IB CS Yr 1: Topic 1: System Design 1.2
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Computer hardware
physical elements of a computer
Software
instructions understood by CPU
Peripheral device
any auxilary device that can communicate/work with a computer. Not essential or core part
Computer network
set of computer systems that are interconnected
Human resources
people who are used in an organization, business, or economy
Dumb terminal
depends entirely on the single connected computer for anything related to data
Thin client
low performance terminal, heavily but not entirely dependent on its connected server
client
Recieves data via network
Server
has saved data and offers it to clients
Email server
manages flow of email, checks addresses, allows users email access
Router
networking device that accepts data packets and redistributes them across networks
Domain name system server
attributes names to network addresses and therefore resolves names by assigning them to the appropriate network entity. (finds websites through search bar)
Firewall
hardware or software network structure that controls data flow access among network entities. Offers protection and limits access to a network.
Client server
clients request info and servers perform tasks in order to provide info
servers vs. clients
servers share data, while clients receive/do NOT share
Reliability
how well an IT system functions
Integrity
protecting the completeness and accuracy of data
Inconsistency
problems that arise from duplicated data, causing inconsistency when one version is updated and the other is not
Security
protect hardware, software, peripherals, computer networks from unauthorized access
Authenticity
person proving their identity for access
Privacy
control how and to what extent data is used and disseminated to others
Anonymity
privacy becomes this when one’s identity is concealed for the purpose of harm
Intellectual property
copywrite laws protect this from being stolen
Surveillance
using IT to monitor individuals/groups with or without their knowledge (privacy issue)
Globalization and Cultural Diversity
diminish importance of real world boundaries while accelerating the spread of news. Traditional values may diminish over time.
IT policies
enforce correct use of technology
Standards and protocols
predefined technical rules and conventions that developers of hardware/software should follow. Allows for compatibility
Digital citizenship
appropriate behaviors in the digital world
Stakeholder
people with an interest in the realization of a project or may be affected by the outcome of a project
End-user
person who uses the product
Interview
face-to-face, obtain info through verbal response
Questionnaires
carefully constructed questions to elicit unambiguous responses
Direct observation
spend time in the facility to observe how it functions
Literature search
reading various resources to find info on a topic
Examining current system
detailed examinations of current system
Examining competing products
analysis of competitive factors, benefits, vulnerabilities, characteristics, design. A successful IT system should include a competitive advantage
Modern information
increase client trust
preserve brand strength
preserve organization reputation
maintain corporate resiliency
enhance organizational piece
Online processing (interactive)
data processing performed by a single processor through the use of equipment that it controls. ex. airline reservation
Real-time processing
data processing performed on-the-fly, generated data influences the process taking place. ex. aircraft control
Batch processing
processing performed on data that has been composed and processed as a single unit. ex. payroll
System flowchart
constructed during analysis activities, represent computer programs, files, databases, manual processes, etc. Only way to refer to hardware.
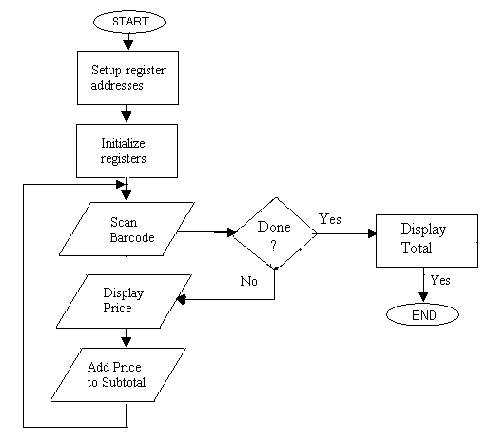
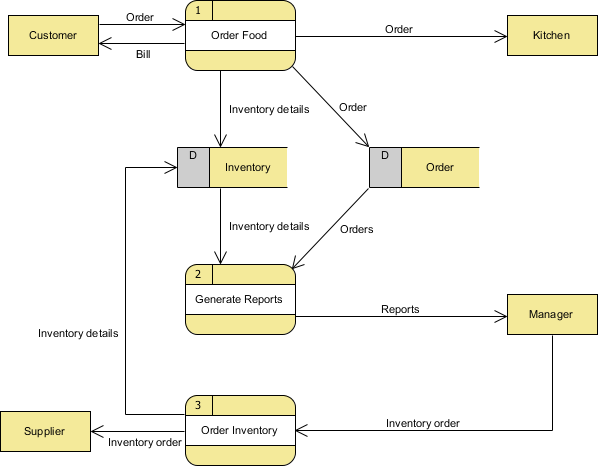
Data flow diagram
shows how data moves from system to system, does not specify type of storage or type of data.
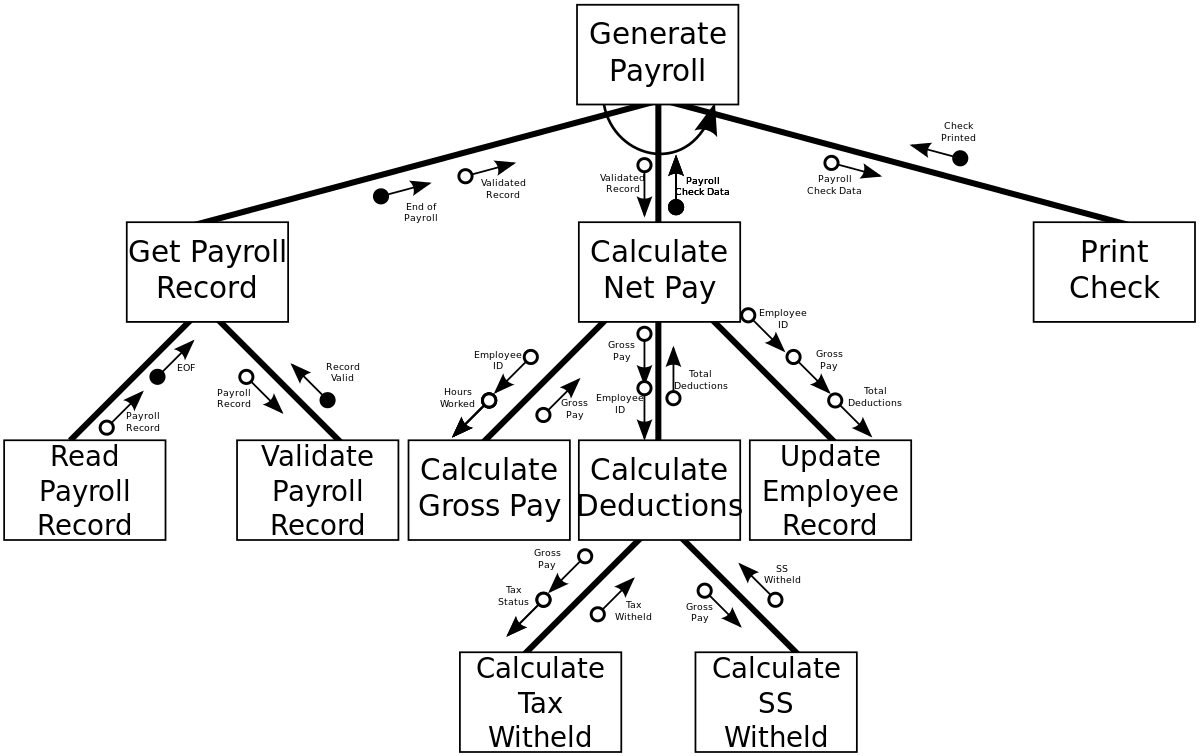
Structure charts
visualizes relationships between modules of a computer program, describes functions of sub-functions of a system.
Modular design
process of designing system modules individually, then combining the modules to form a solution to an overall problem.
top-down design
partition of a problem into smaller problems
pseudocode
used to describe algorithms, artificial language
module
complete/independent part of a program or an algorithm
modular programming
partitioning a computer program into separate sub programs (easily modified and maintained)
modular language
language that supports modular programming
Prototype
preliminary version of a final product
requirements of a prototype
attracts attention of the client
provides enough concept for investors
encourages active participation between users and developers
gives idea of final product
helps identification of problems
increases development speed
Iteration
repetition of a set of instructions a number of times until operations yield desired results
Consequence of no collaboration
the end-user is unsatisfied with the product
High accessibility
meets as many needs as possible
Usability
potential of a product
Egronomics
design of safe and comfortable products
Eight quality components of usability
Complexity / Simplicity - amount of effort for a result
Effectiveness - comparison of user performance against a defined level
Efficiency - task completion time after the initial adjustment period
Error - number, type, time needed to remove from errors
Learnability - time used to accomplish tasks on the first use
Memorability - how memorable the system is
Readability - speed and comprehension
Satisfaction - attitude of users towards the product
Visual impairment and color blindness solutions
braille devices, text to speech, adjust color values on screen
Hearing and speech impairment solutions
replace sound signals with visual effects or vibrations, subtitles
Cognitive problems and learning disability solutions
multi-sensory experience, basic word processor, active participation, positive reinforcement
Mobility impairment solutions
left-handed keyboards, replacement of some devices, tracker ball, special knobs, sip-and-puff (SNP), morse code, natural language processing, word prediction
Usability problems
hard to use
difficult to read
unnecessary pages and redirections
not visually appealing
unable to quickly locate a product
no FAQ or customer support