BIO M02B: Darwinian evolution
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
before Darwin what did people believe?
nature is fixed and never changes, god made them perfect by divine creationism, new creatures arise when god makes them
Lamarck
first person for theory of evolution, had idea that species change overtime (correct) however thought species accumulated changes over their life time and passed them to offspring (incorrect)
what did Charles Darwin propose?
natural selection as a mechanism of evolution and decent with modification
Charles Lyell
major influence on Darwin, created a way to measure the layers of the earth, discovered earth was older than 10,000 years
Thomas Malthus
major influence on Darwin, discovered once a population goes above the production of food line, we will be in famine and start to die off, only a fraction of the population can reproduce
how did finches help Darwin?
he discovered their beak size was different on every island and was related to their food source, he thought they had a common ancestor leading Darwin to natural selection
natural selection
differential survival and reproduction of individuals based on variation in their traits
cell theory
all cells come from prexisting cells
evolutionary theory
all species came from preexisting species
components of Darwins theory of evolution (4)
variation exiss in populations
variations have to be heritable
some offspring will not survive
individuals with favorable traits will survive and reproduce more
what is the base unit for evolution?
populations
what is the source of variation which natural selection acts upon
genes
stabilizing selection
favors average phenotypes over extreme phenotypes
directional selection
favors one extreme phenotype over the other
disruptive selection
extreme phenotypes are favored over average ones, occurs in populations with diverse environments
decent with modification
variation is passed along to the next generation within a population
mutations
sudden change in gene, chromosome, or set of chromosomes
point mutation
a single change in DNA in one nucleotide
deletion
loss of one or more nucleotide
insertion
instert new nucleotide or codon
microevolution
change in gene frequency within a population, can be observed over short periods of time
Artificial selection
intentional breeding ( ex, dogs)
gene flow
migration or immigration
genetic drift
results from random changes/ chance events in gene frequencies, happens in small populations
bottleneck effect
Drastic reduction in population, leads to loss of genetic diversity
founder effect
new population is established by a small number of individuals from a larger population
non-random mating (sexual selection)
individuals choose mates with a particular trait/ phenotype
female choice
male to male competition
fossils
preserved dead animals trapped in sediment (ice, amber, petrified wood, etc)
experimental evolution
can move species to different environments to see how they act and evolve (transplant experiment)
Homology
Similarities in characteristics resulting from common ancestry (human arm vs cat arm), proof of decent with modification
anatomical vestiges
body parts and/or behaviors that no longer serve a function
transitional forms
Transitional animals found in fossil record that are proof of how an animal evolved
embryonic development
can see homologies that are not obvious in adult organisms
ontogeny
how you develop overtime
phylogeny
the evolutionary history of a species or group of related species using phylogenetic trees
molecular homology
links between organisms at the molecular level, can include DNA and protein homologies
convergent evolution
2 different species from different lineages show similar characteristics because they occupy similar environments (traits with similar function that evolved independently, ex bat wings vs bird wings)
analogous structures
different structures adapted to the same ecological niche (ex. evolution of fins and wings)
Homologous structures
same structure adapted to different ecological niches (ex. all mammals have 7 necks bones)
discipline of systematics
classifies organisms and determines their evolutionary relationships
taxonomy
science of naming, describing, and classifying organisms
Carolus Linnaeus
created 2 part naming system (genus species)
created system for classifying organisms based on morphological characteristics
introduced a way to group species in increasingly broad categories (domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species)
taxon
taxonomic unit used at any level of hierarchy
phylogenetic tree
represents a hypothesis about evolutionary relationships (MUST have a root)
basal taxon
Relatively unchanged, most closely related to the common ancestor
sister taxa
most closely related to each other
polytomy
3 way split in evolutionary tree, shows we dont have enough info to classify yet
cladistics
method of constructing evolutionary relationships based on shared characteristics
cladograms
Evolutionary tree where branch length has no meaning, map is based on descent with shared derived characteristics
node
branching point in cladogram, represent speciation event
clade
group of organisms that consist of a common ancestor and all its descendants (cladogram)
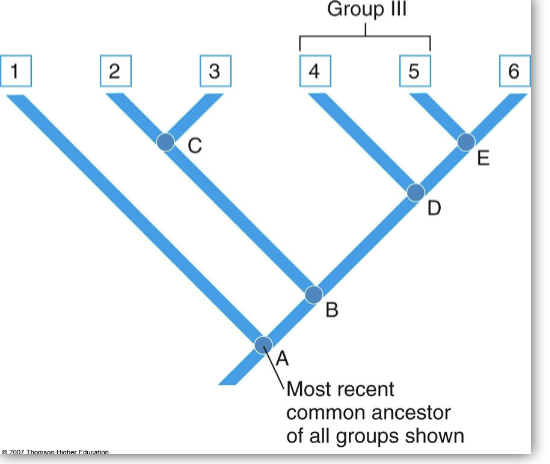
paraphyletic group
consists of an ancestral species and som, but not all, of the descendants ( cladogram)
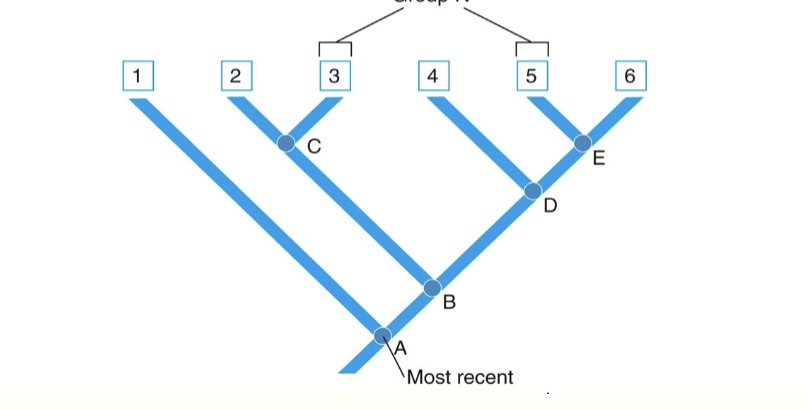
polyphyletic group
consists of taxa evolved from different recent ancestors (cladogram)
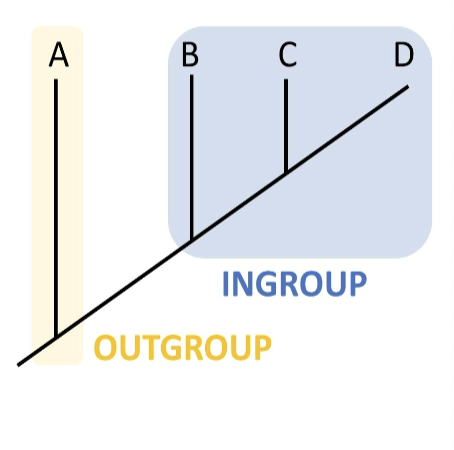
outgroup
a species or group of species that is somewhat closely related to ingroup (the various species being studied), diverged before ingroup
ancestral characters
shared by outgroup and ingroup that predate the divergence of both groups from a common ancestor
symplesiomorphy
shared ancestral characteristic
synapomorphy
indicate more recent ancestor, define a clade