N470: Spinal column disorders (exam 2)
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Which region bears the most weight of the body, is the most flexible region of the body, and contains nerve roots that are vulnerable to injury and disease
the lumbar region
risk factors for backpain (6)
1) lack of muscle tone and core strength
2) excess body weight
3) poor posture
4) cigarette smoking
5) psychological factors
6) occupation/hobbies
non-skeletal causes for lumbosacral spinal pain (5)
1) DM
2) infection
3) inflammation
4) neoplasm or mass lesion
5) vascular disease
top 2 causes of lower back pain
1) disc herniation
2) spondylosis
narrowing of the intraspinal (central) canal, lateral recess or the neural foramen due to degenerative arthritis
spondylosis
When spinal discs lose their elasticity, flexibility, and shock absorbing capabilities; Progressive degeneration; normal process of ageing occurring in any area of the spine from loss of fluid within the disc
degenerative disc disease
what are the two rings that make up the spinal disc?
1) annulus
2) nucleus
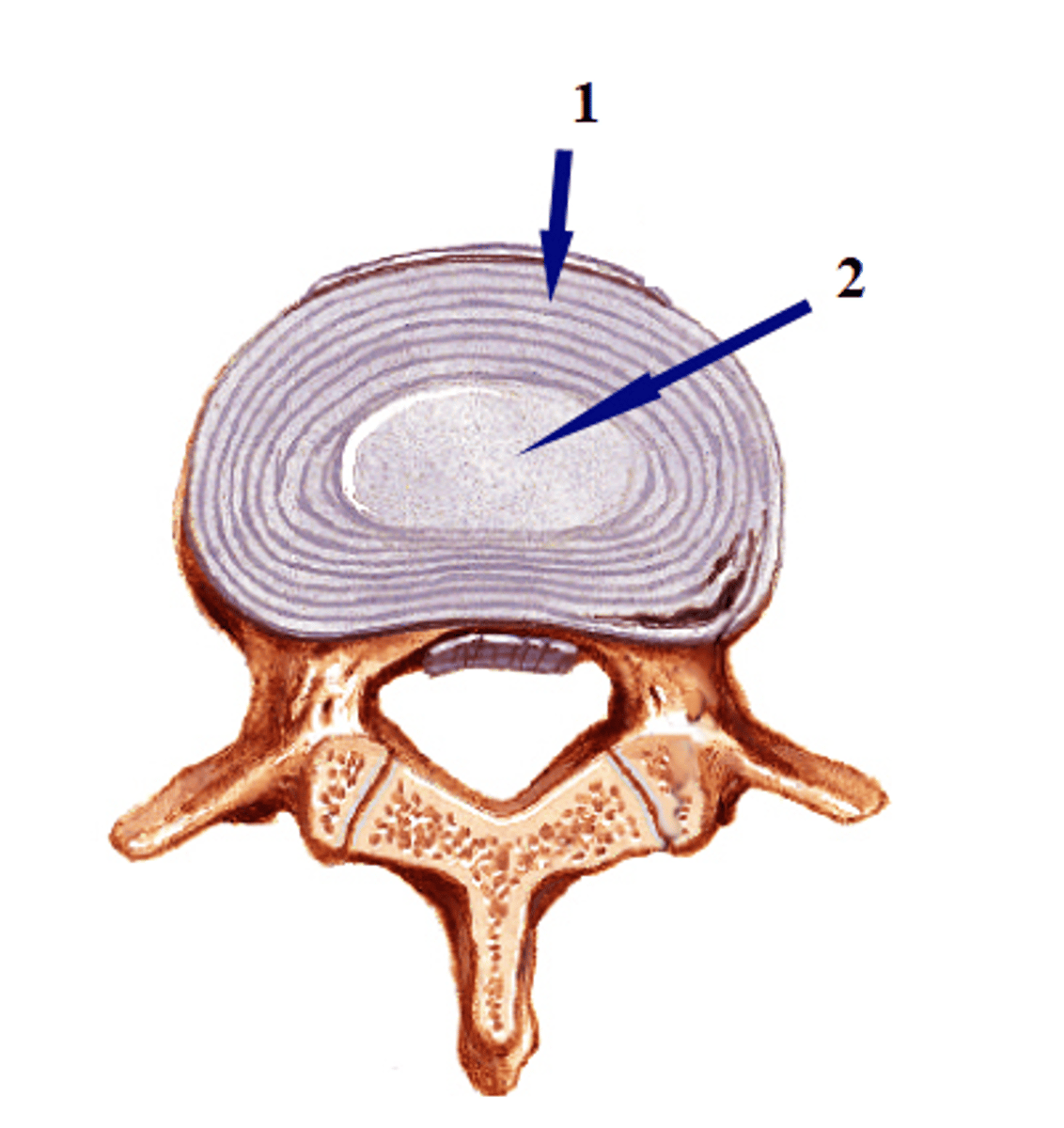
Condition where the spinal disc bulges outward between the vertebrae and can press against the spinal nerves
intervertebral disc disease
In which area is IVDD most common?
lumbosacral area
Bulging disc vs herniated disc
- bulging disc: no tear or rupture (contained)
- herniated: tear or rupture present in outer portion of disc (non-contained)
Causes of bulging or herniated disc
- aging
-repeated stress/trauma to the spine
-spinal stenosis
how to reproduce pain from lumbar disc disease?
raising the leg and flexing the foot at 90 degrees causes back or leg pain
manifestations of IVDD (4)
- if lumbar disc disease- pain in back or legs
- paresthesia/muscle weakness in legs, feet, or toes
- depressed/absent reflexes
- if cervical disc disease- same symptoms but upper extremities
Diagnostic studies for IVDD (7)
- H&P examination
- X-ray
- CT
- MRI
- Nerve conduction studies
- EMG
- lumbar puncture for suspected inflammatory or infectious cause
test that detects the electrical activity generated by muscle cells when electrically or neurologically activated; the signals are analyzed to detect nerve/muscle dysfunction problems with nerve-muscle signaling, activation threshold, or the amount and speed of conduction of an electrical impulse through the nerve
electromyography (EMG)
Why is EMG preferred over NCS for diagnosing IVDD?
provides better localizing information
What is rediculopathy?
a pinched nerve
Non-urgent situations to test for IVDD (2)
- pt with rediculopathy but neuro intact
- if initial imaging negative, NCS ad EMG may be useful after 3 weeks
urgent situations to test for IVDD (4)
- acute radiculopathy with progressive neuro deficits
- rediculopathy with urinary retention, saddle anesthesia (loss of sensation in perineum), or bilateral neuro symptoms
- suspected tumor
- suspected epidural abscess
conservative therapy for IVDD
- restrictive activity
- medications
- local ice or heat
- PT
- epidural corticosteroid injections
- education to prevent more injury
medication classes used for IVDD (3)
- analgesics
- anti-inflammatory
- muscle relaxants
PT for IVDD (3)
- u/s
- massage
- traction
restrictive activities for IVDD (3)
- brace
- corset
- belt
surgical treatments for IVDD
- laminectomy
- intradiscal electro-thermoplasty (IDET)
- radiofrequency discal nucleoplasty
- nerve stimulators
- spinal fusion
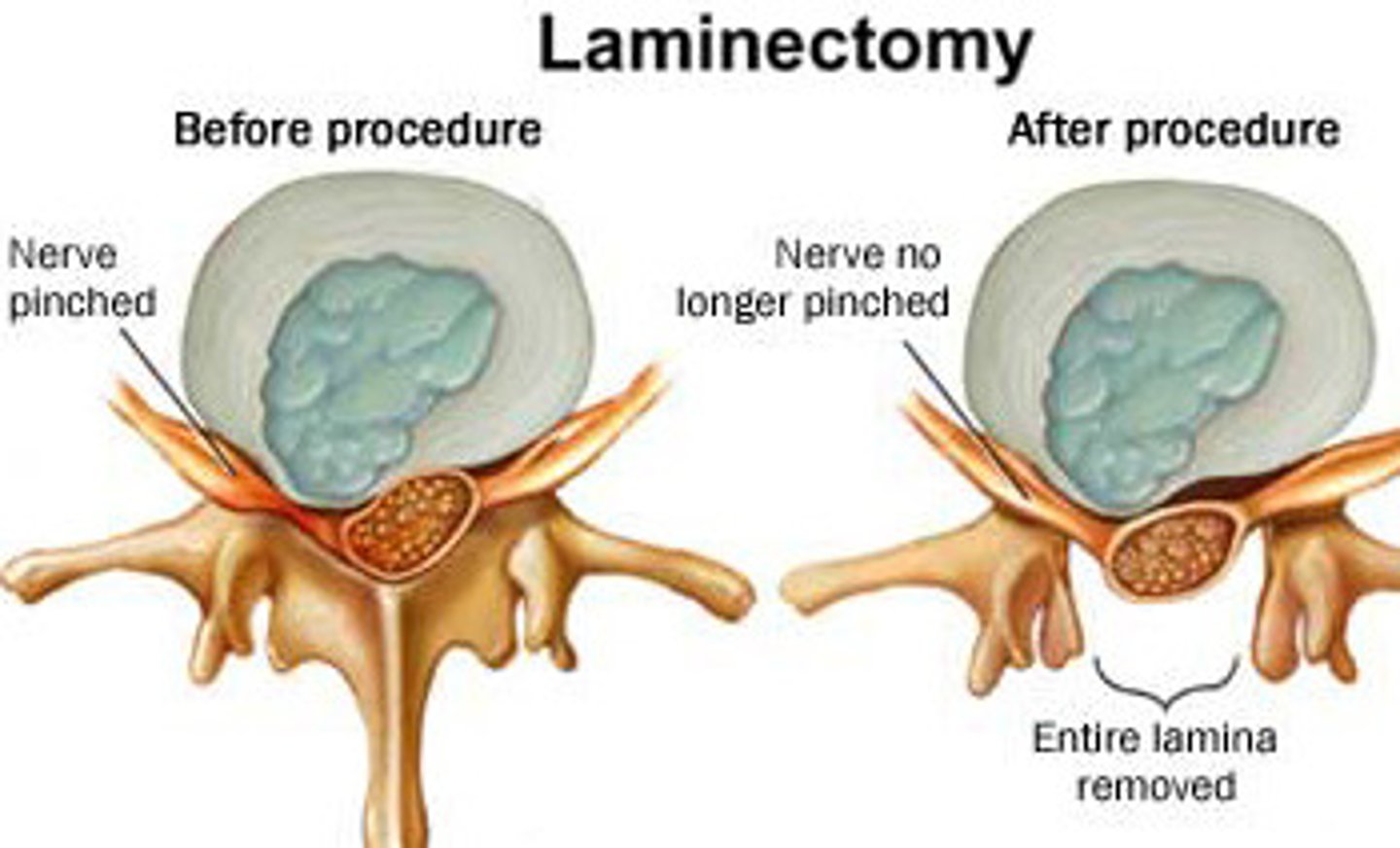
procedure for IVDD, removes posterior arch or vertebra or lamina to gain access to part of or entire protruding disc in order to remove it (makes spinal canal bigger)
laminectomy
What IVDD procedure is contraindicated if disc height <50%
intradiscal electro-thermoplasty (IDET)
procedure for IVDD, where a thermal wire is placed into the nucleus and heat is applied near the annulus lesion; denervates small nerve fibers, lesion shrinks, and scar tissue stabilizes lesion/annulus border
intradiscal electro-thermoplasty (IDET)
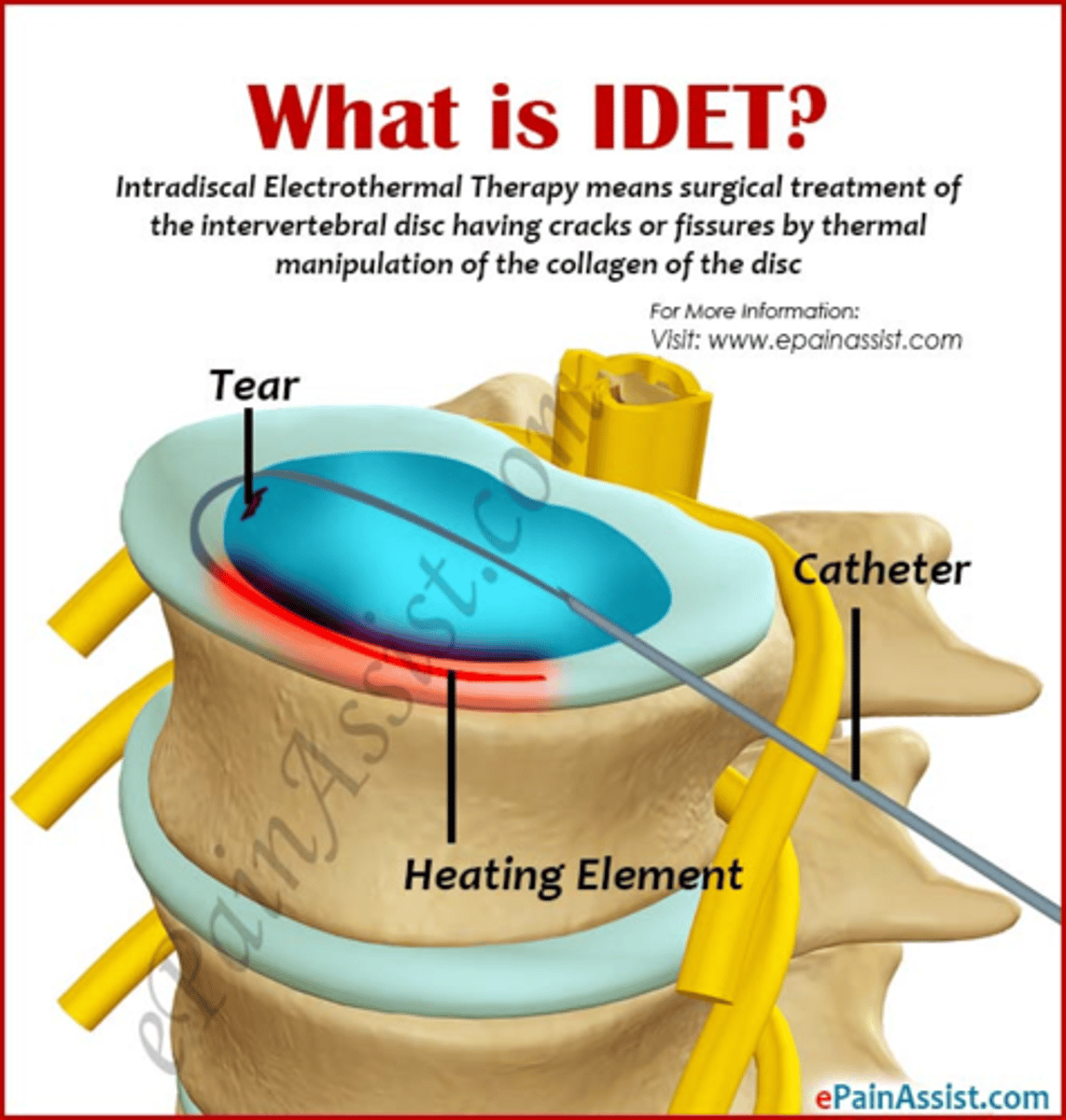
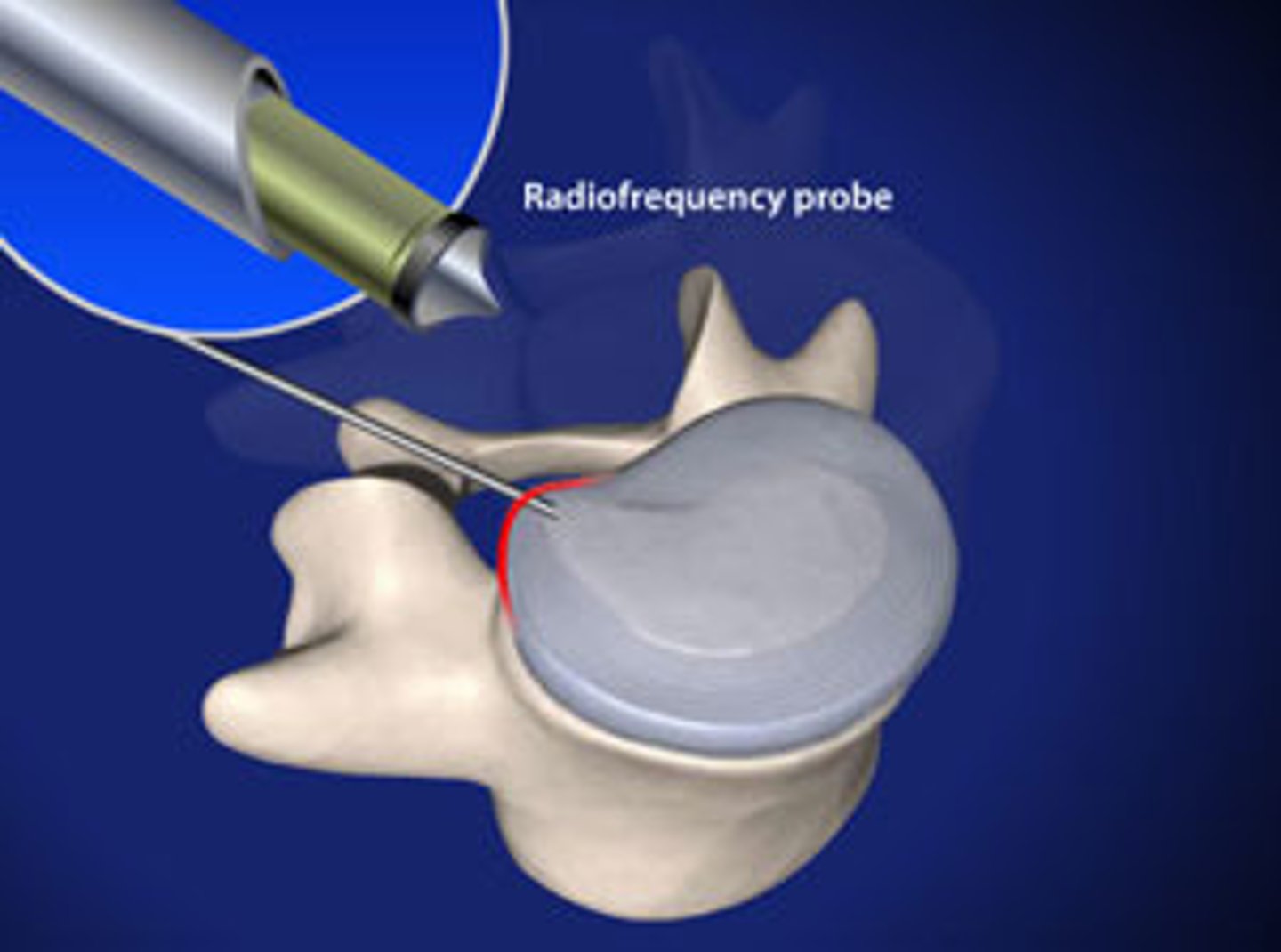
needle inserted into disk, radiofrequency probe used, generates energy that breaks up the molecular bonds of the gel in the nucleus, shrinking it, and decompressing the disk
radiofrequency discal nucleoplasty
procedure to IVDD, probes placed in epidural space; trialed for 1 week then permanent probes placed; blocks pain signals to the brain
nerve stimulators
procedure for IVDD for unstable spine, fuses vertebrae together
spinal fusion
minimally invasive spine surgery (5)
- discectomy
- kyphoplasty
- laminectomy
- lumbar fusion
- vertebroplasty
trimming or removing of the herniated portion of a disc in the back
discectomy
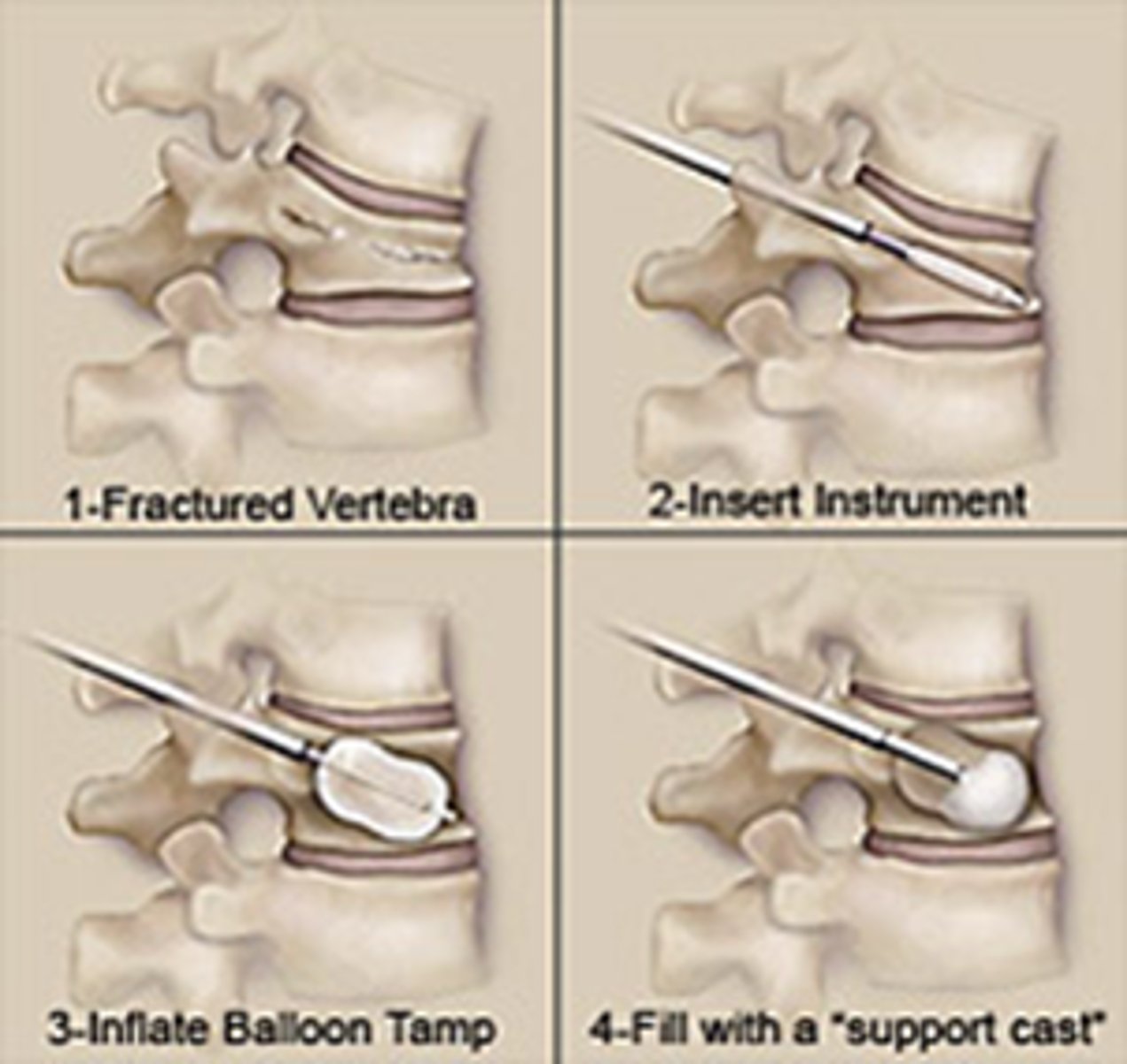
procedure that •relieves vertebrae compression by inserting a balloon to restore the bones original height and injecting cement into it to rebuild the vertebrae
Kyphoplasty
removal of a portion of the bone located at the back of each vertebrae to decompress the spinal nerve roots
Laminectomy
joining together two vertebrae in the lower back together to stabilize them
Lumbar fusion
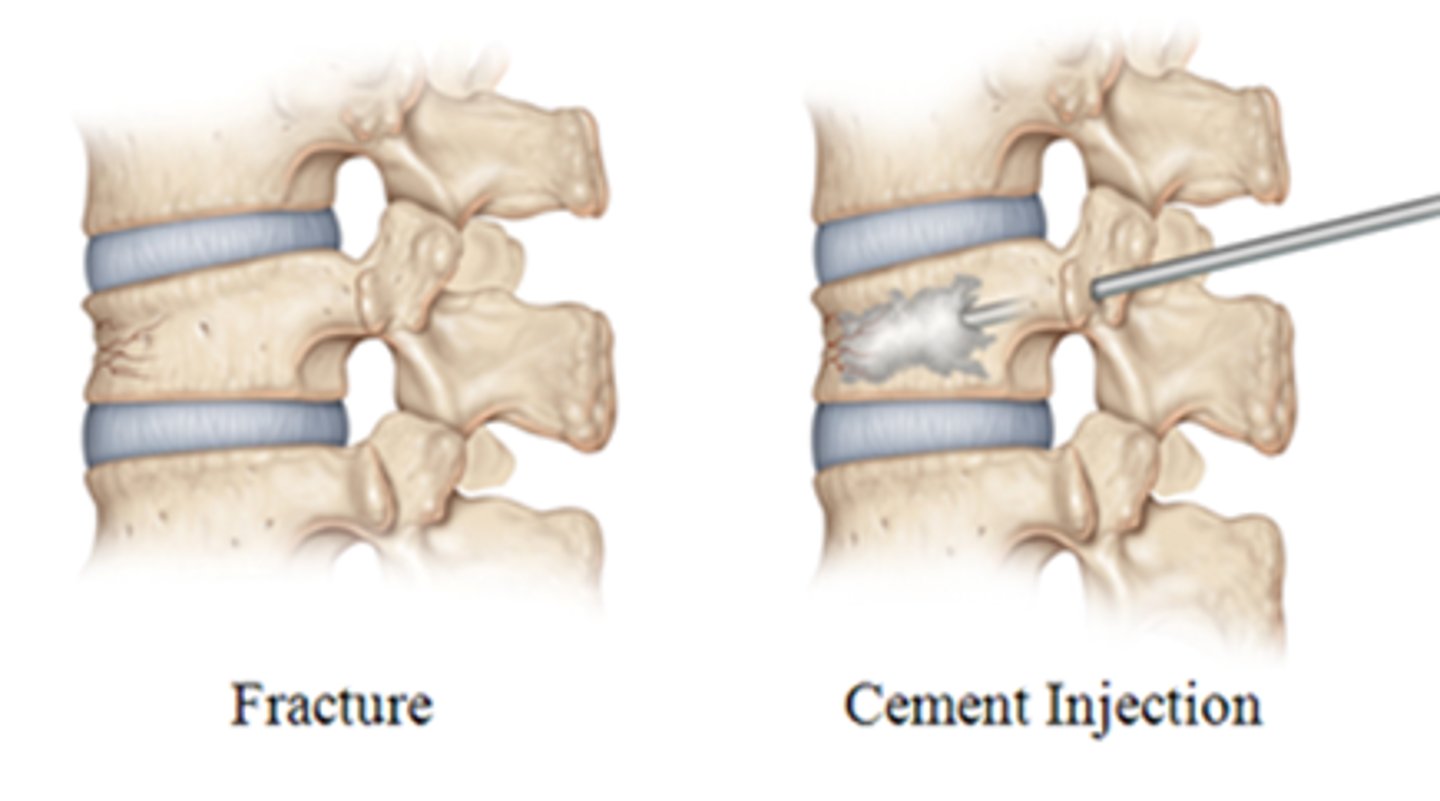
a procedure that injects cement into the bone to keep the bone from collapsing or breaking more
Vertebroplasty
Nursing interventions for spinal surgery (10) *
1) skin assessment-incision and donor site if bone graft
2) pillow under legs or between legs
3) proper body alignment (log rolling)
4) Pain management
5) Assess dressing for CSF leak
6) CMS checks
7) assess for paralytic ileus
8) assess voiding ability
9) lifting restrictions and proper body mechanics
10) log roll Q2H post-laminectomy
Patient education post spinal surgery (6)
1) maintain weight
2) teach proper body mechanics, proper shoes and posture, increase core strength
3) avoid sleeping prone
4) stop smoking
5) PT and follow up appts
6) pain management
why should a post op spinal patient avoid sleeping prone?
excessive lumbar lordosis
____% of spinal chord tumors are ____________ (outside of spinal cord)
90% of spinal chord tumors are extradural (outside of spinal cord)
what are some characteristics of spinal cord tumors? (3)
- usually metastatic
- slow growth
- gradual obstruction of vascular supply
How are spinal cord tumors treated? (4)
- surgery
- radiation
- chemo
- rehab
Who is at greatest risk for spinal cord injury?
- Males 16 - 30 years old or > 65
Can cause temporary or permanent functional alterations in spinal cord
spinal cord injury
How is a spinal cord injury diagnosis made? (3)
- Detailed history of events surrounding incident
- Precise evaluation of sensory & motor function
- Radiographic studies of spine
Some causes of spinal cord injury (5)
- vehicular
- falls
- violence
- sports
- medical
most common causes of death in spinal cord injury patients (2)
Sepsis and pneumonia
initial spinal cord injury in which there is actual physical disruption of axons
resulting in disruption of neurologic tissue or vascular supply
primary spinal cord injury
types of primary spinal cord injury (3)
- Vertical compression, axial loading
- Hyperflexion/ Hyperextension
- Rotation
injury in a 24-hour period (begins within minutes) following SCI from ischemia, hypoxia, microhemorrhage, and edema
secondary spinal cord injury
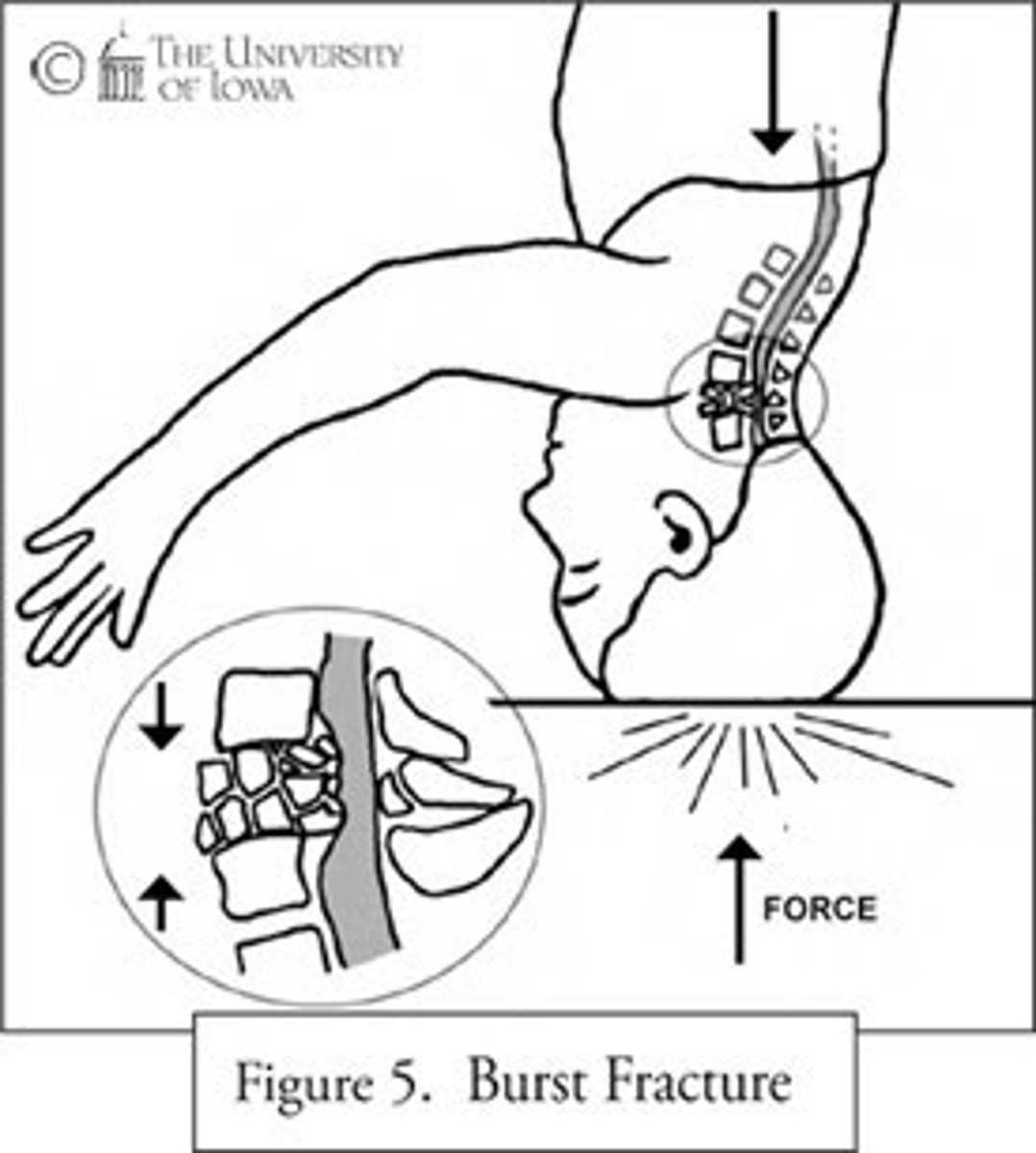
injury from a vertical force along the spinal cord from a fall from heights, landing on feet, or diving; cause burst fractures of vertebral body that often send bony fragments into spinal canal or into spinal cord
Vertical compression, axial loading (primary injury)
Injuries involving backward & downward motion of head/neck; seen in rear-end collisions; spinal cord is stretched, distorted
hyperextension (primary injury)
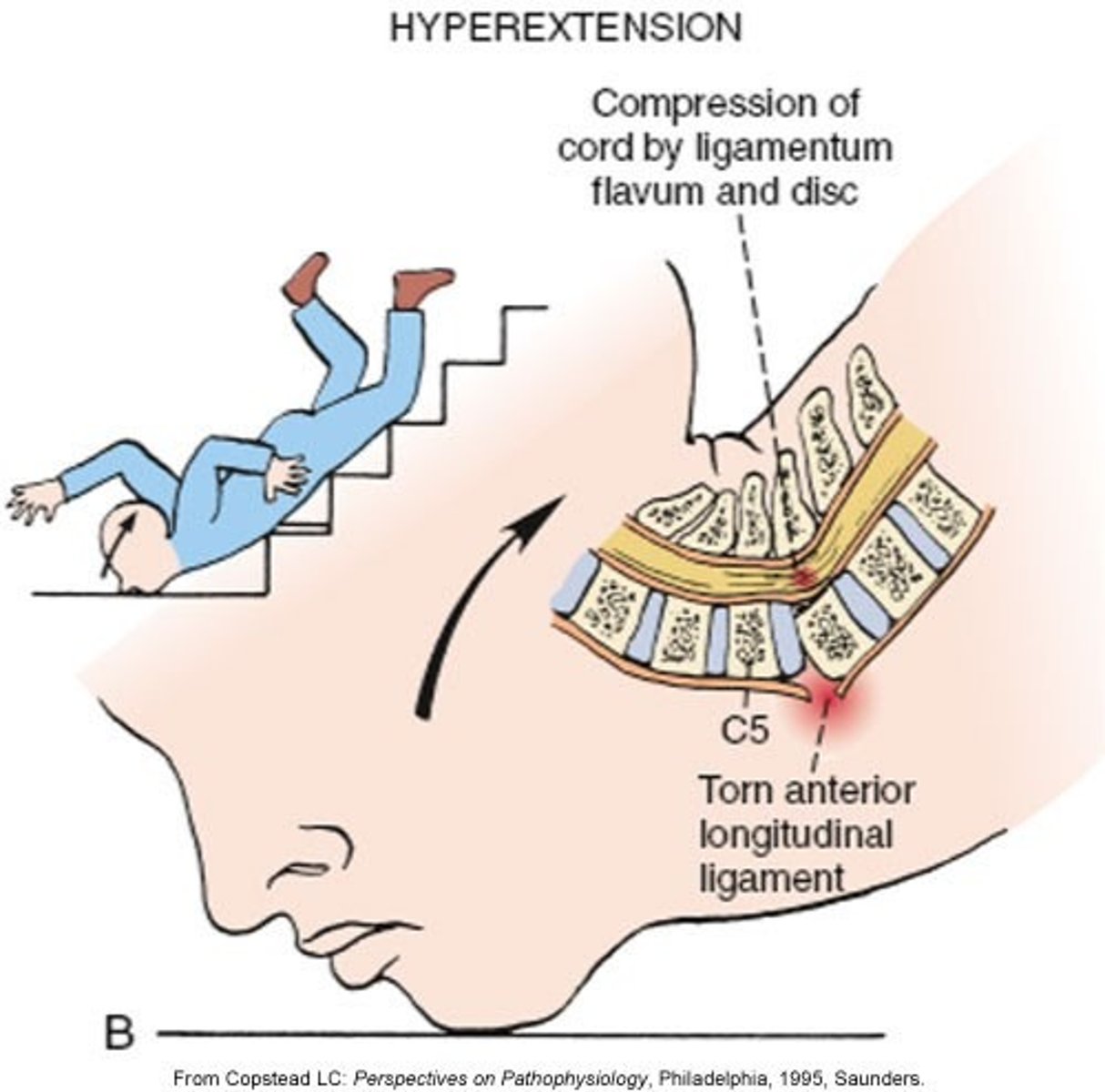
How are neuro deficits caused in hyperextension injuries
contusion & ischemia of cord (without significant bony involvement)
injury from sudden deceleration of the motion of the head; seen in head on collisions; dislocates anterior vertebrae, posterior ligaments of cervical spine torn and cord is compressed
note: Violent flexion of the lumbar spine may occur when wearing a lap belt without a shoulder restraint (e.g., middle passenger in the rear seat) in a MVA
hyperflexion (primary injury)
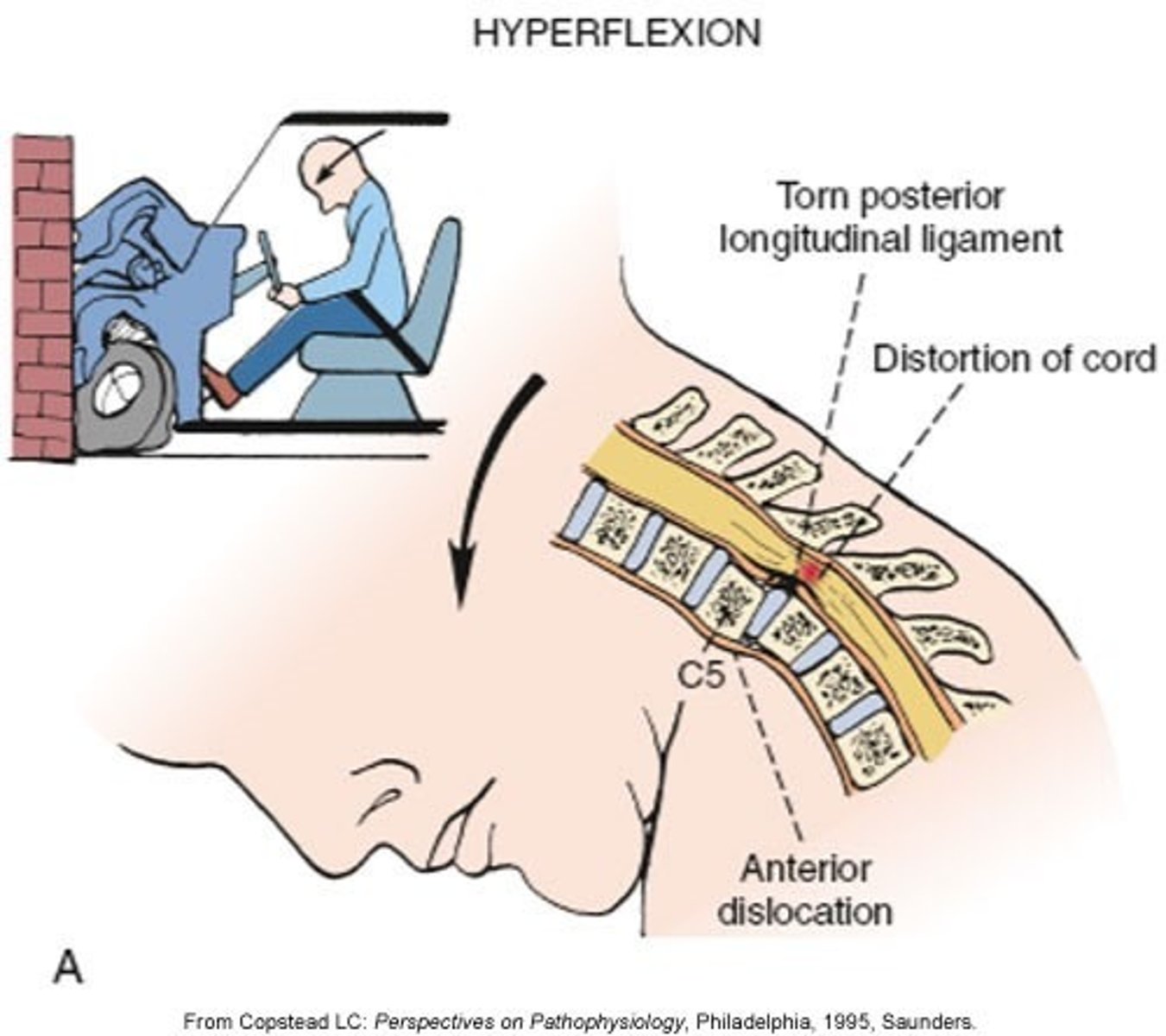
a kind of dislocation in which a lower vertebra's facet joint slips “over” the one above it in a hyperflexion injury
locked facets
Severe rotation of neck or body results in tearing of posterior ligaments & displacement (rotation) of the spinal column; T-bone MVA
flexion rotation (primary injury)
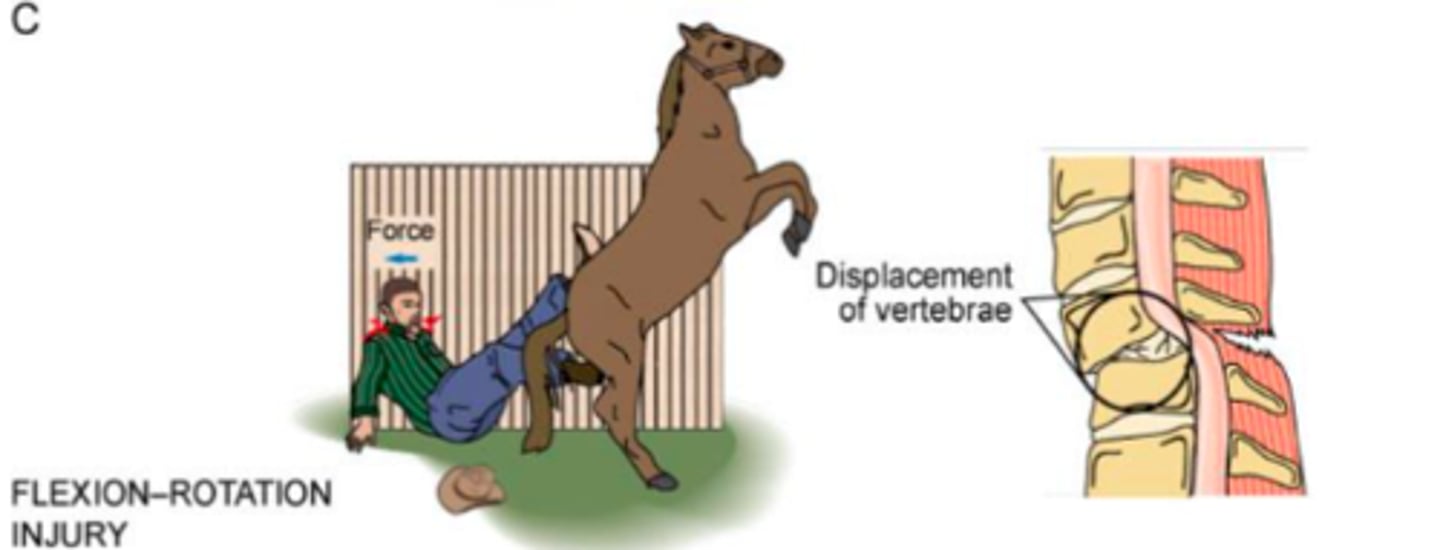
Most unstable form or primary SCI
flexion-rotation
penetrating spinal cord injuries are often ____-__________
one-sided
Refers to the immediate effect of the trauma to the spinal cord from: forces of compression, contusion, shear injury
primary
Secondary injury processes cause spinal cord _______ within hours of injury
edema
patho of secondary spinal cord injury
spinal cord edema secondary to inflammation --> cord ischemia --> by 24 hours, permanent damage may occur --> Edema peaks between 3rd and 6th day --> recedes ~ day 9 --> Edema replaced with central hemorrhagic necrosis
degree of disruption of normal spinal cord function (complete vs. incomplete); dependent on what specific motor structures and nerve tracts within cord are damaged; cannot be classified for several days and until spinal shock has resolved
functional spinal cord injury
C1-C4 functional injury*
- requires ventilatory support
- needs electric WC with breath, head or shoulder controls
Occurs shortly after spinal cord injury (30-60 minutes), can last hours to weeks, but resolves spontaneously; 50% of SCIs have this
spinal shock
Physiologic transection of spinal cord that results in temporary loss or depression of all or most spinal reflex activity below level of injury
spinal shock
manifestations of spinal shock* (6)
1) decreased reflexes
2) loss of sensation
3) absent thermoregulation
4) absent bowel and bladder control
5) priapism (cervical injury)
6) flaccid paralysis below the level of injury
Patho of spinal shock
loss of potassium within injured cells in the cord and accumulates in the extracellular space, causes reduced axonal transmission. As potassium levels normalize, shock wears off
treatment for spinal shock
treat symptoms
resolves on its own
Generally occurs w/ T6 and higher injuries; Significant proportion of SNS has been damaged; Mostly blunt trauma injuries (85-90%)
neurogenic shock
Actions of parasympathetic nervous system* (5)
- Salivation
- Lacrimation
- Urination
- Digestion
- Defecation
* remember SLUDD
Patho of neurogenic shock*
loss of SNS innervation from brainstem --> impulses from SNS cannot reach arterioles --> unopposed vagal stimulation --> loss of vasomotor tone
what are the consequences of loss of vasomotor tone from neurogenic shock? (4)*
1) massive peripheral vasodilation
2) venous pooling
3) decreased venous return to heart
4) decreased cardiac output
in neurogenic shock, unopposed parasympathetic stimulation causes... (4)*
1) hypotension
2) bradycardia
3) decreased CO (decreased preload)
4) hypothermia (cannot sweat below level of injury)
treatment for unopposed parasympathetic stimulation* (4)
1) fluids
2) pacer
3) vasopressors (levophed)
4) warmer
treatment for vagal stimulation in neurogenic shock*
atropine
What can cause vagal stimulation? (3)
- suction
- NG tube insertion
- intubation
Why must we avoid vagal nerve stimulation in patients with neurogenic shock?*
decreases HR
________________ with hypotension differentiates neurogenic shock from hypovolemic shock*
bradycardia
total loss of sensory & motor function below the level of injury; Results in quadriplegia or paraplegia; possible inability to sustain spontaneous ventilation
Complete SCI
Quadriplegia (tetraplegia) occurs from injuries from...
C1 - T1
Paraplegia occurs from injuries from...
T2 - L1
Mixed loss of voluntary motor & sensory function below level of lesion; if any function remains below the level of injury; results in spinal cord syndromes
Incomplete SCI
(incomplete syndrome)
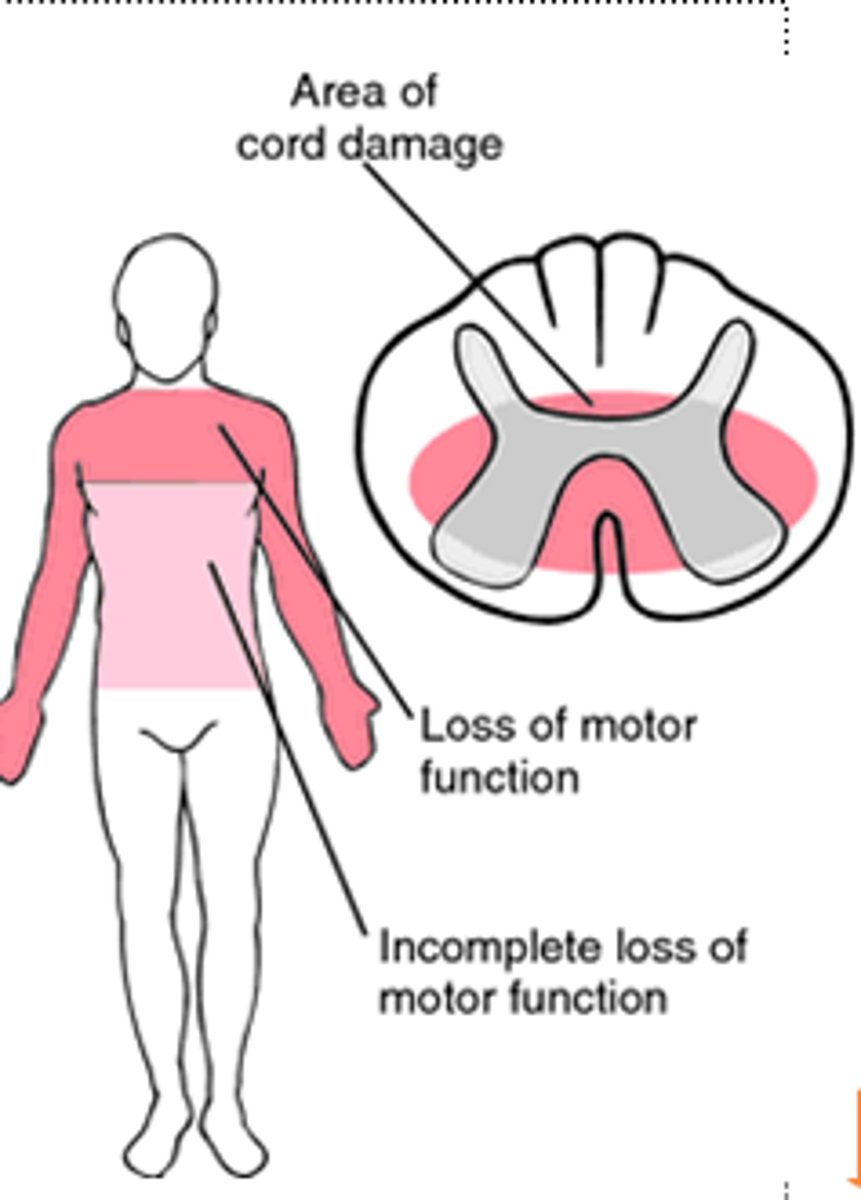
Motor & sensory deficit more pronounced in UE than LE, often spastic (can move lower extremities better); mostly in cervical spine and caused from hyperextension
Central cord syndrome
(incomplete syndrome)
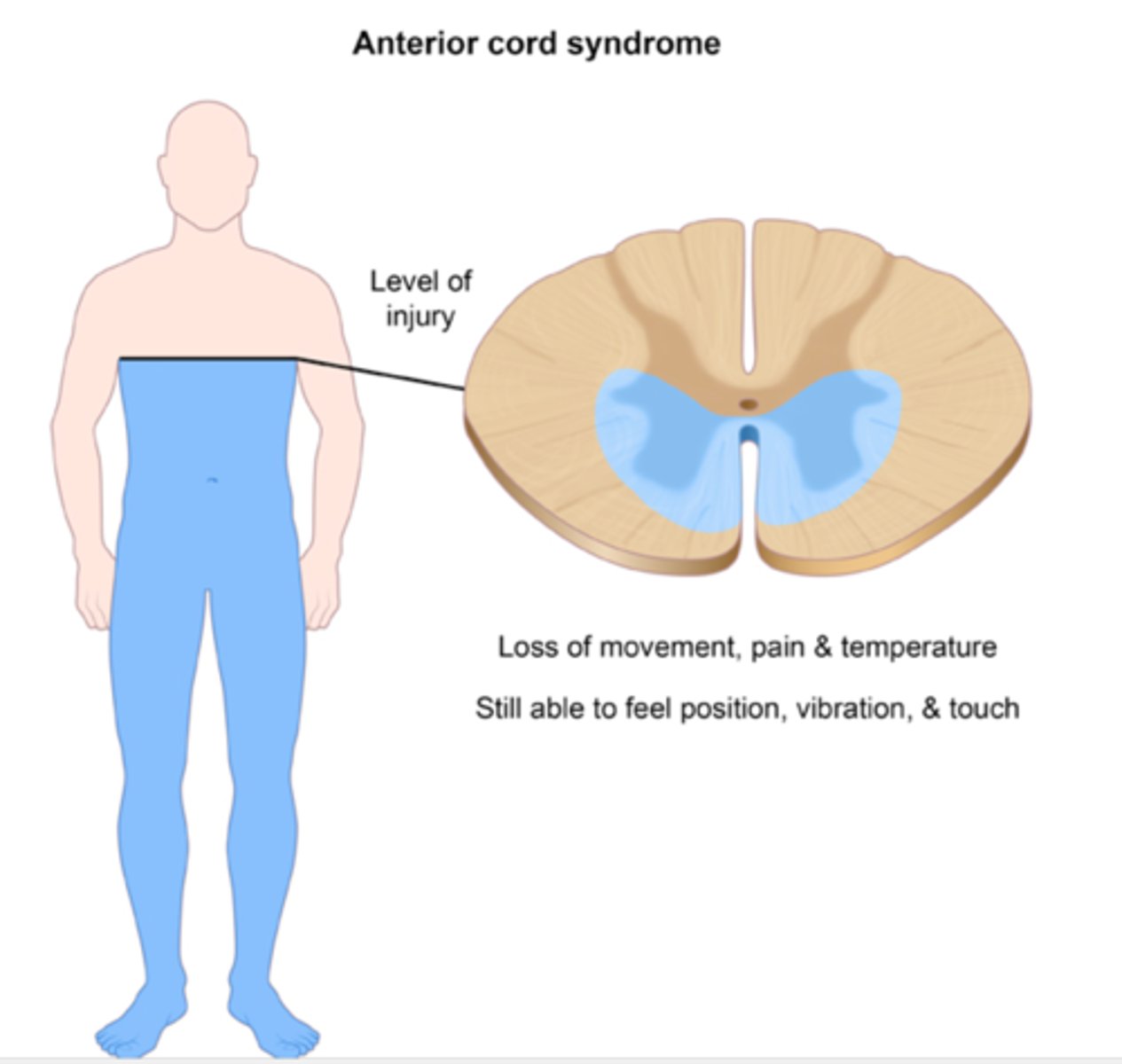
Loss of motor function, pain, temp, paralysis below injury *typically flexion injury
Anterior spinal cord syndrome
(incomplete syndrome)
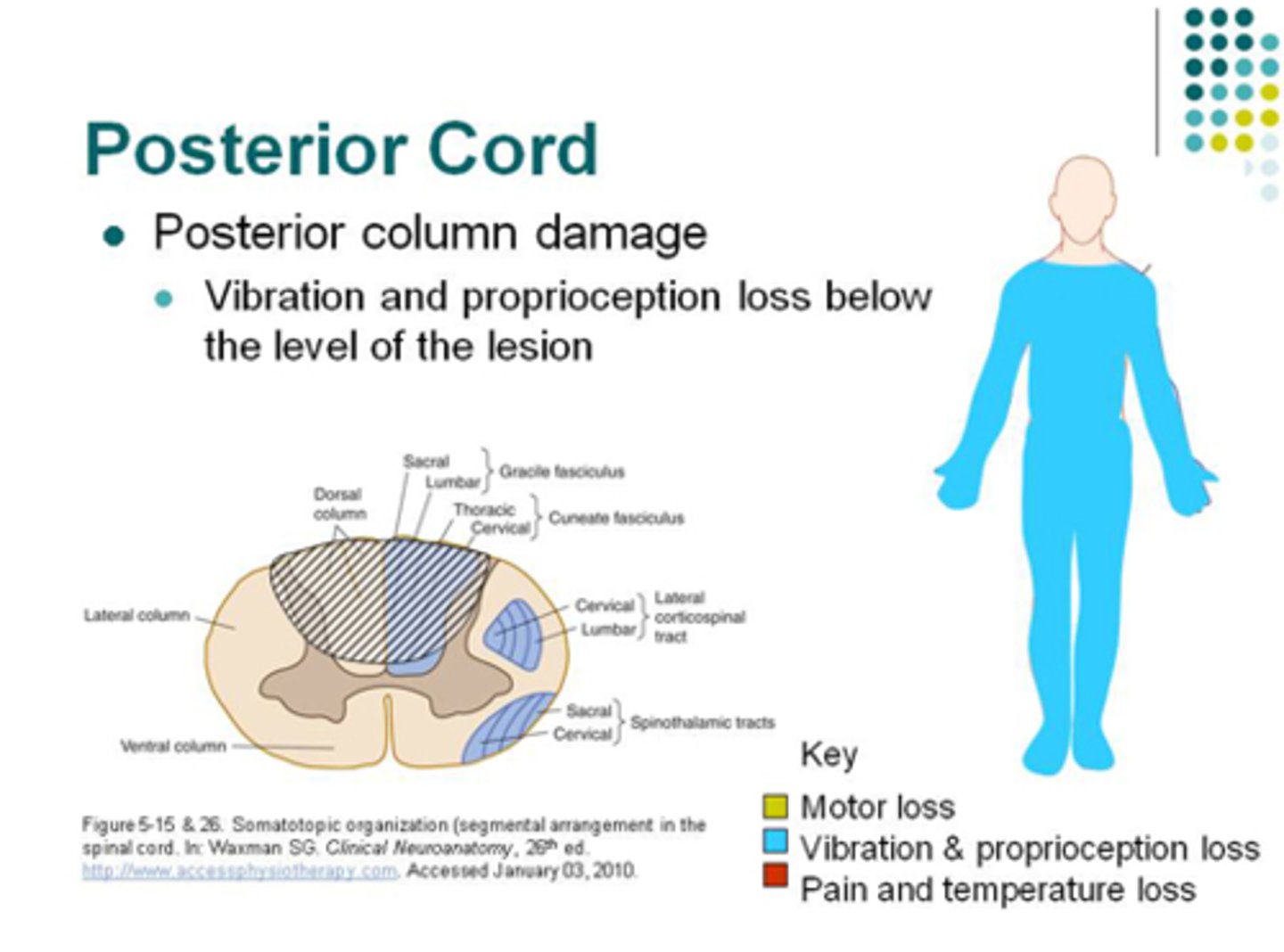
Loss motor function, proprioception, loss of pain and sensation below level of injury -rare
Posterior spinal cord syndrome
(incomplete syndrome)
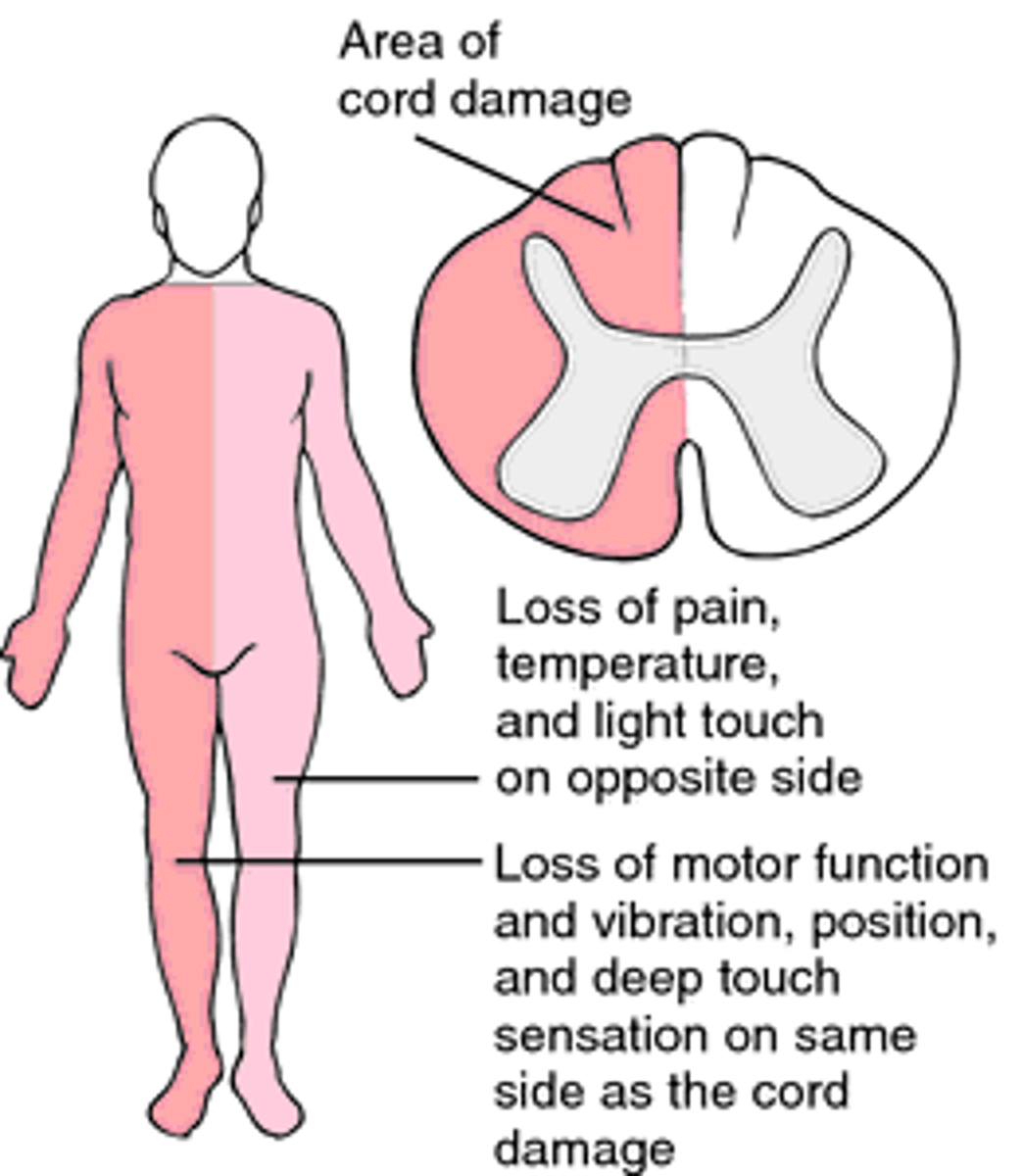
Damage to ½ of spinal cord; Loss of voluntary motor on same side as injury with loss of pain, temp & sensation on other side below level of injury; mostly from knife or sharp instrument
Brown-Sequard syndrome
Medical management of SCI in the ED
- Vital signs including capnography (measures CO2 exhaled over time)
- High cervical injury may require intubation
- Imaging - if obtunded (reduced LOC) assume injury
Types of imaging for SCIs and their advantages (3)
- Plain imaging - quickest, odontoid (C2), swimmers
- CT - more reliable in detecting spinal fractures, better for seeing bone
- MRI - detailed image cord and ligaments, discs, soft tissues
cardiovascular symptoms of SCIs
- bradycardia
- hypotension (shock or blood loss)
how to prevent/treat cardiovascular symptoms of SCIs
- Keep MAP > 85-90 with IVs, blood, pressors
- bradycardia- pacer or atropine
- prevent DVTs
- do not prolong bedrest (chronic peripheral vasodilation = orthostatic hypotension)
- maintain temp (Poikilothermia (inability to thermoregulate) = brady-dysrhythmias)
respiratory complications from SCIs (4)
- respiratory failure
- pulmonary edema
- pneumonia
- pulmonary emboli
general medical management for SCIs (12) *
- DVT and PE prophylaxis
- Pain control
- Urinary management – initially urethral catheter
- Temp control
- Nutrition – start within few days
- skeletal traction
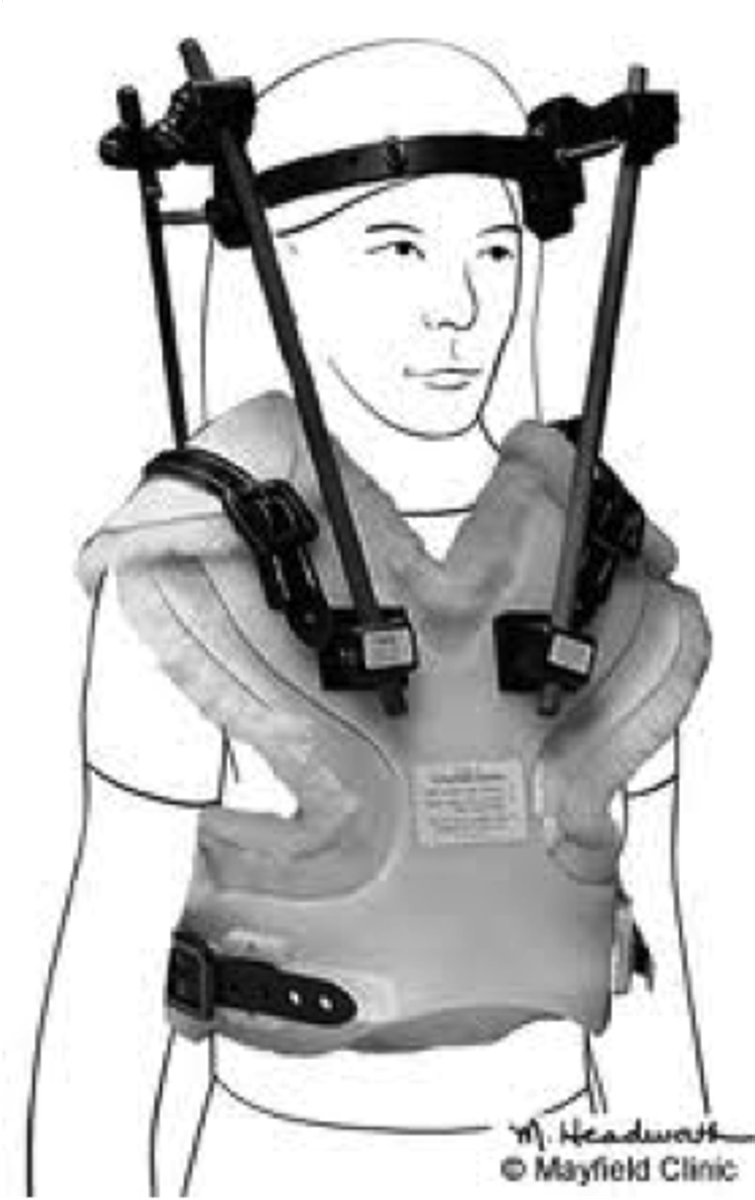
- halo vest
- cervical collar
- log rolling
- ROM to prevent contractures, hand/foot drop splints
- bowel regimen
- meet psychosocial needs- 4 Ds
Only treatment that has been suggested to improve neurologic outcomes in patients with acute, nonpenetrating TSCI (not FDA approved)
Methylprednisone
harmful side effects of Methylprednisone for SCI (3)
-Hyperglycemia
-Impaired wound healing
-Infections
Types of skeleton tractions for SCI
Gardner-Wells, Crutchfield tongs
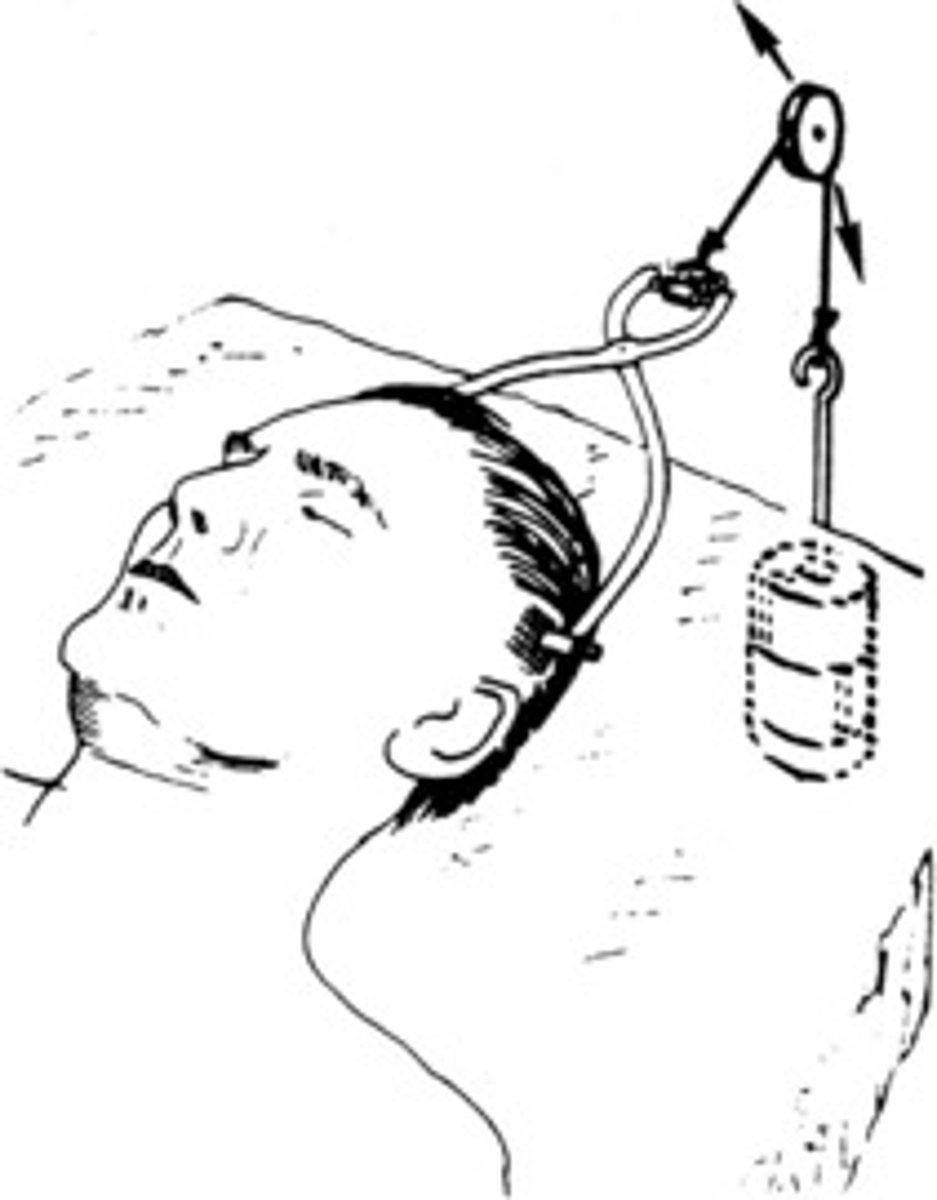
metal ring attached to skull w/ 4 screws for cervical immobilization
halo vest

What is important to remember for patient's with a cervical collar?
skin care
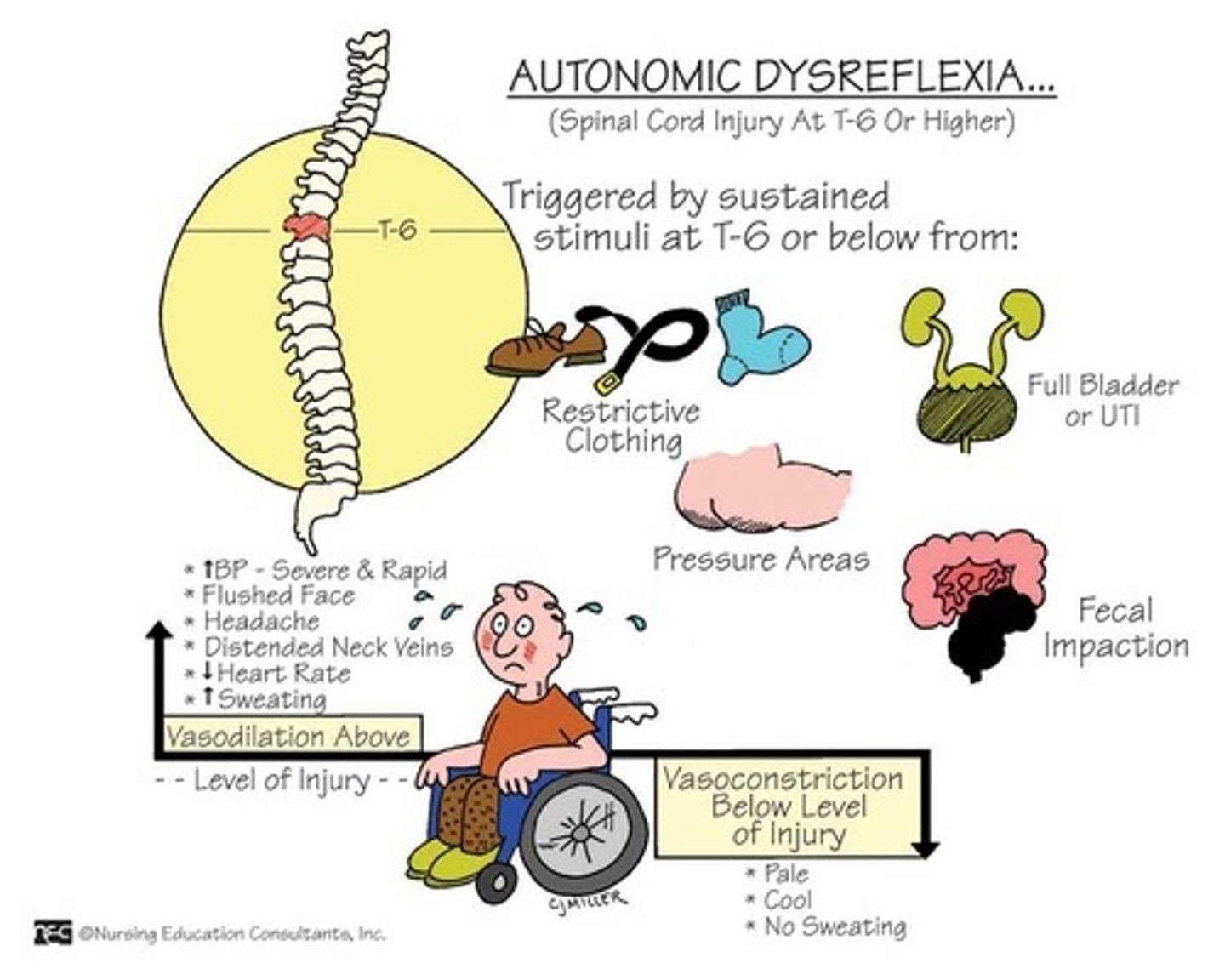
Massive SNS response to noxious stimuli below level of injury; Life threatening & occurs more frequently in quadriplegics
Autonomic Dysreflexia
symptoms of Autonomic Dysreflexia (5) (not on test?)
-Hypertension (SBP > 200, DBP > 130)
-facial flushing
-HA
- anxiety
-sweating
Patho of Autonomic Dysreflexia (not on test?)
Stimulus sends nerve impulses to spinal cord but are blocked by injury and can’t reach the brain --> reflex arc is activated causing SNS response to increase BP --> Nerve (baro)receptors in heart and blood vessels detect ↑ BP and send message to brain to ↓ HR and dilate blood vessels --> PNS compensates = massive vasodilation above level of injury & bradycardia --> Efferent impulses unable to pass through injury so visceral and peripheral vessels below injury cannot respond and therefore problems regulating BP