Unit 6: Chapter 15 - Urban Settlements
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Urbanization
the process of the development of dense concentrations of people into settlements
What are challenges urban areas experience as their population increases?
More people in the city increases the demand for fresh water, housing, food, and electricity.
Urban area
a city and its surrounding suburbs
Today 55 percent of the world's population lives in urban areas.
Metropolis / Metropolitan area
a city and the surrounding areas that are influenced economically and culturally by the city
What were the oldest settlements?
Earliest were in the Fertile Crescent, present day Iraq
What and where is the oldest well-documented settlement?
Oldest well-documented settlement is Uruk in Iraq.
Dates back to 3000 B.C.
Ancient Settlements
-First established in eastern Mediterranean about 2,500 B.C.
-primarily trading centers and organized into city-states
Ex:
Knossos (on the island of Crete)
Troy (in Asia Minor- Turkey)
Mycenae (in Greece)
Athens was the largest city-state in Greece
City-state
a sovereign state comprising a city and its immediate hinterland (surrounding area)
Medieval Urban Settlements
Dense network of small market towns serving the needs of lords covering much of Europe
-Tallest and most elaborate structures were usually churches
-Settlements usually surrounded by walls.
What purpose did the largest settlements serve?
-power centers for the lords & church leaders
-major market centers.
When was the first time in human history urban settlements exceeded rural settlements?
2008
What spurred the development and growth of urban settlements?
The Industrial Revolution and the mechanization of farming equipment
(Mechanization reduced the need for human labor, so people moved to urban areas for jobs because they didn't work on farms anymore)
Why are 8 of the 10 biggest cities in semi-periphery and periphery countries?
because of globalization and the expansion of manufacturing and cheap labor
(Core countries set up factories and plantations in semi-peripheral and peripheral countries due to large amounts of laborers willing to work for lower wages)
Site
the actual place or location of the settlement and the land on which the city is built
Climate, natural resources, absolute location, physical terrain
Ex:
Flat, fertile land with access to fresh water
Situation
The connection between a city's site and other sites.
Rivers, roads, relative location
Ex:
Easy access to trading partners, trade routes.
Why is transportation is one of the most influential factors in urban growth?
-people can move faster (to urban areas)
-moving raw materials to factories
-moving goods to markets
-giving workers to access jobs
How has transportation influenced settlement patterns in the United States?
-In the Colonial period, cities grew along the Atlantic Coast or rivers for travel & trade.
-New Orleans grew to prominence because of its location on the Mississippi River.
-The Erie Canal and railroads helped inland cities such as Chicago, Omaha, and Kansas City grow.
How have communication networks opened new opportunities for businesses?
Communication networks opened new opportunities for businesses to locate where they wanted.
With the invention of the phone and computer (internet), people can live anywhere and still work.
Push factors contributing to urbanization
-fewer opportunities to make a living in rural areas as population grows in those areas
-drought or other environmental or economic factors
Pull factors contributing to urbanization
-availability of jobs in cities
-greater freedom, safety, schools, and health care in cities
What does a city's function depend largely on?
its location and history. Some cities serve specific functions
Ex:
-Houston is the "energy capital of the world" due to large amounts of oil and natural gas reserves
-Washington D.C. is the capital of the U.S. and is the center of the official government business.
How can a city's function change over time?
as the result of technological advances or changes in economic or population trends.
Ex:
Silicon Valley was agricultural land until the 1980s when it became the center of the computer industry and now manufacturing high-tech research and development. It is the home of companies like Apple, Oracle, and Atari.
Most cities have expanded, but how have cities also declined?
some cities experience a decline when their economic or other functions are no longer relevant.
Ex:
The population of Detroit - which was once the hub of General Motors, Chrysler, and Ford - has declined as automobile manufacturing has expanded to other parts of the United States and other countries that offer less expensive labor.
Secondary industries
Secondary industries meet people's needs for housing, food, transportation, etc. and is given rise by the foundational economic activity (basic industry)
Suburbanization
-The development of transportation systems has led to suburbanization.
-Suburbanization increases the land area of a metropolitan area; population does not necessarily grow.
Urban sprawl
Urban areas expand in an unplanned and uncontrolled way
Common in U.S. metropolitan areas, particularly in cities that grew up with the automobile and freeway expansion after World War II.
How has sprawl has greatly increased dependence on personal motor vehicles?
Vehicles are needed to reach faraway activity centers
More roads and other infrastructure must be built and maintained at great cost
Edge city
located on the outskirts of a larger city, usually along a large transportation corridor, like a beltway.
They are commercial centers with their own office space, retail complexes, and other amenities typical of an urban center.
Ex. in Houston:
The Woodlands, Cypress, Kingwood, Katy, Jersey Village, Memorial, Sugarland, Clear Lake
Boomburb
a suburb that has grown rapidly into a large, sprawling city with 100,000+ residents.
Often consists of many planned communities that have begun to merge together.
Ex:
Pearland
Exurb
a fast growing community outside of or on the edge of a metropolitan area where residents and community are closely connected to the central city and suburbs.
Often low density residential communities that may include wealthy estates or small rural towns
Ex:
Frisco
How have urban planners have started efforts to try to address the issues of urban sprawl?
-revitalization: reusing or renovating buildings, beautifying an area through landscaping
-redevelopment: converting existing properties into more desirable uses, creating new mixed-use neighborhoods
-infill
Infill
redevelopment that identifies and develops vacant parcels of land within previously built areas that are already served by transportation and other public infrastructure.
How do different cities have different functions within an urban hierarchy?
Within an urban complex, cities may function as centers of healthcare, manufacturing, finance, commerce, arts, education, or tourism.
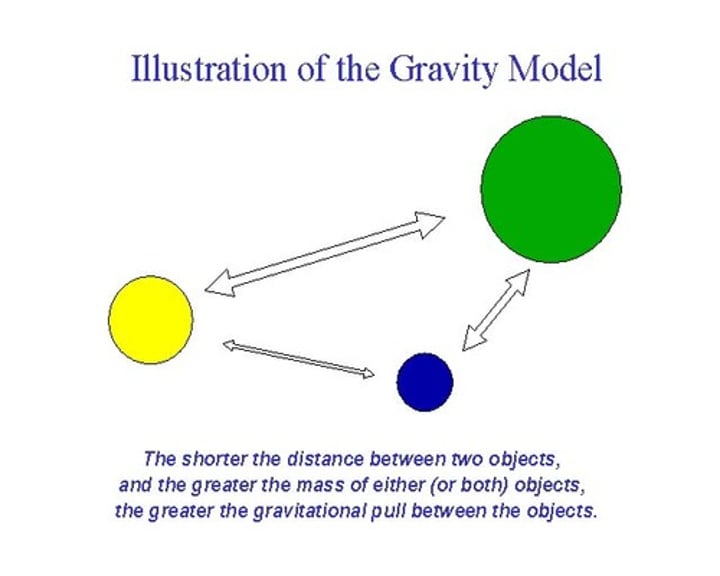
Gravity model
The interaction of people and goods between cities is generally proportional to the product of their populations and inversely proportional to the distance between them.
1.) As the population of a city increases, migration to the city increases.
2.) As the distance to a city grows, migration to that city decreases.
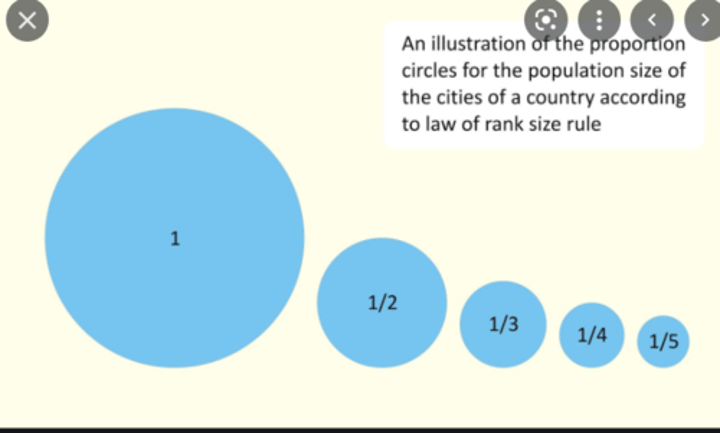
Rank-size rule
The second-largest city will be one-half the size of the largest city, third-largest city will be one-third the size of the largest city, etc.
This is most common in peripheral countries.
Primate city
a city that far exceeds, in population size and influence, the country's next-largest city
Ex:
Mexico City, Dakar, London, Birmingham, Paris, etc.
What are some challenges countries with primate cities might encounter?
-more likely to have unequal economic development
-dependent on one major city for economic prosperity
-citizens that don't live in the primate city most likely lack many goods and services
How do many primate cities trace their origin to a colonial past?
European colonizers concentrated political and economic activities in one place
Megacity
a metropolitan area with a population of more than 10 million people
-2 megacities in 1950
-33 megacities in 2018
-43 megacities expected in 2030
Ex:
Paris, Buenos Aires, Los Angeles
When was Rome, the first megacity, founded?
Founded April 21, 753 BCE by Romulus and Remus
What was Rome's population?
between 250,000 and 1 million
What allowed Rome to become the first megacity?
the creation of roads and aqueducts
Without infrastructure (roads, water, sanitation) the city could not have supported that large of a population.
Metacity
a metropolitan area with a population of more than 20 million
-9 metacities in 2020
Ex:
Tokyo, Delhi, Mumbai
Where are most of the world's most populous megacities and metacities projected be in?
Periphery and semi-periphery countries.
This is due to global migration patterns, differences in birth rate, and lack of employment opportunities.
Birth rates are declining in core countries, and people are looking to live in suburbs and edge cities more than urban areas.
(remember the DTM!)
World cities
cities that wield political, cultural, and economic influence on a global scale
Ex:
London, New York City, Tokyo, Paris,
What are world cities major centers of?
-banking, communications, and finance
-innovation, manufacturing, and trade, which are exported through diffusion
What are world cities sites of?
-leading global markets for commodities, investment, and foreign exchange
-trade associations, professional associations, nongovernmental organizations
What are world cities headquarters for?
media organizations & multinational companies
How do world cities influence culture globally?
-home of fashion, design, entertainment, cultural industries
-Many elements of contemporary culture, such as hip-hop, Bollywood, and fast food, have diffused from world cities.
How are world cities globally linked?
-World cities are connected globally and are drivers of globalization.
-Multinational corporations have a major presence in world cities, creating linkages.
-Have international airports and serve as destinations for both visitors and migrants
Other cool facts of world cities!!
-Big world cities are not necessarily the largest in population size.
-The cities that host Summer and Winter Olympics are usually world cities
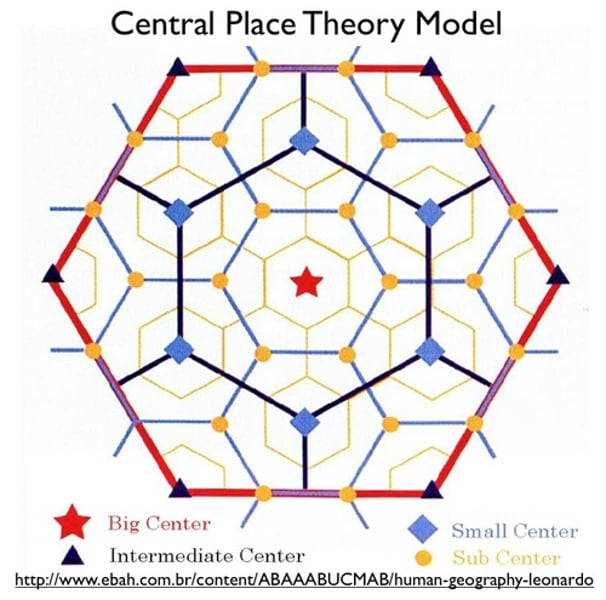
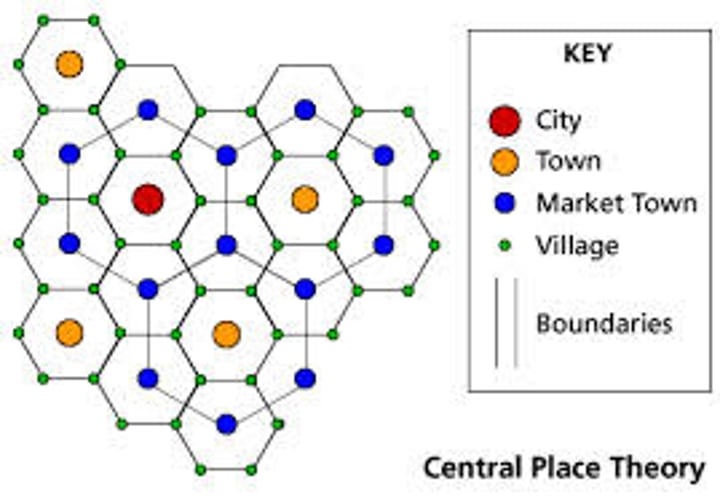
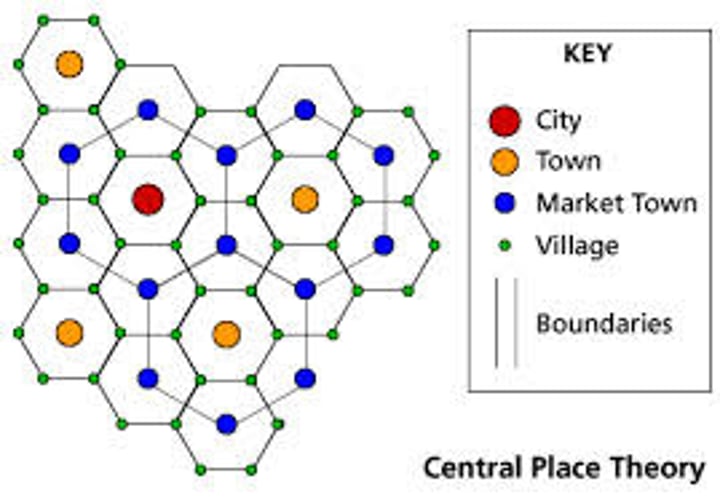
Central Place Theory
explains the hierarchical patterns in the number, size, and location of cities and other settlements.
-proposed by Walter Christaller in 1933
-helps to determine the most profitable location for a business
-pattern based on consumers' behavior and decision-making
Urban Hierarchy
1. City - Largest
2. Town
3. Market Town
4. Village
5. Hamlet - Smallest
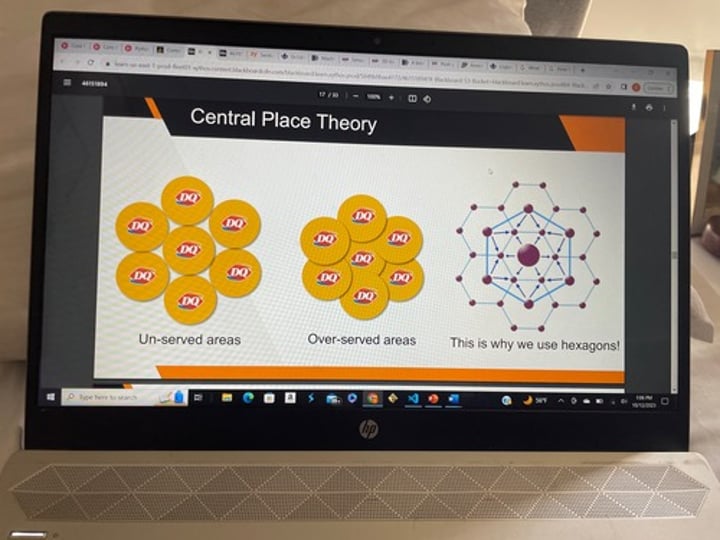
Why does the Central Place Theory use hexagons?
Geographers use HEXAGONS to represent market areas.
They combine the EQUIDISTANCE of circles with the TOTAL COVERAGE of squares
term-71
(do not overlap & cover all areas)
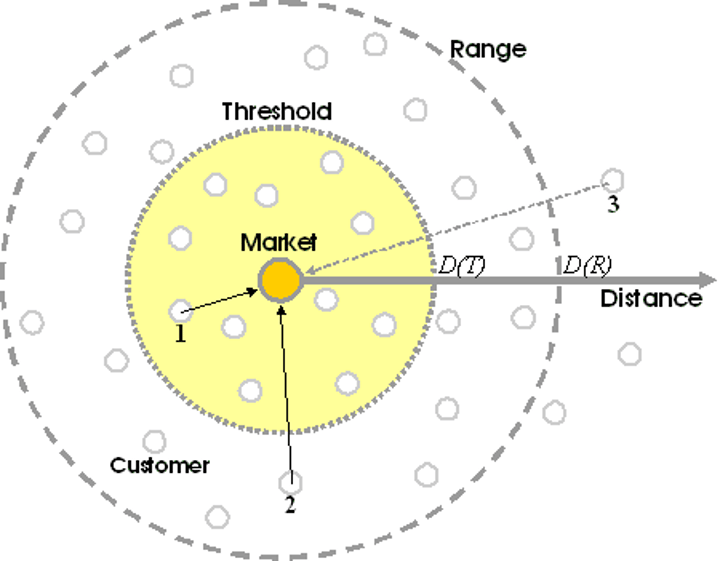
Central Place
a settlement that provides goods and services for the surrounding area
Market Area
The area around a central place is called its market area or hinterland (the area inside the hexagon)
Range
the maximum distance people are willing to travel for a certain good or service
How do some services/goods have different ranges?
the more unique, important, or specialized the good or service is, the larger the range will be
goods and services that are more common and easily replicable have a smaller range
Ex:
fast-food restaurant might have a range of 5 miles, a pro sports facility might have a range of 60 miles or more
How does the amount of time it takes to travel affect a good/service's range?
As a rule, people tend to utilize the closest available service or a service that takes the least amount of time.
Ex:
In densely populated and busy urban areas, a service's range is smaller due to larger amounts of traffic and longer commute times.
For example, Subways are more clustered in Downtown Houston than in areas with less traffic and a lower population density.
What is an exception to this rule?
People will usually only break this rule ONLY if substantial cost savings are involved, or if there is a substantial quality difference.
Threshold
the minimum number of people needed to support a service.
Once a range has been found, a business must decide if enough people live within that area.
If the THRESHOLD is larger than the RANGE, then a service will not be profitable.
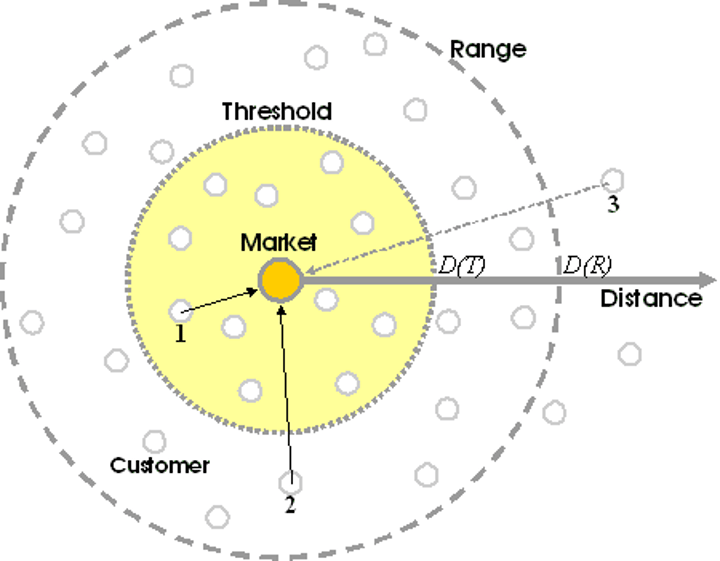
How do consumers determine the locations of different stores?
Not everyone matters for threshold, however; each business looks for a certain type of CUSTOMER.
Ex:
-A thrift store like MARSHALLS would look for a location where plenty of low-income people reside.
-An upscale department store like NEIMAN MARCUS would look for a market area with plenty of wealthy residents.
What is used to help locate these consumers to help businesses meet their threshold?
Census Data
How does the size of settlements impact the services they offer?
-The smaller the settlement, the fewer amenities and opportunities they have because they can't meet the threshold to support those businesses
-The city, which has the largest population, will have the largest variety of specialized services and have the most unique goods
-The other towns will have more general services and goods people use on a daily basis.
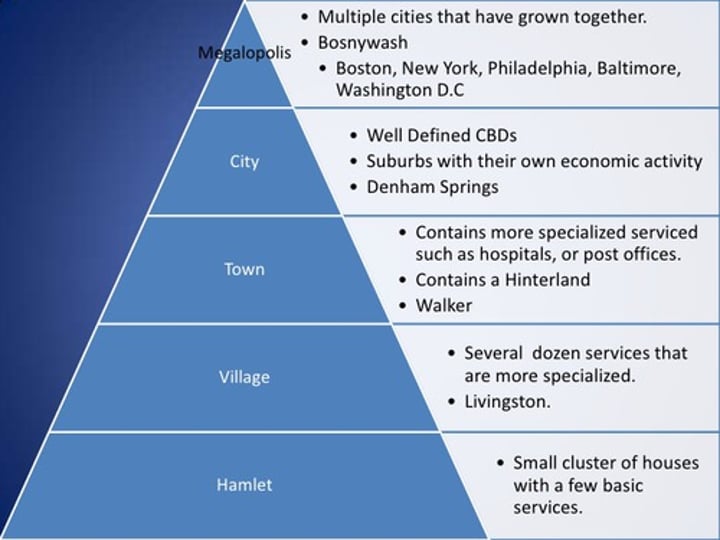
How does the size of settlements impact their location?
-The smaller the settlement the closer they will have to be to a major urban area or a larger settlement because they need to depend on other settlements for goods and services
-The larger a settlement the farther away it can be from another major urban area since they're more likely to have their own services
(Notice villages - the smallest settlements - surround larger settlements to gain access to different goods and services)
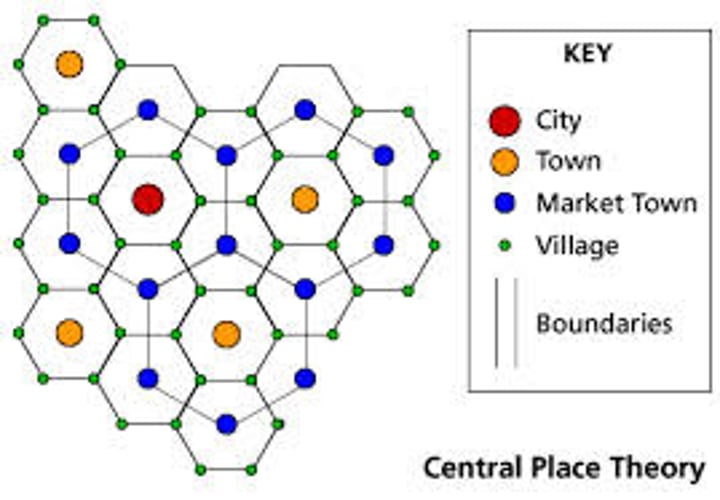
How do the number of settlements vary in proportion to their size?
The larger the settlements, the less the number of the settlements. (fewer cities)
The smaller the settlements, the greater the number of the settlements. (more villages)
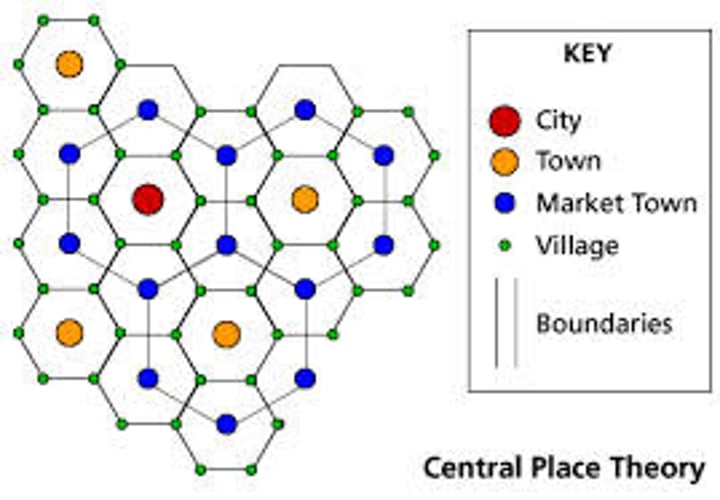
What are limitations of the Central Place Theory?
-based on a flat surface with no natural, political, or other barriers
-assumes equal range in all directions
-does not account for physical geography or differences in transportation linkages
-assumes retail market is the most important influencer
-doesn't take into account changes in technology
Are cities built from scratch?
No, they grow and evolve over time.
How is it a useful exercise to imagine what an ideal city of the future might look like if urban planners were able to design one from scratch?
Knowing what an ideal city looks like in the future can help urban planners make improvements today.
Ex:
Urban planners can incorporate green roofs, urban farms, backyard and school gardens, etc. which can be built upon and improved in the future.
