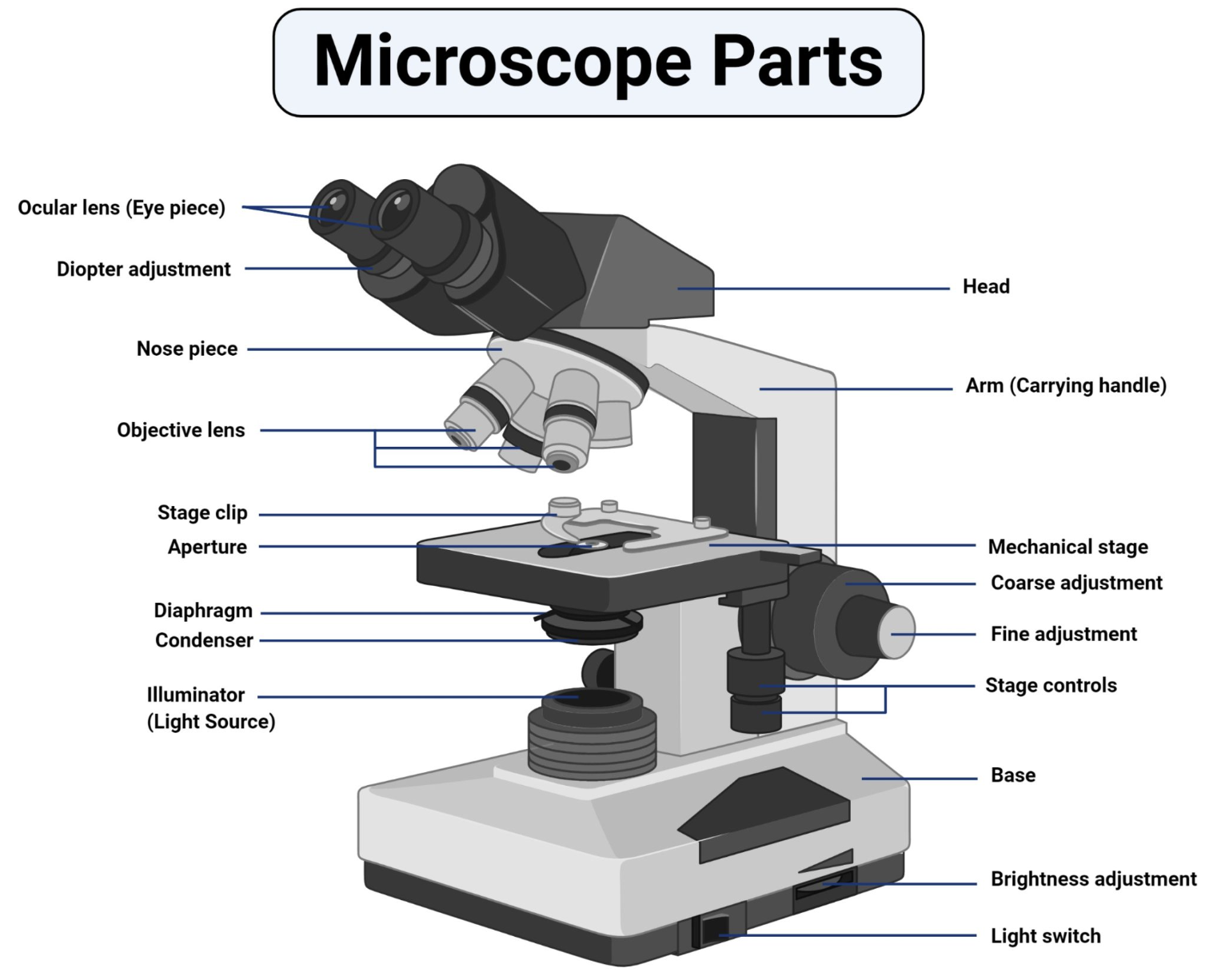
Parts of a microscope
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
1
New cards
Total magnification formula
Eye piece x objective lens
2
New cards
Head
This is also known as the body. It carries the optical parts in the upper part of the microscope.
3
New cards
Base
It acts as microscopes support. It also carries microscopic illuminators.
4
New cards
Arms
This is the part connecting the base and to the head and the eyepiece tube to the base of the microscope. It gives support to the head of the microscope and it is also used when carrying the microscope. Some high quality microscopes have an articulated arm with more than one joint allowing more movement of the microscopic head for better viewing.
5
New cards
Eyepiece
also known as the ocular. This is the part used to look through the microscope. Its found at the top of the microscope. Its standard magnification is 10x with an optional eyepiece having magnifications from 5X to 30X.
6
New cards
Eyepiece tube
it’s the eyepiece holder. It carries the eyepiece just above the objective lens. In some microscopes such as the binoculars, the eyepiece tube is flexible and can be rotated for maximum visualization, for variance in distance. For monocular microscopes, they are none flexible.
7
New cards
Objective lenses
These are the major lenses used for specimen visualization. They have a magnification power of 40x-100X. There are about 1- 4 objective lenses placed on one microscope, in that some are rare facing and others face forward. Each lens has its own magnification power.
8
New cards
Nose piece
also known as the revolving turret. It holds the objective lenses. It is movable hence it cal revolve the objective lenses depending on the magnification power of the lens.
9
New cards
The Adjustment knobs
These are knobs that are used to focus the microscope. There are two types of adjustment knobs i.e fine adjustment knobs and coarse adjustment knobs.
10
New cards
Stage
This is the section in which the specimen is placed for viewing. They have stage clips that hold the specimen slides in place. The most common stage is the mechanical stage, which allows the control of the slides by moving the slides using the mechanical knobs on the stage instead of moving them manually.
11
New cards
Aperture
This is a hole on the microscope stage, through which the transmitted light from the source reaches the stage.
12
New cards
Microscopic illuminator
This is the microscopes light source, located at the base. It is used instead of a mirror. It captures light from an external source of a low voltage of about 100v.
13
New cards
Condenser
These are lenses that are used to collect and focus light from the illuminator into the specimen. They are found under the stage next to the diaphragm of the microscope. They play a major role in ensuring clear sharp images are produced with a high magnification of 400X and above. The higher the magnification of the condenser, the more the image clarity. More sophisticated microscopes come with an Abbe condenser that has a high magnification of about 1000X.
14
New cards
Diaphragm
it’s also known as the iris. Its found under the stage of the microscope and its primary role is to control the amount of light that reaches the specimen. It’s an adjustable apparatus, hence controlling the light intensity and the size of the beam of light that gets to the specimen. For high-quality microscopes, the diaphragm comes attached with an Abbe condenser and combined they are able to control the light focus and light intensity that reaches the specimen.
15
New cards
Condenser focus knob
this is a knob that moves the condenser up or down thus controlling the focus of light on the specimen.
16
New cards
Abbe Condenser
this is a condenser specially designed for high quality microscopes, which makes the condenser to be movable and allows very high magnification of above 400X. High
17
New cards
The rack stop
It controls how far the stages should go preventing the objective lens from getting too close to the specimen slide which may damage the specimen. It is responsible for preventing the specimen slide from coming too far up and hitting the objective lens.
18
New cards
microscope parts/diagram