BIS 2C Angiosperms
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
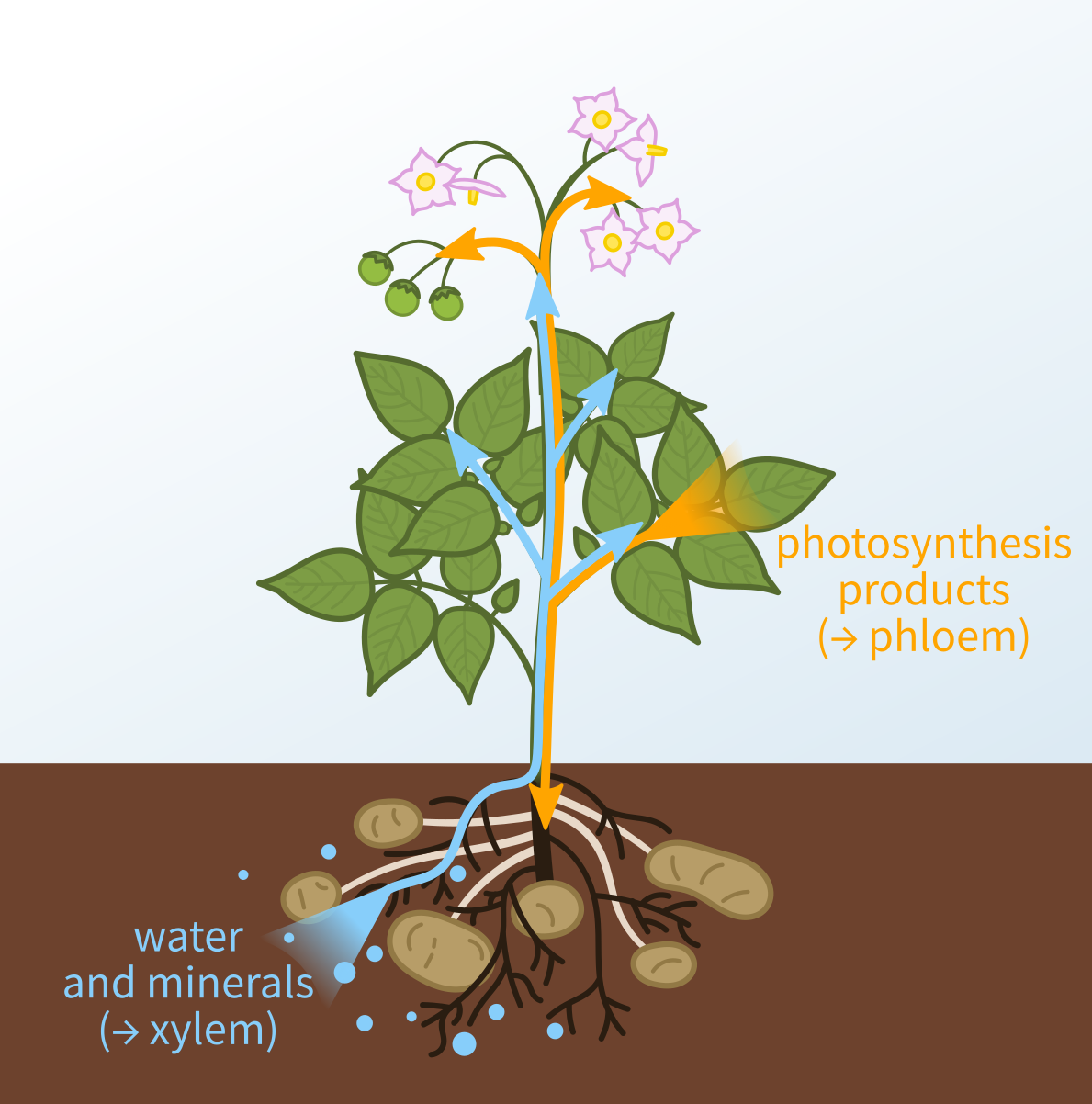
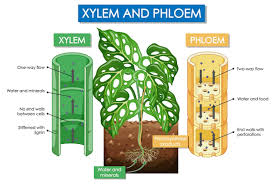
What structures do all vascular plants have?
xylem and phloem

What are the synapomorphies of vascular plants?
branching, independent sporophyte, roots, tracheids
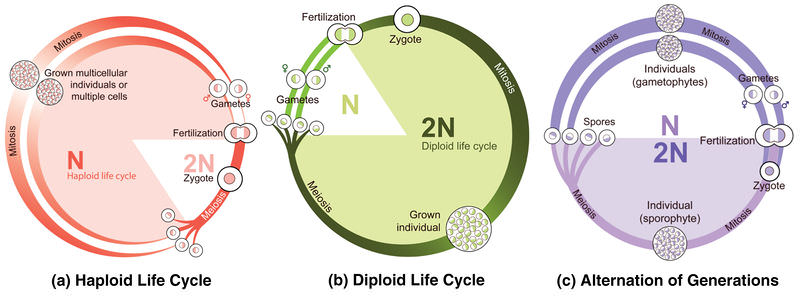
Which life stage dominates vascular plants?
Sporophyte (diploid, 2n)
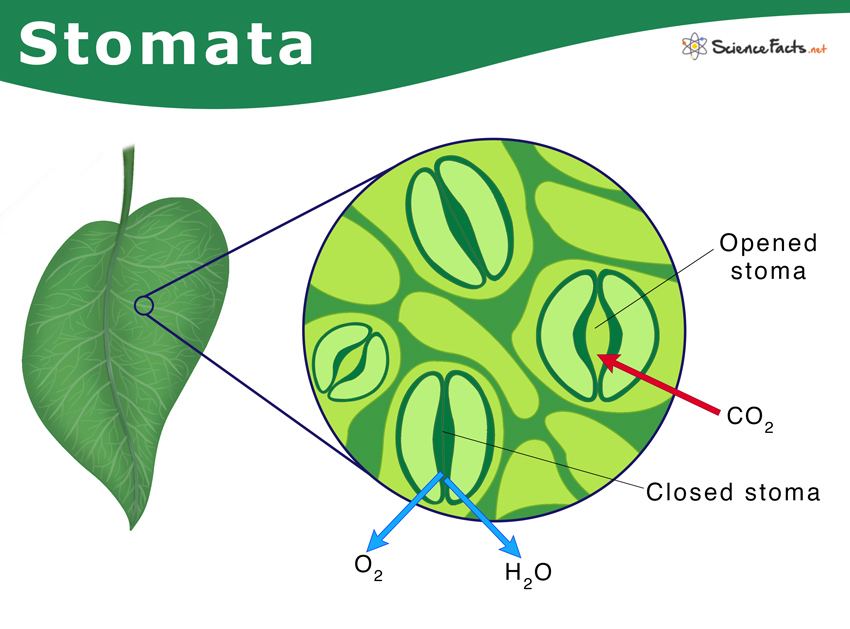
What is the function of guard cells?
Regulate gas exchange by opening and closing stomata
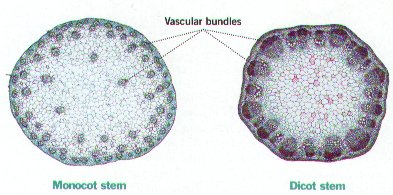
How are vascular bundles arranged in monocots vs. eudicots?
Monocots = scattered; Eudicots = in a ring
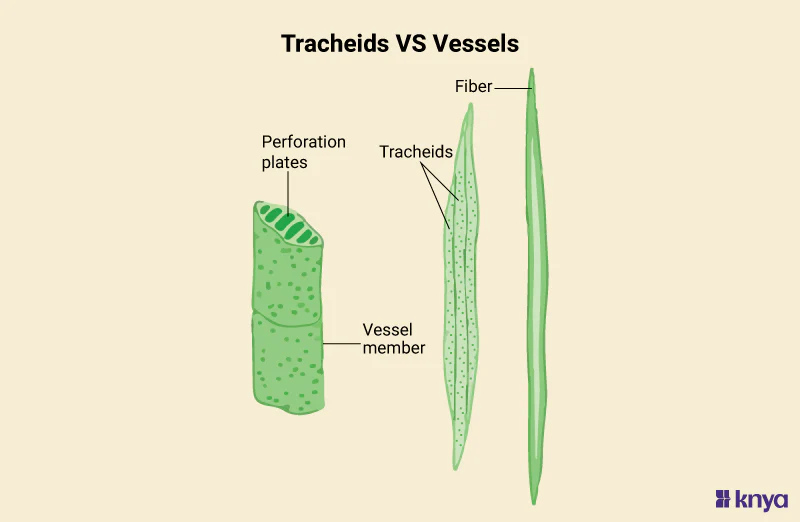
What are tracheids and vessel elements?
xylem cells that transport water; dead at maturity and lignified
What group first evolved vessel elements?
Angiosperms and gnetophytes
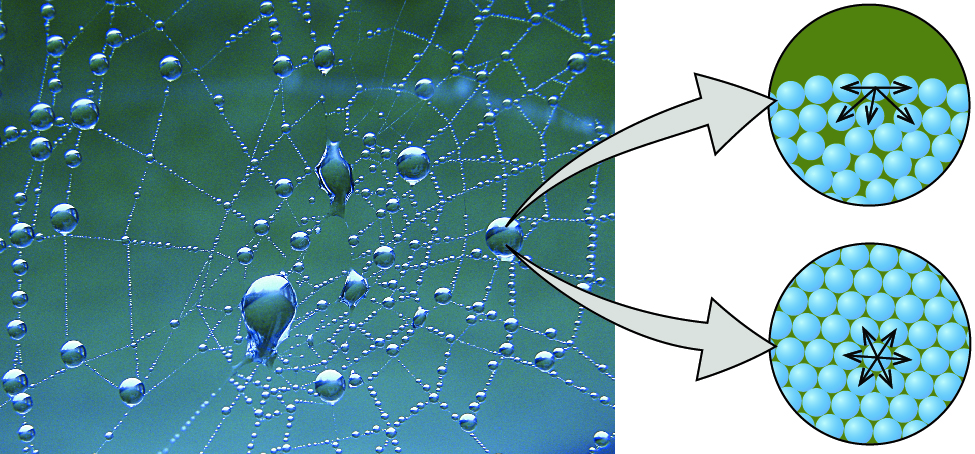
What’s the difference between cohesion and adhesion in water?
Cohesion = water sticks to water; Adhesion = water sticks to other surfaces
What does the Pressure-Flow Model explain?
How sugars move through the phloem from sources (high pressure) to sinks (low pressure)

What kind of leaves do lycophytes have?
Microphylls = small leaves with one unbranched vein
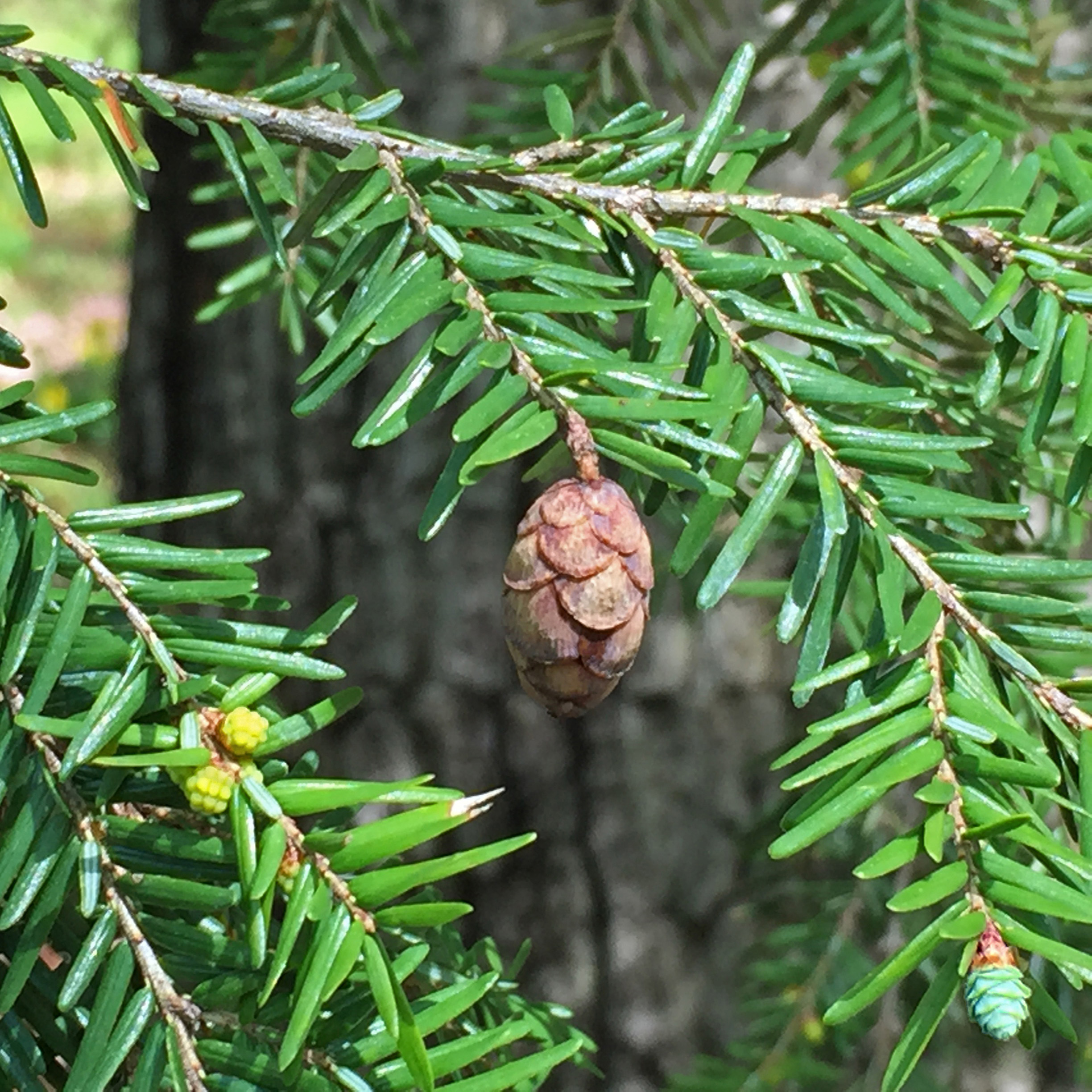

What is a strobilus?
A cone-like cluster of sporangia (spore-producing structures)

What is heterospory?
Having two types of spores: microspores (male) and megaspores (female)
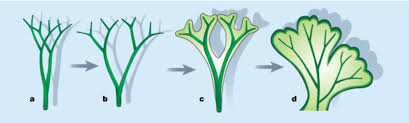
What are megaphylls?
Large, branched leaves that are highly vascularized
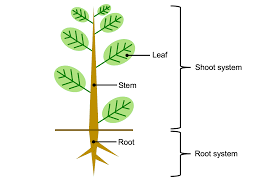
What are the three main organs of a vascular plant?
Roots, shoots, and leaves

What are root hairs for?
Increase surface area for water and nutrient absorption
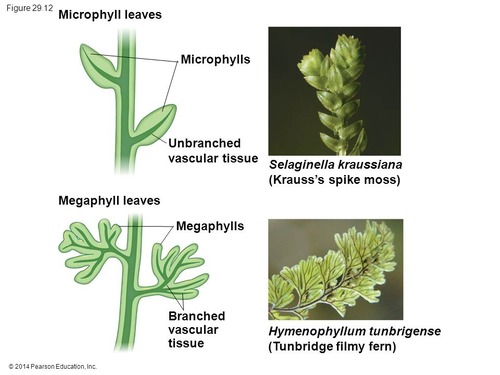
What’s the difference between microphylls and megaphylls?
Microphylls = one vein (lycophytes); Megaphylls = branched veins (ferns + seed plants)
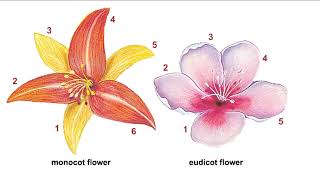
How do monocots and eudicots differ in their floral parts?
Monocots = multiples of 3; Eudicots = multiples of 4 or 5

What root system do monocots have vs. eudicots?
Monocots = fibrous roots; Eudicots = taproot

What is the evolutionary trend from bryophytes to vascular plants?
Shift from gametophyte dominance to sporophyte dominance
What are the # of cotyledons on monocots and eudicots?
Mono = 1; Eudi = 2
What are the main innovations of vascular plants?
Vascular tissue, lignin, roots, true leaves, and dominant sporophyte