OMFPR 2 - Principles of Tomography and Panoramic Imaging (Dr. Ramesh)
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
_____________ radiography is based on body-section radiography and it blurs out the shadows of superimposed structures
Panoramic
What are the five advantages of a panoramic x-rays?
- Broad coverage of facial bones and structures
- Low patient dose
- Simple and convenient
- Can be used on patients with trismus (inability to open mouth)
- Minimal time
What are the four disadvantages of panoramic x-rays?
- Critical positioning
- Inherent magnification
- Poor resolution (compared to intraoral radiographs)
- Incorrect interpretation of ghost image
Which of the following are an indication for panoramic x-ray?
A) Evaluation of trauma
B) Evaluation of third molars
C) Extensive disease
D) Suspected large lesions
E) Mixed dentition
F) Developmental abnormalities
All are indications!
Panoramic radiographs are obtained by rotating a narrow beam of radiation in the __________ plane
horizontal
Panoramic radiographs are obtained by rotating a __________ beam of radiation in the horizontal plane
narrow
What direction is the film rotated in while the object (jaw) is stationary?
Opposite direction
Define the following:
Body section radiography
tomography
Define the following:
- Technique that blurs out shadows of superimposed structures
- Object of interest less blurred
- Doesn't improve sharpness
body section radiography
when taking a tomographic image the part of the body that you want to appear the most clearly should be positioned within the _________
focal trough (image layer)
Define the following:
A three-dimensional curved zone or image layer in which structures are reasonably well defined
focal trough (image layer)
t/f: Measurement on a panoramic is often very accurate
false (often inaccurate)
t/f: Magnification of radiographic structures varies with error in patient positioning
true
_______ objects may project as single or double images
midline
how many centers of rotation are used to take a pano?
3
What has the following characteristics:
- Objects are imaged (intercepted) twice by beam
- One image is mirror image of the other
double image formation
double image formation often occurs with what type of objects?
midline objects
What type of image is formed when the object is located between the rotation center and film?
real image
What type of image is formed when the object is located between the x-ray source and the rotational center?
ghost image
A real image is formed when the object is located between the rotation center and the _____________
film
A ghost image is formed when the object is located between the rotational center and the _____________
x-ray source
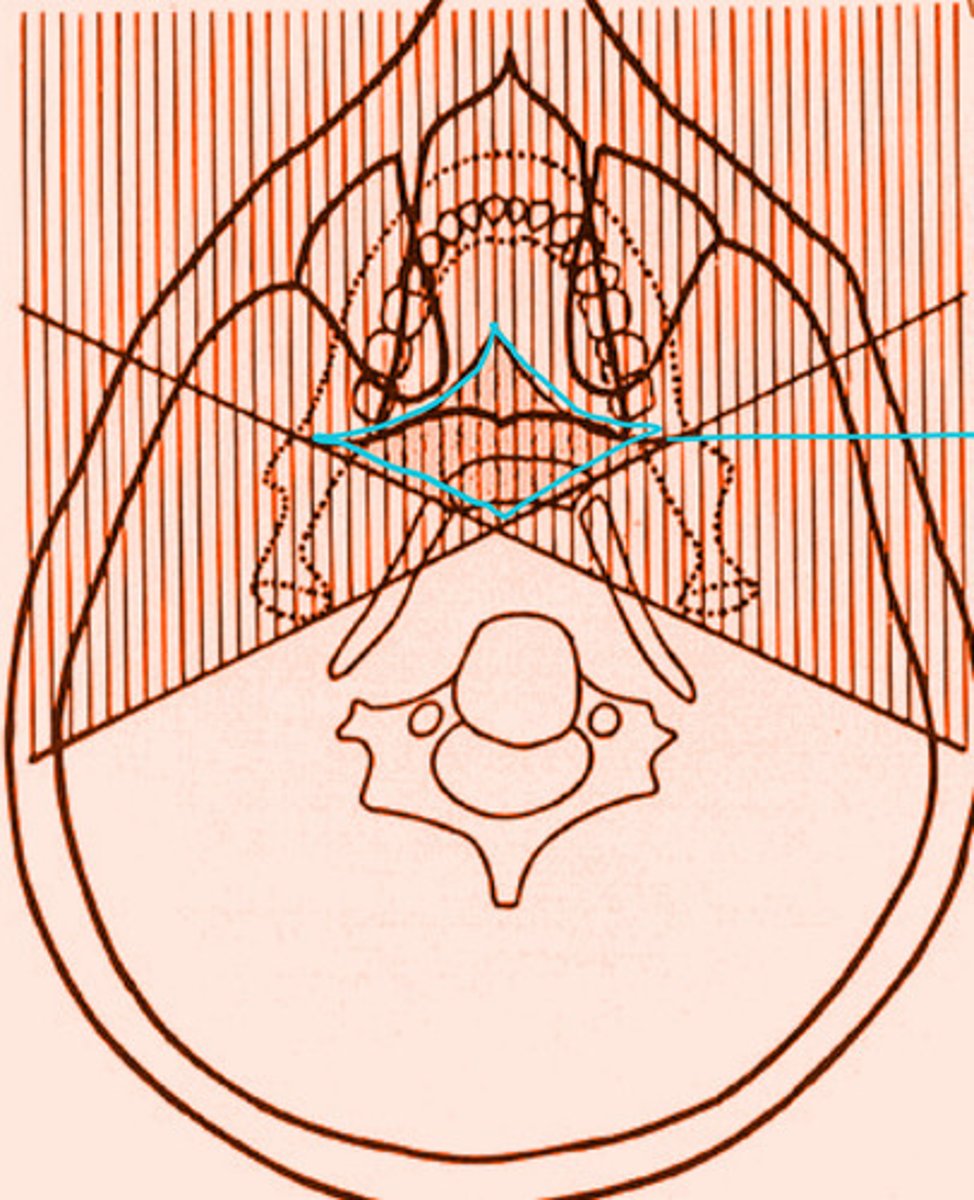
the shaded regions will produce what type of images?
real and double image
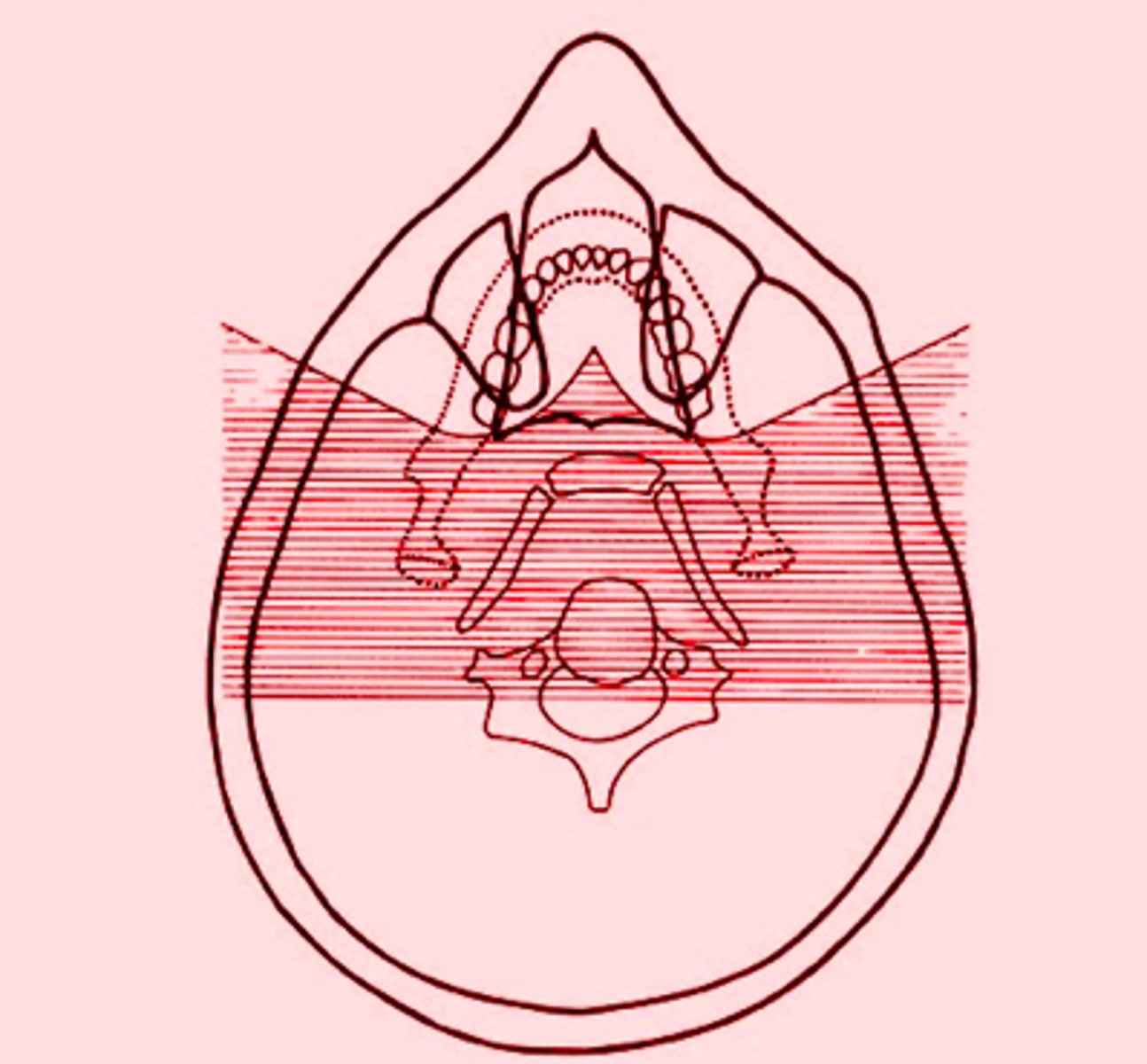
the shaded regions will produce what type of images?
ghost image/shadows
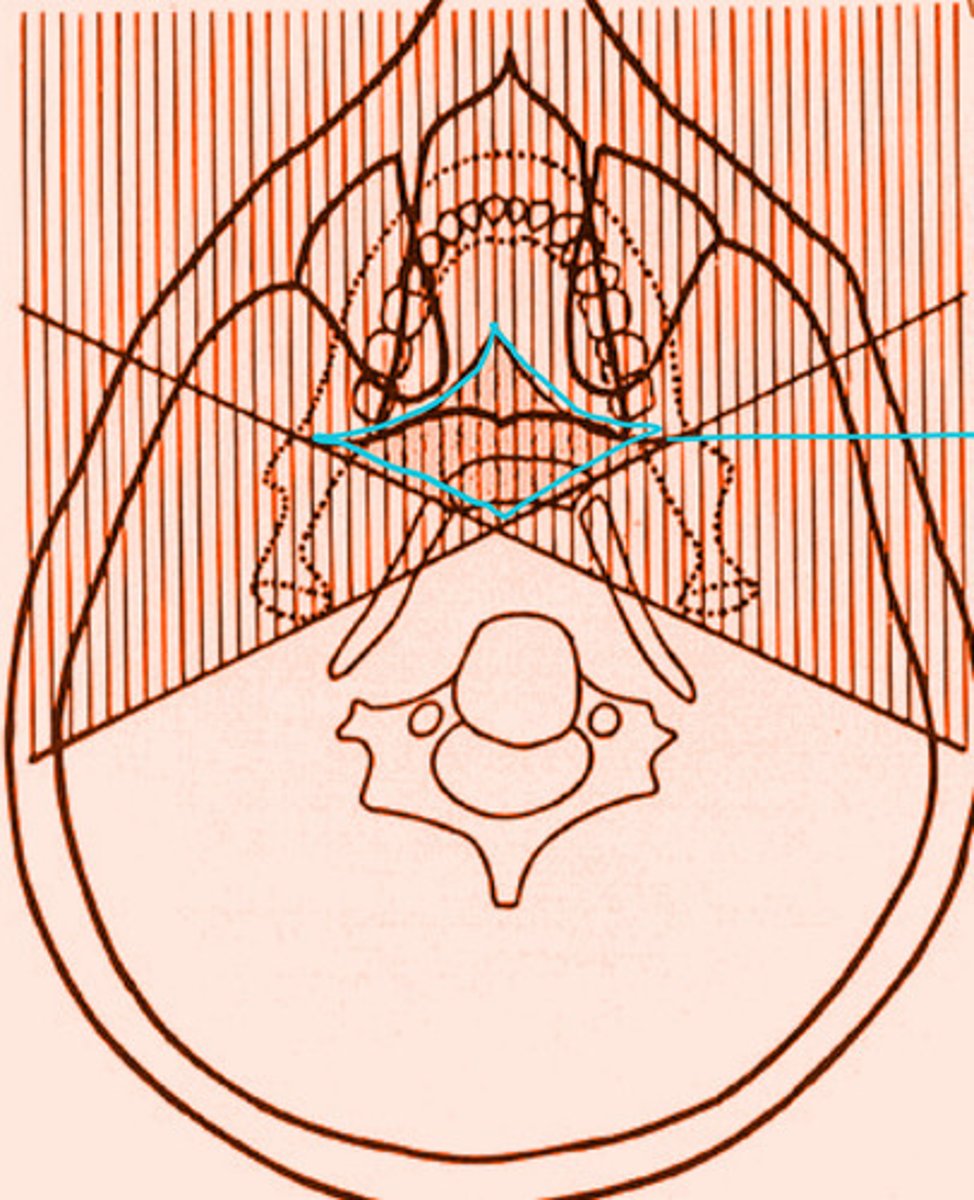
the shaded region within the blue diamond will produce a total of __ images
3
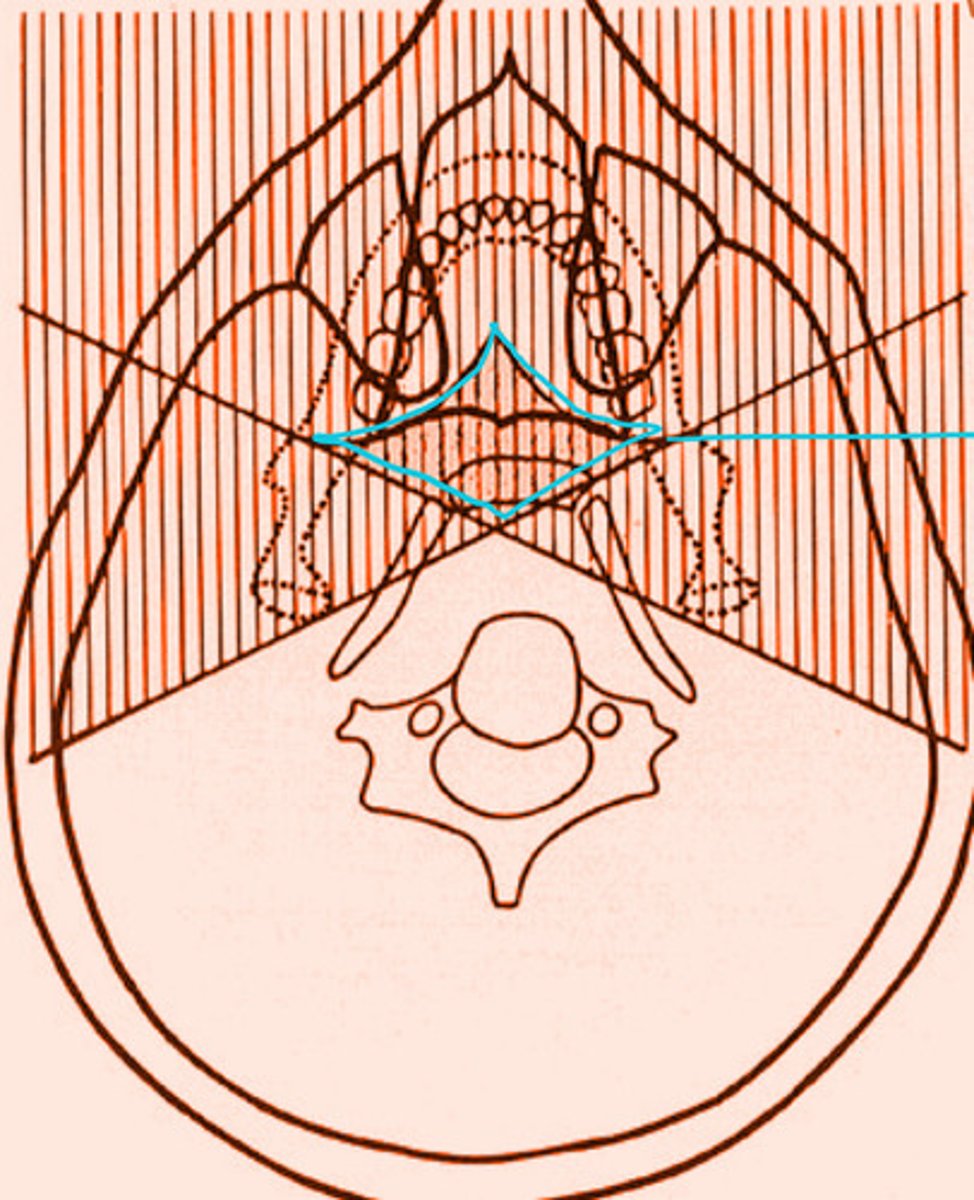
the shaded region within the blue diamond will produce a total of 3 images. What types of images are they?
2 real
1 ghost
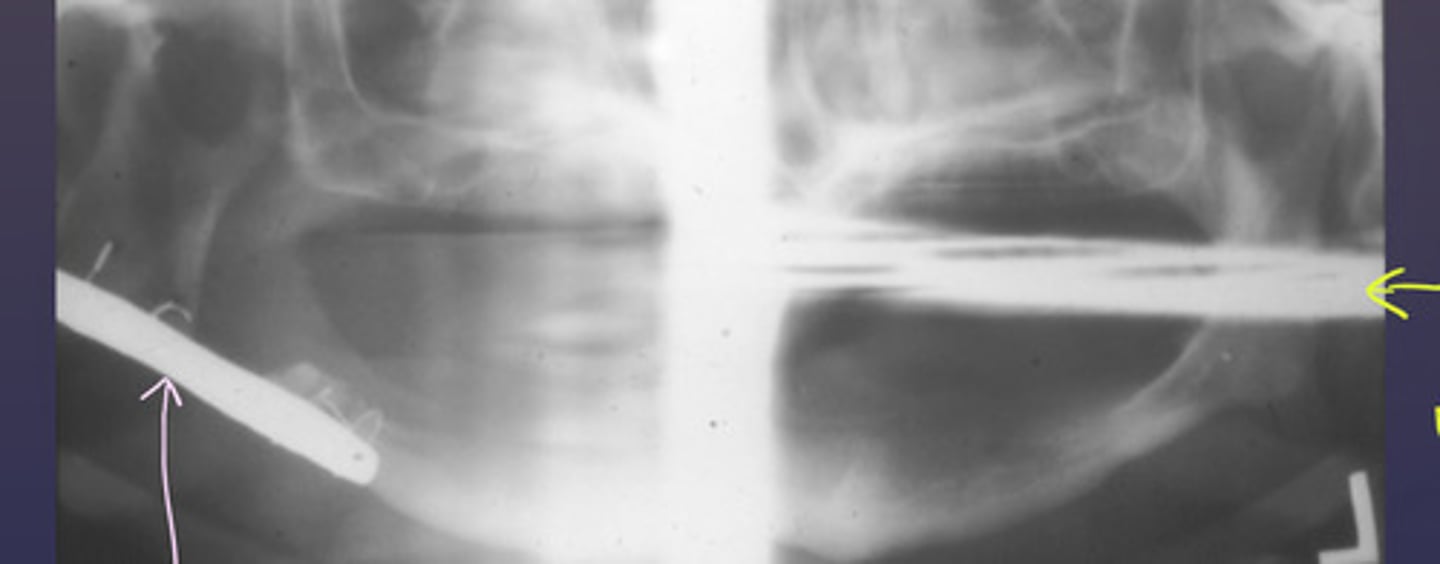
the following patient has a surgical plate. What type of image is the purple arrow pointing to?
real image
______________ arise from structures located on the posterior aspect of the head of opposite side
ghost shadows
t/f: ghost shadows have same general shape and appear on the opposite side
true
ghost shadows are positioned __________ than real structures
higher
ghost shadows are __________ blurred than real structures
more
vertical component of ghost shadows are __________ blurry and __________ magnified
more, highly
What are five common types of errors with panoramic radiographs?
- Antero-posteriorly (too far back or front)
- Supero-inferiorly (chin up or down)
- Mid-sagittal plane (face turned towards right or left)
- Tongue positioning
- Spinal Column positioning
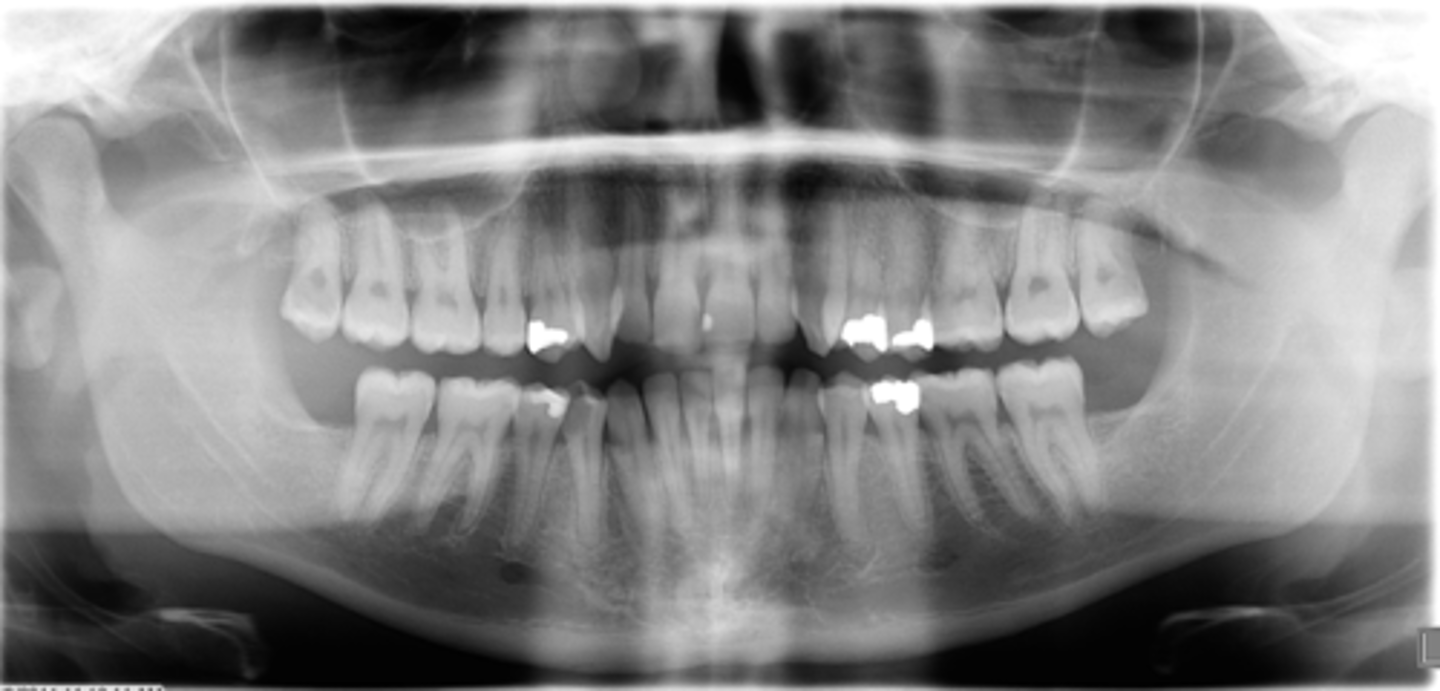
ID the positional error from the radiograph:
None - ideal
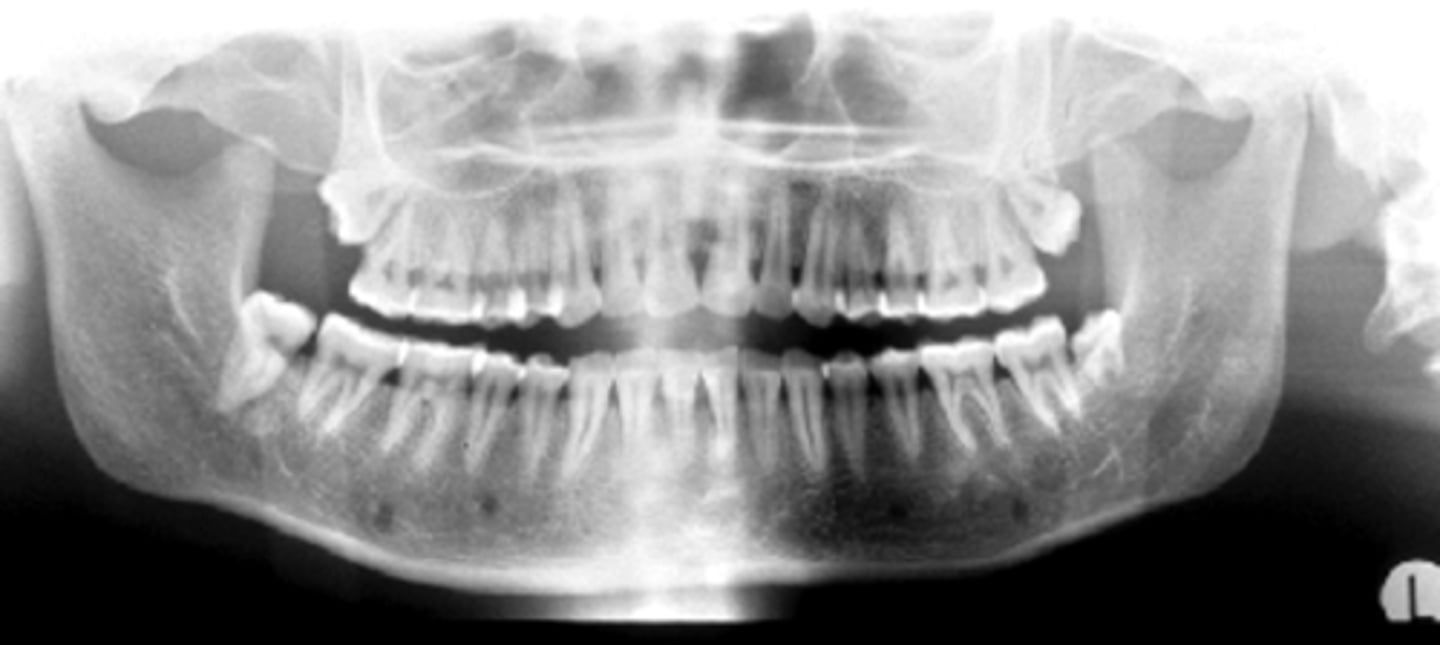
ID the positional error from the radiograph:
right rotation (pts right side is larger)
(And too far back)
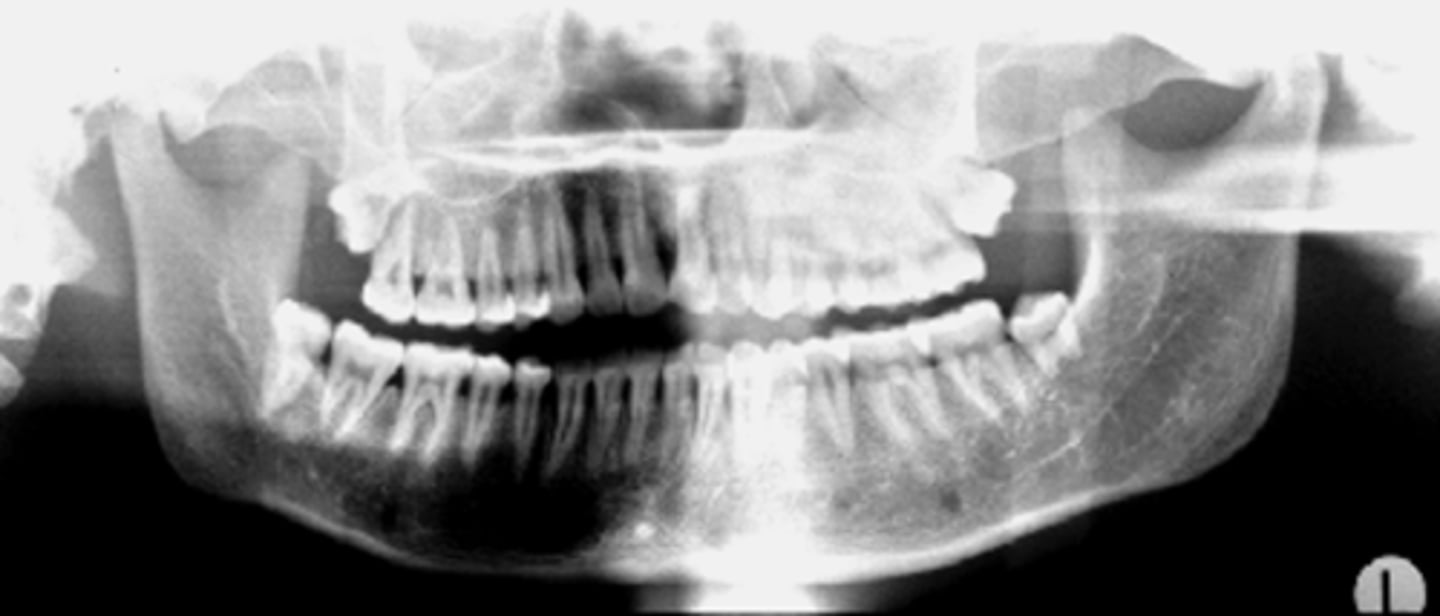
ID the positional error from the radiograph:
left rotation (pts left side is wider)
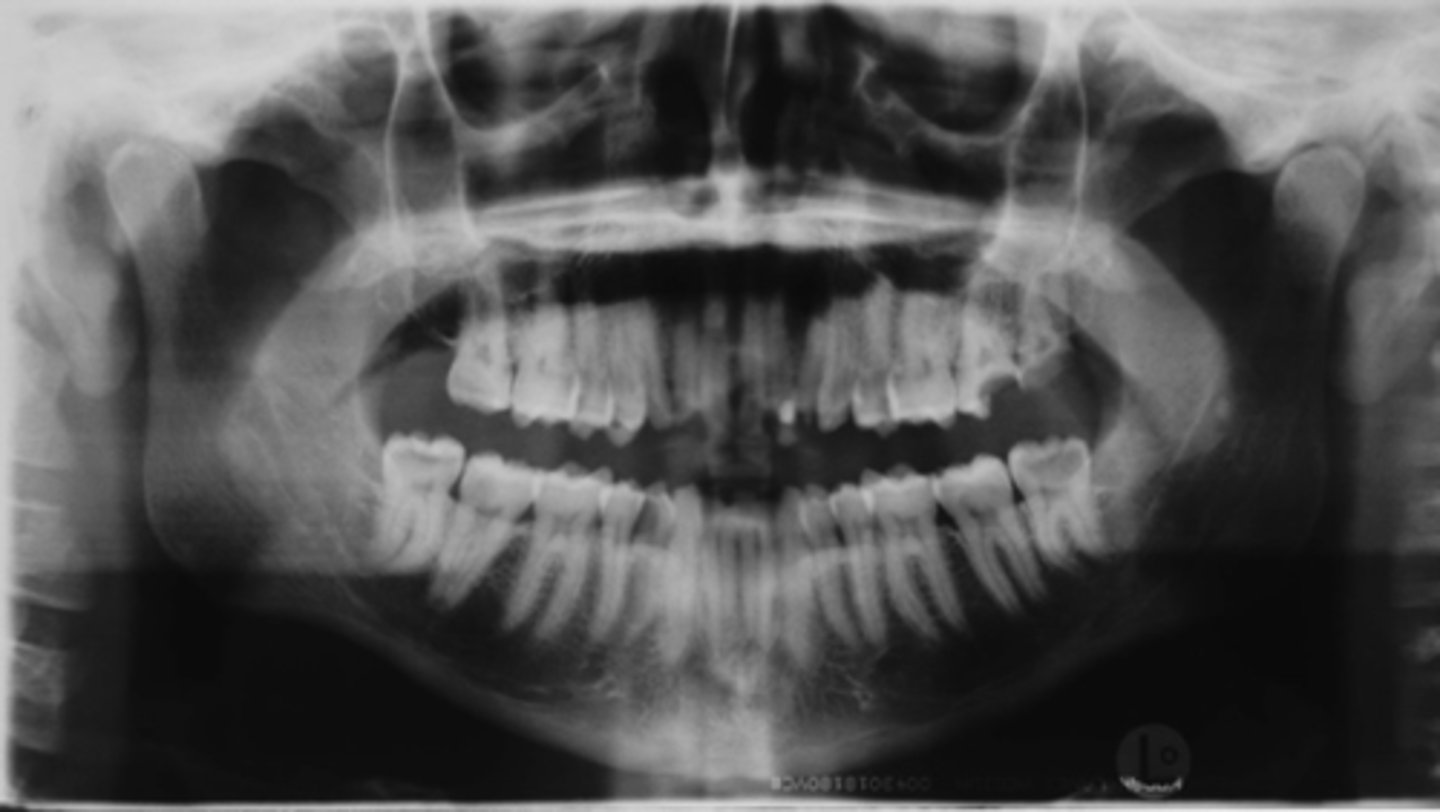
ID the positional error from the radiograph:
too far front (narrow/elongated incisors)
(And improper tongue positioning)
when you're looking on a radiograph and the mandibular anteriors look narrow and tall, the pt is ...
too far forward
when you're looking on a radiograph and the mandibular anteriors look wider and short, the pt is...
too far back
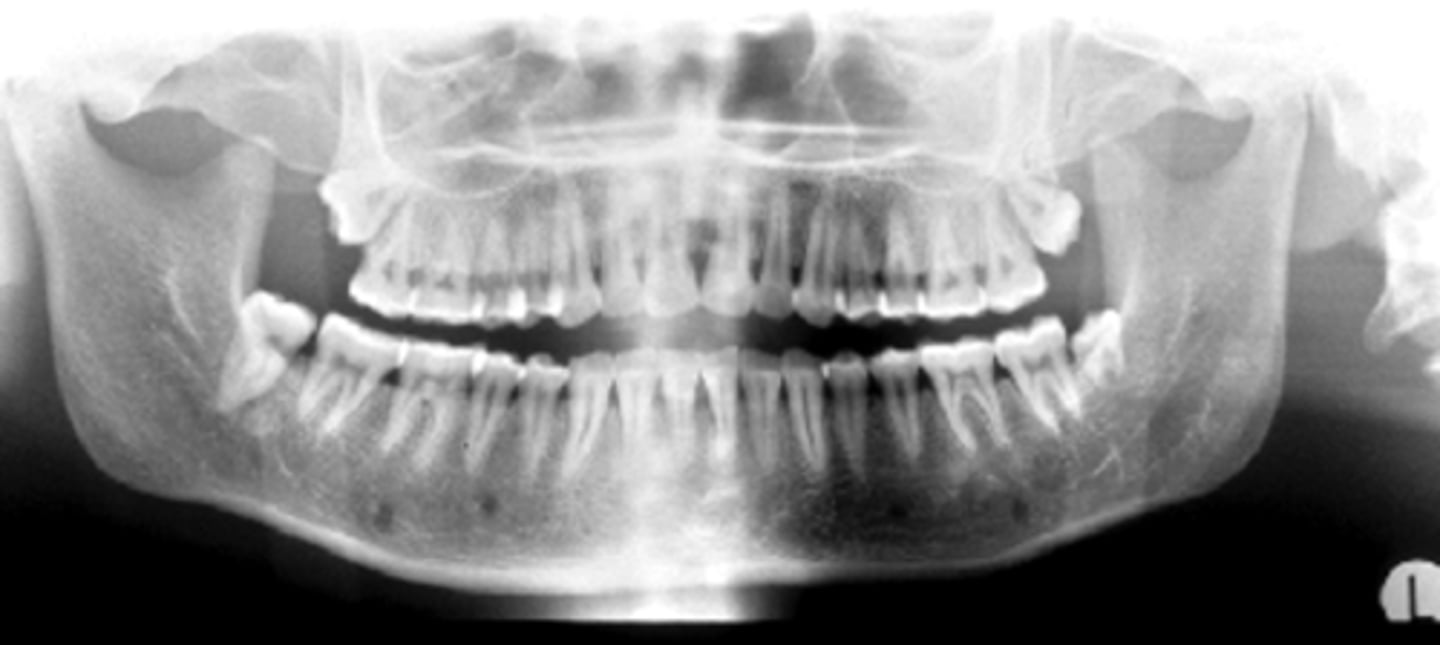
ID the positional error from the radiograph:
too far back (short/wider incisors)
(and right rotation)
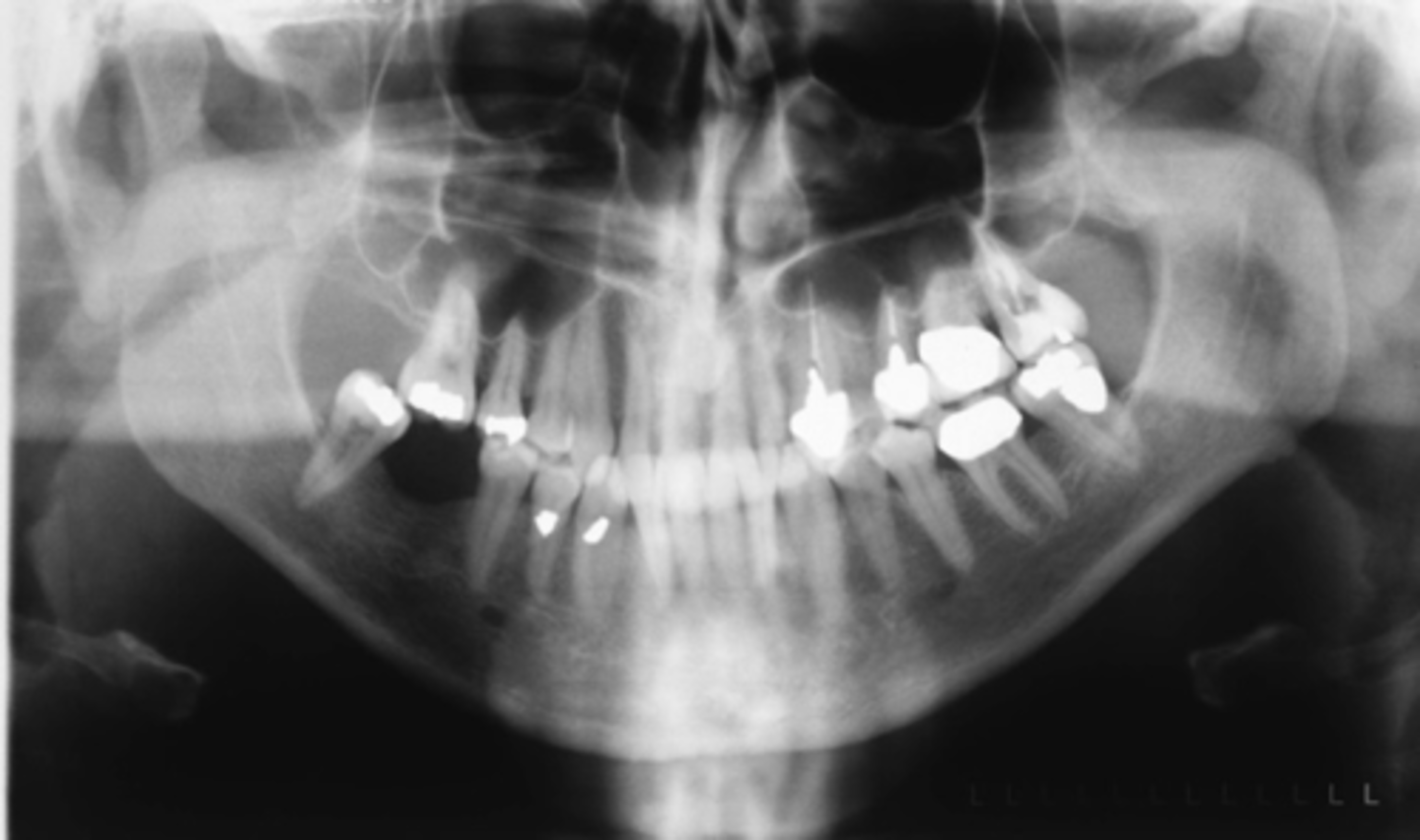
ID the positional error from the radiograph:
chin down
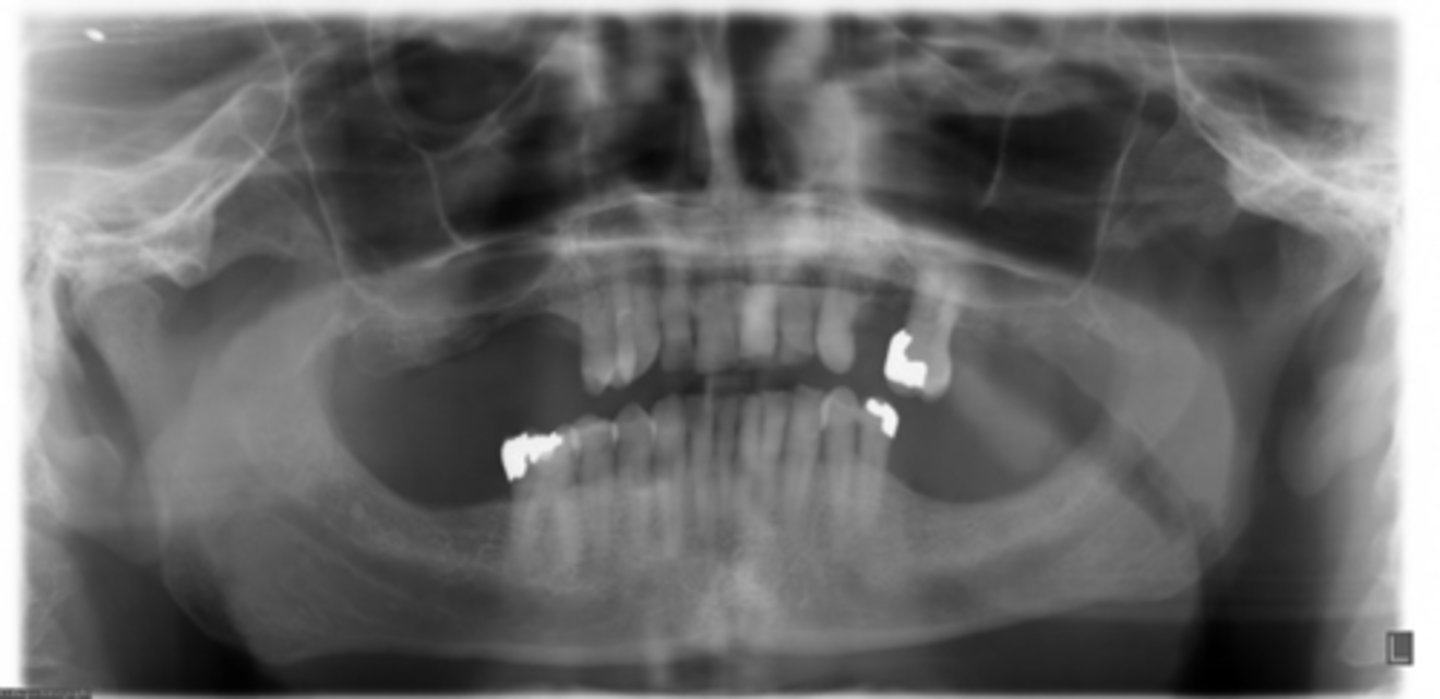
ID the positional error from the radiograph:
chin up
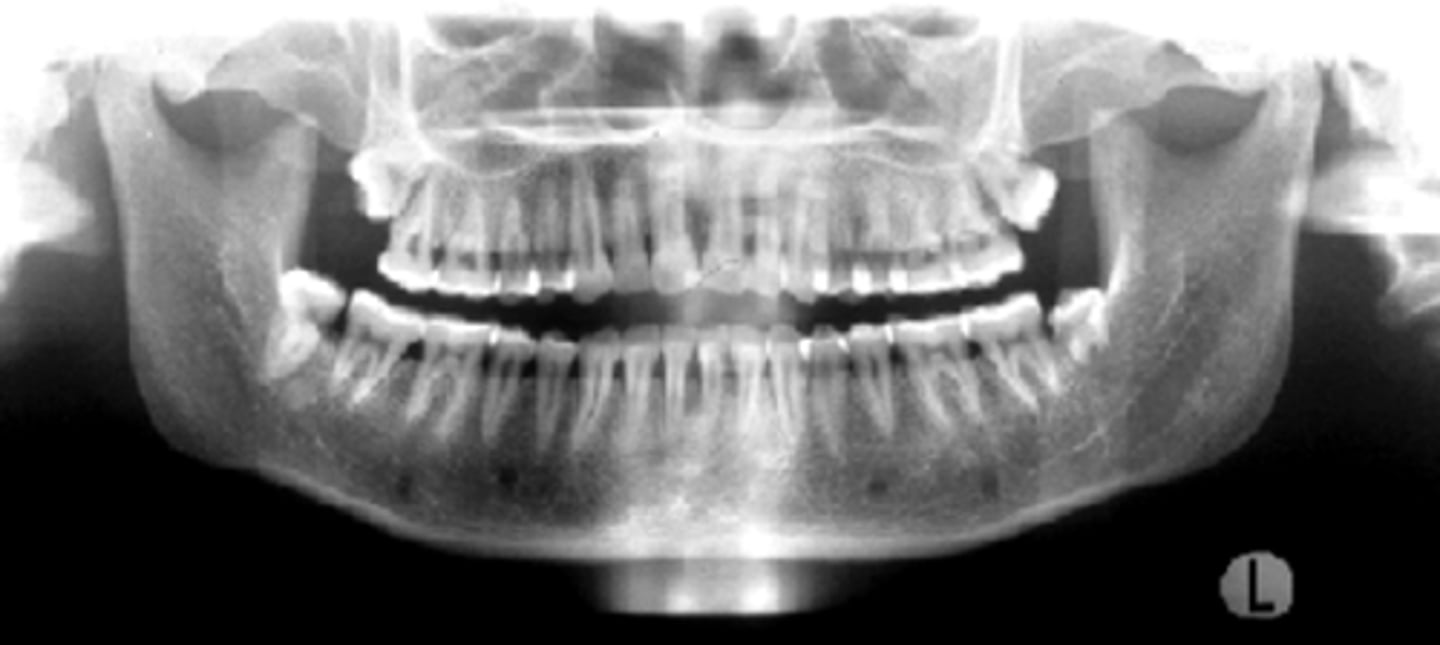
ID the positional error from the radiograph:
none - ideal
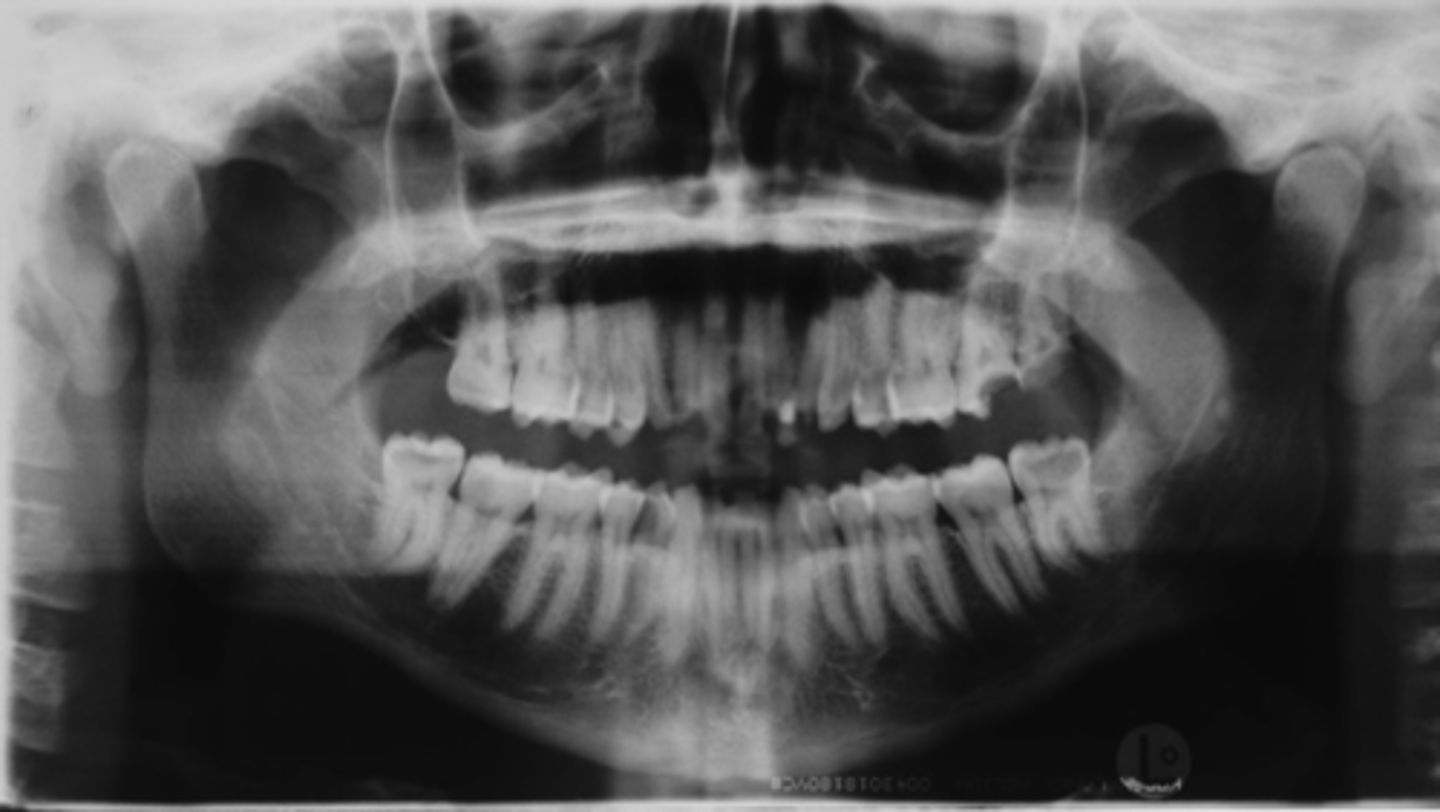
ID the positional error from the radiograph:
Improper tongue placement
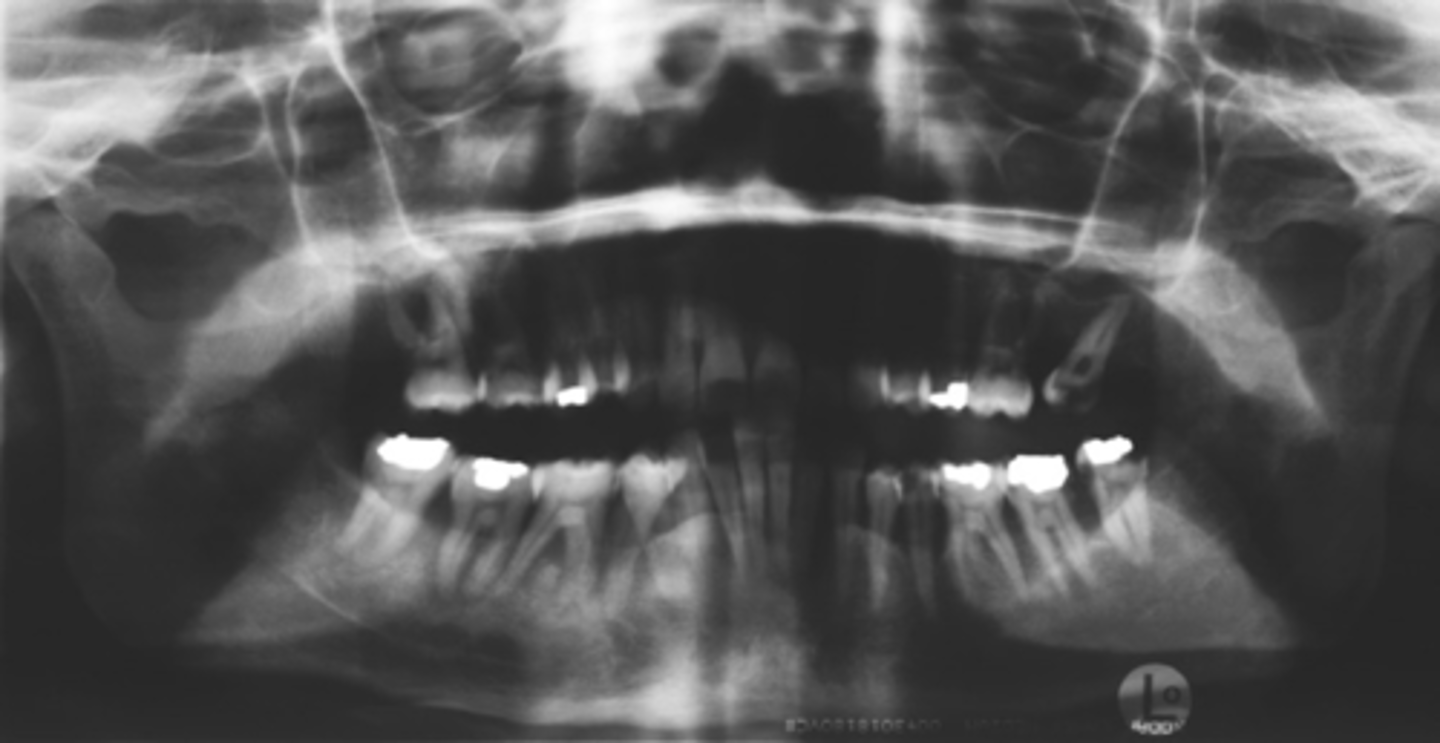
ID the positional error from the radiograph:
Improper tongue placement
(and too far front?)
if a patient is positioned where the incisors are anterior to the center of the focal trough, the image of the incisors will experience ________
minification
if a patient is positioned where the incisors are posterior to the center of the focal trough, the image of the incisors will experience ________
magnification
in order to prevent the cervical vertebrae from appearing on a pano, you can make sure that the patient's chin is tilted slightly _____
downward
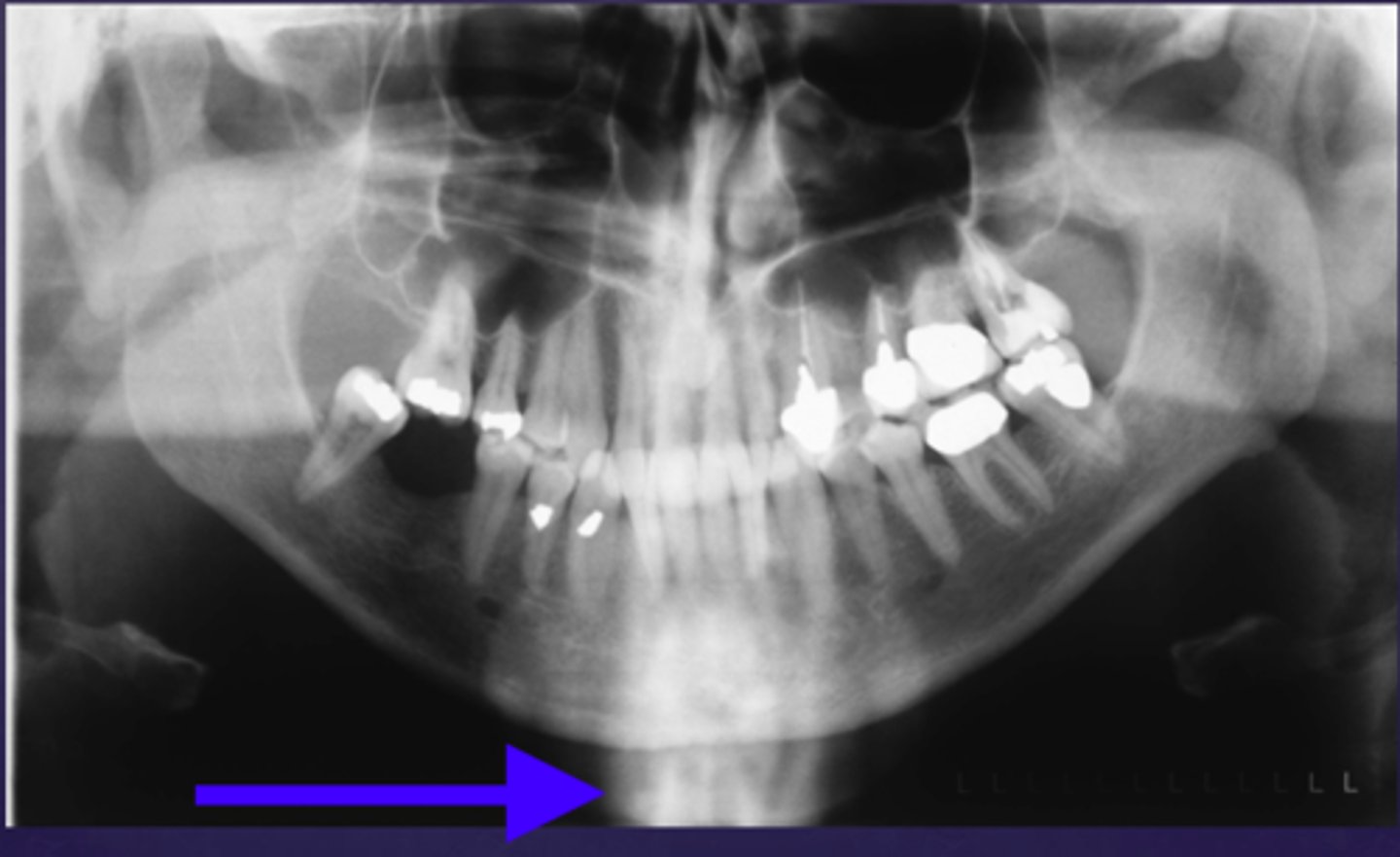
the blue arrow is pointing to what type of image of the cervical vertebrae?
ghost image
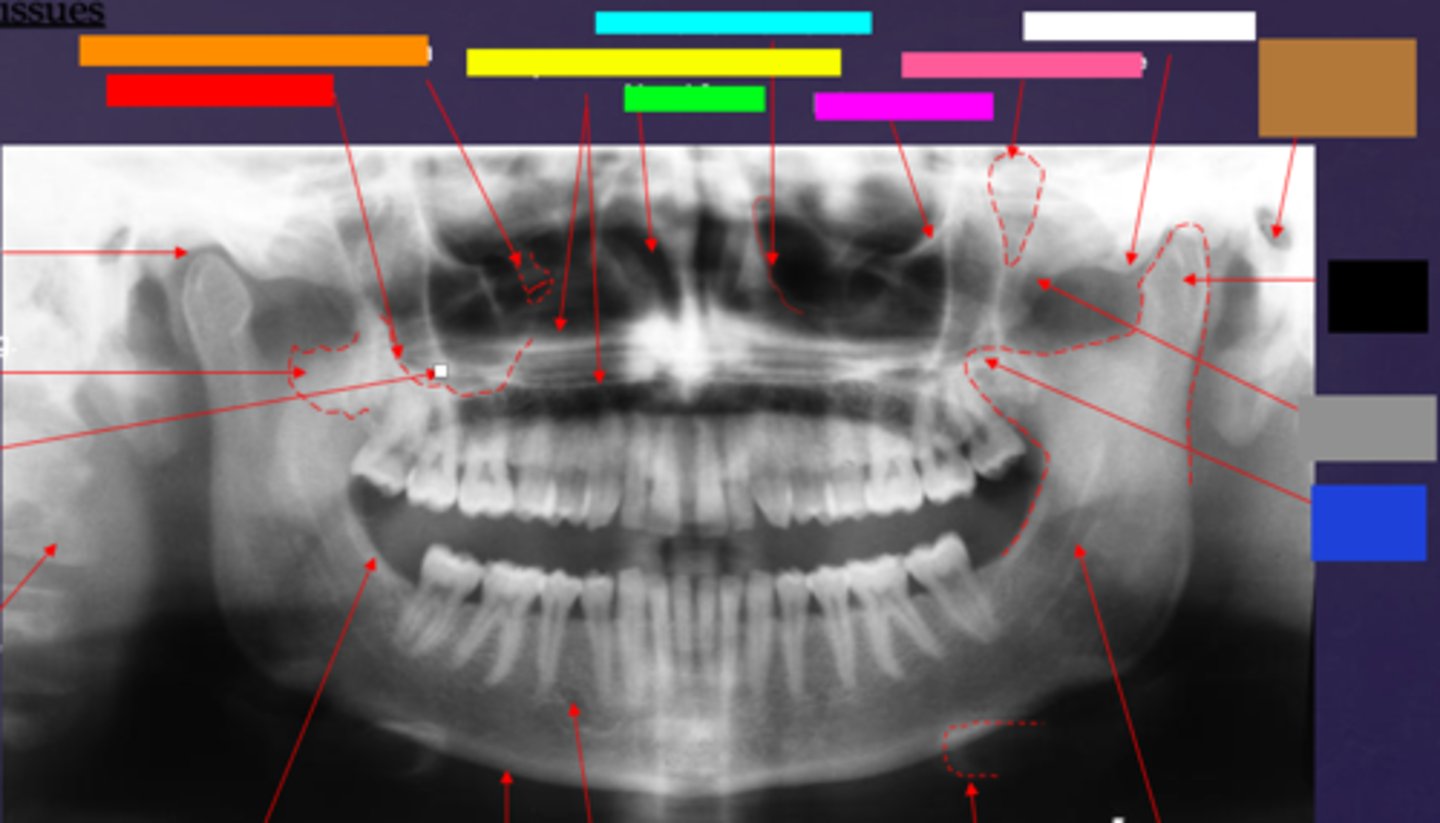
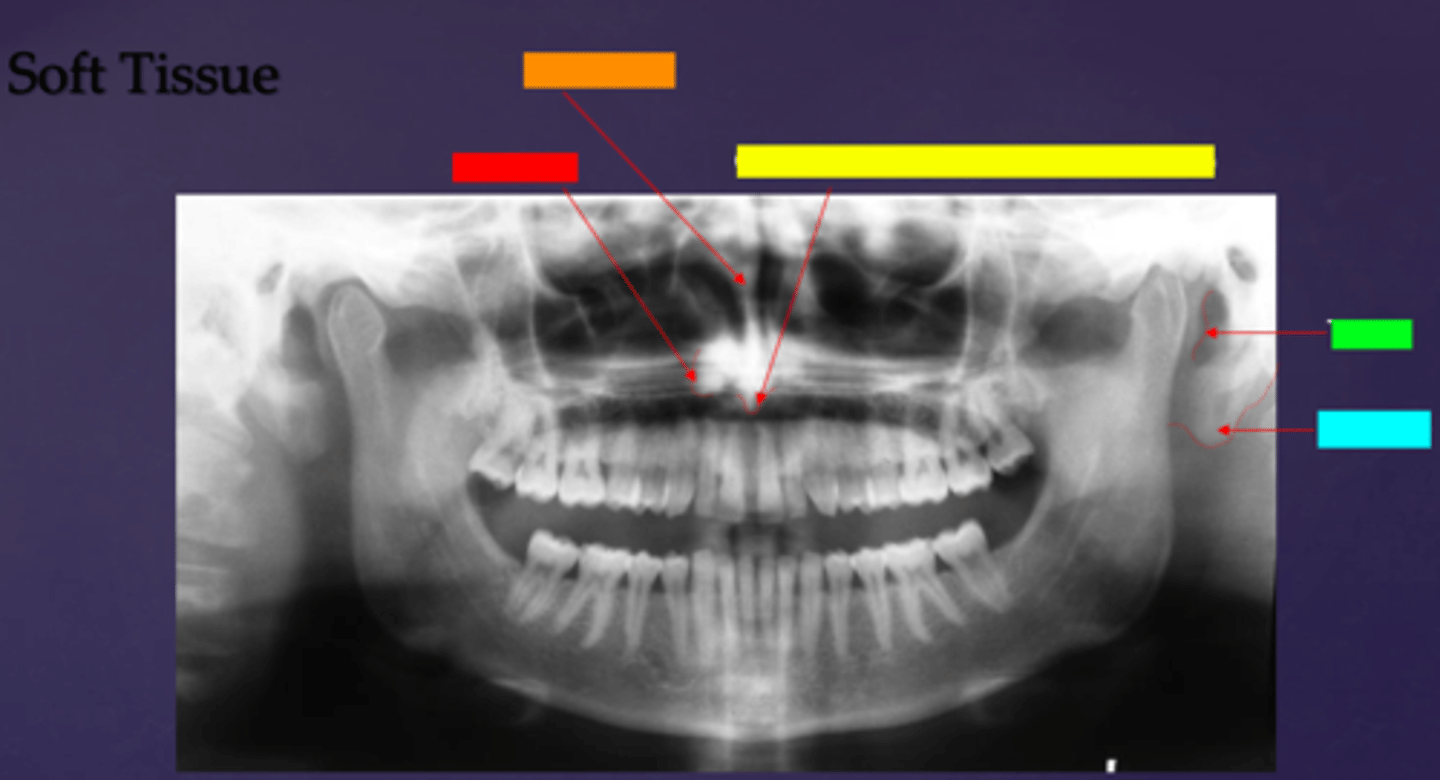
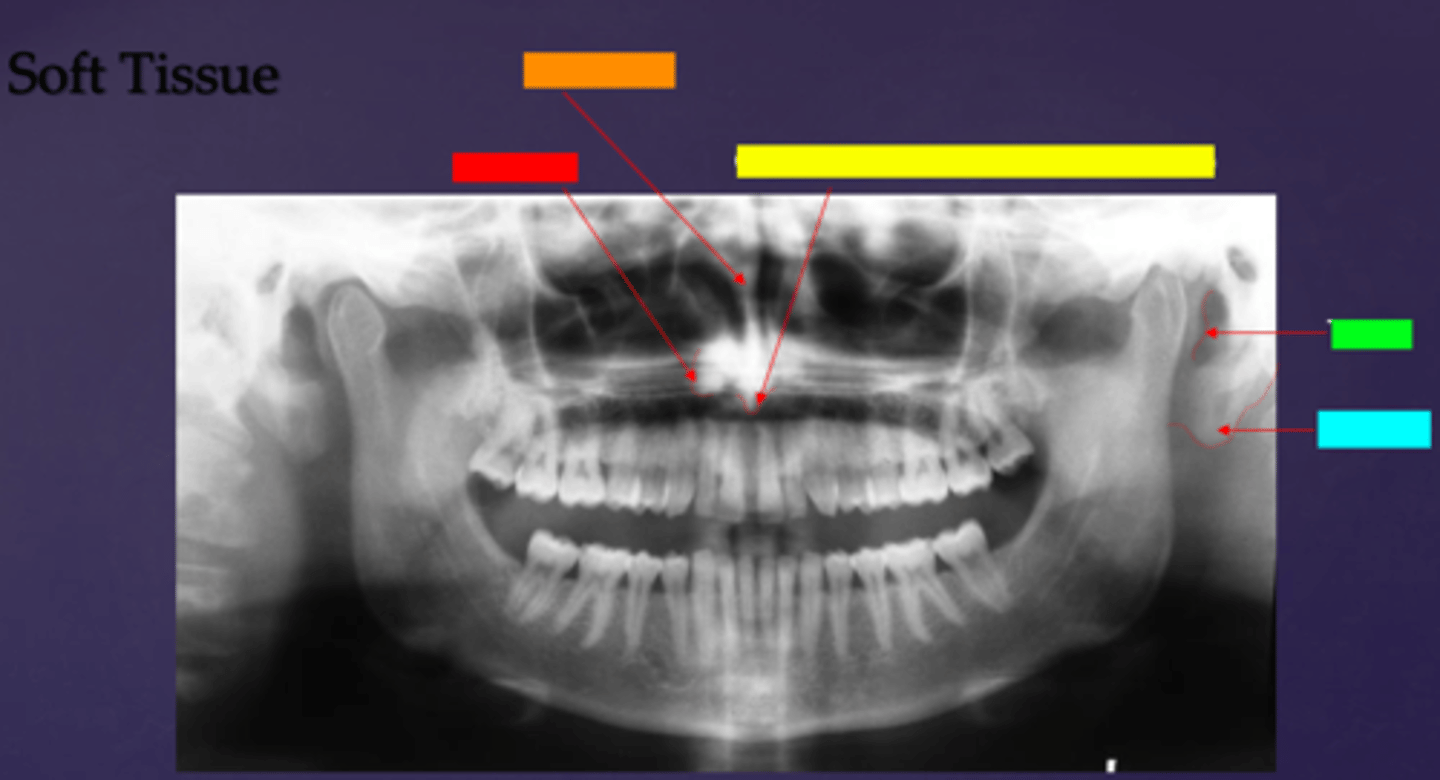
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the red box:
floor of max. sinus
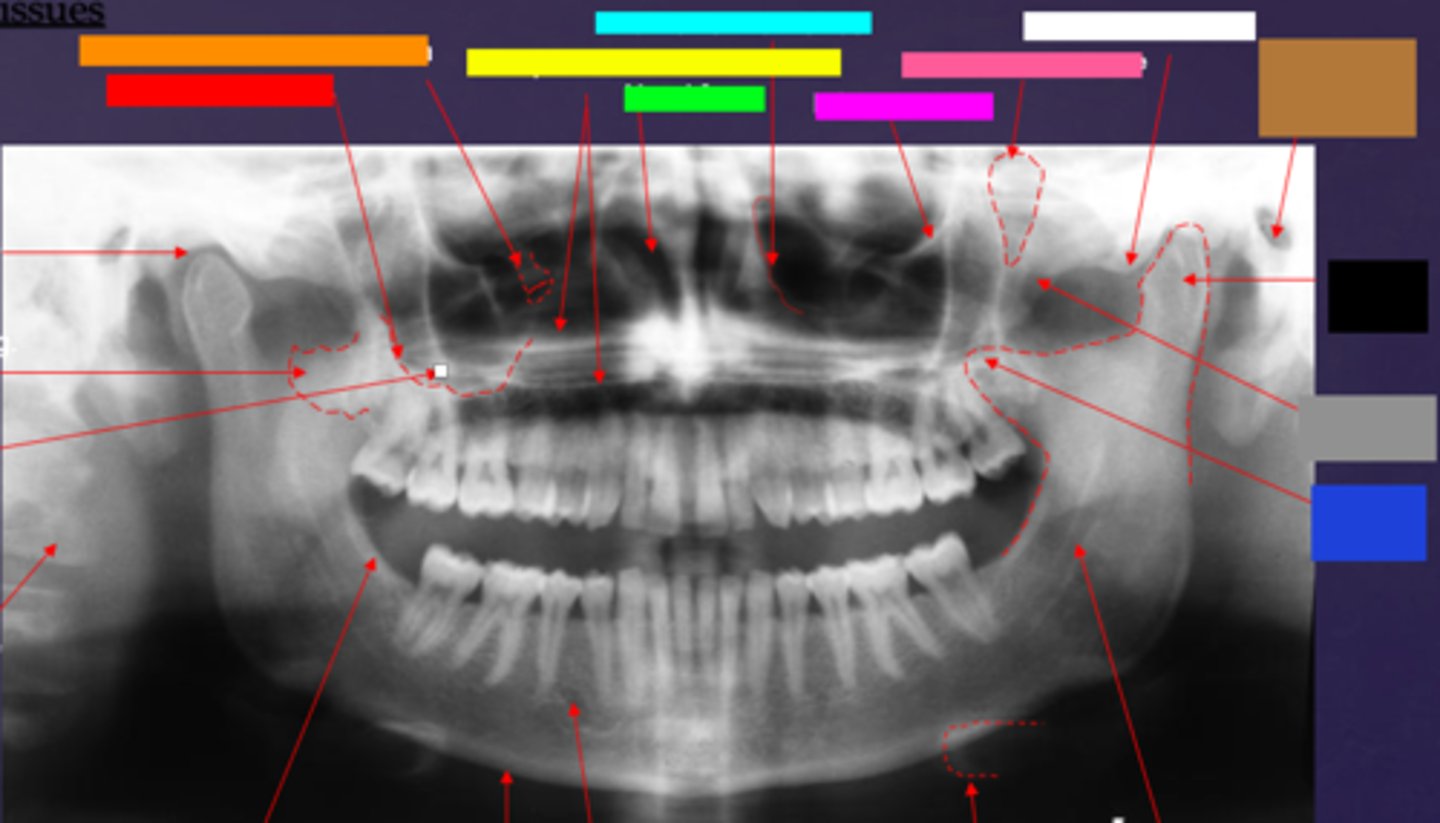
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the orange box:
infra orbital canal and foramen
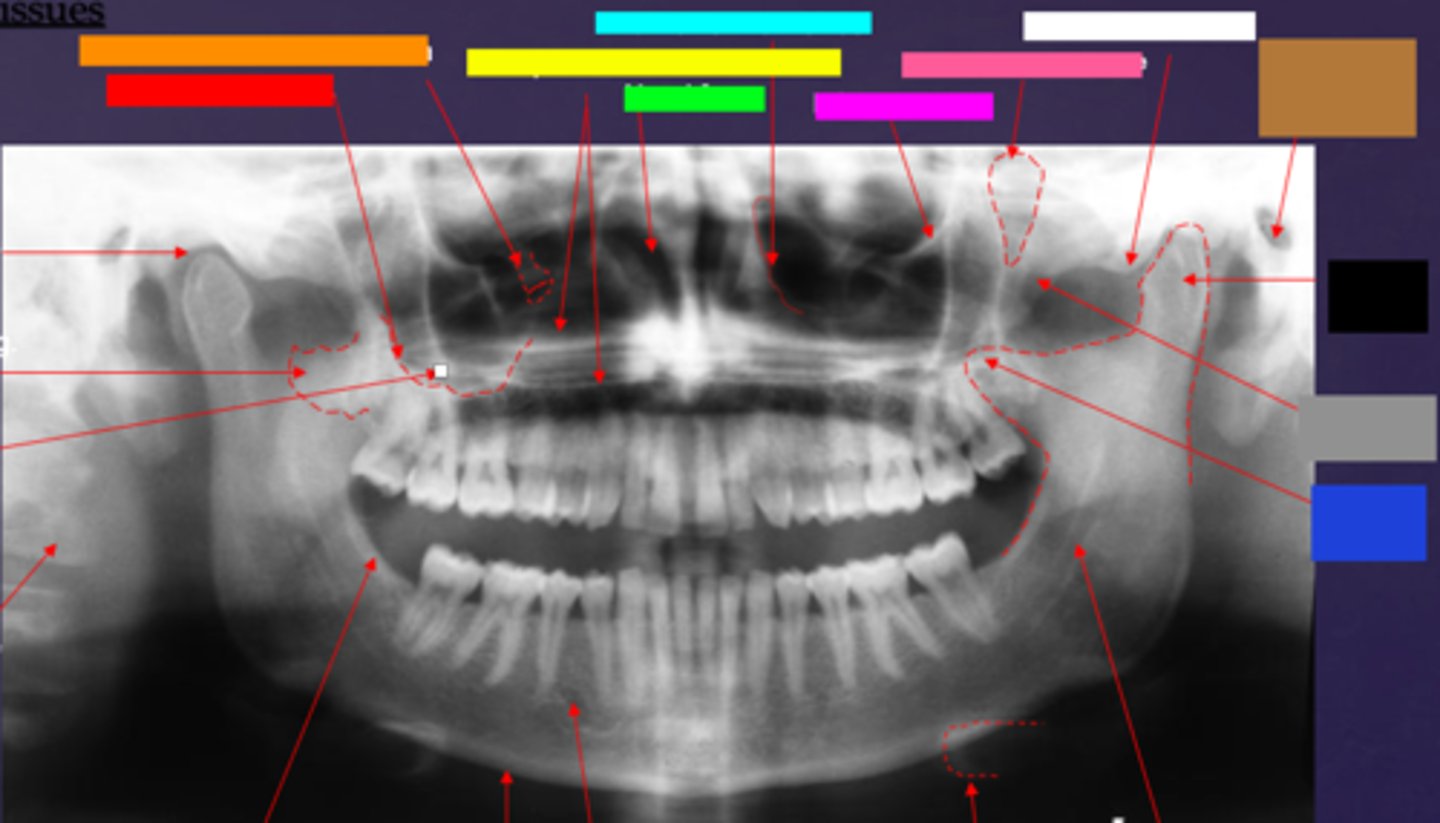
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the yellow box:
hard palate/floor of nasal fossa
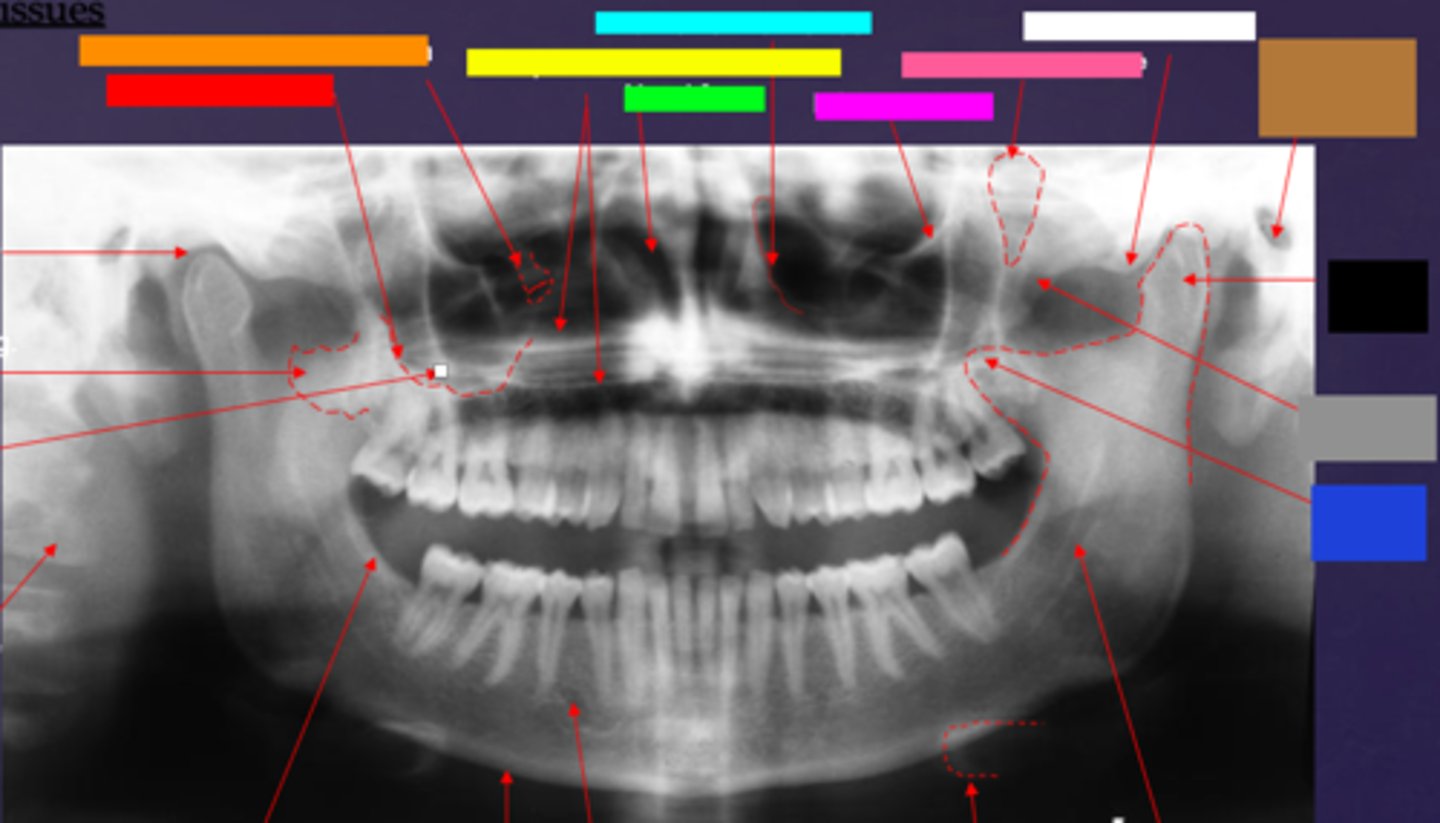
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the green box:
nasal fossa
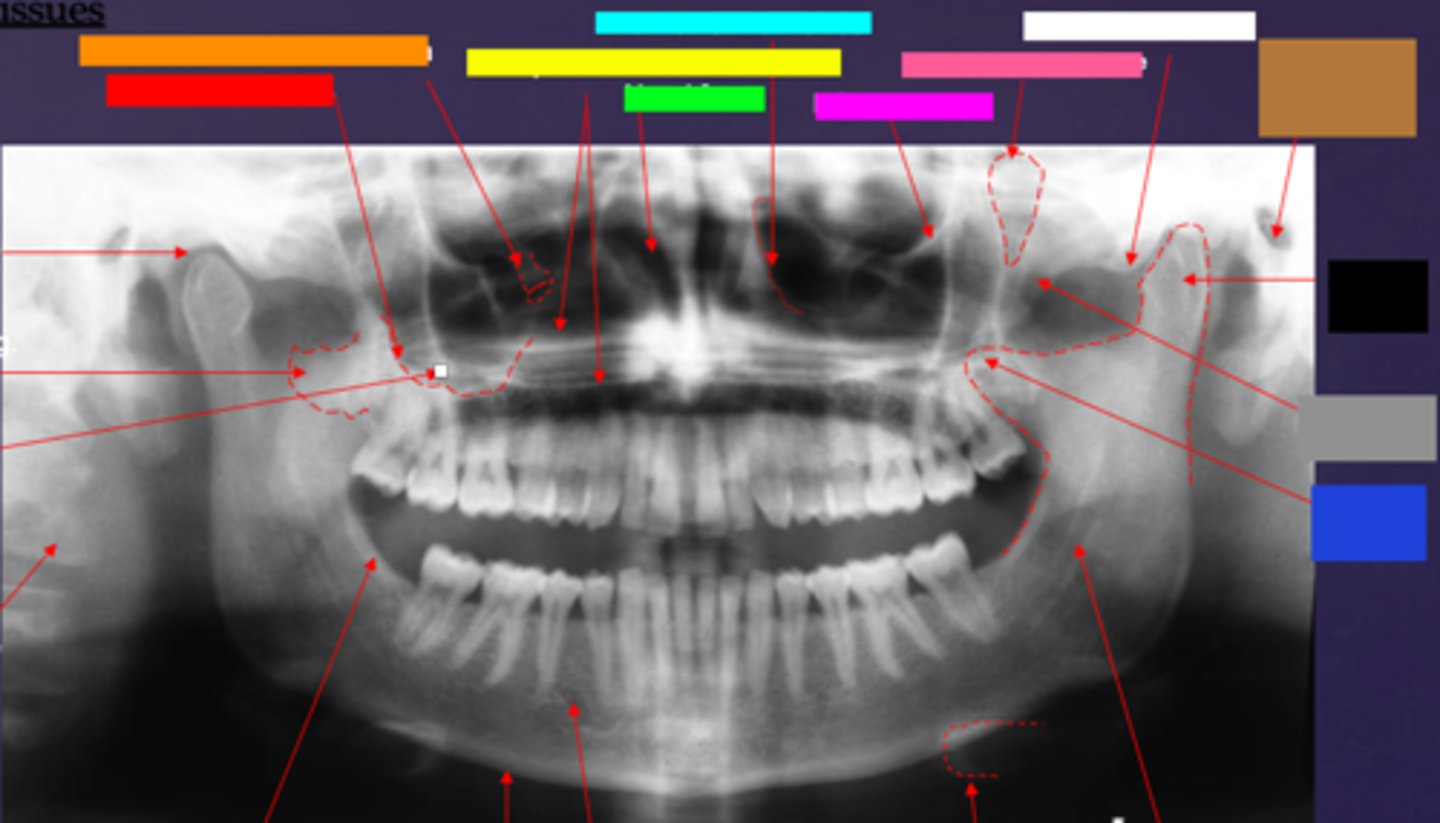
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the light blue box:
ant. wall of max. sinus
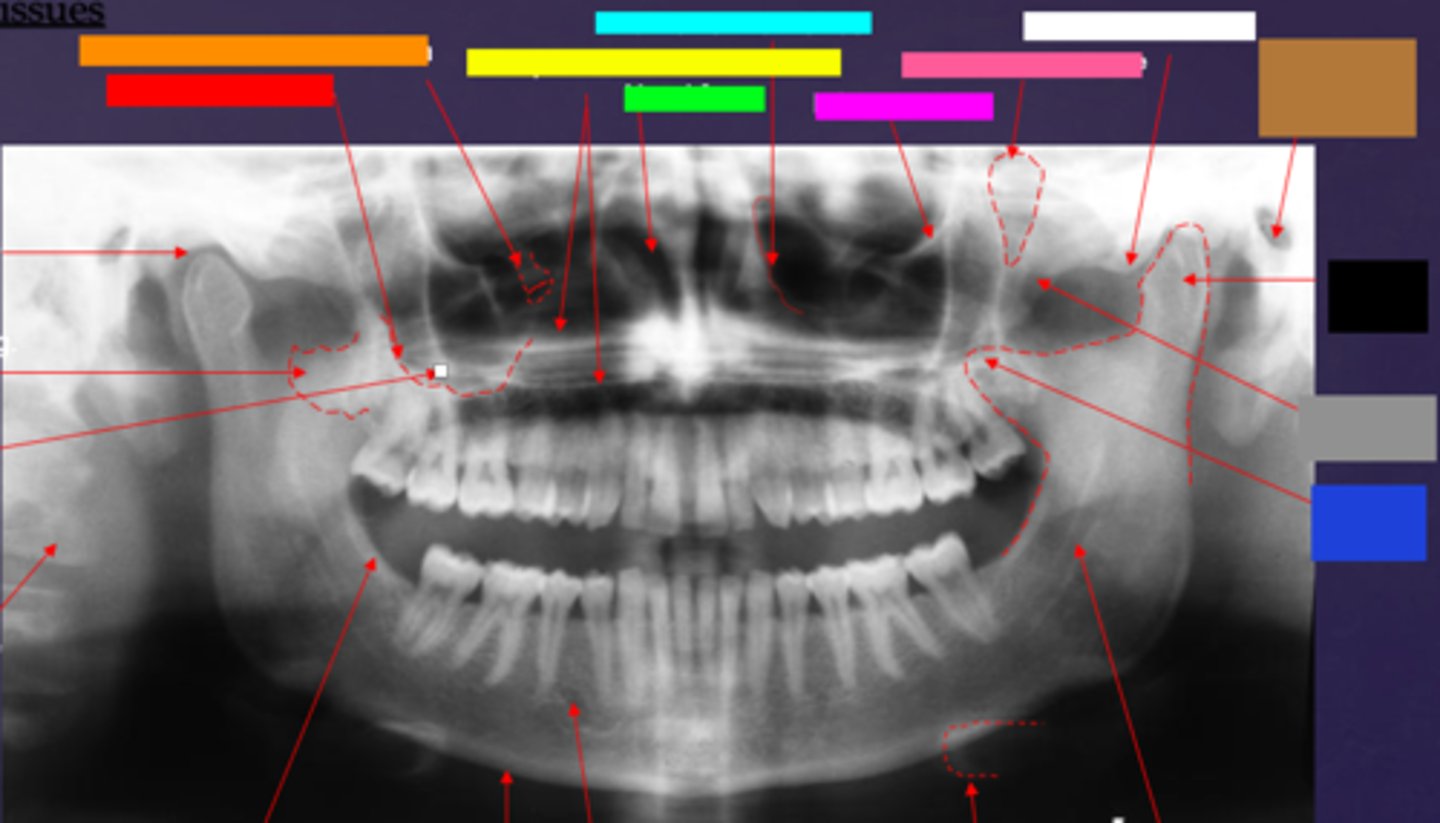
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the dark blue box:
coronoid process
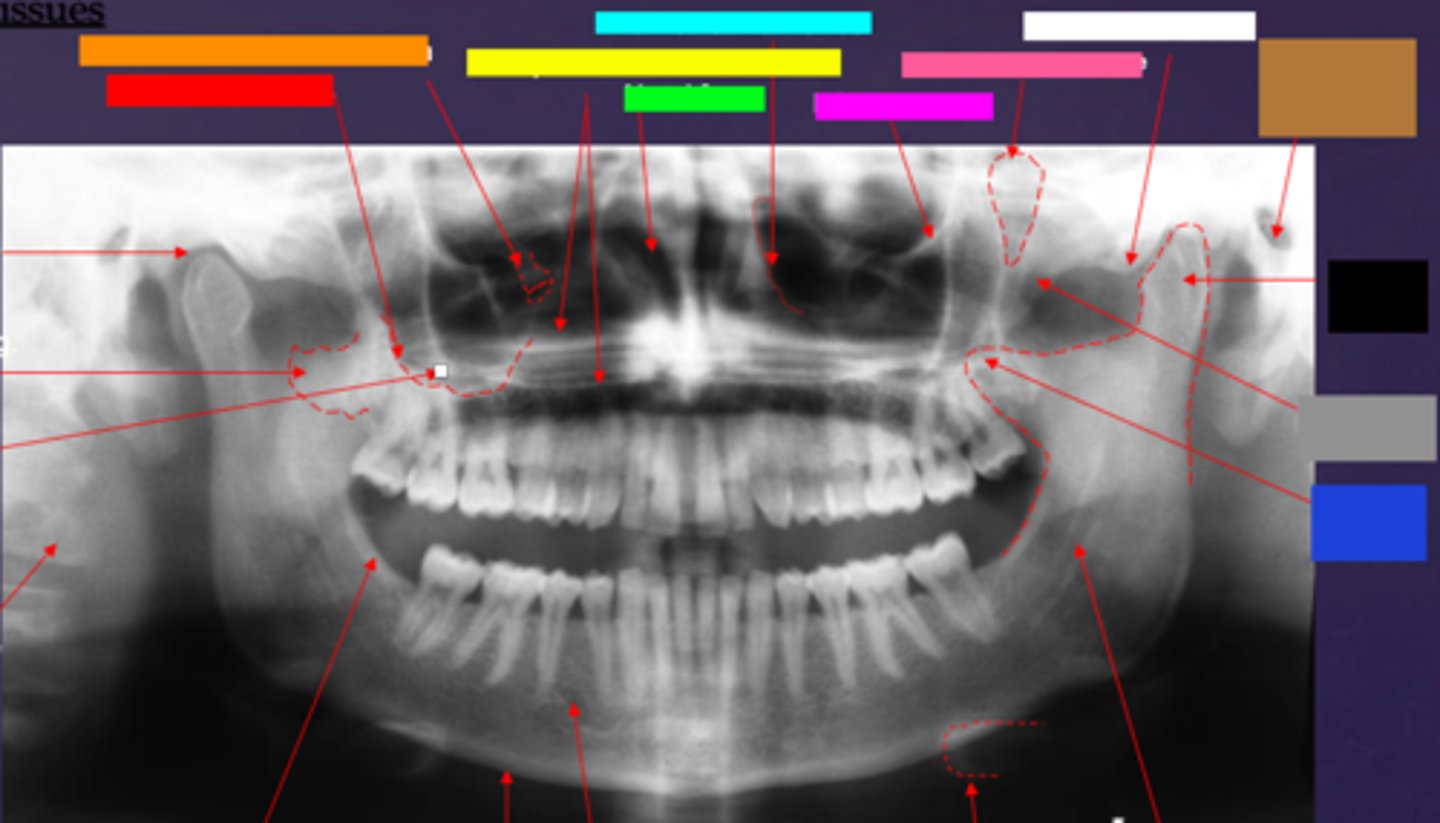
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the hot pink box:
infra orbital rim
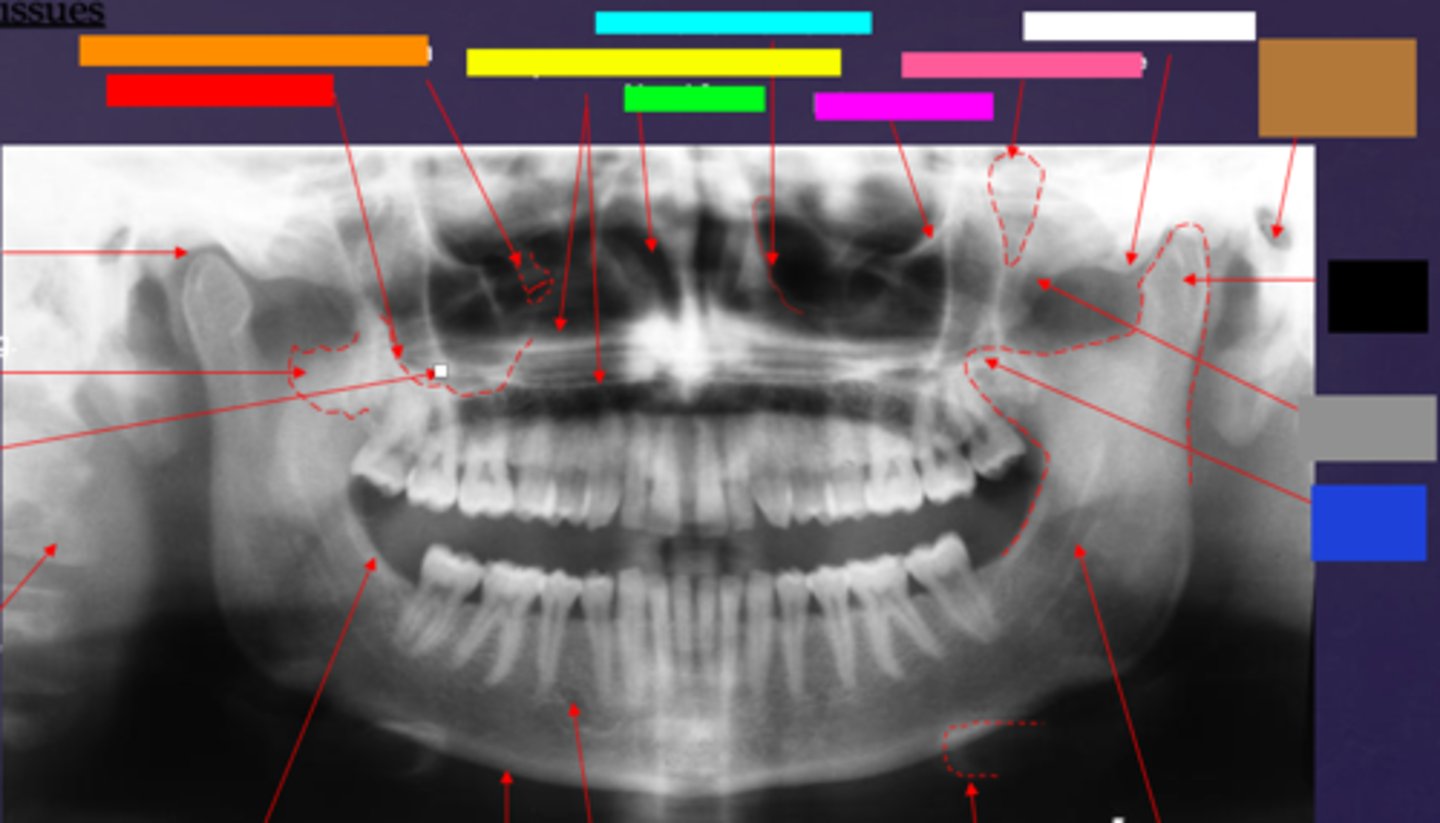
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the pink/salmon box:
pterygomaxillary fissure
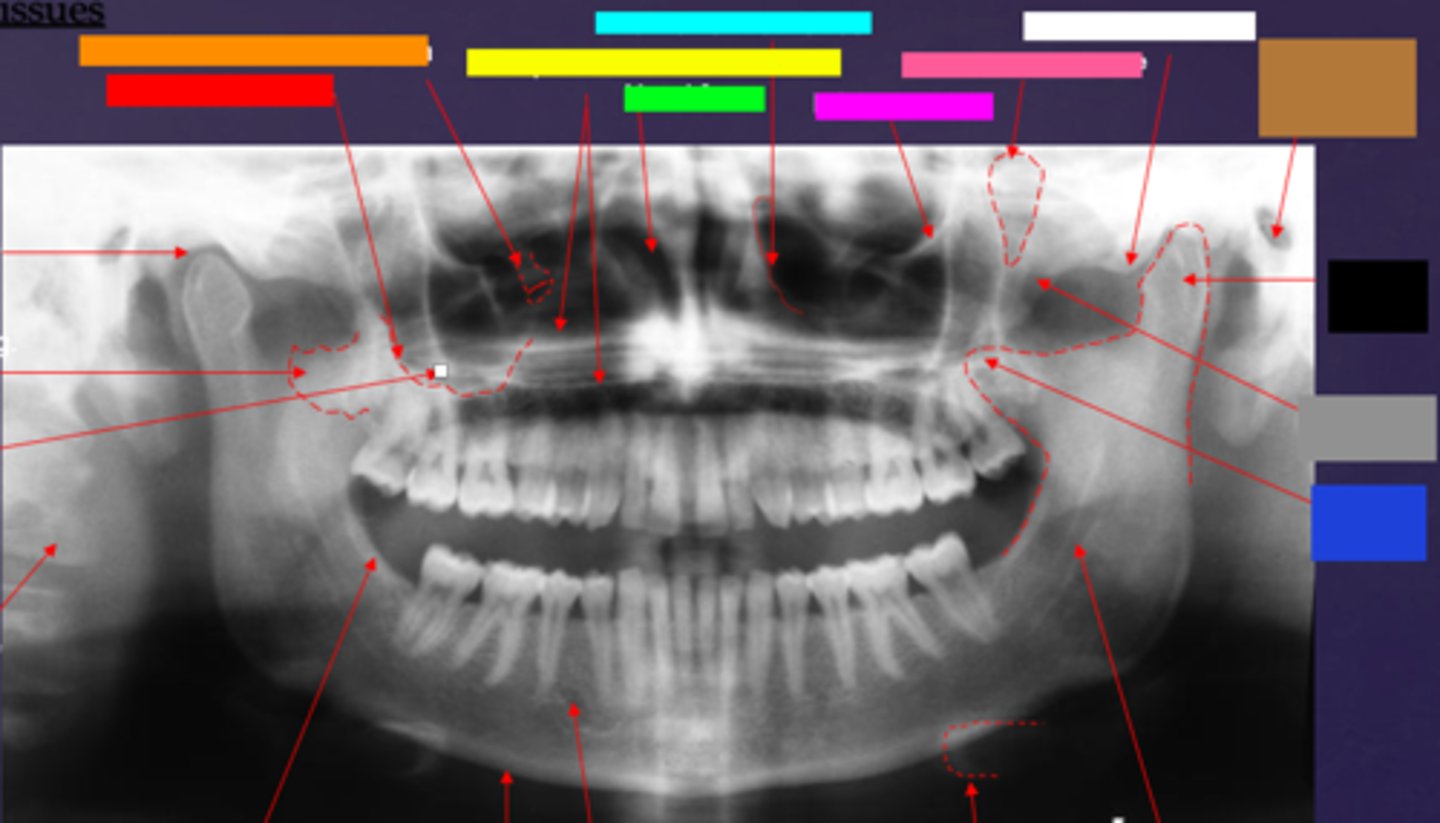
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the brown box:
external auditory meatus/ear canal
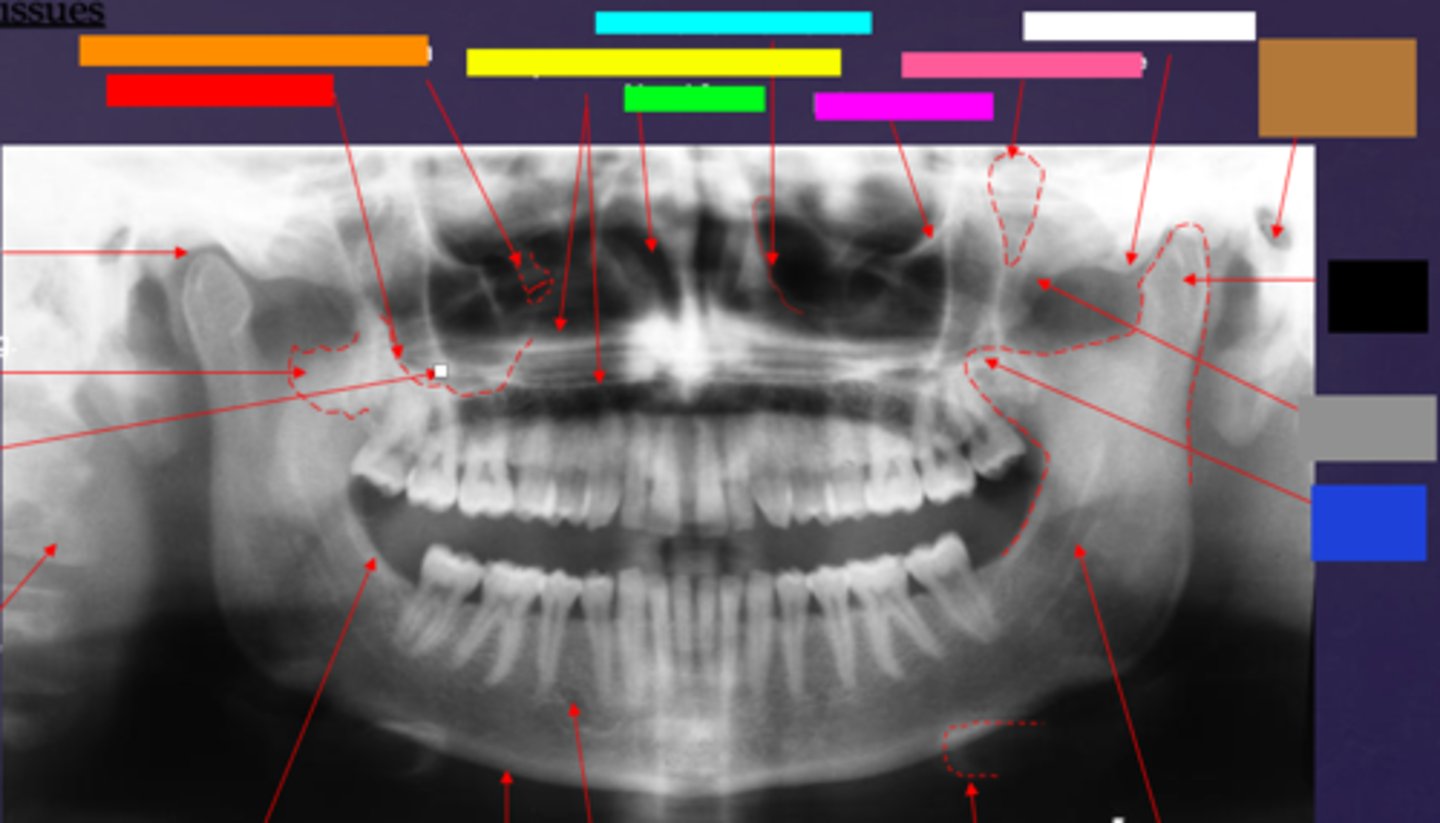
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the white box:
articular eminence
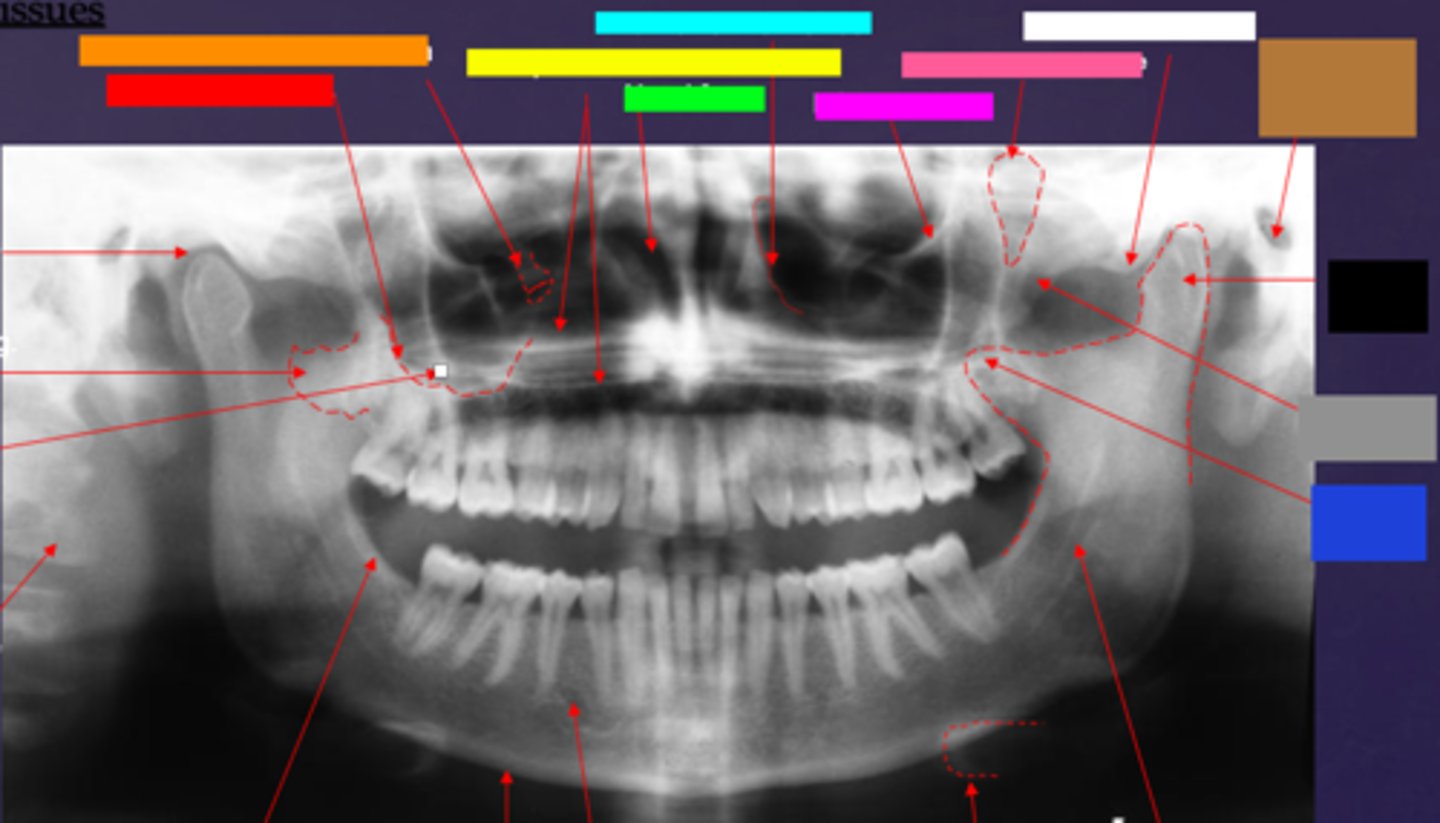
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the black box:
mandibular condyle
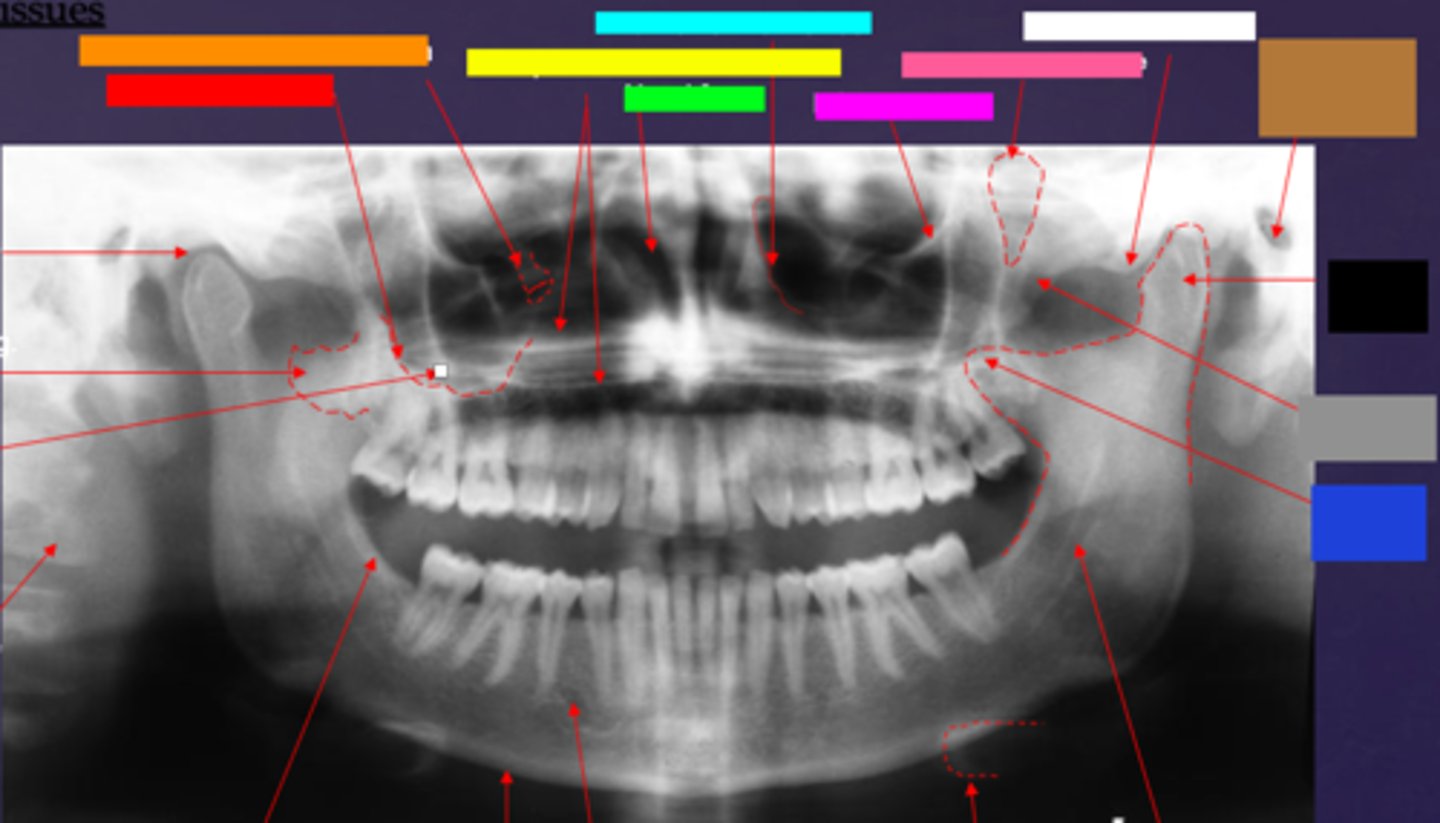
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the gray box:
zygomatic bone
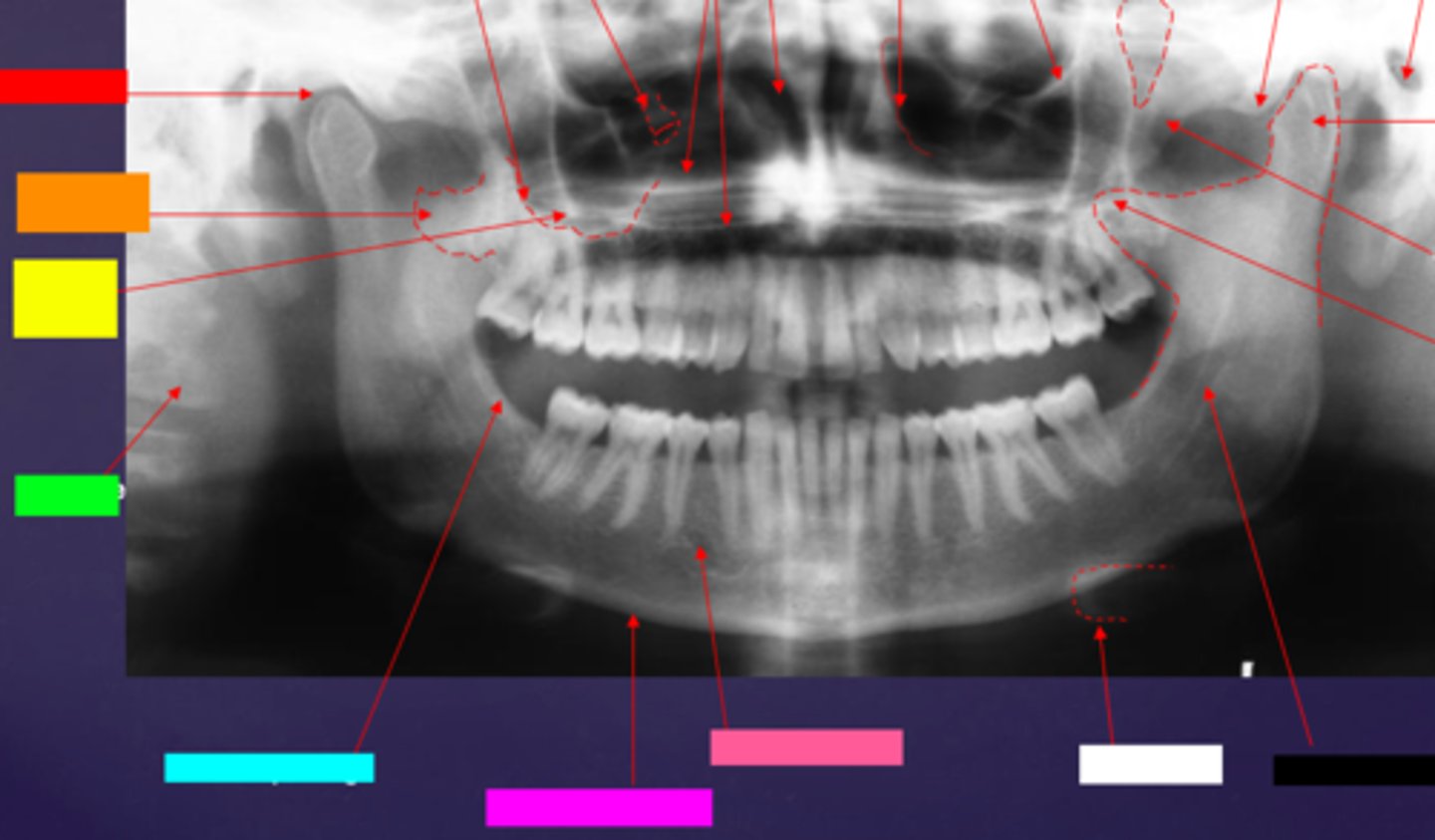
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the red box:
mandibular fossa
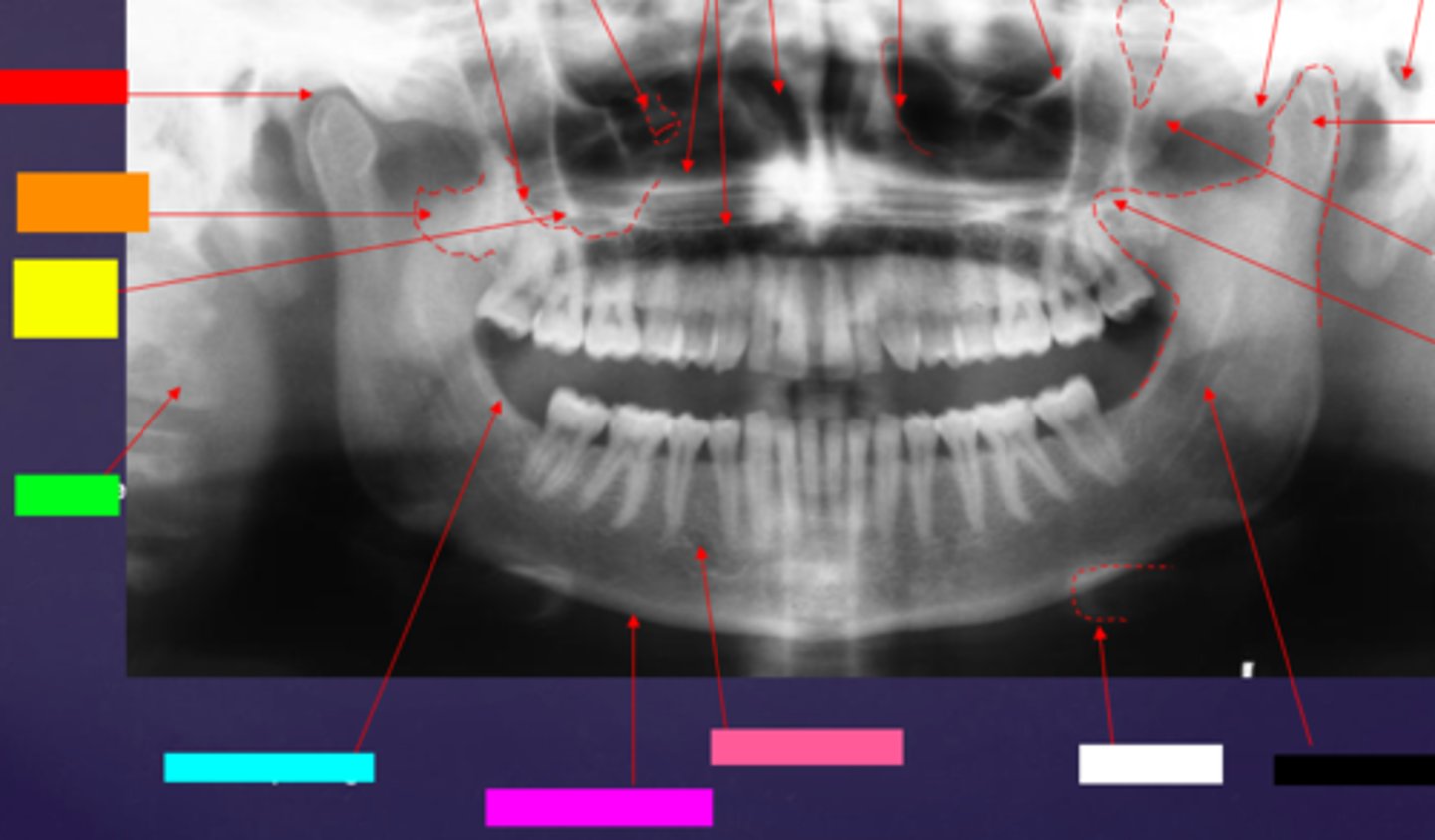
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the orange box:
lateral pterygoid plate
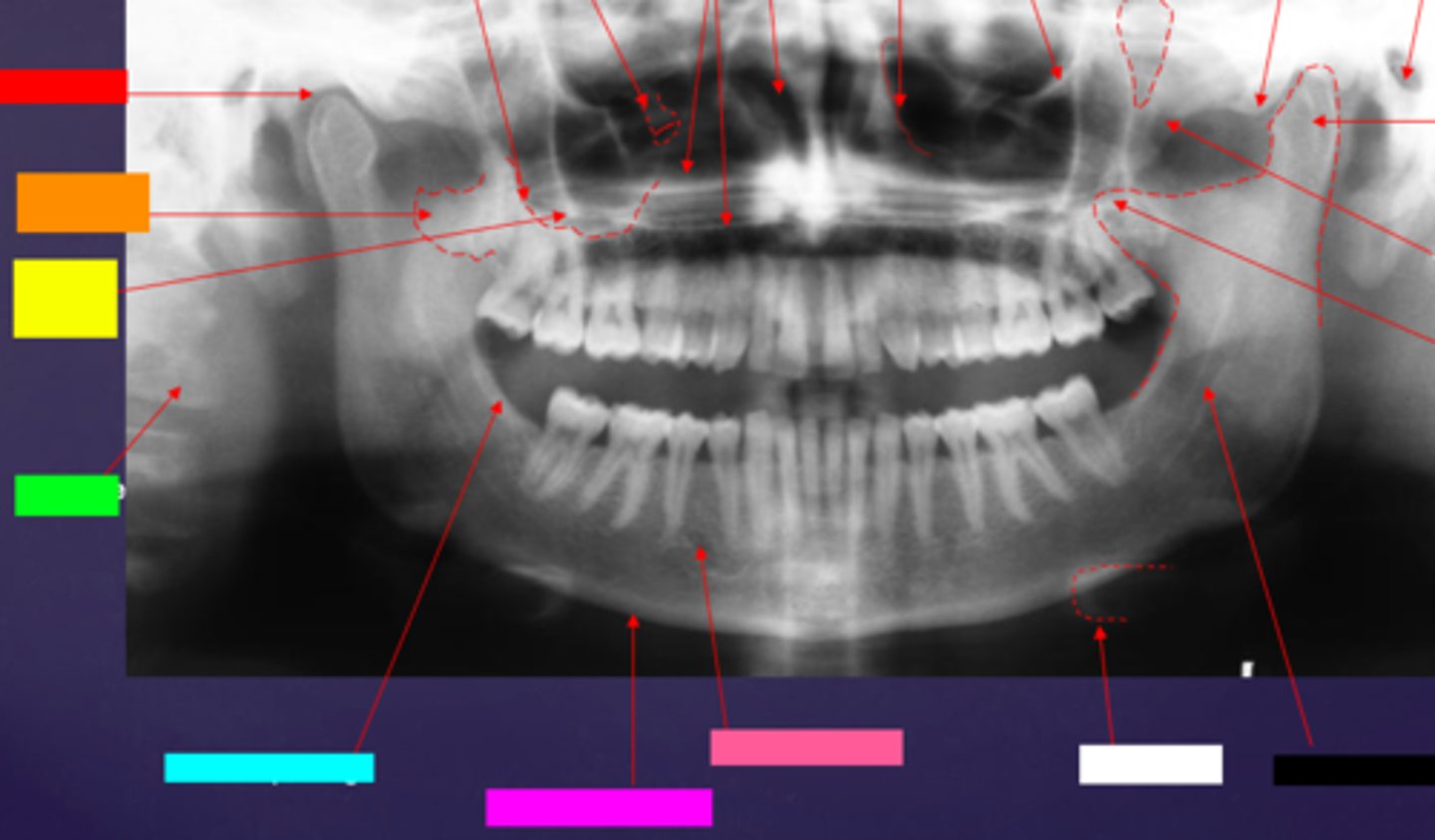
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the yellow box:
zygomatic process of maxilla
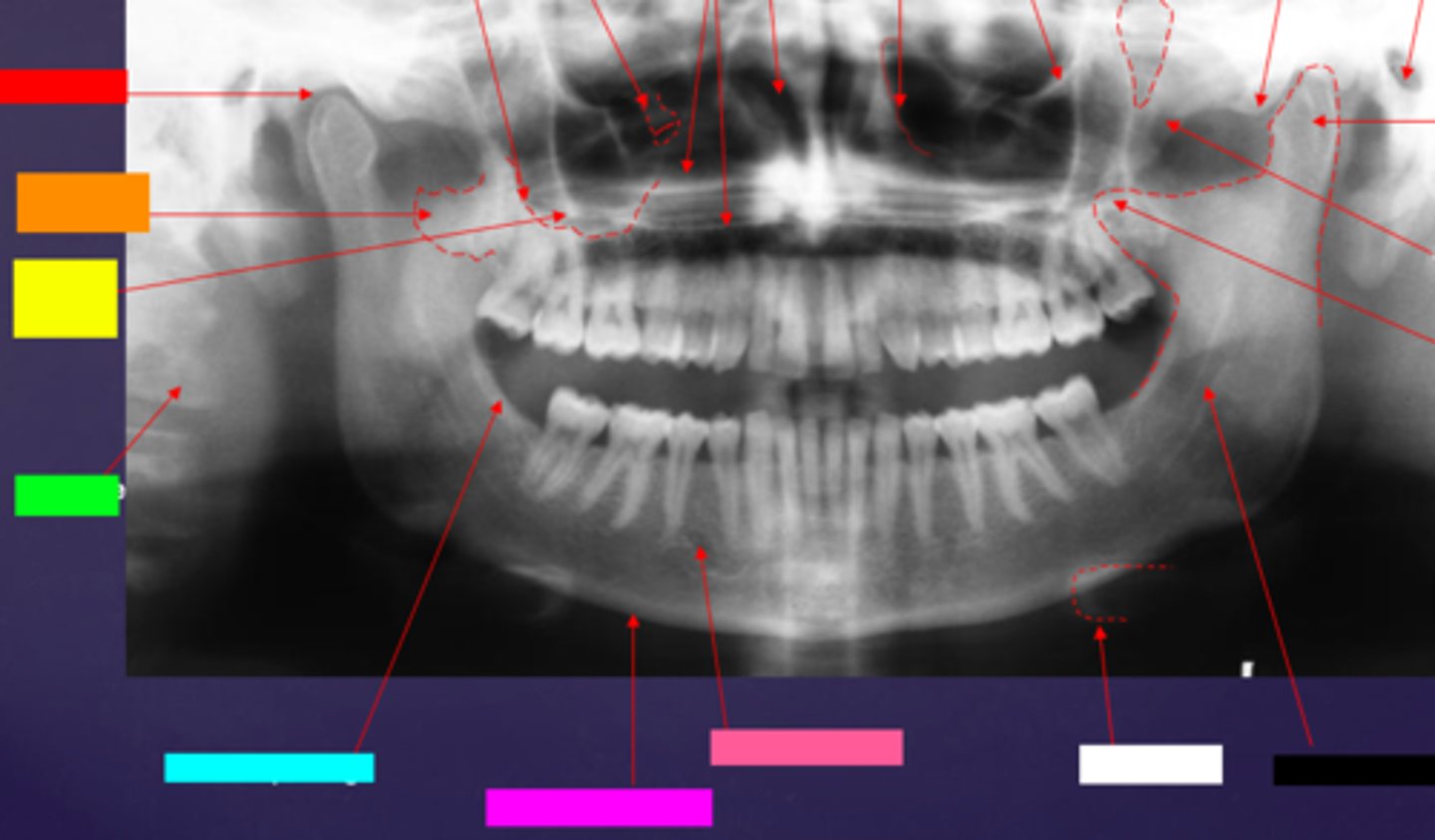
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the green box:
cervical spine
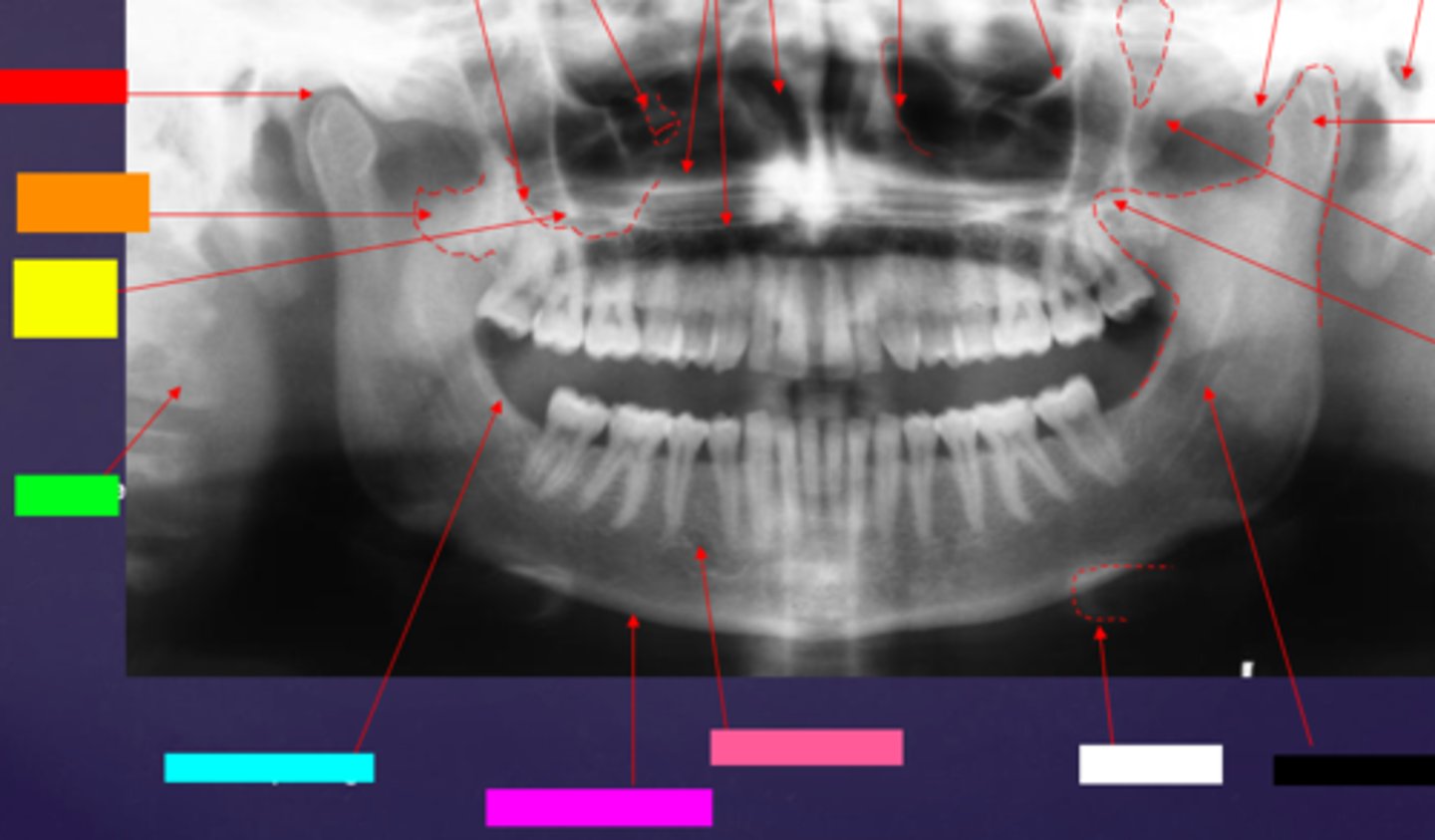
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the light blue box:
external oblique ridge
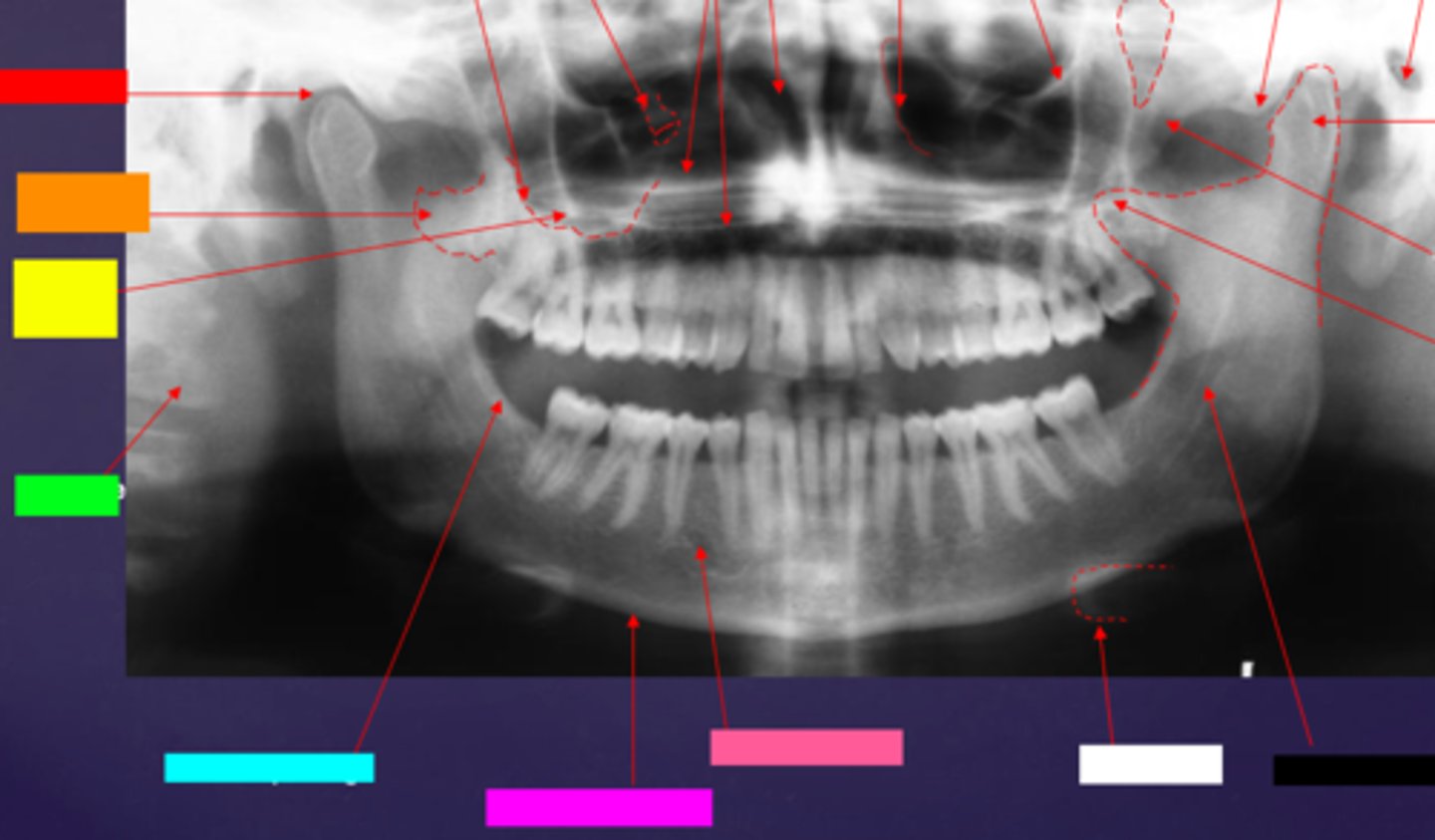
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the hot pink box:
inferior boarder of the mandible
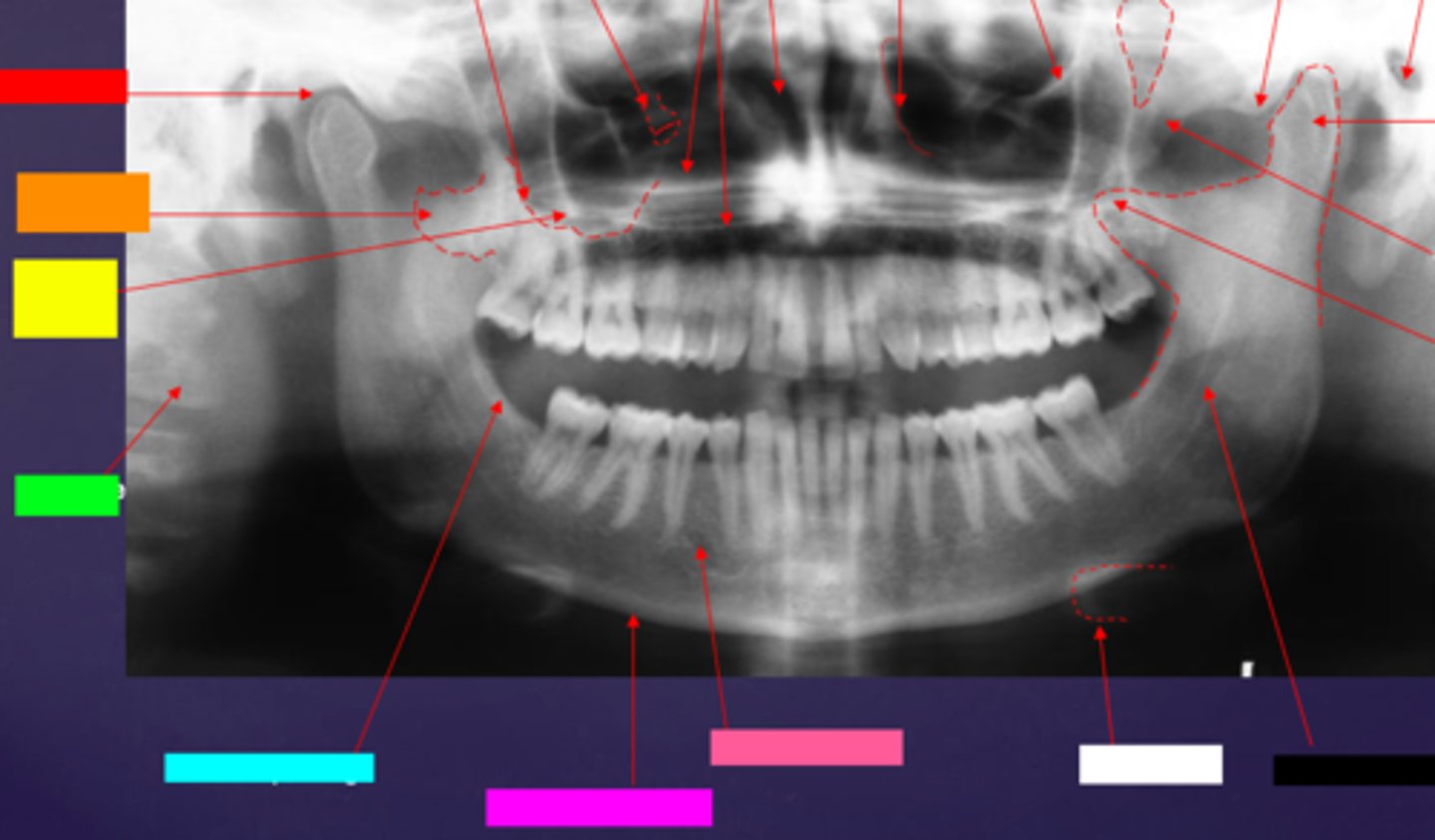
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the pink/salmon box:
mental foramen
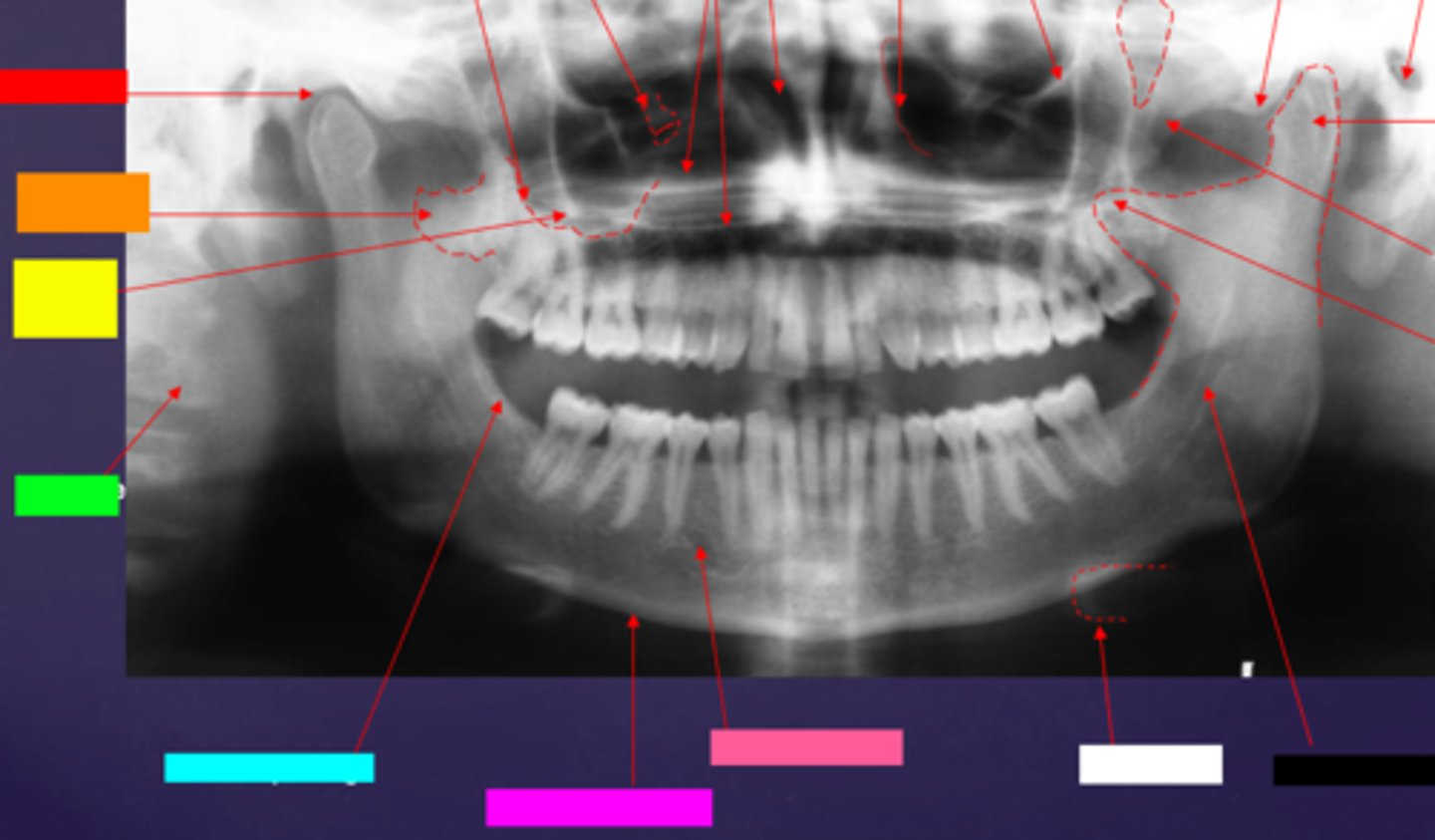
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the black box:
inferior alveolar canal
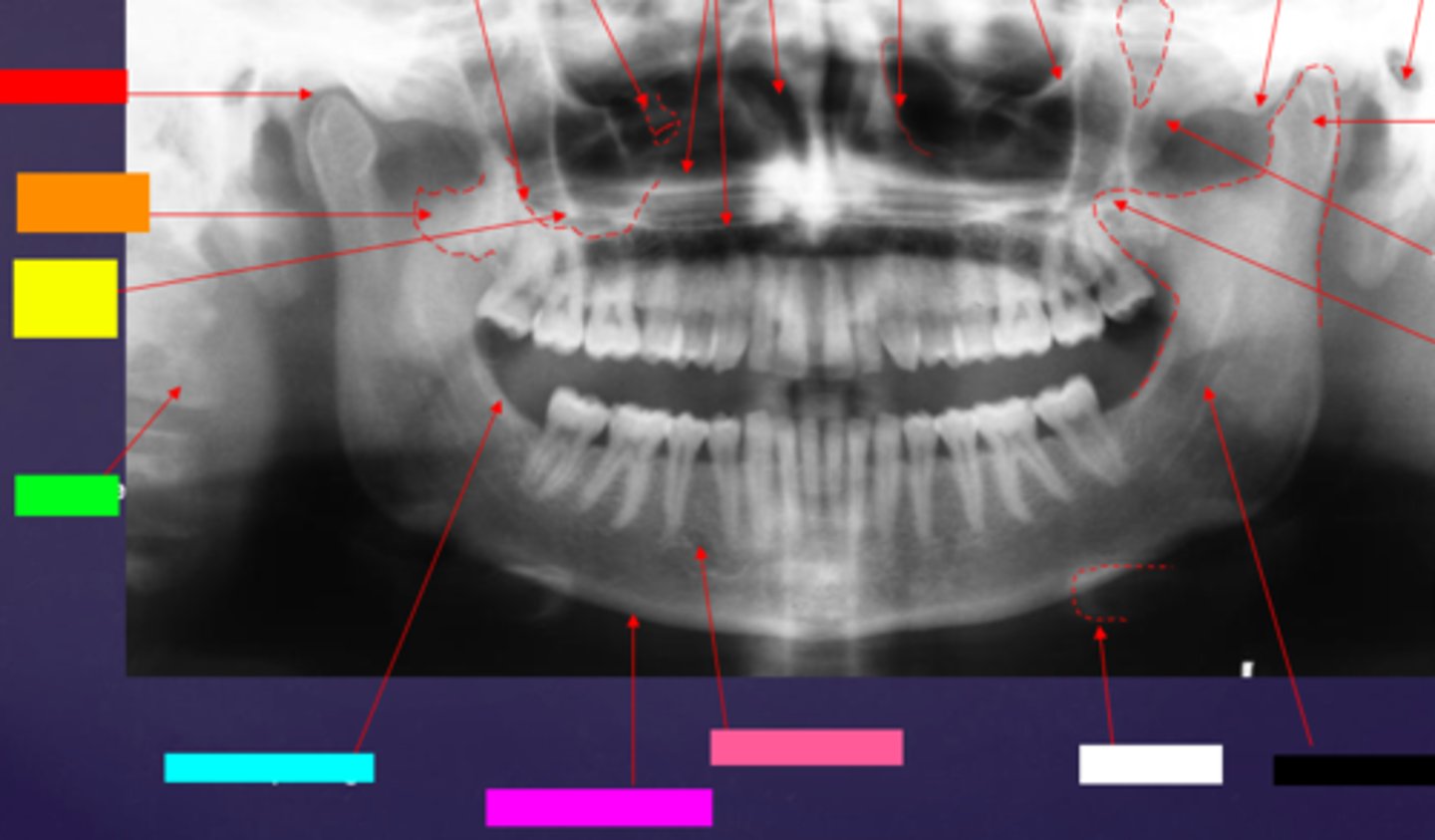
ID the hard tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the white box:
hyoid bone
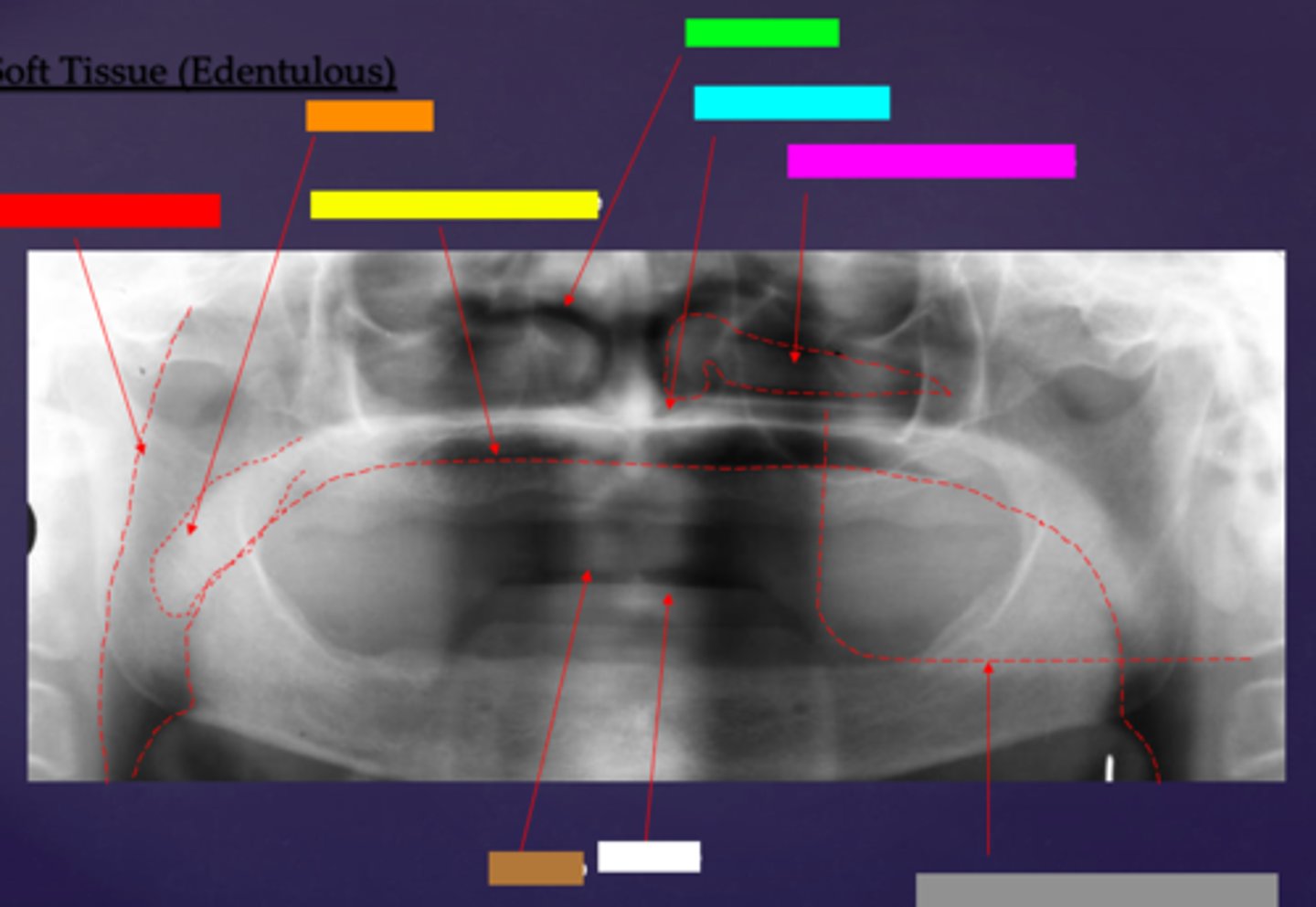
ID the soft tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the red box:
posterior pharyngeal wall
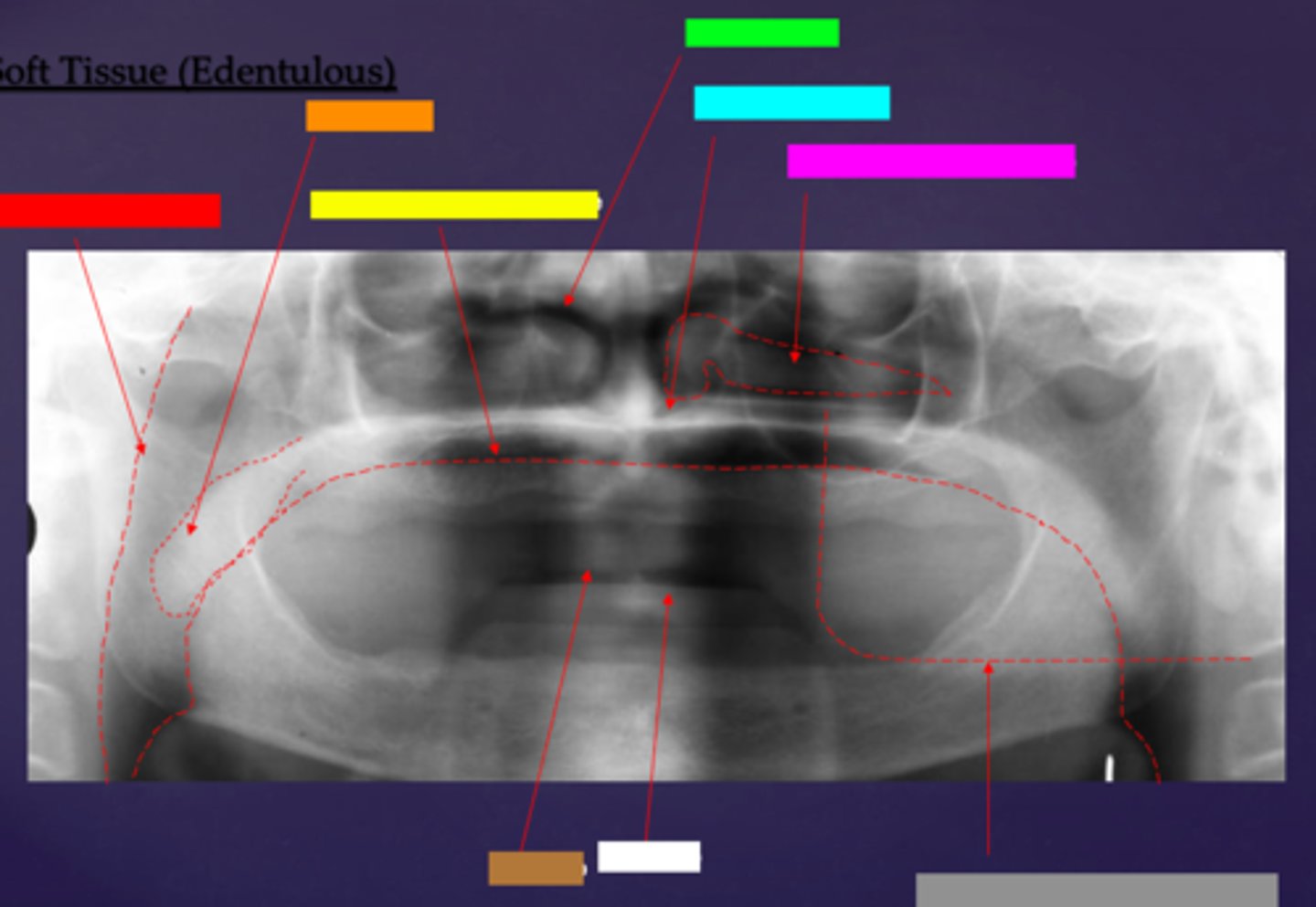
ID the soft tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the orange box:
soft palate
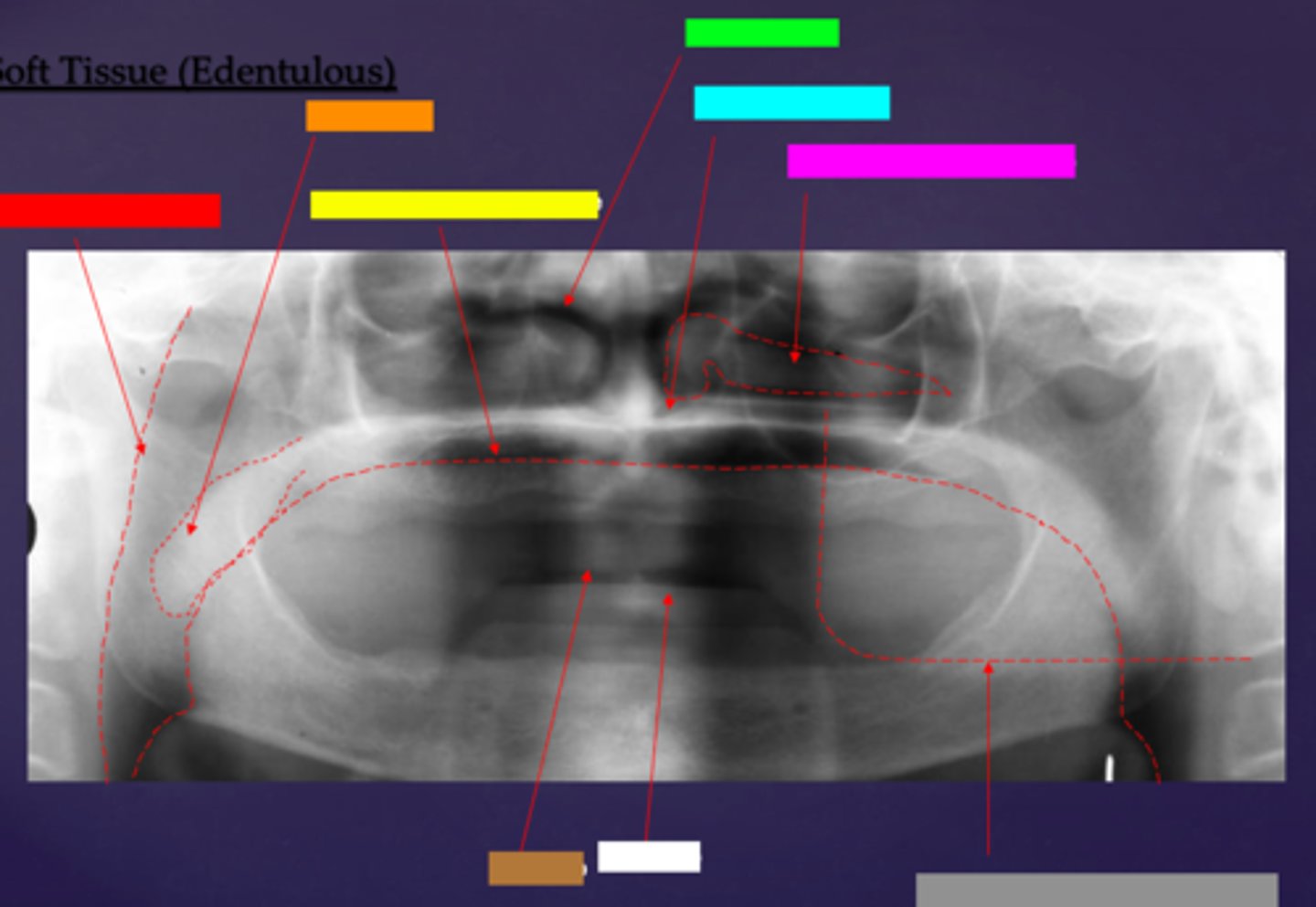
ID the soft tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the yellow box:
dorsal surface of tongue
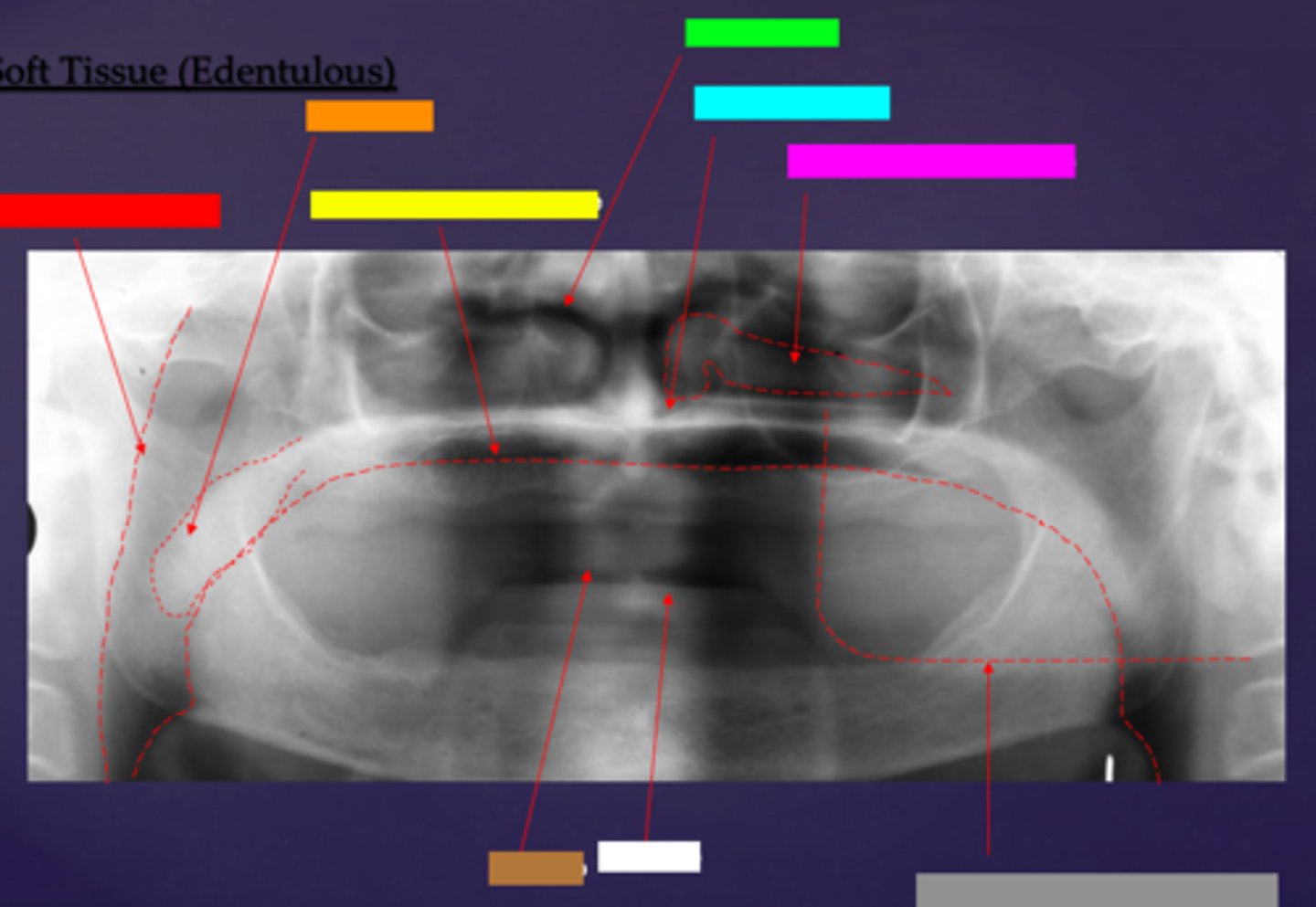
ID the soft tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the green box:
middle nasal meatus
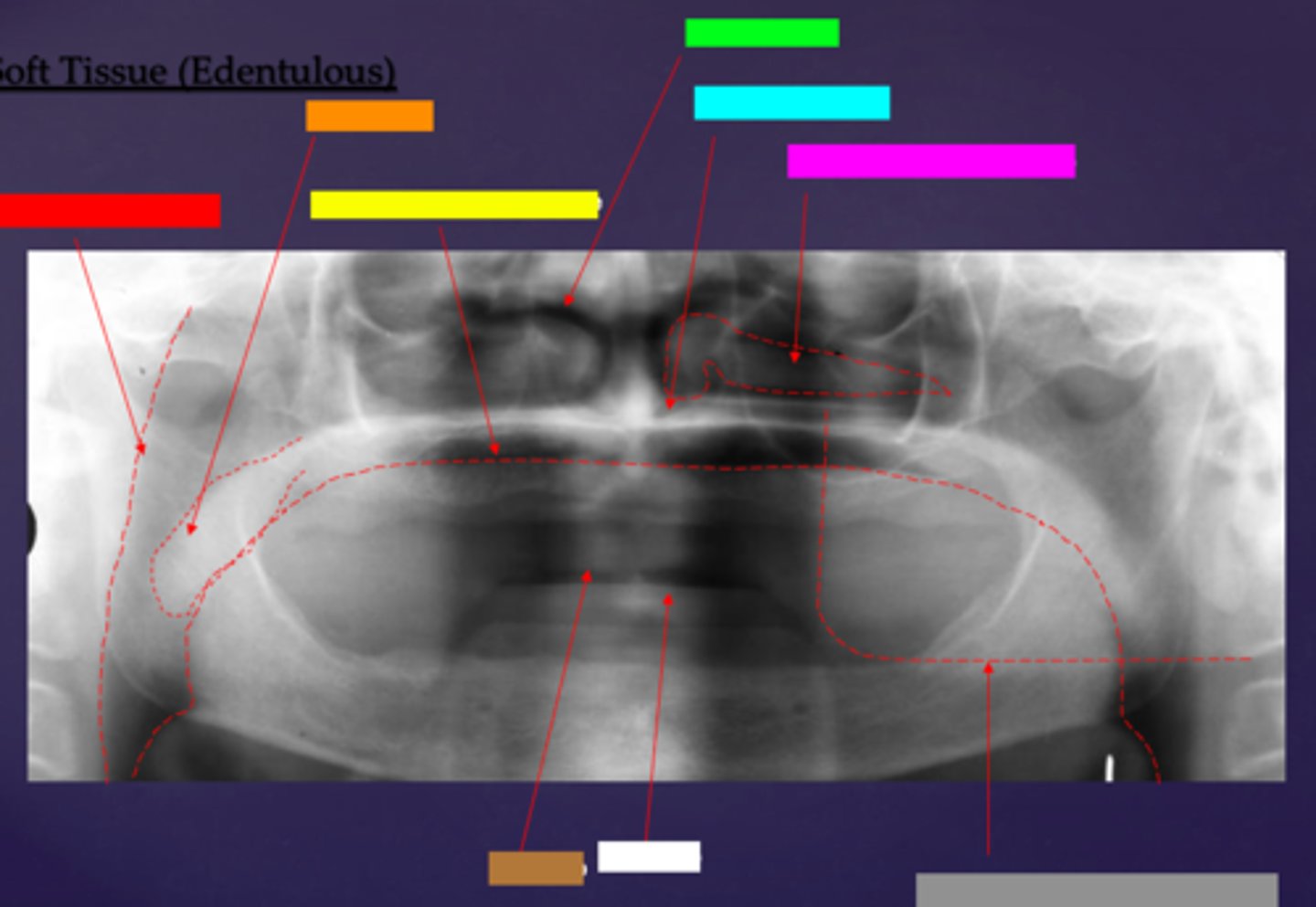
ID the soft tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the light blue box:
inferior nasal meatus
ID the soft tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the hot pink box:
inferior nasal concha (turbinate)
ID the soft tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the brown box:
upper lip
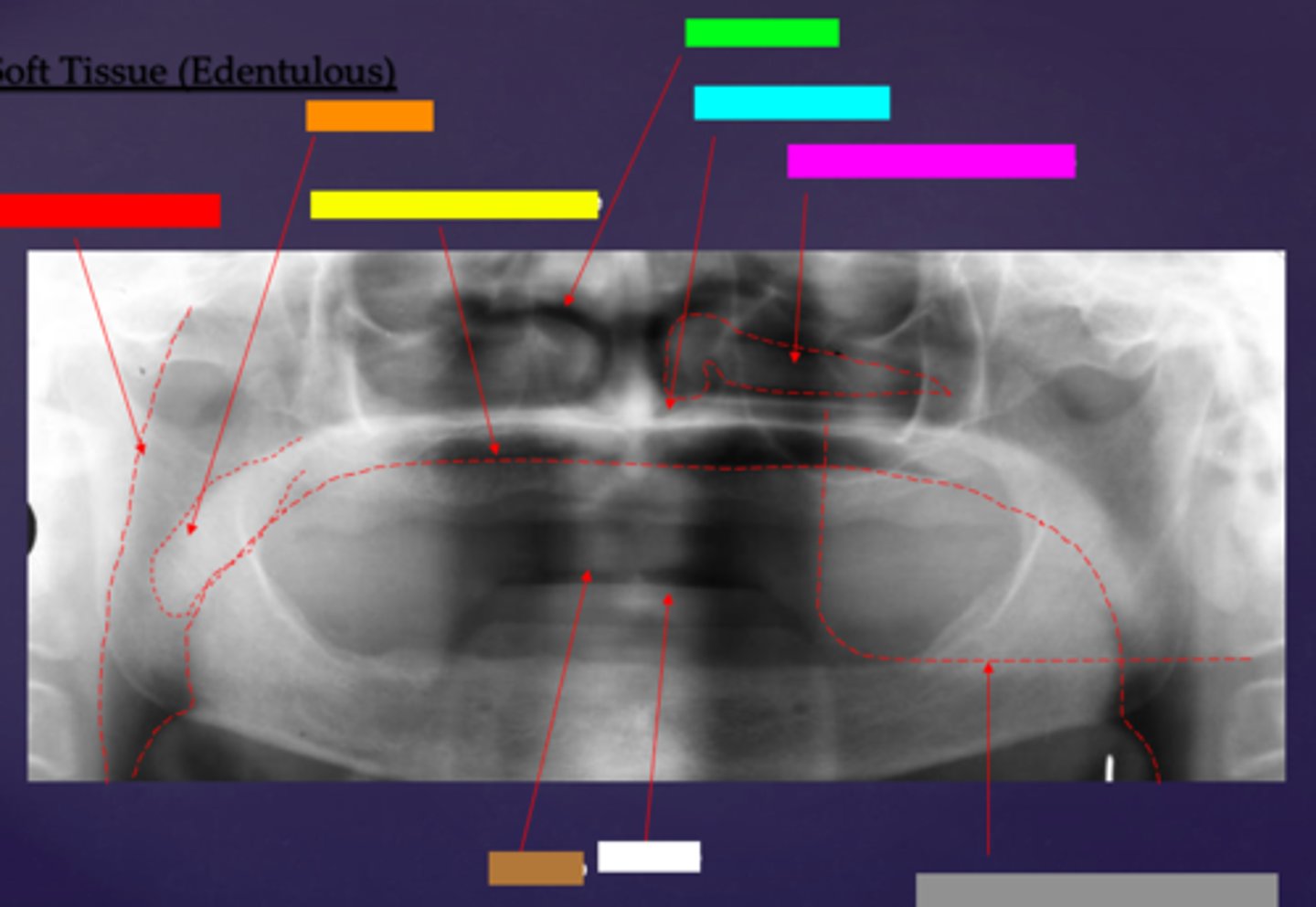
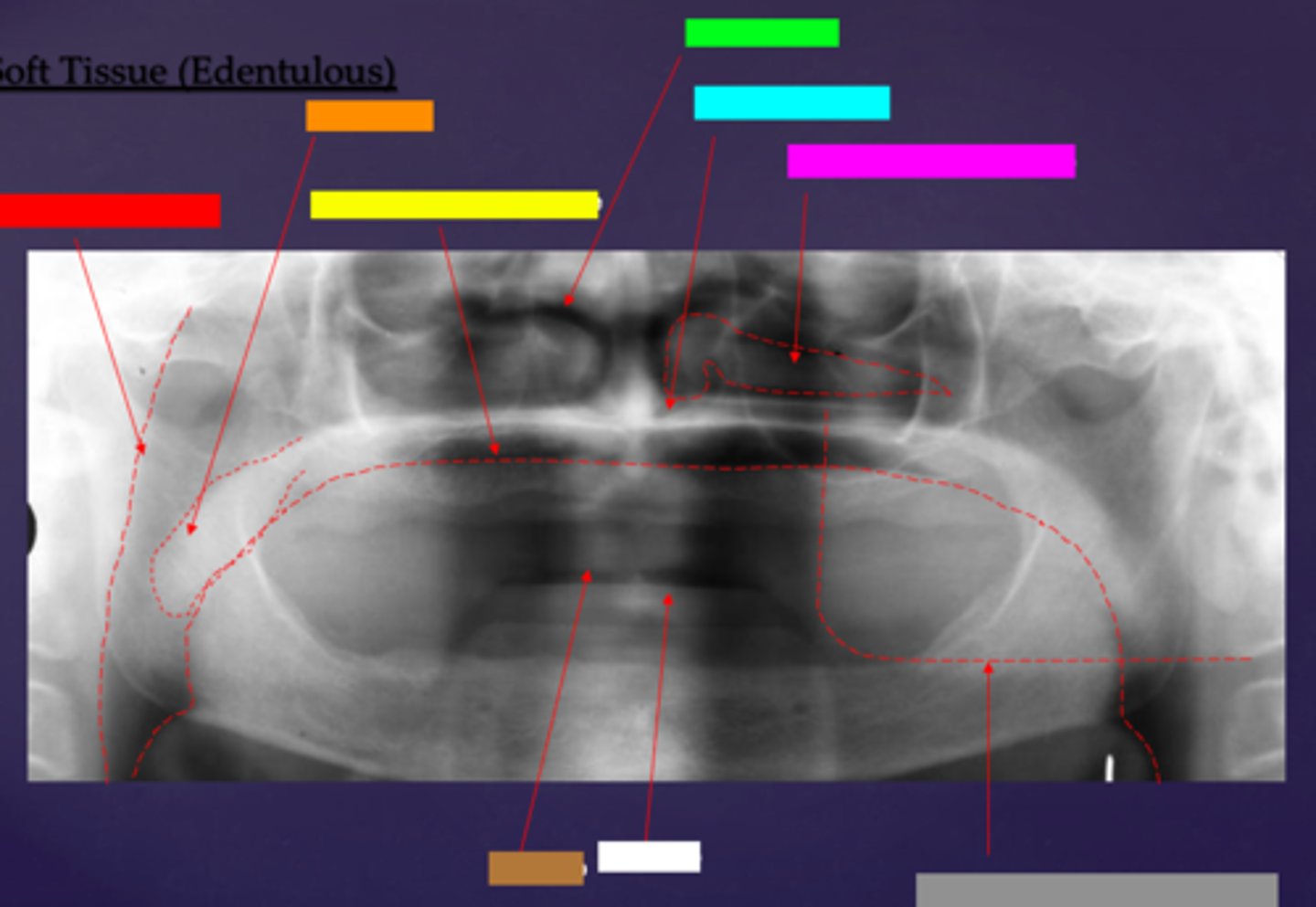
ID the soft tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the white box:
lower lip
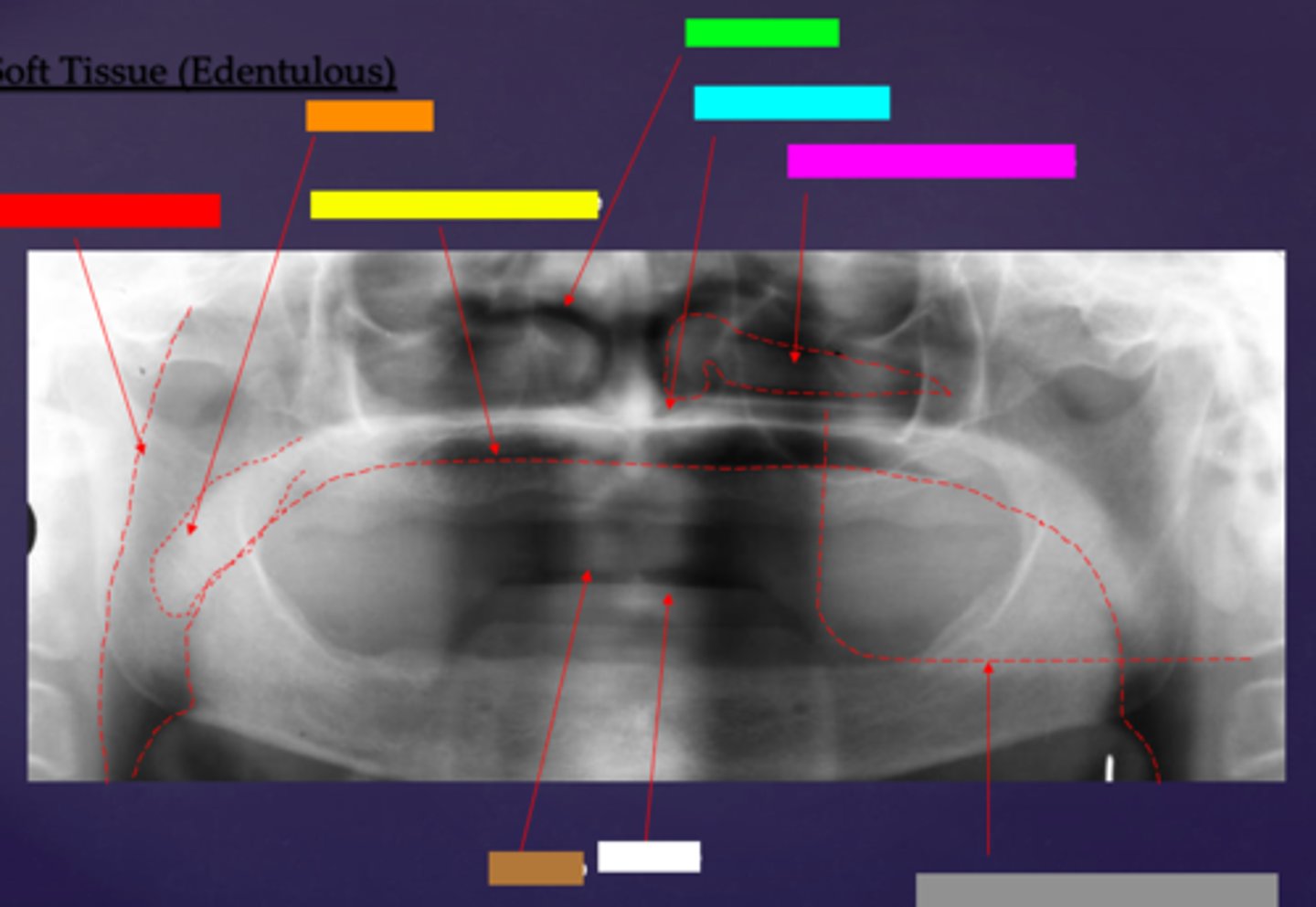
ID the soft tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the grey box:
ghost image of opposite mandible
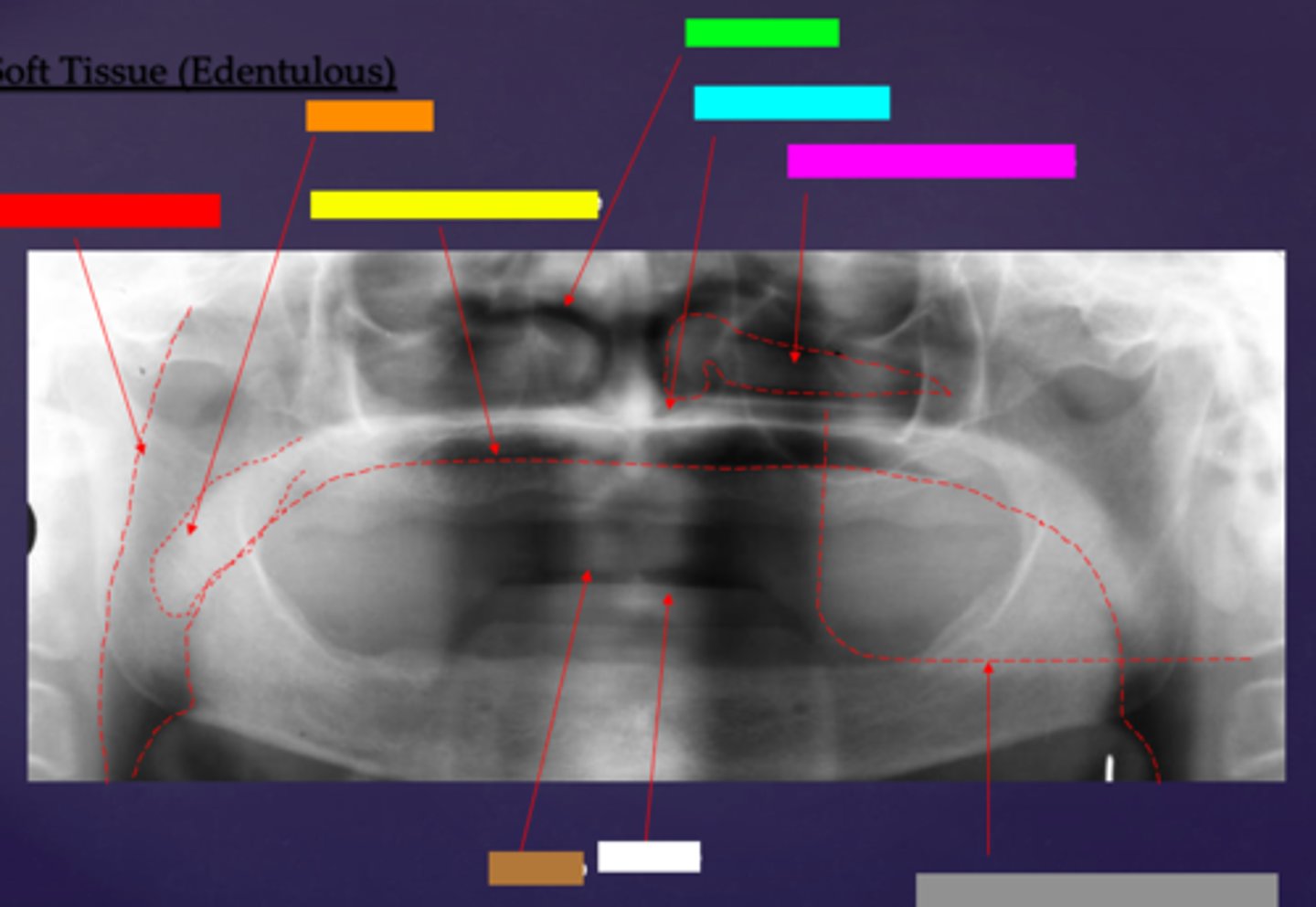
ID the soft tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the red box:
ala of nose
ID the soft tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the orange box:
nasal septum
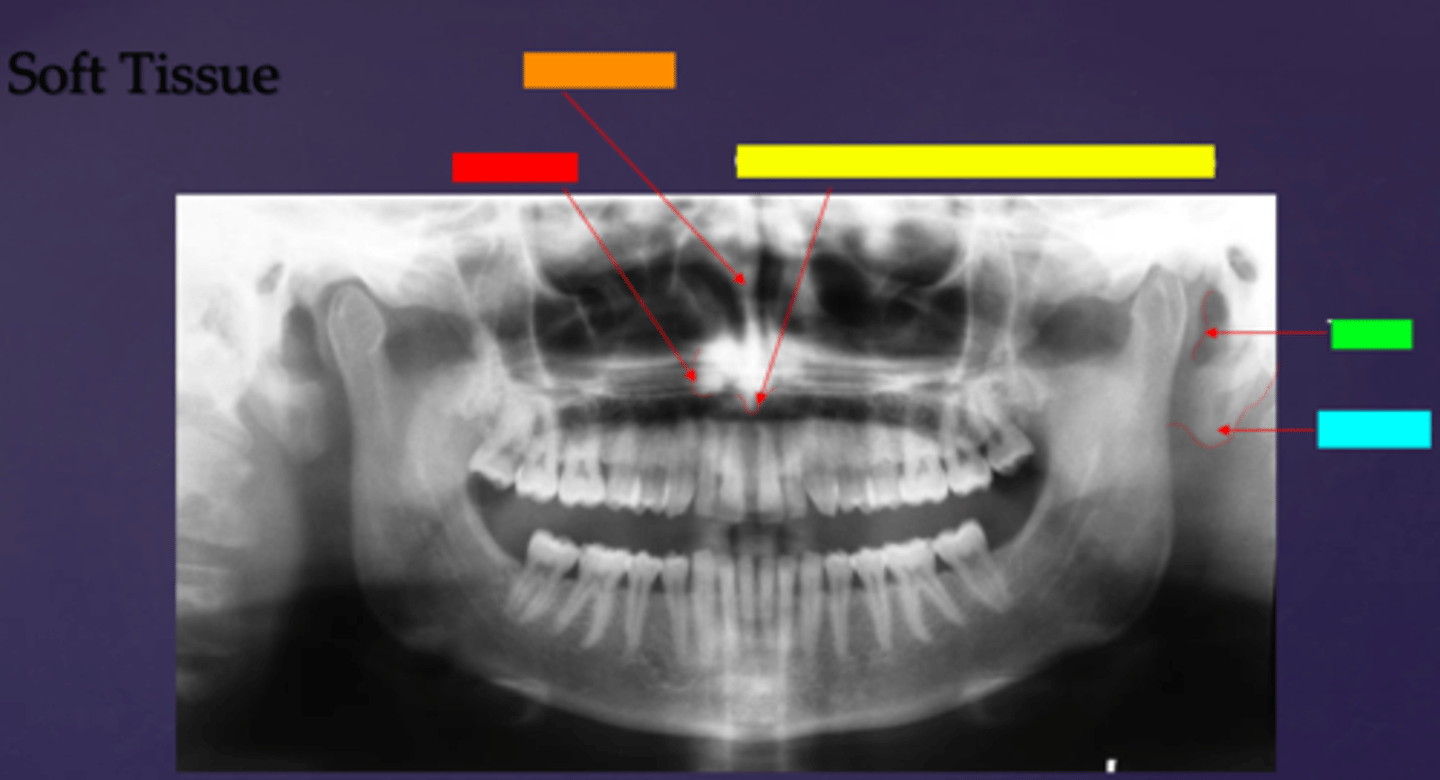
ID the soft tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the yellow box:
columna (the septum separating the nostrils)
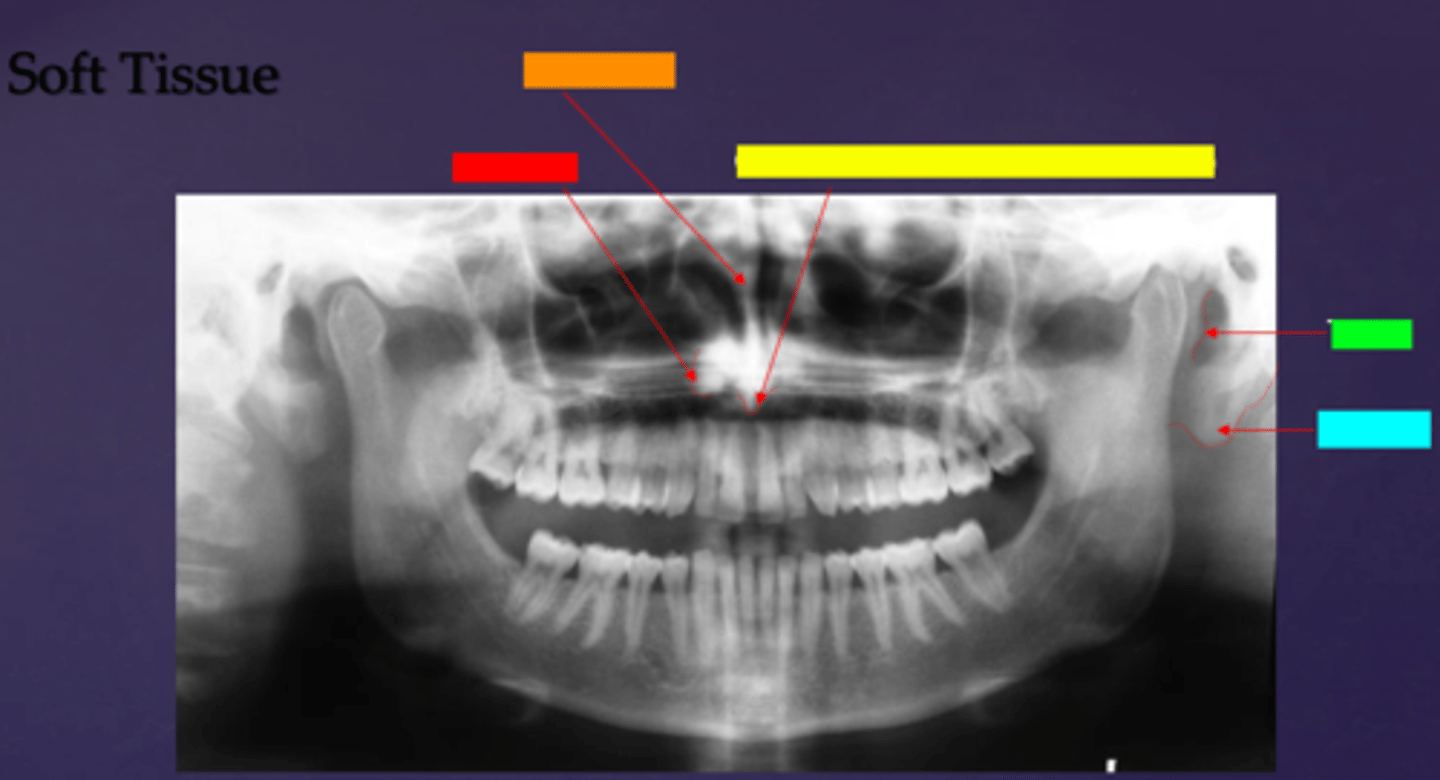
ID the soft tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the green box:
tragus
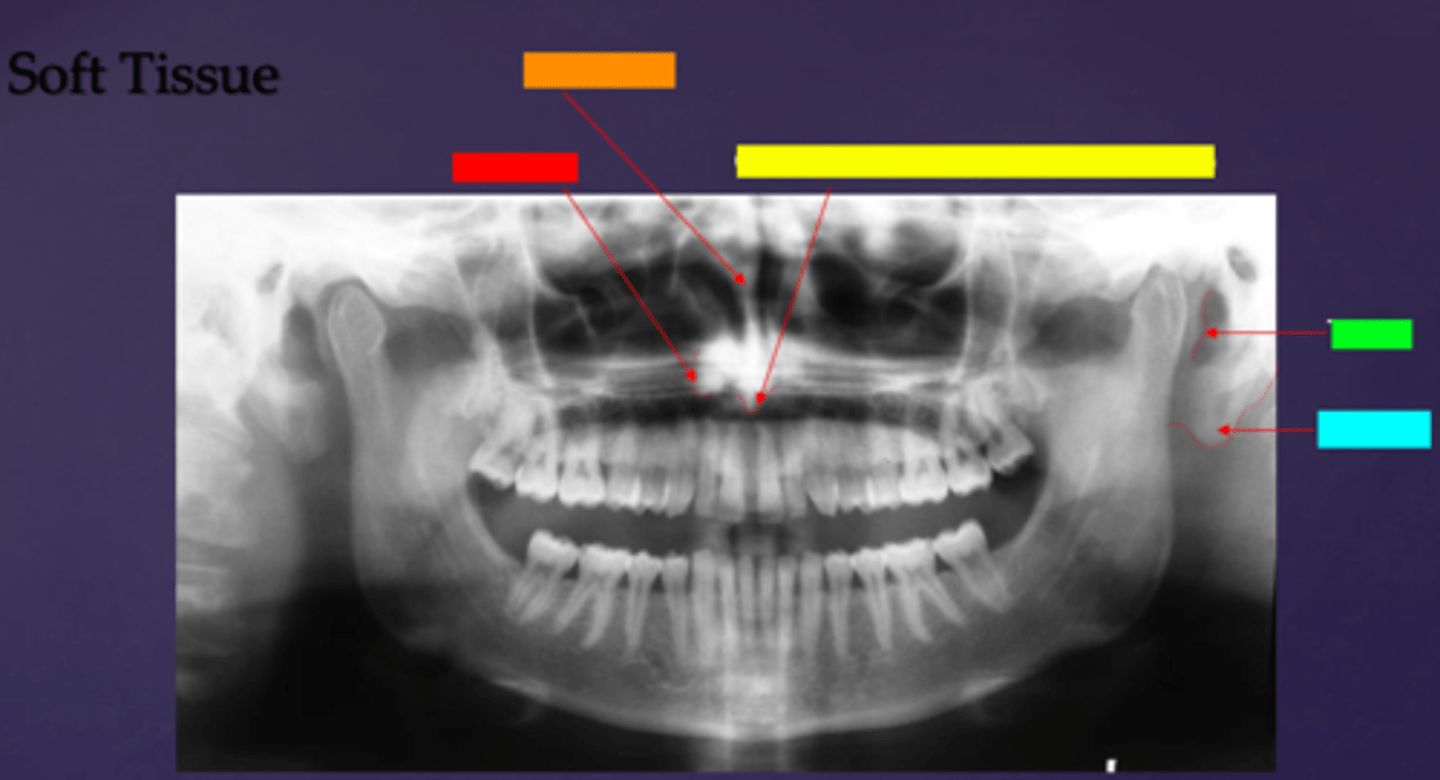
ID the soft tissue anatomy indicated by the arrow pointing from the light blue box:
ear lobe
What midline objects have the ability to project as single/double images? (4)
- Hard palate
- Epiglottis
-Hyoid bone
- Cervical vertabrae
The farther the sensor is from anatomy, the ____________ magnification
More (ex: hands on a desk with light above)
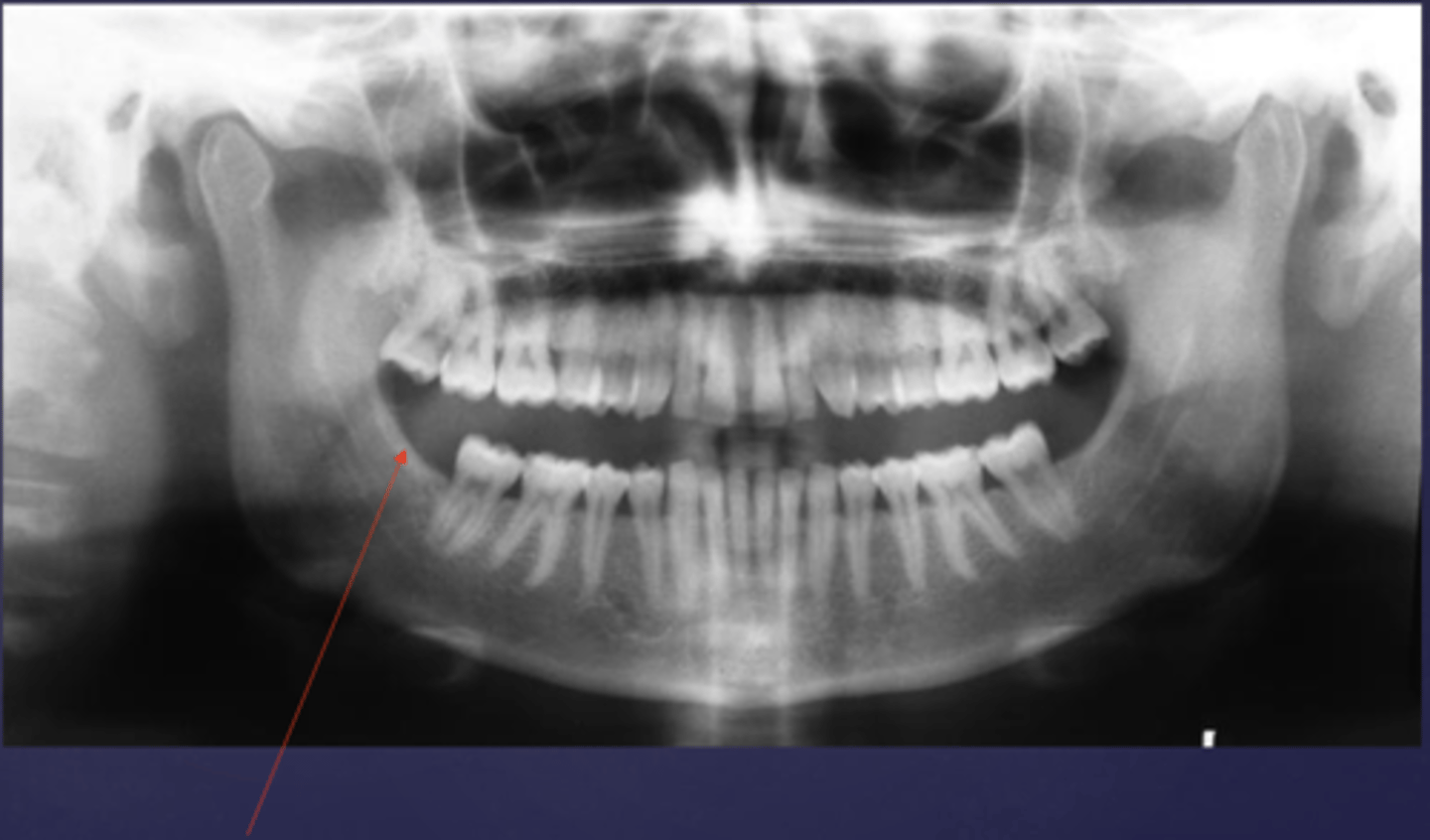
What muscle attaches here?
Buccinator (attaches to the external oblique ridge of the mandible)