Global economic history lecture 4
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is meant by modernisation and developmental ism?
Society must go through several stages, kind of evolution. To do so, they must follow certain prescriptions which were heavily linked to the English experience: Parliament, Property rights, Privatisation. This is how agrarian and non-industrial societies were going to move the ladder. It reflected the belief that each society could achieve this. Therefore, it has been called a theory of imitation. This process Rostow believed could be induced by changing some institutions..
What part of the five stages of Roto growth?
Traditional society: Economic system stagnation. Population growth is contained.’
The preconditions for takeoff. Creativity and risktaking. Capital accumulation
The takeoff: Investment in key sectors. Launching self sustaining productivity growth.
The drive to maturity: A phase of slower growth and stagnation. More resources devoted to consumption.
The age of mass consumption: Firms producing consumption goods. Systemic rates of growth are maintained through mass consumption.
What are substitutable factors?
The factors that replace typically British factors in imitating the British model on the European continent. Industrialisation could thus be achieved in different ways.
What two parts did Alexander Gerschenkron have to his theory?
Countries can cut corners in industrialisation. They could to this through substitutable factors.
Advantage of relative backwardness. They can use other countries already perfected tech to be industrialized faster.
What are the four points in the standard model of industrialisation by Robert Allen?
Creation of unified national markets by eliminating tariffs and building transportation infrastructure
The erection of an external tariff to protect industries from British competition
Large banks to stabilise the currency and financing industrial investment
Mass education to upgrade labour force
Why the standard model of industrialisation not too good after 20th century?
Ask the technology from the expanded, Industrialisation required larger capital investments and economics of scale had to be achieved This proved difficult to achieve instantaneously. Most technology is invented in rich countries and they develop technologies that use more and more capital to increase the productivity of their ever more expensive labour, Much of this new technology is not cost-effective in low wage countries but it is what they need to get up to the west. Most countries have adopted modern technology to some degree but not rapidly enough to overtake the rich countries.
What is big push industrialisation?
Radically and coordinated industrialisation strategy based on making a huge number of investment all at the same time ahead of supply and demand
Why was Belgium the second to industrialize?
Coal
Dense population
Lots of agriculture to feed more people
Pre-industrial commerce activity and manufacturing
How was Belgium doing based on the standard model when it industrialized?

Did the US follow the standard model of industrialisation?
Yes,
Railroads
Erie canal
Interstate commerce clause
Invested in education
Tariffs (protected us businesses from British)
The industrial expansion in the US was fuelled by large corporations which differ from earlier industrial model due to their scale integration. Why? 2
Large national market: The US have significantly larger market than Europe supported by an extensive railroad network, enabling businesses like US steel and standard to operate on the national scale.
Second industrial revolution: New tech technologies required substantial capital investments making large scale production economically viable. Investment in specialised costly equipment justified by economies of scale.
The expansion of American corporations were marked by two characteristics, which were they?
Horizontal integration: Firms expanded within the same sector monopoly production by acquiring competitors or specialising in mass production this approach allowed economies of scale and expertise development.
Vertical integration: Firms to cover parts of the production chain to reduce the dependency and suppliers or distributors. This strategy improved coordination cost efficiency and control over profit margins.
What was the ford river rouge complex?
The Ford River Rouge complex exemplified vertical integration by controlling every step of production from raw materials like cool Aaron and rubber finished automobiles all within a single facility for eliminated reliance on external suppliers by owning mines and even rubber plantations enabling the factory to produce vehicles entirely in house.
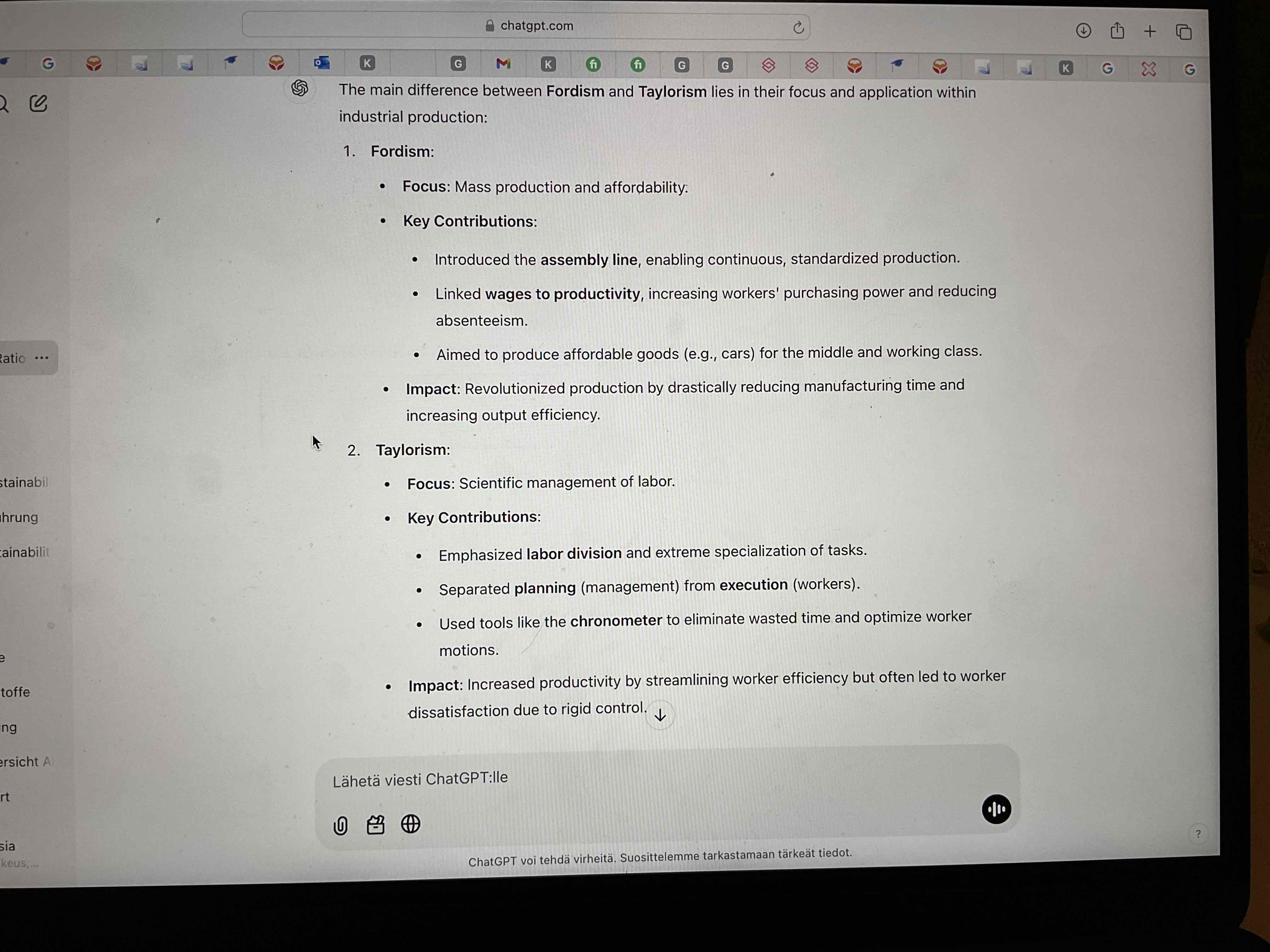
What were the differences between fordism and Taylorism?
What are the five reasons Japan’s starting position for industrialisation was stronger than often and assumed?
Urbanisation by 1800 13% of Japan’s population lived in towns over 10,000 people. Much higher than China 3 to 4%
Economic growth: During the Tokugawa period markets and internal trade expanded with peasants engaging in double cropping and handcraft production to pro industrialisation in Europe
Land markets: Despite no formal property rights, land markets operated through mortgage contracts ensuring functioning factor markets
Human capital: High literacy and numeracy rate supported by tens of thousands of schools and private academies enabled the adoption of industrial technologies.
What four steps did Japan take to industrialise?
The administration was centralised instead of fragmentation. As a result, the state invested heavily in mining and in the construction of national landlord system.
The state favoured and supported the formation of business. The support led to the formation of very large business groups
Compulsory education
That Meiji reforms could not protect business through tariffs because of the trade treaties in the 1850s.
What is the Suwa method?
The Suwa method is a production system developed in Japan that emphasizes efficient and flexible manufacturing processes. It allows companies to quickly adapt to changing market demands while minimizing waste. This method focuses on the principles of just-in-time production, continuous improvement (Kaizen), and the involvement of all employees in the production process. By optimizing workflow and reducing inventory levels, the Suwa method aims to enhance productivity and responsiveness in manufacturing.