CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND ESTERS
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
carboxylic acids
contian the carboxyl functional group -COOH

carboxylic acids are weak acids
in water they partially dissociate into carboxylate ion and H+ ion
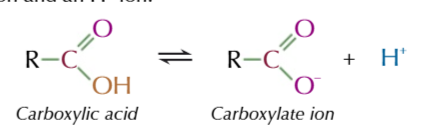
the dissociation of carboxylic acids is a reversible reaction
but the equilibrium lies on the LEFT ebcause most of the molecuels DONT dissociate
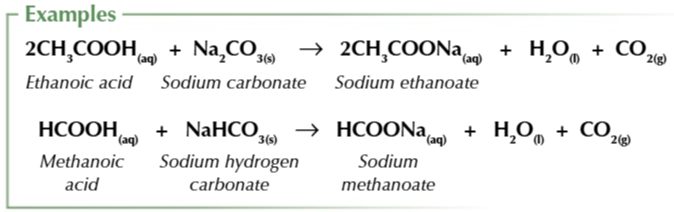
carboxylic acids react with carbonates (CO32-) or hydrogen carbonates (HCO3-)
to form a salt, carbon dioxide and water
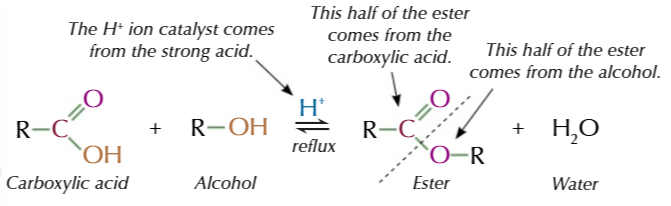
esterification
heating carboxylic acids with an alcohol in the presence of a strong acid catalyst produces an ester
concentrated sulfuric acid/ hydrochloric acid/ phosphoric acid
all strong catalysts that can be used
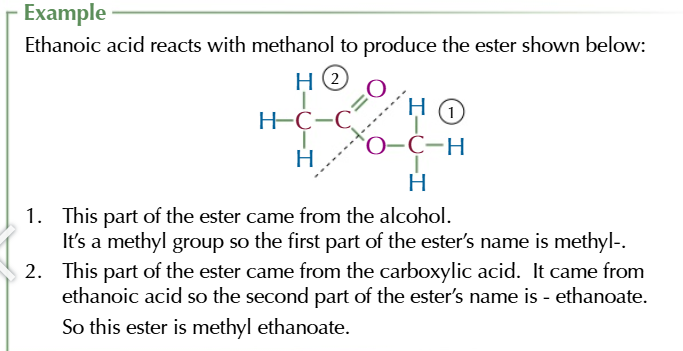
naming an ester
(alcohol)-ly (carboxylic acid)-oate
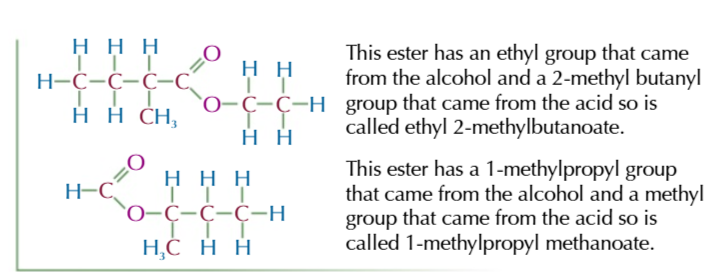

esters are sweet smelling
useful for perfumes/drink flavours/sweet flavour
esters are polar liquids
dissolve other polar organic compounds
esters have low boiling points
evaporate easily from mixtures making them good solvents in glues and printing inks
esters make good plasticisers
added to plastics during polymerisation to make the plastic more flexible
hydrolysis
the splitting of a substance by water
there are two types of hydrolysis of esters
acid hydrolysis
base hydrolysis
acid hydrolysis of esters
splits esters into an acid and an alcohol
acid hydrolysis of ester conditions
reflux ester with dilute acid: HCl/H2SO4
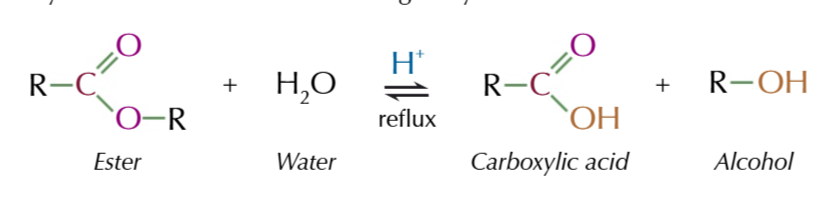
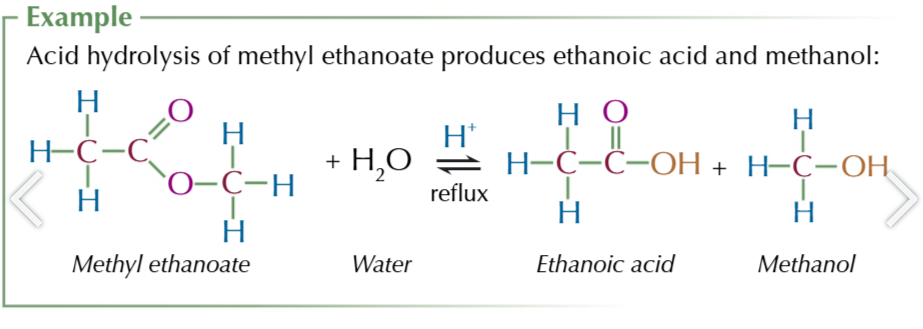
reservible reactions to require alot of water to shift the equilibrium over to the right so you get lots of product
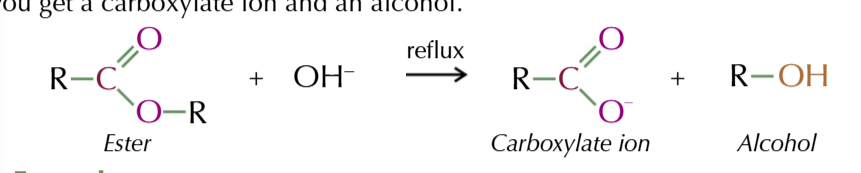
base hydrolysis conditions
reflux the ester with dilute alkali: NaOH
OH- ions from the base react with the ester and you get a carboxylate ion and an alcohol
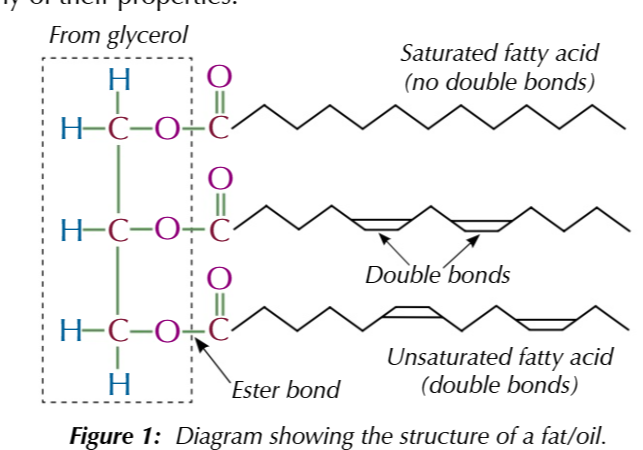
animal fats and vegetable oils are
esters of glycerol and fatty acids
fatty acids
long chain carboxylic acids
glycerol
propane-1,2,3-triol
fatty acids can be saturated
no double bonds
fatty acids can also be unsaturated
double bond
most fat/oil is made from the fatty acid chain
so the chain gives them their properties
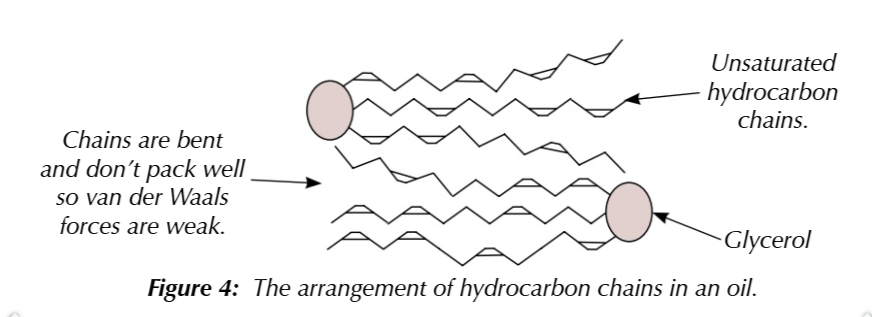
fats have mainly saturated hydrocarbon chains ncreasing the van der waals forces between them
this means higher temperatures are needed to melt them and they are solid at room temperature

oils have undasurated hydrocarbon chains, the double bonds bend the chain and dont pack well together, decreasing the effect of van der waals forces
so theyre easier to melt and are liquids at room temeprature
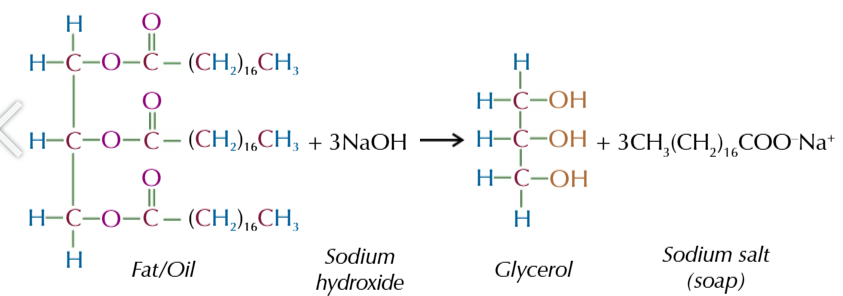
you can hydrolyse oils in base hydrolysis by heating them with sodium hydroxide
OH- from the sodium hydroxide reacts with the fat/oil to form a carboxylate ion and an alcohol.
the alcohol that is formed is glycerol
and the carboxylate ions combine with Na+ to form a sodium salt AKA SOAP
you can convert the sodium salt back into a long chain carboxylic acid (fatty acid) by adding HCl
the H+ ions displace the Na+ to form the carboxylic acid
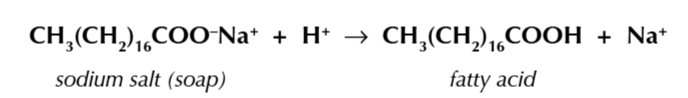
vegetable oils make good vehicle fuels when converted into biodiesel
reacting vegetable oil with methanol using a strong alkali: KOH/NaOH as a catalyst to produce a mixtuer of methyl esters of of long chain fatty acids(biodiesel)
biodiesels are thought to be carbon neutral
because when you grow crops they absorb the same amount of CO2 produces when theyr burned
energy is used to make fertilizer, plant the crops, harvest the crops, convert into oil
this enrgy comes from fossil fuels so the process is not carbon neutral overall
acyl (acid) chlorides functional group
COCl
acyl chloride general formula
CnH2n-1OCl

acyl chloride naming
-oyl chloride and the carbon atoms are numbered with accordance to the carbon with the functional group
reactions of acyl chlorides
involve Cl being substituted by oxygen/nitrogen with misty fumes of hydrogen chloride produced
acyl chloride reacts vigorously with cold water producing a carboxylic acid
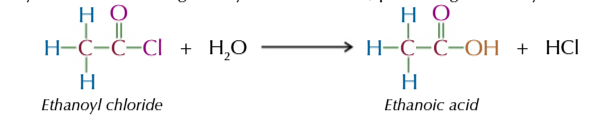
acyl chloride + alcohol → (vigorously+ at room temp) produces an ester
this is a faster method of esterification
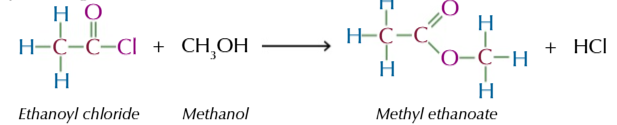
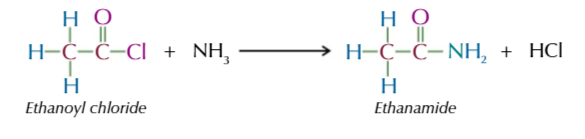
acyl chloride + ammonia → (vigorously @ room temp) produces amides
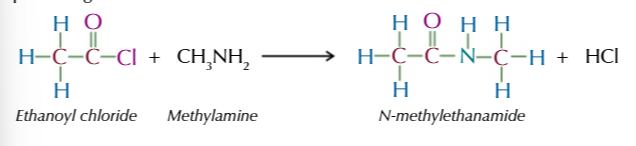
acyl chloride + primary amines → (vigorously @ room temp) produces N-substituted amide
acyl chloride reactions all have the same mechanism
nucleophilic addition-elimination
nucleophilic addition elimination reactions have 2 steps
nucleophile adds onto the acyl chloride, displacing the Cl- ion
the hydrogen leaves to create an acyl chloride derivative
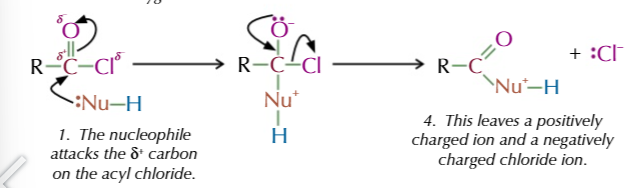
step 1 of addition elimination:
nucleophile attacks delta +ve carbon on acyl chloride
pair of electrons transferred from C=O to just oxygen so the nucleophile can bond with the carbon
the pair of electrons on oxygen reforms the double and the chlorine is kicked off
this leaves a positively charged nucleophile and a negatively charged chloride ion
step 2 of addition elimination:
a pair of electrons from the Nu-H bond is transfered to the nuceophile to cancel its charge
produces an acyl chloride derivative and a hydrogen ion
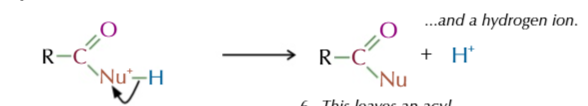
possible nucleophiles
H2O
CH3OH
NH3
CH3NH2
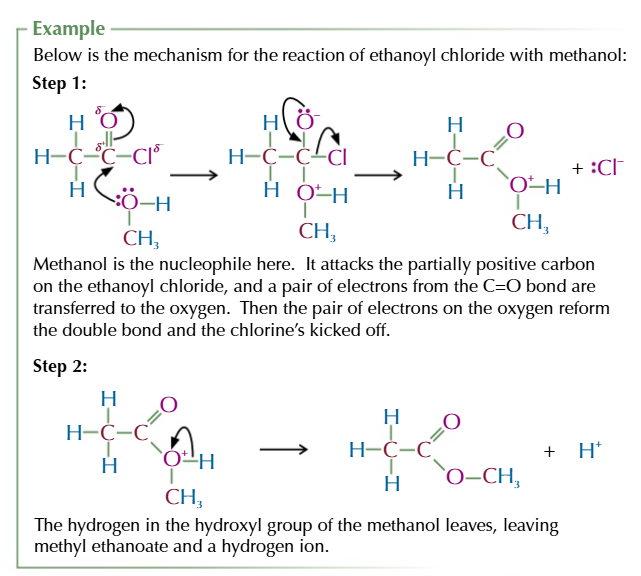
acid anyhydride
formed from 2 identical carboxylic acid molecules joined via an oxygen with the carboxyl group on either side,
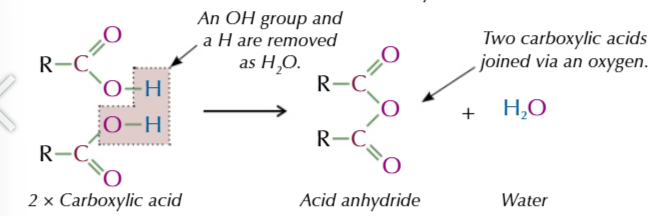
the oxygen comes from the OH of 1 of the carboxylic acids
the other OH group and the spare hydrogen are released as water
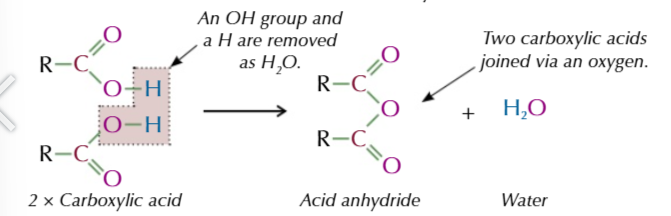
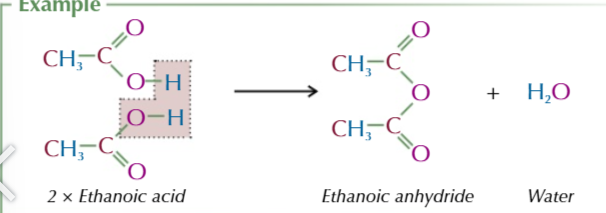
acid anhydride naming
-oic anhydride
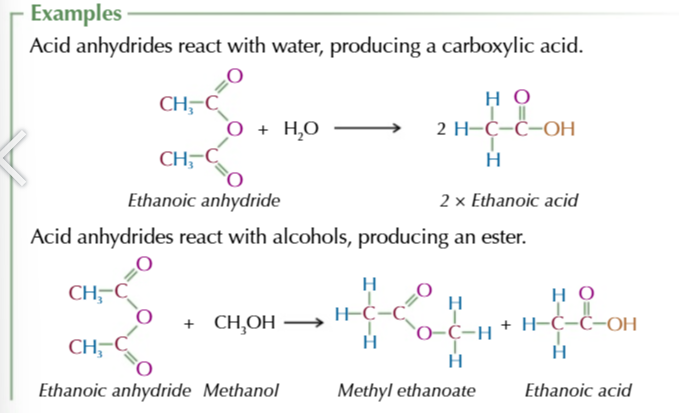
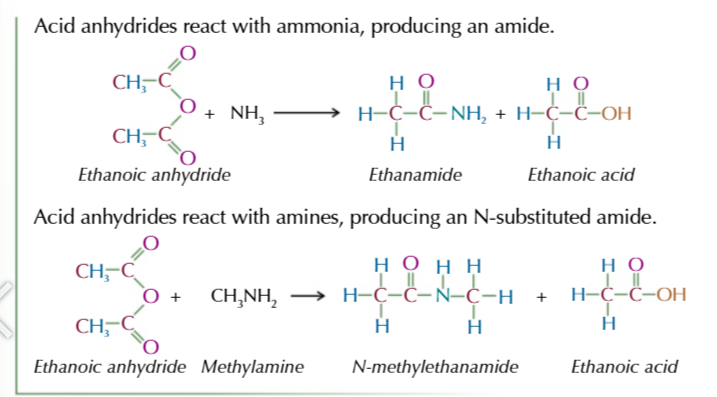
acid anhydrides react similarly to acyl chlorides only less vigorous and producing a carboxylic acid instead of HCl
asprin is an ester
formed by salicylic acid (contains alcohol group) + ethanoic anhydride OR ethanoyl chloride
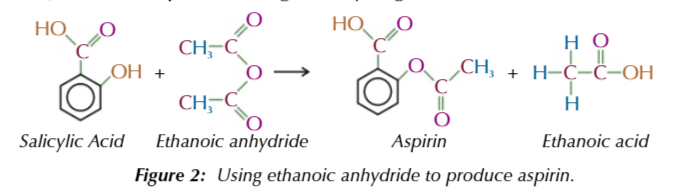
ethanoic anhydride is preferred in the industry over ethanoyl chloride
cheaper
safer (less corrosive)
reacts more slowly with water
doesn’t produce dangerous hydrogen chloride fumes
insoluble organic products
can be seperated to remove impurities that do dissolve in water like salts, water or soluble organic compounds like alcohol
organinc layer and aqueous layer ()containing water + impurities) don’t mix
are immiscible
organic layer usually less then than aqueous layer
you can open the stopper on the separating funnel run off the aqueous layer and collect your organic product
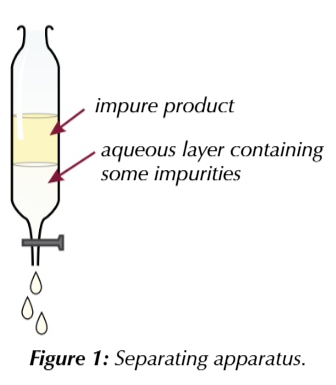
if your organic product has impurities you can use another form of separation
solvent extraction
solvent extraction method
vigorously shaking impure product with an immiscible solvent so they temporarily mix
your product needs to be more soluble in the added immisvible solvent than the one it was initially dissolved in
this was the producr will dissolve in the added solvent and seperate from the solution containing impurities
the solvent containint the product can then be run off
using a separating funnel
using seperation to purify a product will leave trace amounts of water in your product
so it must be dried
add anhydrous salts: MgSO4/CaCl
drying agents which binds to any water rpesent to become hydrated
when you first add the salt it will form clumps
meaning you need to add more
all the water is gone when
you can swirl the mixture and it looks like a snow globe
to remove the drying agent
filter out the mixture
the product of a reaction can still be condaminated with unreacted reagents or unwanted side products
you can remove these by washing the product

distillation seperates liquids with different boiling points
by gently heating a mixture in distilation apparatus
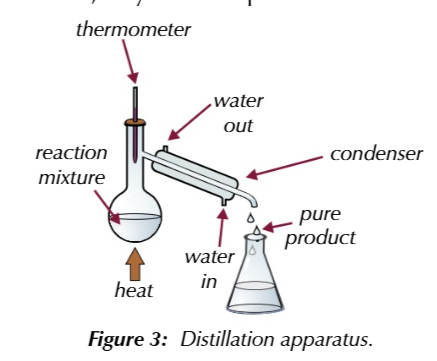
thermometer
placed at the neck of the condenser and shows the boiling point of the substance that is evapourating at any given time
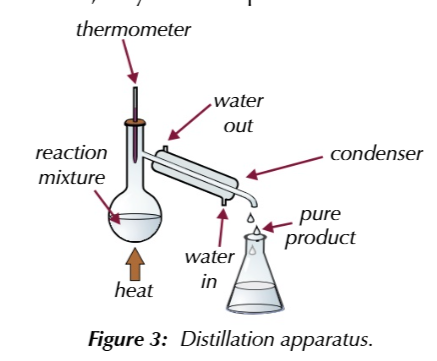
if you know the boiling point of your pure product
you can use ther thermometer to tell you when its evapourating and therefroe when its condesing
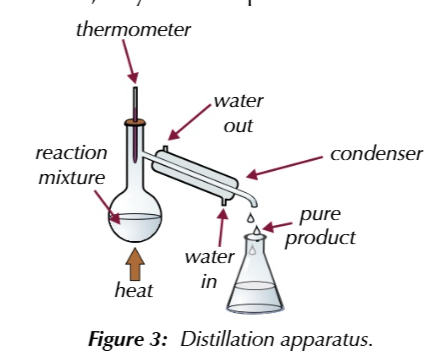
if product of reaction has a lower boiling point than the starting materials
the reaction mixture can be heated in distilation aparatus to the product evapourates from the reaction mixture as it forms
if the starting materials have a higher boiling point than the product
as long as the temeprature is controlled, they wont evapourate out from the reaction mixture

mixtures containing volatile liquids can be purified using
redistillation
if a product and its impurities have different boiling points
redistilation can be used to seperate them
the different between distilation and redistilation
you are heating the IMPURE PRODUCT not the reaction mixture
when the liquid you want boils
you place a flash at the open end of the condenserreadt to collect your product
when the thermometer shows the temperature changing
put another flask at the end of the condenser because a different liquid is about to be delivered
is product solid you can silplify it via
recrystalisation
firstly you dissolve your solid product in a HOT solvent to make a saturated solution then le tit cool down
as it cools down the solublilit of the product decreases
once crystals begin to form:
add a VERY HOT solvent to the impure solid until is just about dissolves
this gives a saturated solution of the impure product
leave the solution to cool down slowly so crystals of the product form
the impurities stay in the solution as they are rpesent in much smaller amounts than the product so they take much longer to crystalise
remove the crystants by filtration and wash them with a ICE COLD solvent
dry the crystals leaving you with a much purer solid product
to accurately determine the melting point of an roganic solid
you can use the melting point apparatus
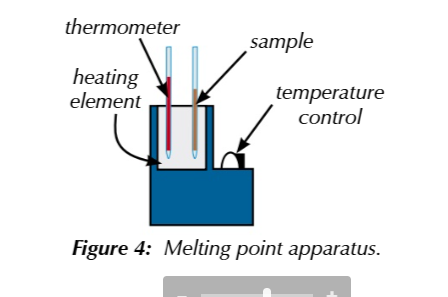
pack a small amount of sample into a glass capilary tube
place inside heating elemt
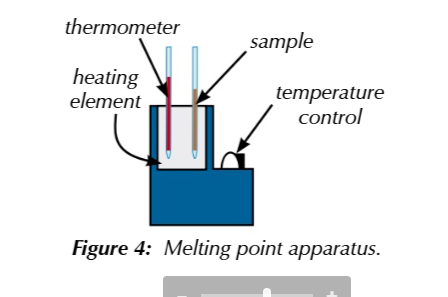
increase temperature until the sample turns from solid to liquid
measure a melting range from when the solid started to melt to where its fully melted
look up the melting point of the substance in the data book and compare results
impure samples have lower melting points and increase the melting range