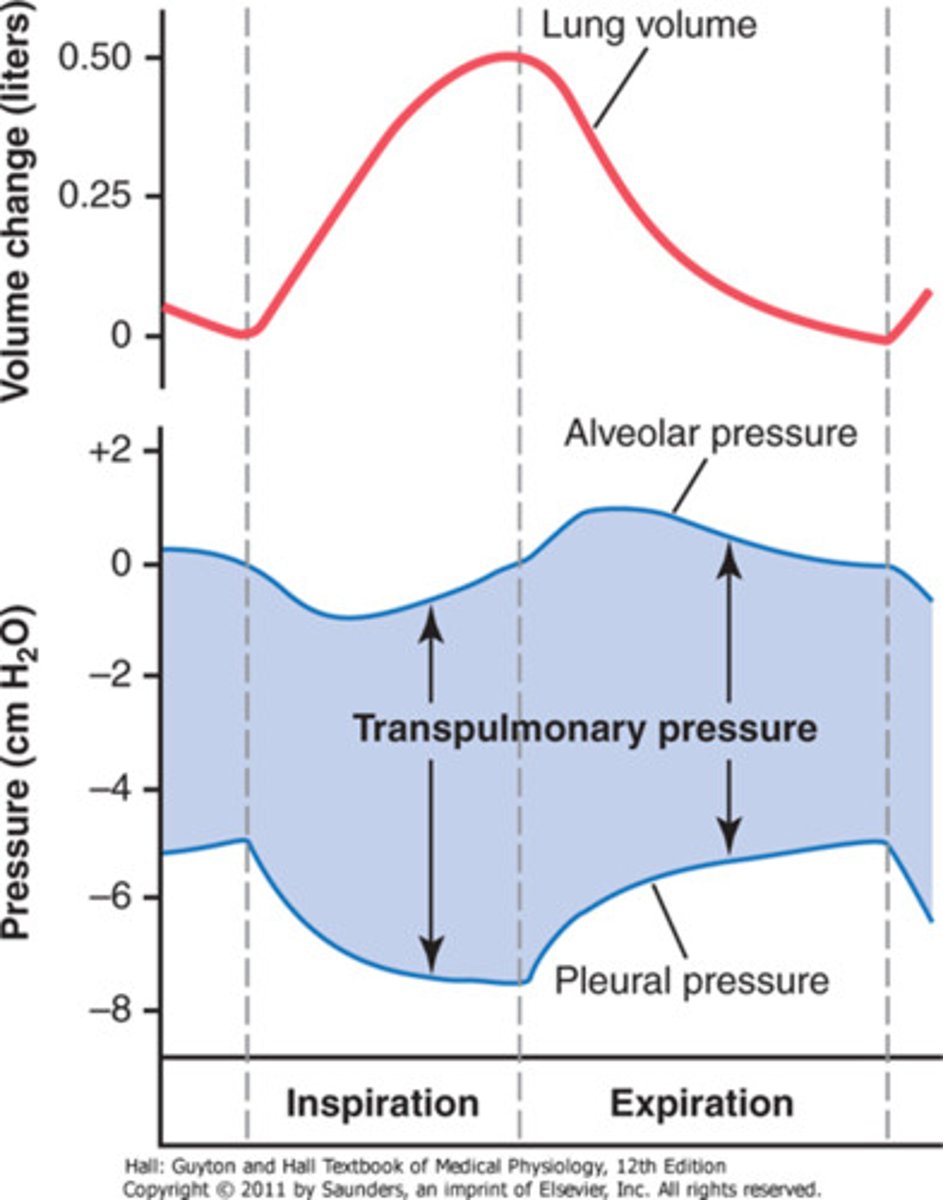
Alveolar pressure
pressure within the lungs
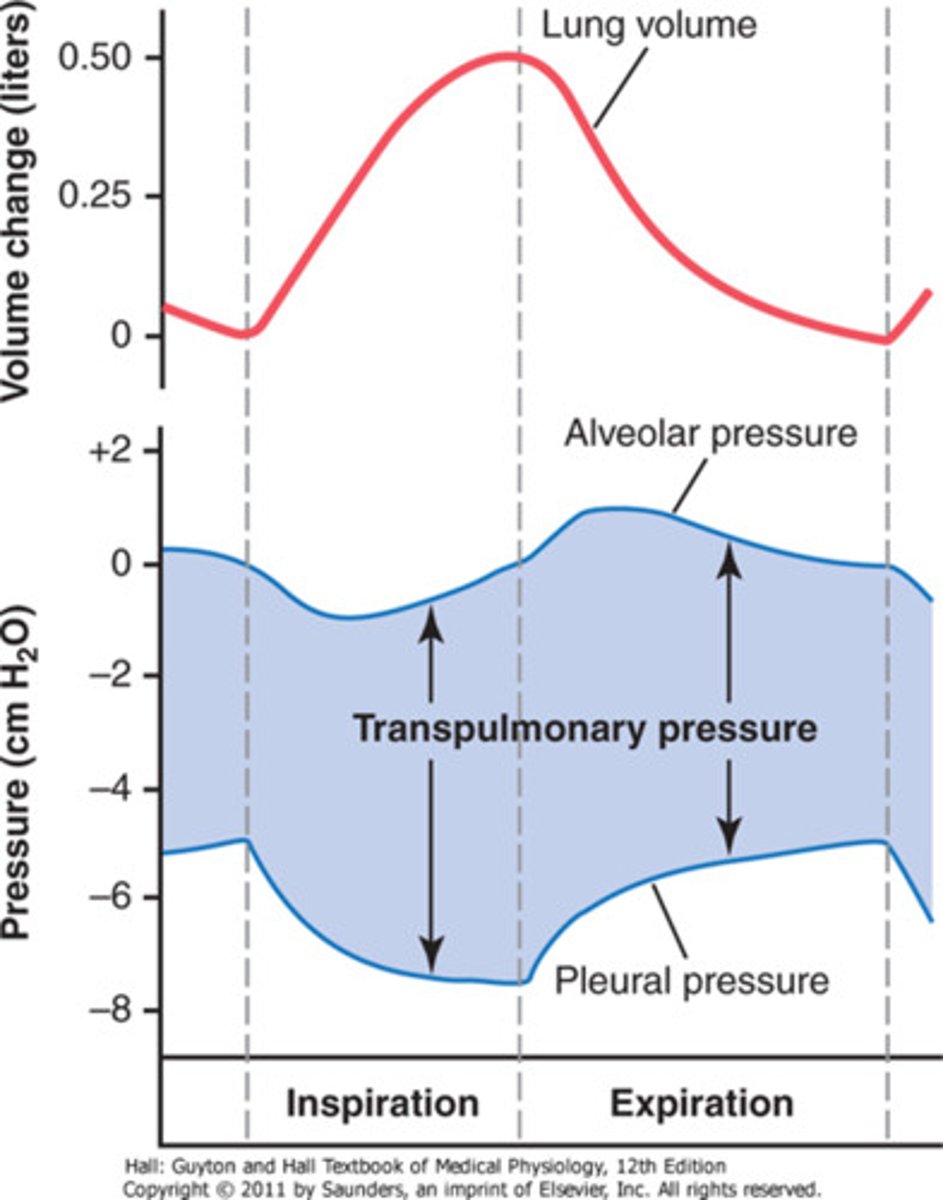
Pleural pressure
the pressure in the narrow space between the lung pleura and the chest wall pleura
Jaw moves to chew food
Masseter, geniohyoid, milohyoid
Jaw tears food
temporalis
Jaw grinds food
lateral/medial pterygoid
Tongue seep oral cavity/buccal cavity to gather food particles
superior and inferior longitudinal
Tongue makes a bolus
geniolglossus, superior/inferior longitudinal
Create a bowl around bolus
verticalus
buccinator
risorius
Buccal cavity (don't get food stuck here pls)
Vestibule of the oral cavity; the space between the lips, gums, and teeth.
back of tongue meets soft palate to contain bolus
palatoglossus + styloglossus
tongue elevates to squeeze bolus against hard palate
superior longitudinal, genioglossus, palatoglossus, styloglossus
velum elevates to close off nasal cavity
levator veli palatini
posterior tongue squeezes bolus against hard palate to push bolus back
styloglossus, palatoglossus,
vocal folds adduct to close airway
lateral cricoarytenoid, oblique arytenoid, transverse arytenoid
vellum remains elevated
levator veli palatini
hyoid/larynx elevate
laryngeal elevators (suprahyoid)
epiglottis reflects horizontally
hyglossus, stylohyoid, thyrohyoid
pharynx connects at the top
constructors and longitudinal superior constrictors
cavity superior to oral cavity
Nasal cavity
these vibrate to produce phonation
vocal folds
Muscle that elevates and closes off the nasal cavity during pronunciation of consonants
velum
Vocal register is the lower limit of the pitch range
glottal fry
Instrument that measures lung volume
spirometer
Structure comprised of 16-20 cartilaginous rings
trachea
Cavity between teeth/gums and cheeks
Buccal cavity
Structure that closes airway in response to foreign objects
larynx
Tension of the vocal folds in crease, and ....
pitch rises
Quiet flow of air into and out of the lungs
tidal respiration
primary muscle of inspiration
diaphragm
Muscle of the larynx that abducts the vocal folds
posterior cricoarytenoid
During expiration, this force returns structures to original state
recoil forces
this volume cannot be voluntarily expelled
residual volume
Vowels that are longer in duration and have more acoustic power
tense vowels
Cavity of the larynx is considered to be entryway from the pharynx
adits
muscle that makes up most of the vocal folds
thyroarytenoid
this type of elf attack occurs when air flows prior to adduction of vocal folds
breathy attack
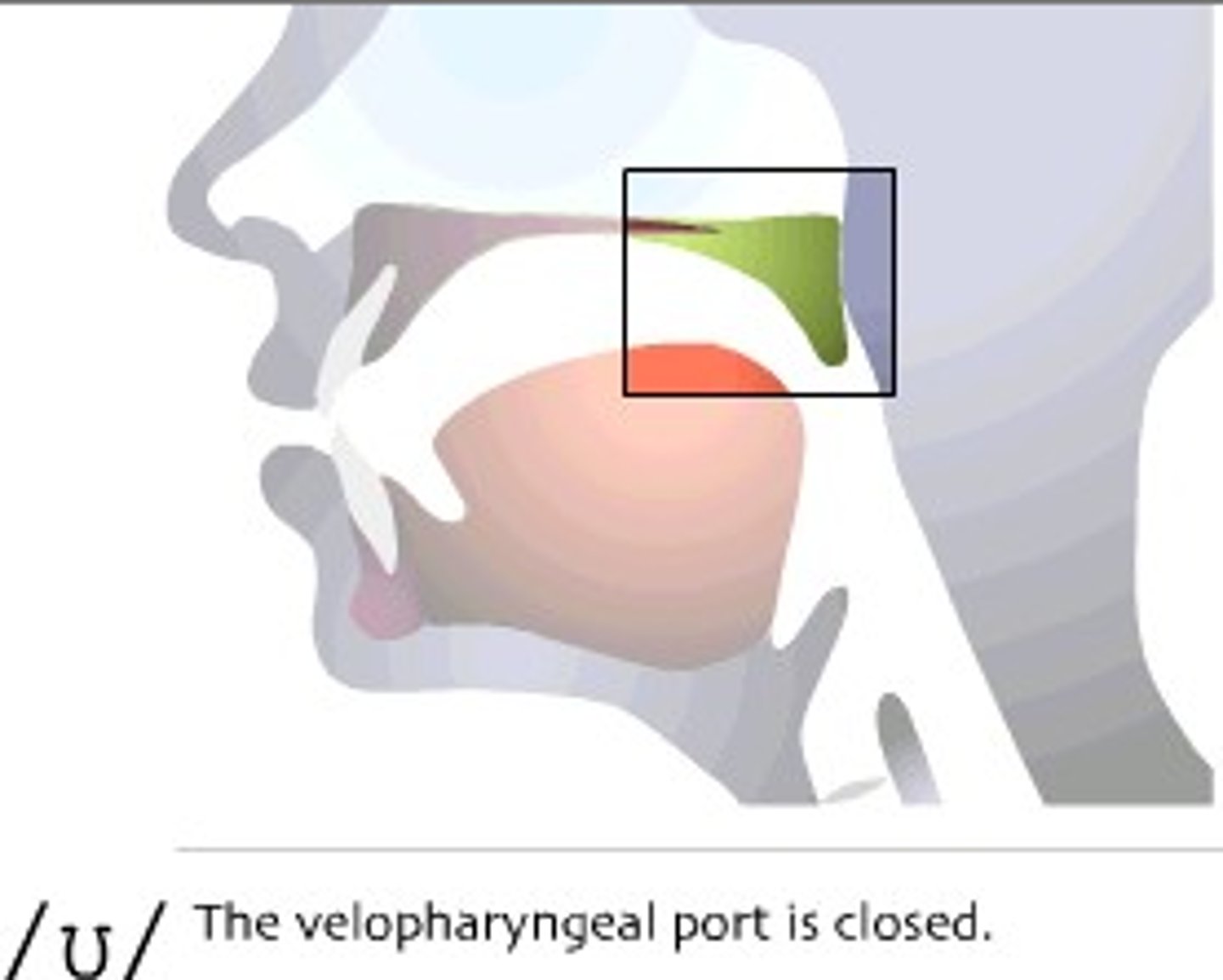
Consonant sounds that require the opening of the velopharyngeal port
nasals
velopharyngeal port
opening between oropharynx and nasopharynx
Consonants made by putting tongue against the bony ridge behind front teeth.
Alveolars
Also known as false vocal folds
ventricular folds
Ligaments that connect the larynx to adjacent structures
extrinsic ligaments
Muscle encircles the mouth and is shaped like an oval ring
orbicularis oris
Extrinsic muscle of the tongue is the largest and forms the bulk of the tongue
genioglossus
Air-filled sacs together at the terminal bronchioles
alveoli
Pouting muscle, lip protrusion and depression
mentalis muscle
structure is tree-like, connects trachea to lungs
bronchial tree
House and protect lungs and provide smooth, easy glide when breathing
pleurae