gcse physics topic 2
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
electri
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
sources of potential difference:
a cell, batteries, electrical generator
what is potential difference
the energy transferred per unit charge flowing from one point to another
formula for potential difference including work done and charge
v = w/q
what is an electric current
the rate of flow of electrical charge
what is a unit of charge called
a coulomb
what is a columb
the quantity of charge that passes a fixed point per second when a current of 1a is flowing
formula for charge flow:
q = it
what is p.d
work done by a unit of charge passing through a component
formula for p.d with current and resistance
v = ir
what is ohms laq
the current through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across it.(at a constant temperature)
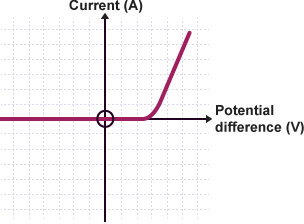
what does filament lamp graph look like and why
it is non ohmic. the resistance of the filament lamp increases as the temperature of the filament increases. this is because as the current increases the temperature of the filament increases and the higher temperature causes the atoms in the metal lattice of the filament to vibrate more making it more difficult for the current to pass through.
why does resistance increase with temperature
becuase when temperature increases atoms vibrate faster. electric current is the flow of these electrons in a material and the electrons will collide with the vibrate atoms decreasing the current.
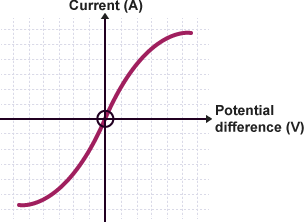
what does diode iv graph look like and why
examples of linear compinents
fixed resistors, wires, heating elements
non linear components examples
filament lamps, diodes and leds, ldr, and thermistors
what is a thermistor
a resistore that changes with temperature, as temp increases the resistance decreases and vice versa.
what are the applications of thermistors
they act as a temperature sensor and can automatically regulate temperatured. ovens, fire alarms, digital thermometers, boilers.
what is an ldr
a light dependant resistor
how does ldr resistance change
as light intesity increases the resistance of the ldr decreases and vice versa.
applications of ldrs
it is found in lights that switch on when it gets dark, alarm clock, light intensity meters, security lights.
current in series circuit
it is the same at all points
current in parallel circuit
the current splits at junctions
p.d in series circuit
the voltage of the power supple is shared between the componenets
p.d in parallel circuit
the voltage across each component is the same
resistors in series and why
total resistance is the sum of the resistance in each components. becuase charge has to push thorugh multiple components while flowing through the circuit.
resistors in parallel circuit and why
total resistance decreases and is less than the resistance of any of the individual components.this is because two resistors in parallel have a smaller overall resistance than just one because the charge has more than one pathway to take so only some will flow along each path.
what is a dc current
a current that is steady, constantly flowing in the same direction in a circuit, from positive to negative
what is an ac current
a current that continuously changes its direction, going back and forth around a circuit
what is mains electricity
electricity generated by powerstations and transported arounf the country through the national grid
what is the voltage and frequency of the amins current in the uk
230 v and 50 hz
what wires are in a plug
live wire, earth wire and neutral wire
what is the live wire for
carries the alternating potential difference from the mains supple to a circuit
what is the nneutral wire for
forms the opposite end of the sircuir to the live wire to complete the circuit
what is the earth wire for
acts as a safety wire to stop the appliance from becoming live
how does the earth wire help
if the live wire touches the metal case of the appliance the appliance would become live, the earth wire would then complete this circuit providing a low resistance path to the earth. this causes a surge of current in the earth wire which passes through the fuse in the circuit causing it to melt hence breaking the circuit.
what is electrical power
the rate of energy transfer or the amount of energy transferred per second
what is the formula for power
p = vi
another formula for power
p = i2 r
what is the formula for energy / work done
e = pt and e = qv
what is the national grid
a system consisting of cables and trasformers linking power stations to consumers