AS103 Astronomy Exam 2
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Planets’ orbits are
elliptical with the sun at a focus
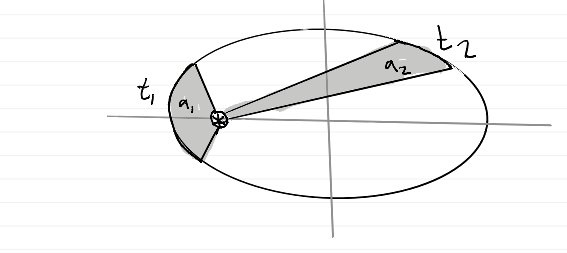
The line between a planet and the sun sweeps out
equal areas in equal times
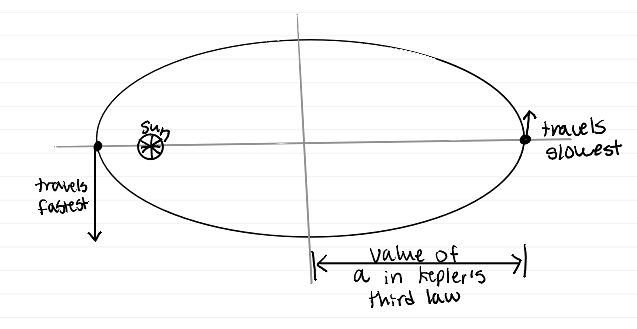
A complete orbit has P^2 = a^3, where P and a represent
sidereal orbital motion (yr) and semi major axis (Au) (conservation of angular momentum)
Newton’s first law
an object’s velocity will remain constant if there is no net external force acting on it
Newton’s second law: the acceleration of, mass of, and net force on an object are related as (equation)
acceleration = net force / mass (F = ma)
Newton’s third law
the action and reaction forces between two bodies are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. ΣF12 = -F21
Why do we say that an object traveling at constant speed on a circle is accelerated, even though its speed is not changing?
its direction of motion is changing. acceleration is a change in velocity and velocity is speed and direction
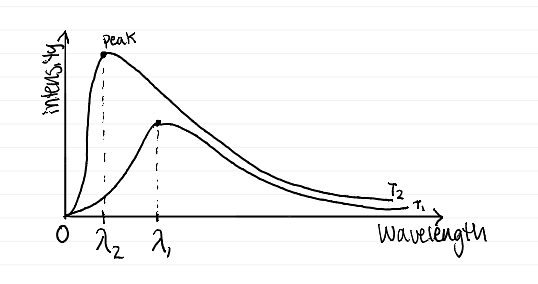
SB law says
total emission is proportional to T^4
Wien’s law says
different temperatures peaks at a wavelength is inversely proportional to the temperature
What is special about the Kelvin/absolute scale?
kelvin has zero temperature at minimum molecular kinetic energy. As cold as you can get. Energy is proportional to temperature. (more convenient)
What is conservation of energy
initial energy = final energy
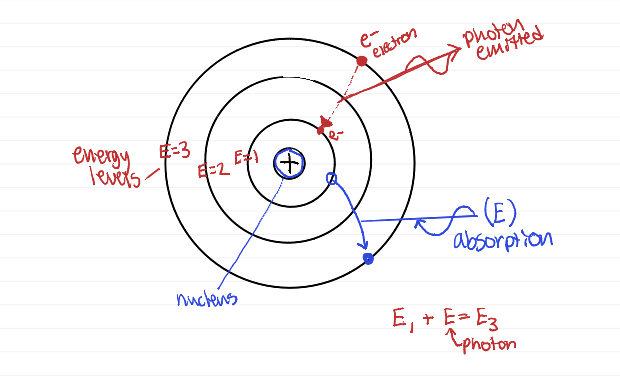
Equation that relates initial and final energy of system (e- jumps from level 3 to level 1)
E1 + E = E3
Why is it possible to use the emission/absorption spectra of atoms to identify what element the atoms are?
the spectra (the photons) are unique to each element or chemical compound
What is the biggest obstacle to Earth-bound viewing in astronomy?
the atmosphere
Why are telescopes placed in high locations?
to get above some of the atmosphere. (less absorption)
Why are telescopes placed in remote locations?
darker, less light pollution (reflection)
What are two main types of telescope mounts
Altitude-azimuth, equatorial
How is alt-az aligned
zenith aligned
How is equatorial mount aligned
polar aligned
Which mount can carry the most weight
altitude-azimuth
Which mount is easier to use for taking pictures
equatorial
Rank eye, photo film, CCD based on sensitivity, linearity, data analysis
poor: eye, good: film, excellent: CCD
If you increase the diameter of telescope 3 times, by what factor does the image brightness change
B α D^2 … B’/B = (3D)^2 / (D)^2 = 9
If you increase the diameter of telescope 3 times, by what factor does the image resolution change
R α D … R’/R = 3D/D = 3
Rank the importance of magnification, brightness, and resolution
brightness=1, resolution=2, magnification=3
Is magnification improved by a larger diameter?
no
Is brightness improved by a larger diameter?
yes
Is resolution improved by a larger diameter?
yes
Mathematical relation to diameter (magnification)
none (D^0)
Mathematical relation to diameter (brightness)
D^2
Mathematical relation to diameter (resolution)
D^1
Which telescope (reflector or refractor) performs better with construction
reflector
Which telescope (reflector or refractor) performs better with spherical aberration
they perform the same
Which telescope (reflector or refractor) performs better with chromatic aberration
reflector
Which telescope (reflector or refractor) performs better with atmospheric transmission
they perform the same (relates to location)
Which telescope (reflector or refractor) performs better with light pollution
they perform the same (relates to location)
Why do we sometimes speak of light as rays and sometimes as "electromagnetic waves"?
they can behave as particle and have magnetic field. Light travels in a straight line
Why do we have to use the absolute temp scale in describing blackbody radiation
because this scale is based on thermal energy
What are the two processes used by lenses and mirrors to focus light and create an image?
reflect and refract
What countermeasures can we employ against things that make for poor viewing
high, dry, and dark places
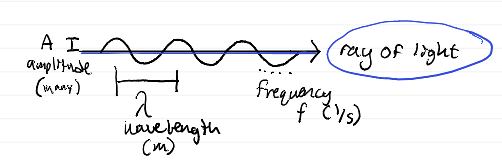
parts of a wave diagram
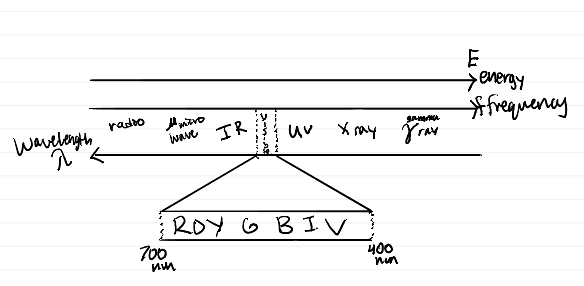
Electromagnetic spectrum diagram
blackbody diagram
photon emission/absorption diagram
equal areas equal times diagram
object traveling around sun diagram
object traveling in a circle diagram
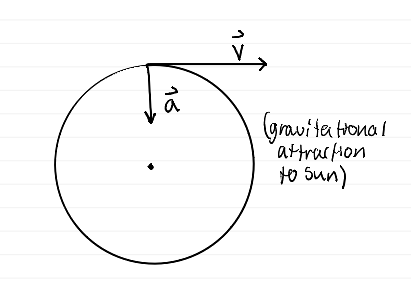
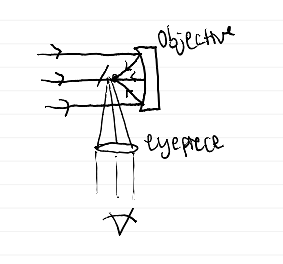
diagram of refractor
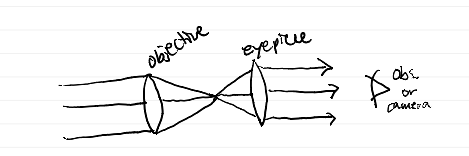
diagram of reflector
equation relating wave speed (v), frequency (f), and wavelength (lambda)?
v = f * λ