872: Intro to EKG Interpretation
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Cardiac conduction system begins with the
Sinoatrial (SA) node
SA node
Located in the right atrium
Spontaneously and repeatedly depolarizes
After leaving the SA node the action potential will
Spread throughout the right and left atria
AV node
Depolarization is delayed which allows enough time for the ventricles to fill with blood before they are stimulated to contract
After leaving the AV node the action potential will
Bundle of HIS, right and left bundle branches, and finally the Purkinje fibers
Three main waves in a normal EKG
P wave
QRS complex
T wave
P wave
Represents atrial depolarization (action potential spreading through the atria)
QRS complex
Represents ventricular repolarization (action potential spreading through the ventricles)
T wave
Represents ventricular repolarization (point at which the ventricular cardiac muscles return to their resting electrical state)
The 6 second method
Count to the nearest half the number of R-R intervals in 6 seconds and multiply the number by 10
Sinus bradycardia
HR less than 60 bpm
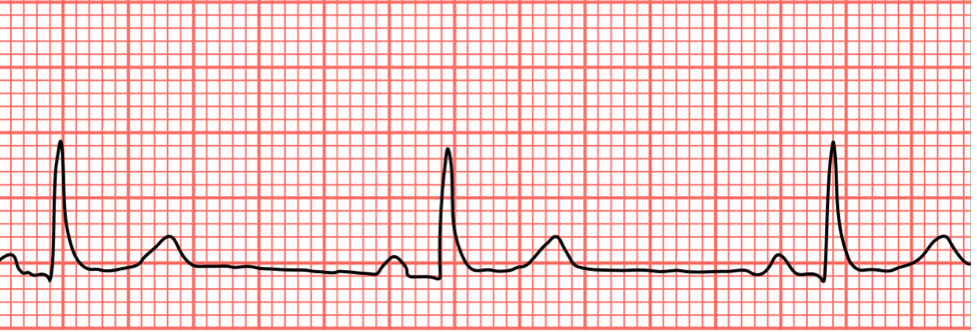
Causes of sinus bradycardia
exercise training adaptation
Medications
Decreased automaticity of the SA node
TBI
Increased vagal stimulation
Sinus tachycardia
HR is above 100 bpm
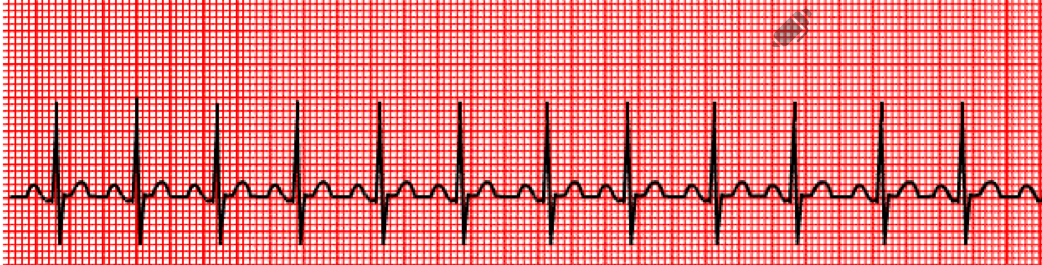
Causes of sinus tachycardia
usually benign
Increased sympathetic stimulation (fear, exercise, emotion, stimulants)
Fever
CHF
Infection
Anemia
Hemorrhage
Myocardial injury
Hyperthyroidism
Sinus pause
SA node fails to initiate an impulse
Usually only for one cardiac cycle
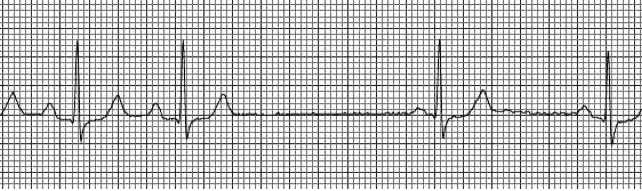
Causes of sinus pause
sudden increase in parasympathetic activity
Sick sinus syndrome
Infection
Rheumatic disease
Severe ischemia or infarction of the SA node
Premature atrial complex, PAC
Early, premature beat
This impulse arises from somewhere above the ventricles but not the SA node
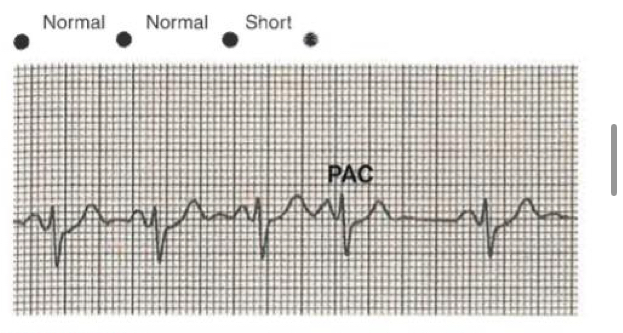
Causes of premature atrial complex
emotional stress
Nicotine
Caffeine
Alcohol
Hypoxemia
Infection
Ischemia
Rheumatic disease
Atrial damage
Atrial flutter
Rapid succession of atrial depolarization caused by one ectopic focus in the atria that depolarizes at a rate of 250-350 times per minute
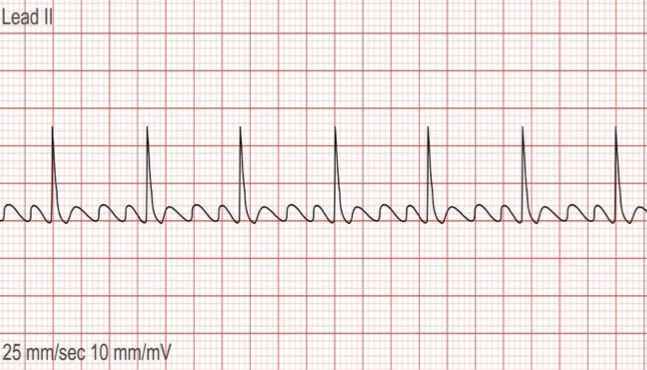
Causes of atrial flutter
rheumatic heart disease
Mitral valve disease
CAD
Stress
Drugs
Renal failure
Hypoxemia
Pericarditis
Atrial fibrillation
Erratic quivering or twitching of the atrial muscle caused by multiple ectopic foci in the atria that emit electrical impulses constantly
No true p waves found
Atria do not contract
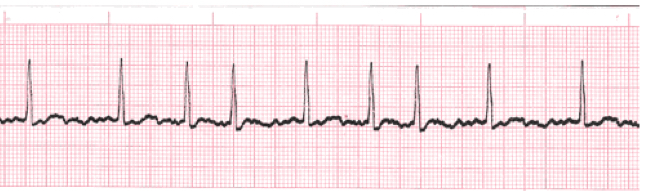
Causes of atrial fibrillation
advanced age
CHF
Ischemia or infarction
Cardiomyopathy
Digoxin toxicity
Drug use
Stress or pain
Rheumatic heart disease
Renal failure
Premature ventricular complexes
an ectopic focus causes an impulse from one of the ventricles
Occurs early before the SA node actually fires
Wide QRS without a p wave
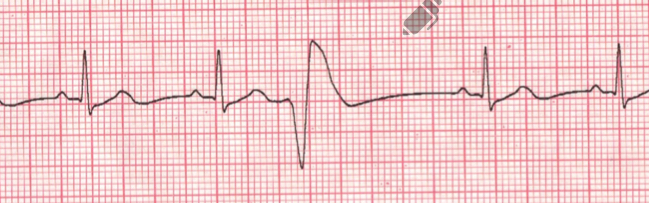
Causes of premature ventricular complexes
caffeine, nicotine
Stress/anxiety
Over exertion
Electrolyte imbalances
Ischemia
Cardiac disease
Overdistension of the ventricle
Irritation of the myocardium
Lung disease
Hypoxemia
Medications
Ventricular tachycardia
Three or more PVCs in a row
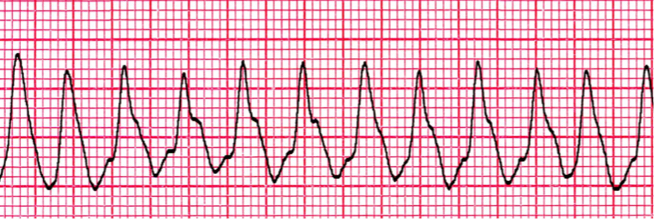
Causes of ventricular tachycardia
ischemia or acute infarction
Hypertensive heart disease
Reaction to meds
Electrolyte imbalance in athletes during exercise
Ventricular fibrillation
An erratic quivering of the ventricular muscle resulting in no cardiac output
Multiple ectopic foci are firing
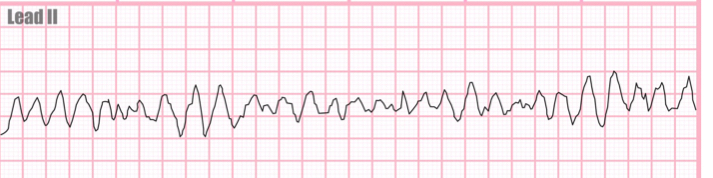
Causes for ventricular fibrillation
Same as those for v tach
V tach can progress into v fib