MA TSA Review
1/896
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
897 Terms
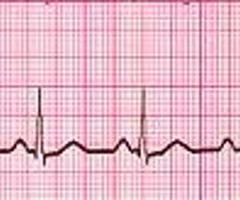
AC interference
Electrical interference that appears as small, uniform spikes on ECG tracking
Amplifier
Device on the ECG that magnifies or enlarges the heart's electrical impulses so they can be recorded
arrhythmia
Abnormal heart rate, rhythm and conduction system
dysrhthmia
Abnormal heart rate, rhythm and conduction system
artifact
Unwanted changes in an ECG tracing caused by movement, machine malfunction or other factors
atrioventricular node (AV)
Knot of specialized cells in the lower portion of the right atrium that produces the heart's electrical impulses
augmented leads
leads that measure cardiac activity from one electrode on the body at a time; recordings are made larger so they can be read
baseline
Line that separates the various cardiac waves; representative of the space between heartbeats while the heart is "resign" AKA iosoelectric line
bipolar leads
standard limb leads
bundle banches
branches of cardiac fibers that receive electrical impulses from the bundle of His
bundle of His
small band of atypical cardiac muscle fibers that receive electrical impulses from the AV node
cardiac cycle
one heartbeat; one contraction/relaxation phase of the heart
precordial leads
chest leads that measure in only one direction
depolarization
discharge of electrical energy that causes contraction such as in heart muscle
electrocardiogram
graphic picture of the heart's electrical activity
electrocardiograph
machine that records the electrical activity of the heart
electrocardioraphy
noninvasive procedure used to detect the heart's electrical activity
electrodes
devices made of a conductive material to pick up the electrical activity of the heart; sensors
Holter monitor
ambulatory heart monitor that records heart activity during a 24-48 hour period
interval
ECG pattern that shows the length of a wave with a sigment
ischemia
poor blood supply to body tissue causing a lack of oxygen to that tissue
leads
covered wires that carry electrical impulses from the sensor to the ECG machine
MI - myocardial infactction
heart attack; death of heart tissue caused by blockage of the heart's blood vessels
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR)
rhythm measurement that starts at the SA node, occurs within an established time frame, and follows an expected, established pattern
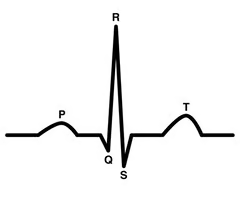
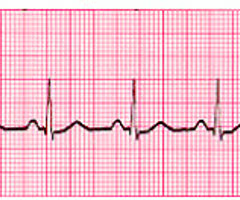
P wave
ECG pattern that shows atrial contraction originating at the SA notde
pacemaker
devie that delivers electrical impulses to the heart muscle when the SA node is unable to do so
PAT, paroxysmal atrial tachycardia
sudden onset and ending of atrial tachycardia, 150-250 bpm
polarization
phase when the heart is in a ready state to contract
PR interval
time interval between atrial contraction and the beginning of ventricular contraction
PR segment
time interval necessary for an electrical impulse to cause contraction of the atria and begin contraction of the ventricles
PAC premature atrial contractions
condition in which an electrical impulse in the atria starts before the next expected heartbeat
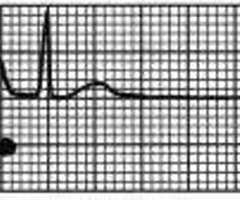
PVC premature ventricular contractions
condition in which the ventricles receive an impulse prematurely and contract early
Purkinje fibers
cardiac fibers that receive impulses from the bundle branches and take them throughout the heart muscle
QRS complex
ECG pattern that shows when the impulse moves through the ventricles and reaches the Purkinje fibers, depicting contracction of both ventricles
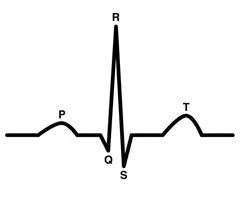
QT interval
time interval on ECG that shows the time needed for the ventricles to contract and recover
repolarization
rest phase of the ECG cycle
rhythm strip:
lead II recording on ECG that show the heart's rhythm
segment
ECG pattern between two waves
SA node sinoatrial
Pacemaker of the heart, knot of specialized cells cells located in the upper right atrium
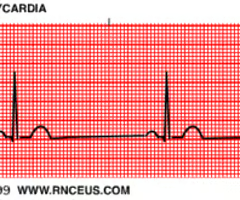
sinus bradycardia
slow heart rate, less than 60bpm
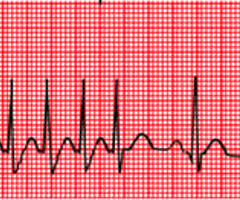
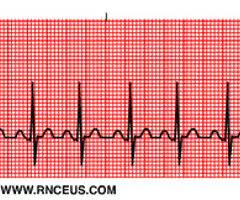
sinus tachycardia
rapid heart rate, 100-180bpm
somatic tremor
body tremor caused by voluntary or involuntary muscle movement
ST segment
time interval between the ventricular contraction and the beginning of ventricular relaxation
standard limb lead
insulated device that carries the electrical impulses to the ECG and traces the electrical impulse of the heart in two different directions simultaneously
standardization
process of ensuring that an ECG taken on one machine will compare to a tracing taken on another machine
standardization mark
mark made on the ECG paper that indicates the ECG is standardized
stylus
heated device that records the heart's activity on heat-sensitive graph paper
T wave
ECG pattern that shows resting of the hear; repolarization
tracing
recording of the ECG cycle
treadmill test
exercise electrocardiography that is done to determine if the heart is receiving enough blood during exercise.
cardiac stress test
exercise electrocardiography that is done to determine if the heart is receiving enough blood during exercise.
U wave
normal, small upward curve that occasionally follows a complete ECG cycle after the PQRST: has unknown indication
unipolar leads
augmented leads
V leads
chest/precordial leads
ventricular fibrillation (V fib)
life-threatening condition of ventricular twitching that causes ineffective pumping action, stopping blood circulation
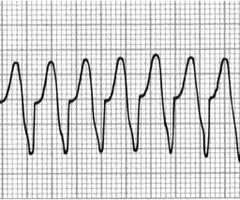
ventricular tachycardia (V tach)
Three or more consecutive PVC's with heart rate exceeding 100bpm
wandering baseline
shift on the ECG tracing from the baseline or center of the paper
wave
ECG pattern that represents specific electrical heart activity
V1 placement
4th ICS Right of sternum
V2 placement
4th ICS Left of sternum
V4 placement
5th ICS, midclavicular
V3 placement
between V2 and V4
V6 placement
5th ICS midaxillary
V5 placement
5th ICS between V4 and V6
Scalpel
small, straight knife with a thin, sharp blade used for surgery and dissection
B/B scissors
cutting instrument with ring handles, both blades are dull

B/S Scissors
cutting instrument with ring handles, one tip is dull and the other is a point
S/S Scissors
cutting instrument with ring handles, both blades are at a point
Suture Scissors
an instrument used to cut sutures
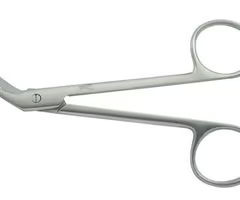
Bandage Scissors
special instrument with a blunt lower end used to remove dressings and bandages
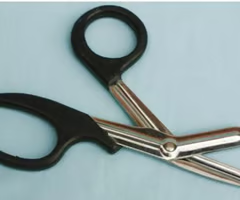
Dissecting scissors
For cutting tissue, but NEVER use for cutting sutures.
Forceps
instrument used to pick up or hold small items or tissue

Kelly Hemostatic Forceps
Provides hemostasis (teeth run 1/2 the length of jaws)
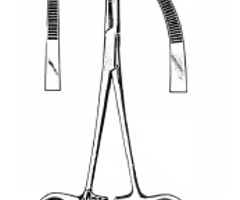
Allis Tissue Forceps
Inward curving forcing toothed blades and a ratcheted handle designed for grasping
Thumb forceps
two-pronged instrument with serrated tips to hold tissue

Tissue forceps
Instruments with teeth, used to grasp tissue

Splinter Forceps
instruments with sharp points used to remove splinters and foreign objects from the skin and tissues

Dressing Forceps
used in the application and removal of dressings

Mosquito Hemostatic Forceps
small fine tips, smaller and more delicate than standard hemostatic forceps
Sponge Forceps
instrument used for grasping or clamping surgical sponge or gauze.

Needle holders
serrated tips, ring handles, ratchets, and box locks. Used to firmly grasp curved needles for insertion

Retractors
used to hold tissue aside to improve the exposure of operative areas

Inflammation
a localized physical condition in which part of the body becomes reddened, swollen, hot, and often painful, especially as a reaction to injury or infection.
Abrasion
Scrape of the skin due to something abrasive
Infection
invasion of the body by a pathogenic organism
Abscess
localized collection of pus
Absorbable suture
Suture material that is gradually digested and absorbed by the body
Ligate
To tie off and close a structure, such as a severed blood vessel
Approximation
The process of bringing two edges together through the use of sutures or other materials.
Bandage
a piece of soft material that covers and protects an injured part of the body
Biopsy
the removal of living tissue from the body for diagnostic examination
capillary action
The action that causes liquid to rise along a wick, tube, or gauze dressing
Colposcope
A lighted instrument used to examine the vagina and cervix
colposcopy
visual examination of the vagina and cervix using a colposcope
Contaminate
to make impure
Contusion
An injury to the tissues under the skin that causes blood vessels to rupture (bruise)
Cryosurgery
destruction of tissue by using extreme cold, often by using liquid nitrogen
Exudate
fluid that accumulates in a wound; may contain serum, cellular debris, bacteria, and white blood cells
Fibroblast
An immature cell from which connective tissue can develop
Furuncle
boil; a painful nodule formed in the skin by inflammation originating in a hair follicle; caused by staphylococcal infection