3. Grammer
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
148 Terms
Nouns
are used to describe
person
place
thing
idea

Nouns can be ideas ( something MENTAL )
why?
because we can NAME them!
( If you can name it, even just in your , it’s probably a noun )
examples
“Stress” = a feeling you can name ➡ noun
“Friendship” = an idea you can name ➡ noun
2 main types of nouns?
_____ noun
_____ noun
Common noun
Proper noun
Nouns can also be
1._______
2._______
Abstract ( general )
Concrete ( specific )
Common Nouns
are
generic names for
people
places
things
Common nouns _____ capitalized
Common nouns are not capitalized
common noun examples
people: boy , girl , worker , manager
places : school , bank , library , home
things : dog , cat, truck , car
Proper Nouns
will
name specific
people
places
things
Proper nouns _____ capitalized
Proper nouns are capitalized
proper noun examples
people: Abraham Lincoln, Martin Luther King Jr.
places: Los Angeles, California ; New York
things: Statue of Liberty
note
when referring the planet we live on = Earth
when referring to dirt, rocks, land = earth
General Nouns
are
names of conditions or ideas
Condition
describes the
qualities that exist about someone/something
that we cannot physically hold

General Noun for Condition
example
beauty ( state of being beautiful )
strength ( state of being strong )
Idea
describes the
concepts or beliefs in our minds that we mentally feel ( not physically )
General Noun for Idea
example
peace ( concept of harmony )
truth ( concept of honesty )
justice ( concept of fairness )
Specific Nouns
will
name
people
places
things
that are understood by our senses
( see, touch, hear, smell )
Specific Nouns
example
people : baby , friend, father
places : town , park , city hall
things : rainbow, cough , apple, silk, gasoline
Collective Nouns
are
names for a group of
people
places
things
that may act as a whole
Collective Noun
examples
class
team
public
dozen
group
herd
Collective Nouns
usually require an
Article that indicates the noun as a single unit
example
A choir is a group of singers.

even though there are many singers
choir is grammatically treated as a
single unit
if we refer to the members of the group and not the group itself
→ it is no longer a collective noun
correct or incorrect?
The choir are going to compete nationally this year.
incorrect
correct or incorrect?
The choir is going to compete nationally this year.
correct
correct or incorrect?
The members of the choir is competing nationally this year.
incorrect
correct or incorrect?
The members of the choir are competing nationally this year.
correct
Pronouns
are
words that stand in for nouns
7 Ways to Classify Pronouns
1.____
2.____
3.____
4.____
5.____
6.____
7.____
Personal
Intensive
Relative
Interrogative
Demonstrative
Indefinite
Reciprocal
Personal Pronouns Subdivisions include
______
______
______
Nominative
Objective
Possessive
Nominative Personal Pronouns
are for
nouns or pronouns that are the subject of a sentence ( doing the action )
Nominative Personal Pronouns
example
She runs fast.
He runs fast.
It runs fast.
They run fast.
We run fast.
I run fast.
You run fast.
Objective Personal Pronouns
are for
nouns or pronouns that are an object jn a sentence ( receiving the action )
Objective Personal Pronouns
example
The baker called me.
This cake is for you.
She hugged him / her / it.
I gave the cake to them.
Quick way to think about it:
👉 Subject does it. Object gets it.
(subject = nominative, object = objective!)
Possessive Personal Pronouns
are
nouns or pronouns that show possession or ownership ( belongs to someone )
Possessive Personal Pronouns
examples
That is my / your / his / her cookie
That is mines / yours / hers pie
That is its donut
Intensive Pronouns
will
emphasize a noun or pronoun
examples
I myself
You yourself
He himself
She herself
The ( thing ) itself
We ourselves
You yourself
They themselves
Intensive Pronouns
sentence example
I made this whole cake myself.
Relative Pronouns
will
connect a clause ( phrase ) to a noun/pronoun
examples
which
who
whom
whose
Relative Pronouns
sentence example
The student who studies hard will pass.
Interrogative Pronouns
will
ask questions
examples
what
which
who
whom
whose
Interrogative Pronouns
sentence example
Which flavor do you prefer?
Demonstrative Pronouns
will
point to specific things
examples
this
that
these
those
Demonstrative Pronouns
sentence example
These are my favorite yogurt toppings.
Indefinite Pronouns
will
refer to nonspecific people or things
examples
all
any
each
everyone
either/neither
one
some
several
Indefinte Pronouns
sentence example
Someone left their book here.
Reciprocal Pronouns
will
show a mutual action or relationship
examples
each other
one another
Indefinte Pronouns
sentence example
They hugged each other after the game.
If you want to write a sentence you need a
verb
Verbs
shows
Action
State of Being

Action
means
something is happening
example
She runs fast.
( jump, drive, think )
State of Being
means
something is a certain way
example
He is tired.
( are, was, seem, feel )
Transitive Verb
is a
verb whose action DOES indicates a receiver
Transitive Verb
sentence example
She plays the piano.
John joined the crowd.
Intransitive Verb
is a
verb whose action DOES NOT indicate a receiver
Intransitive Verb
sentence example
He slept.
Sharon collapsed.
Action Verbs
will
show what the subject is doing ( their action )
true or false
Action Verbs can be an entire sentence.
true
Action Verb
examples
He sings.
Run!
Go!
I talk with him everyday
She reads.
Linking Verbs
will
link the subject of a sentence to a
noun
pronoun
adjective
that DESCRIBES the subject
( connects the subject of a sentence to more information about that subject )
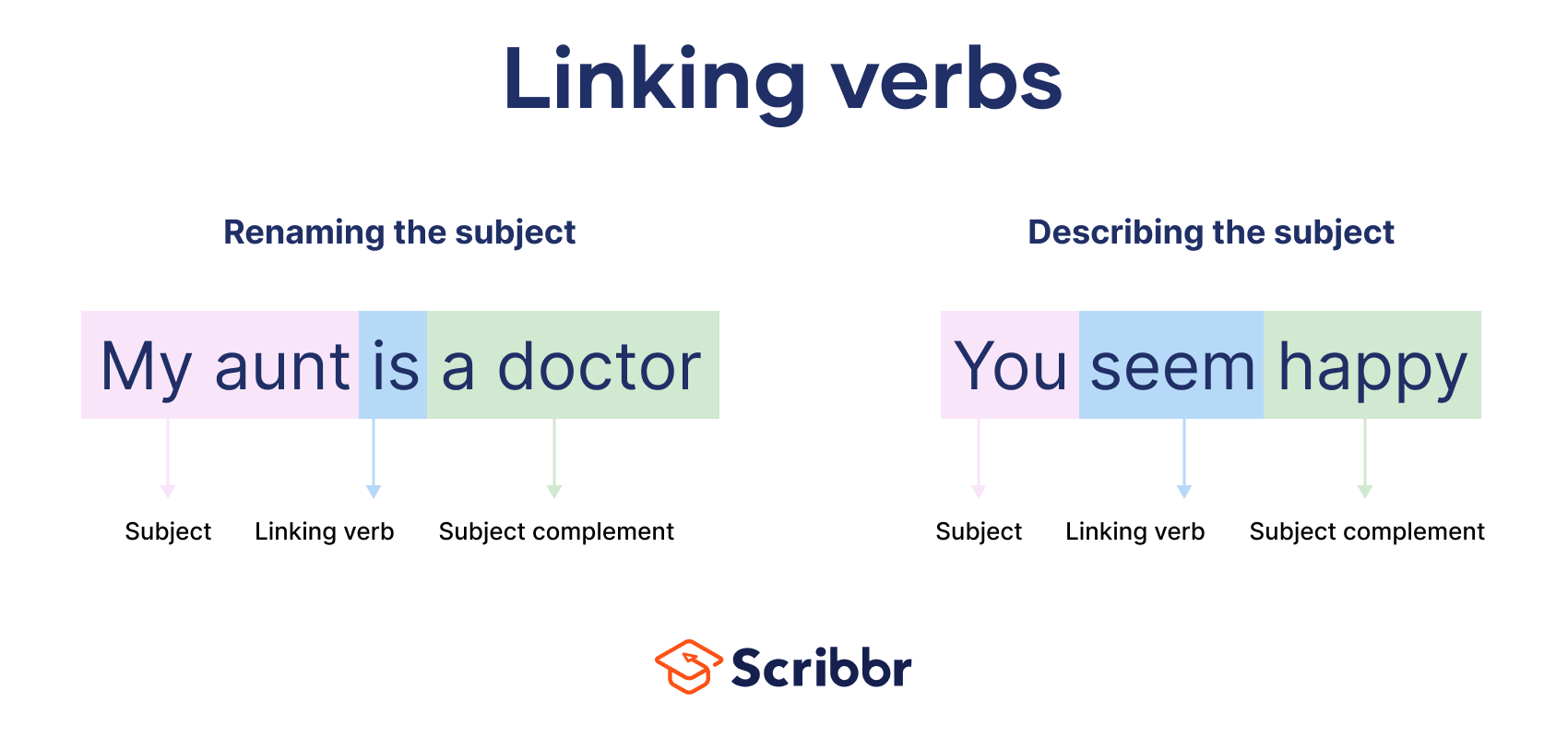
common linking words
appear
be
become
feel
grow
look
seem
smell
sound
taste
true or false
Linking Verbs can be an entire sentence.
false
Linking Verb
examples
I am John.
( I = subject )( John = noun )
That soup smells good.
( soup = subject )( good = adjective - describes the smell )
Shirley felt tired.
( Shirley = subject )( tired = adjective - describes the feeling )
note
Phasal Verbs
are
verbs with extra words that look like prepositions ( shows where or when )
but they actually belong to the verb and change it’s meaning
prepostion examples
The cat is on the table
( shows place )
We walked after lunch
( shows time )
She went through the door
( shows direction )
Phrasal Verbs
examples
drop off
look up
call off
Transitive Verbs
come in active or passive ______
voice
Active Voice
is when
the subject of the sentence is doing the action
Active Voice
example
Jon drew the picture
(The subject Jon is doing the action of drawing a picture)
Passive Voice
is when
the subject is being acted upon
( receiving the action )
Passive Voice
example
The picture is drawn by Jon.
( The subject picture is receiving the action from Jon )
A Verb Tense
will
tweak the form of a verb to
indicate the time of an action
( when it happened )
examples
I eat (present)
I ate (past)
I will eat (future)
an action in the present ( I talk ) can change form to for the past ( I talked ) by itself
many other tense changes need
Auxiliary ( Helping ) Verbs
Auxiliary ( Helping ) Verbs
are
words that help change tense form
( so that it makes sense )
Auxiliary ( Helping ) Verbs
examples
am - are - is
have - has - had
was - were - will - shall
6 Verb Tenses?
______
______
______
______
______
______
Past
Present
Future
Perfect Past
Perfect Present
Perfect Future
Perfect ( when talking about verb tenses ) means the action is
Completed / Finished
( before the time word it’s connected to )

Present
means the action ( verb )
happens at the current time
example
He walks to the store every morning.
To show that something is happening right now we use the
progressive present tense
( am/is/are + a verb ending in -ing )
example
I am walking.
Past
means the action ( verb )
happened in the past
example
He walked to the store an hour ago.
Future
means the action ( verb )
is going to happen later
example
I will walk to the store.
Present Perfect
means the action ( verb )
started to complete in the past
( before the present )
and
continues into the present
( or took place previously at an unspecified time )
example
I HAVE walked to the store three times today.
Past Perfect
means the
second action was completed in the past
first action came before the second
example
Before I walked to the store ( Action 2 ), I HAD walked to the library.
Future Perfect
means the
action was completed before a future moment
example
When she comes for the supplies ( future moment ), I WILL HAVE walked to the store.( action completed before the future moment )
Changing the form of a verb is called
Conjugating
“conjugating a verb”
3 Key Forms of a Verb
Singular, Present Tense ( dream )
Singular, Past Tense ( dreamed )
Past Participle ( have dreamed )
notice
Past Participle needed an
auxiliary ( helping ) verb
to make it’s verb tense make sense
example
I have dreamed of this day.
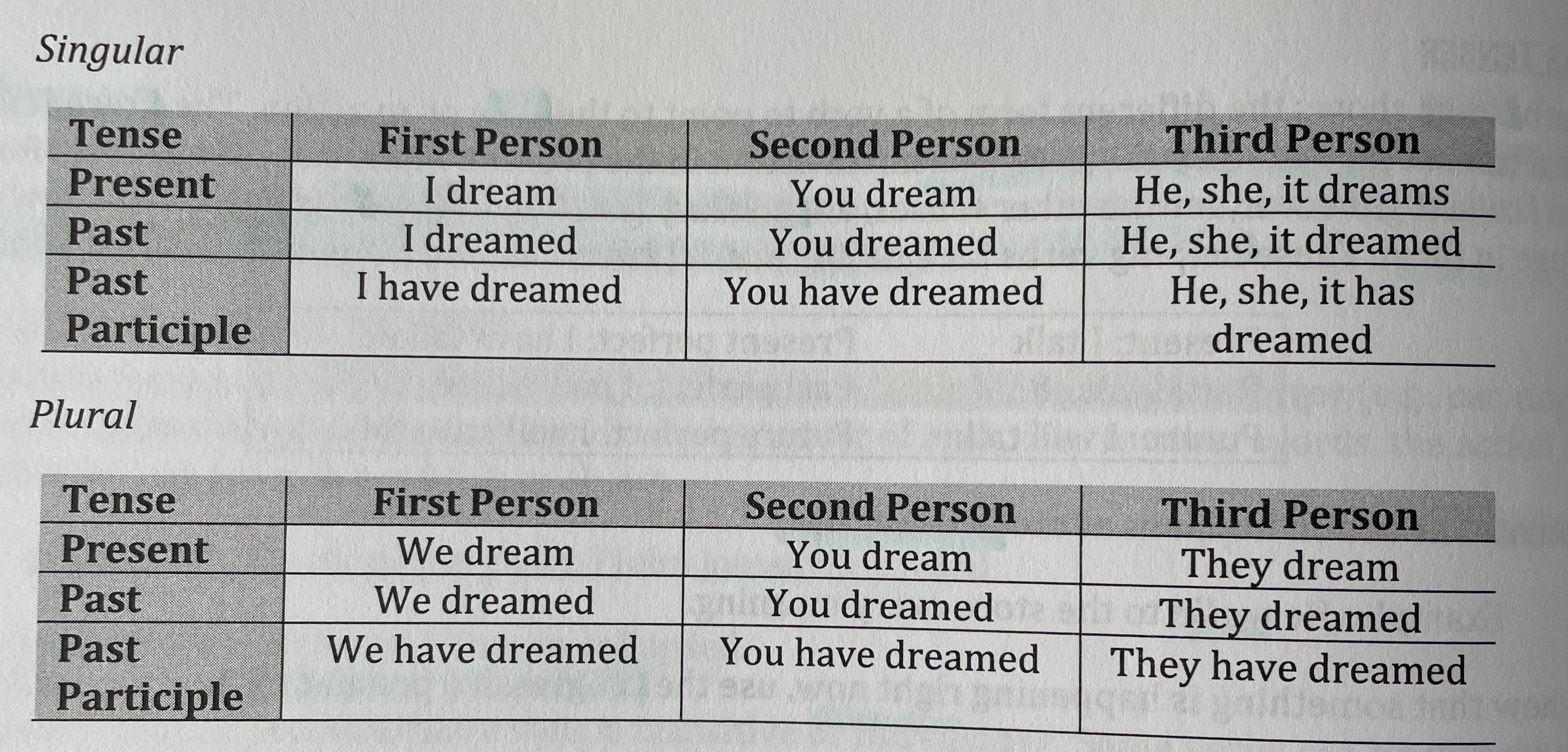
some different ways to
conjugate ( change forms ) of a verb
Adjectives
are
words used to
modify ( describe or add detail to )
a noun or pronoun
Adjectives
answer the questions of
Which one?
What kind?
How many?
Which one?
example
The third dress is my favorite.

What kind?
example
This dress is navy blue.
How many?
example
I am going to buy four pairs of shoes to match the dress.
note
adjectives
usually come
before the words they modify
sometimes are
after a linking verb

Articles
are
adjectives used to distinguish nouns as
Definite Noun
Indefinite Noun
Definite Nouns
are
nouns that DO indicate a specific
person
place
thing
idea
Definite Nouns
go after the article
the
Definite Noun
example sentence
I lost the bottle that belongs to me.