chapter 12.1 case study, Distinct patterns of host adherence by Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolated from experimental gonorrhea.
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
aim
hypothesis
variants in pili genes will impact N. gonorrhoeae adherence and impact severity of infection
background
Neisseria gonorrhoeae: pathogen that has an adherence mechanism mediated by pilli
The poli genes undergo changes during infection
Mutations: so whey look different physiologically to the immune system (DNA level)
Phase changes: expressed at different levels, in different places throughout infection (RNA level)
Help gonorrhoeae avoid the immune system, help adhere to cervical epithelial cells, promotes infection
Mutations and phase changes help N. gonorrhoeae avoid the immune system, increases adherence and promotes infection
Pili genes change during infection
It will alter adherence
And the changed adherence will change infection severity
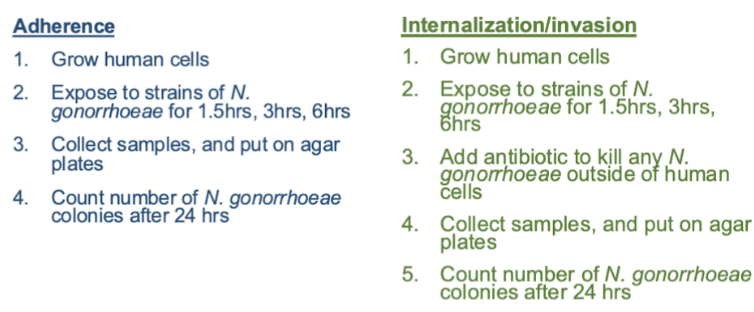
Step 1: monitor changes in adherence and internalization
How well bacteria do the first step of pathogenesis lifestyle Like charges repel
| Determine how many cells got into the epithelial cells Get rid of the outer cells that are not invaded. Adhered but not invade Certain types of pilli (mutations) result in increased internalization |
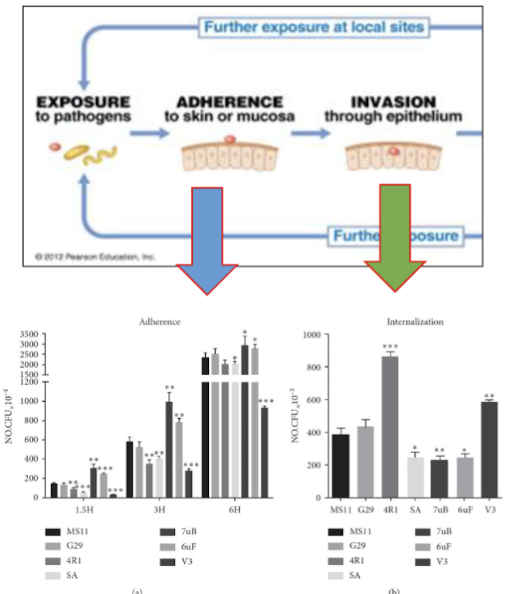
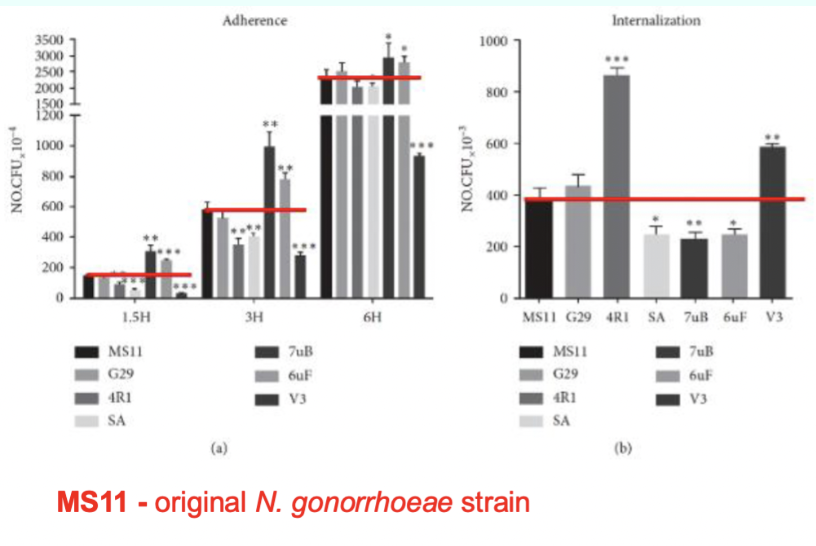
step 1:
Improved | Reduced | |
Adherence | 7uB, 6uF
| 4R1, SA, V3
|
internalization | 4R1, V3
| SA, 7B, 6uF
|
Is there a correlation between better adherence and better internalization?
No. SA both impacts negatively therefore there is no better
recall// positive and negative correlation
+ve: both variables incr or dcr together
-ve: one variable increases and the other decreases
conclusion
Some strains showed improved or reduced ability to adhere and internalize
There was NO CLEAR CORRELATION between improved adherence to internalization
Pattern was mostly followed
Hypothesis was that variants will either increase or decrease N. gonorrhoeae adherence abilities and turn increase or decrease severity of infection
There is no clear correlation for all strains, hypothesis is NOT supported