Pathophysiology 1: Exam 2
1/254
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
255 Terms
Atherosclerosis
-Common form of arteriosclerosis
-Buildup of cholesterol plaques in tunica intima
-Disease of elastic arteries and large/medium sized muscular arteries
Where is atherosclerosis most commonly found?
-Abdominal aorta > Coronary artery > Popliteal artery > Carotid artery > Circle of Willis
What are modifiable risk factors of atherosclerosis?
-Hypertension
-Tobacco smoking
-Dyslipidemia
-Diabetes
What are non-modifiable risk factors of atherosclerosis?
-Age
-Sex
-Postmenopausal status
-Family history
What are the symptoms of atherosclerosis?
-Angina
-Claudication (Muscle pain, weakness)
-Can be asymptomatic
What is the progression of atherosclerosis?
1) Endothelial cell dysfunction
2) Macrophage and LDL accumulation
3) Foam cell formation
4) Fatty streaks
5) Smooth muscle cell migration proliferation and extracellular matrix deposition
6) Fibrous plaque
7) Complex atheromas
8) Calcification (Risk of complications)
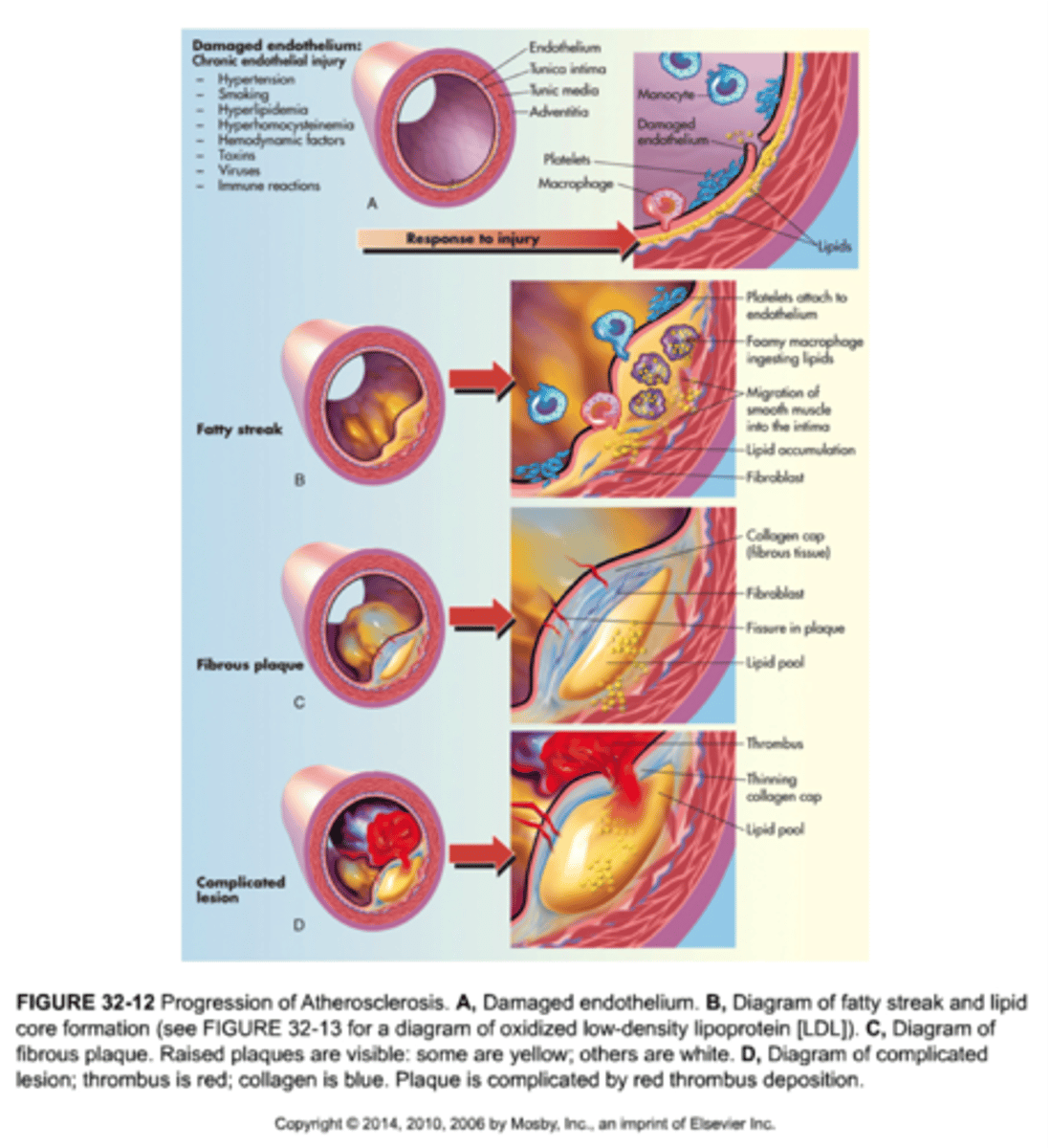
What are complications of atherosclerosis?
-Ischemia
-Infarction
-Aneurysm formation
-Peripheral vascular disease
-Thrombosis
What is the procedure for atherosclerosis?
-Guidewire with stent and balloon
-Balloon inflated
-Guidewire and balloon removed leaving stent
What is the most common type of cardiomyopathy?
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
What percentage of cardiomyopathy cases does Dilated Cardiomyopathy account for?
90%
What are the common causes of Dilated Cardiomyopathy?
-Drugs (Alcohol, cocaine, doxorubicin)
-Infection (Coxsackie B virus, Chagas disease)
-Ischemia
-Systemic conditions (Hemochromatosis, sarcoidosis, thyrotoxicosis, wet beriberi)
-Peripartum cardiomyopathy
Which gene mutation is associated with familial Dilated Cardiomyopathy?
TTN gene encoding sarcomeric protein titin
What structural changes occur in the left ventricle in Dilated Cardiomyopathy?
Thinning and enlargement of the left ventricle
What are symptoms of dilated cardiomyopathy?
-Heart failure
-S3 sounds
-Systolic regurgitant murmur
-Systolic dysfunction
-Dilated heart on echocardiogram
-Balloon appearance of heart on CXR
What is the treatment for dilated cardiomyopathy?
-Na+ restriction
-ACE inhibitors/ARBs
-β blockers
-Diuretics
-Mineralocorticoid receptor blockers
-Heart transplant
What percentage of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy cases are familial?
60-70%
What is the inheritance pattern of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy?
Autosomal dominant
Which genes are commonly mutated in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy?
Myosin binding protein C and β-myosin heavy chain
What symptom can Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy cause during exercise?
Syncope
What serious condition can Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy lead to?
Sudden death due to ventricular arrhythmia
What are two potential causes of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy?
Chronic hypertension and Friedreich ataxia
What are symptoms of Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
-S4 heart sounds
-Systolic murmur
-Diastolic dysfunction ensues
-Possible mitral regurgitation (Impaired mitral valve closure)
What is the treatment for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
-Cessation of high-intensity athletics
-β-blockers
-Calcium channel blockers
-Avoid drugs that decrease preload
What structural changes occur in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy?
-Interventricular septum is enlarged
-Decreases size of the left ventricle
What is a common histological finding associated with Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm?
Cystic medial degeneration
What condition may result from aortic root dilation in Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm?
Aortic valve regurgitation
Which infection can be associated with Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm?
3° syphilis
What are risk factors for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms?
-Hypertension
-Bicuspid aortic valve
-Connective tissue disease (Marfan syndrome)
What is associated with transmural inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation?
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
How may an abdominal aortic aneurysm present?
As a palpable abdominal mass
What are the symptoms of a ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm?
Triad of abdominal mass, acute abdominal/back pain, and resistant hypotension
Where is an abdominal aortic aneurysm most often located?
Infrarenal
What are risk factors for and abdominal aortic aneurysm?
-Tobacco smoking
-Increased age
-Male sex
-Family history
What is the most common primary cardiac tumor in adults?
Myxomas
Where do 90% of myxomas occur?
In the atria, primarily the left atrium
How are myxomas described in terms of obstruction?
As a 'Ball Valve' obstruction in the left atrium
What symptoms are associated with myxomas?
Multiple syncopal episodes
What cytokine is produced by myxomas that leads to constitutional symptoms?
IL-6
What constitutional symptoms can be caused by myxomas?
Fever and weight loss
What sound may be auscultated in patients with myxomas?
An early diastolic 'tumor plop' sound
What does the gelatinous material of myxomas consist of?
Myxoma cells immersed in glycosaminoglycans
What is Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT)?
A blood clot within a deep vein.
What are the symptoms of Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT)?
Swelling, redness, warmth, pain.
What triad predisposes someone to Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT)?
Virchow triad (Stasis, Hypercoagulability, Endothelial injury).
Where does Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) usually form?
In a proximal deep vein of the lower extremity.
What is a potential consequence of Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT)?
It can serve as an embolic source.
What is the Virchow Triad?
-Stasis (Post-op, long drive/flight)
-Hypercoagulability (Pregnancy, defect in coagulation cascade proteins, oral contraceptive use)
-Endothelial damage (Exposed collagen triggers clotting cascade)
What test may be used clinically to rule out Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) if disease probability is low or moderate?
D dimer test
What imaging technique is commonly used to diagnose Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Compression ultrasound with Doppler
What type of heparin is used for prophylaxis and acute management of Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Unfractionated heparin or low molecular weight heparins (e.g. Enoxaparin)
What type of anticoagulants are used for treatment and long-term prevention of Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Direct anticoagulants (e.g. Rivaroxaban, apixaban)
What is Acute Pericarditis?
Inflammation of the pericardium
What are the typical symptoms of Acute Pericarditis?
Sharp pain, aggravated by inspiration, relieved by sitting up and leaning forward
What complication is often associated with Acute Pericarditis?
Pericardial effusion (Accumulation of fluid)
What ECG changes are associated with Acute Pericarditis?
Widespread/diffuse ST-segment elevation and/or PR depression
What is the most common cause of Acute Pericarditis?
Usually idiopathic
What are some potential causes of Acute Pericarditis?
Viral infections, malignancy, myocardial infarction (MI), autoimmune diseases, renal failure (Uremia), cardiac surgery, thoracic radiotherapy, trauma
What are some treatments for Acute Pericarditis?
-NSAIDs
-Colchicine
-Glucocorticoids
-Dialysis
What is the major concern with acute pericarditis?
-Cardiac tamponade (Compresses heart)
What does tertiary syphilis disrupt in the aorta?
The vasa vasorum
What are the consequences of vasa vasorum disruption in tertiary syphilis?
Atrophy of vessel wall and dilation of aorta and valve ring
What appearance may calcification of the aorta have in syphilitic heart disease?
"Tree bark" appearance
What can result from syphilitic heart disease affecting the aorta?
Aneurysm of ascending aorta or aortic arch, aortic insufficiency
What is coarctation of the aorta?
Aortic narrowing near the insertion of the ductus arteriosus (after the ascending aorta)
What heart valve complication is commonly associated with coarctation of the aorta?
Bicuspid aortic valve
What genetic condition is associated with coarctation of the aorta?
Turner syndrome
What are some symptoms of coarctation of the aorta?
-Hypertension in upper extremities
-Lower extremities are cold with weak, delayed pulses (Brachiofemoral delay)
-With age, intercostal arteries enlarge due to collateral circulation
What are complications of coarctation of the aorta?
-Heart failure
-Increased risk of cerebral hemorrhage (Berry aneurysms)
-Aortic rupture
-Possible infective endocarditis
What is the QRS complex duration in Narrow Complex Tachycardias?
Less than 120 msec
How is rapid ventricular activation achieved in Narrow Complex Tachycardias?
Via normal ventricular conduction system
Where does tachycardia originate in Narrow Complex Tachycardias?
Within or above the AV node (Supraventricular arrhythmia)
What is the characteristic rate and rhythm of Atrial Fibrillation?
Irregularly irregular rate and rhythm with no discrete P waves
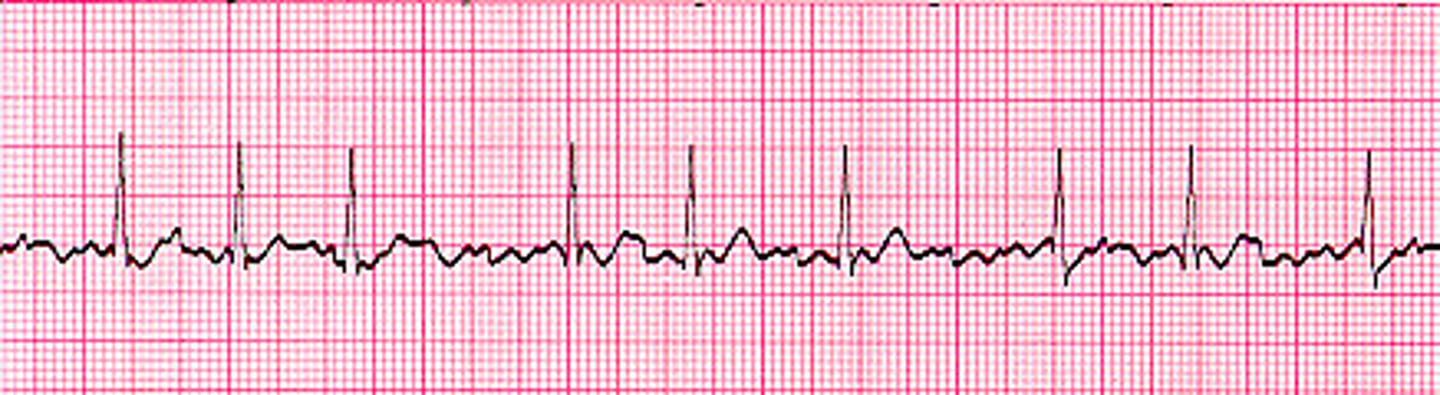
Where does the arrhythmogenic activity in Atrial Fibrillation usually originate?
From automatic foci near pulmonary vein ostia in the left atrium
What condition may Atrial Fibrillation predispose patients to due to left atrial blood stasis?
Thromboembolic events, particularly stroke
What is the most common site of thrombus formation in Atrial Fibrillation?
Left atrial appendage
What are common risk factors of atrial fibrillation?
-Hypertension
-CAD
-Advanced age
-Atrial dilation
Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation (Rate and rhythm control)
-Beta blockers
-Calcium channel blockers
-Digoxin (ABCD)
-Cardioversion
What is the characteristic rate and rhythm of Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia?
-Irregularly irregular rate and rhythm with at least 3 distinct P wave morphologies
-100 to 180 BPM
What causes Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia?
Due to multiple ectopic foci in atria (Multiple points in atria try to pace the heart)
What conditions are Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia associated with?
COPD, Pneumonia, pulmonary hypertension, and Heart Failure (HF)
What is the treatment for Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia?
-Oxygen
-Treatment of underlying condition
-Rate control
What is the characteristic appearance of P waves in Atrial Flutter?
Sawtooth appearance
Where does the arrhythmogenic activity in Atrial Flutter usually originate?
Reentry circuit around the tricuspid annulus
How should Atrial Flutter be treated?
Like atrial fibrillation, possibly with catheter ablation of the region between the tricuspid annulus and IVC
What is the most common cause of Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia?
Reentrant tract between atrium and ventricle
Where is Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia most commonly located?
AV node
What are common symptoms of Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia?
Sudden onset palpitations, lightheadedness, diaphoresis
How can Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia be terminated?
By slowing AV nodal conduction with Adenosine
What is the definitive treatment for Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia?
Catheter ablation
First-Degree AV Block
-Prolonged PR interval (>200 msec)
-No treatment (Asymptomatic)
-Conduction block
What are the two types of second-degree heart block?
-Mobitz Type 1 (Wenckebach)
-Mobitz Type 2
What are some symptoms of decreased cardiac output in second-degree heart block?
Fatigue, dyspnea, chest pain, hypotension, bradycardia, hemodynamic instability
What can cause second-degree heart block?
Heart attack, disorders affecting heart muscle walls, infection of inner layer of heart
What is Mobitz Type 1 also known as?
Wenckebach
What characterizes Mobitz Type 1 in terms of PR interval?
Progressive lengthening of PR interval until a beat is dropped (P wave not followed by QRS complex)
How is the PR interval described in Mobitz Type 1?
Variable PR interval with a pattern (Regularly irregular)
What is the typical treatment for Mobitz Type 1?
No treatment, usually asymptomatic
What characterizes Mobitz Type 2?
Dropped beats that are not preceded by a change in PR interval (PR intervals are consistent but some P-waves don't conduct)
What may Mobitz Type 2 progress to?
A 3rd-degree block
What does Mobitz Type 2 usually indicate?
A structural abnormality (Ischemia, fibrosis)