Zoology Lab 9 Arthropoda II
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Characteristics of Phylum Arthropoda
A durable polysaccharide cuticle called chitin
A hardened exoskeleton
Fused segments of body/ functional regions called tagma
Specialized appendages
Characteristics of Subphylum Crustacea
Feeding appendages called mandibles, biramous appendages, 2 pairs of antennae
External anatomy of Order Decopoda
2 pairs of antennae, compound eyes, chelipeds, walking legs, swimmerets, carapace, telson
What species belong to Order Decapoda
Shrimp, crayfish, crab, hermit crab
What orders make up Class Malacostraca
Orders Decopoda, Isopoda, Amphipoda
What organisms belong to order Isopoda
Sow bugs and rolly polies
What organisms belong to Order Amphipoda
Scuds and sand fleas
Characteristics of Subphylum Hexapoda
A head with mandibles, thorax with 3 pairs of uniramous appendages , abdomen
Represents Class Insecta
What orders make up Class Insecta, Subphylum Hexapoda
Orders Odonata, Orthopotera, Hemiptera, Coleoptera, Lepidoptera, Diptera, Hymenoptera
Order Odonata
dragonflies, damselflies
Long, slender bodies with two pair of elongate, membranous wings; chewing mouthparts; incomplete metamorphosis
Order Orthopotera
grasshoppers, crickets
Hind pair of legs often modified for jumping; wings, when present, with membraneous hindwings folded underneath thickened forewings; chewing mouthparts; incomplete metamorphosis
Order Hemipatera
true bugs, hoppers, whiteflies, and others
Piercing-sucking mouthparts; wings, when present with membranous hind wings held underneath forewings that may be membranous or partially thickened; incomplete metamorphosis
Order Coleoptera
beetles
Forewings hardened, hindwings membranous and folded underneath forewings; chewing mouthparts; complete metamorphosis
Order Lepidoptera
butterflies, moths
Two pair of large membranous wings covered with scales; mouthparts tubular and coiled underneath head; complete metamorphosis
Order Diptera
flies
Membranous forewings only, hind pair modified into balancing organs; mouthparts piercing-sucking or sponging; complete metamorphosis
Order Hymenoptera
ants, bees, wasps
Two pair of membranous wings coupled together, with hindwings smaller; mouthparts chewing or lapping; female with ovipositor or stinger; complete metamorphosis
What classes make up Subphylum Myriapoda
Classes Chilopoda and Diplopoda
Class Chilopoda
Centipedes
Flattened bodies with single pair of appendages per trunk segment, venom claws used to subdue and kill their prey before using their feeding mandibles
Class Diplopoda
Millipedes
Cylindrical bodies, downward facing mouthparts for feeding on decaying or living plant material, two pairs of legs per trunk segment(hence common class name, “di”)
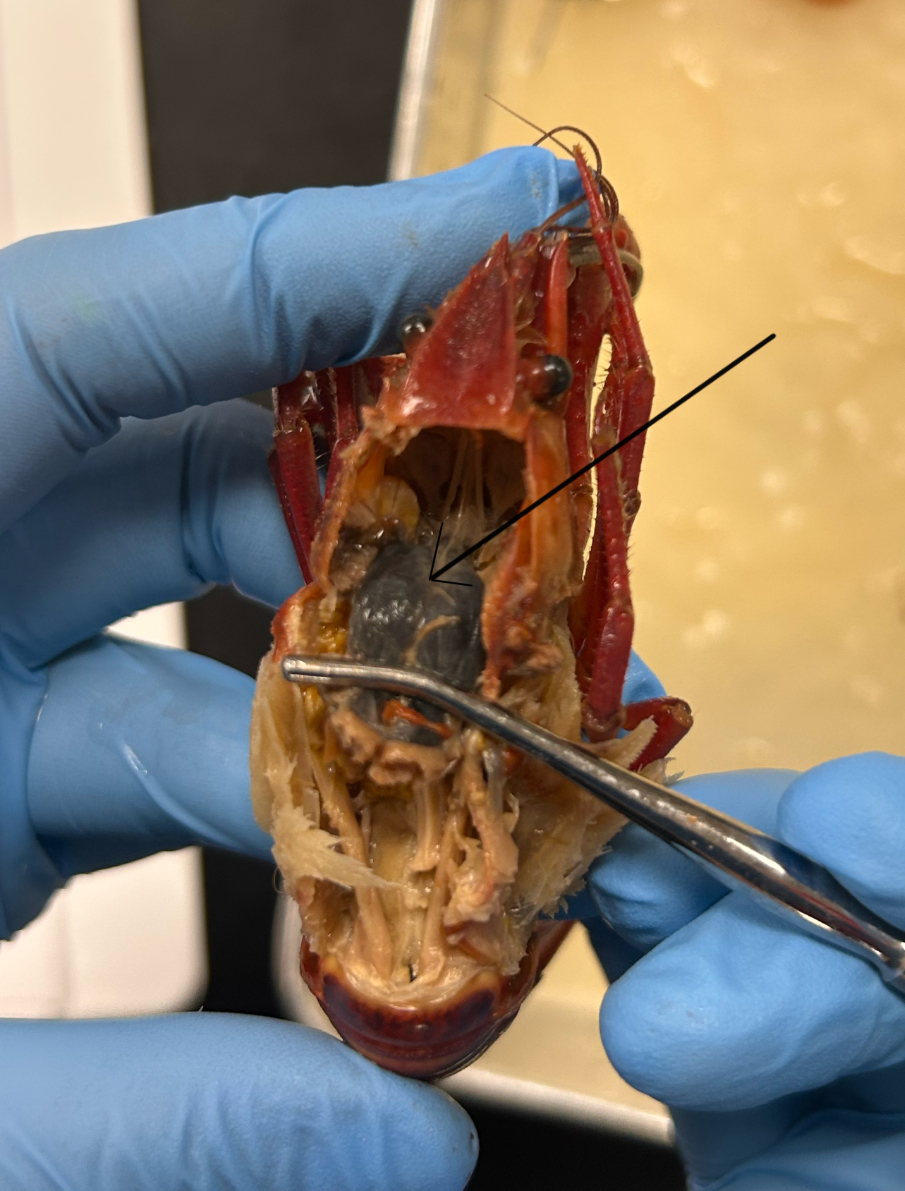
Identify this structure (1)
Green glands: antennae glands, used to excrete urine and are important for the réabsorption of salts and water
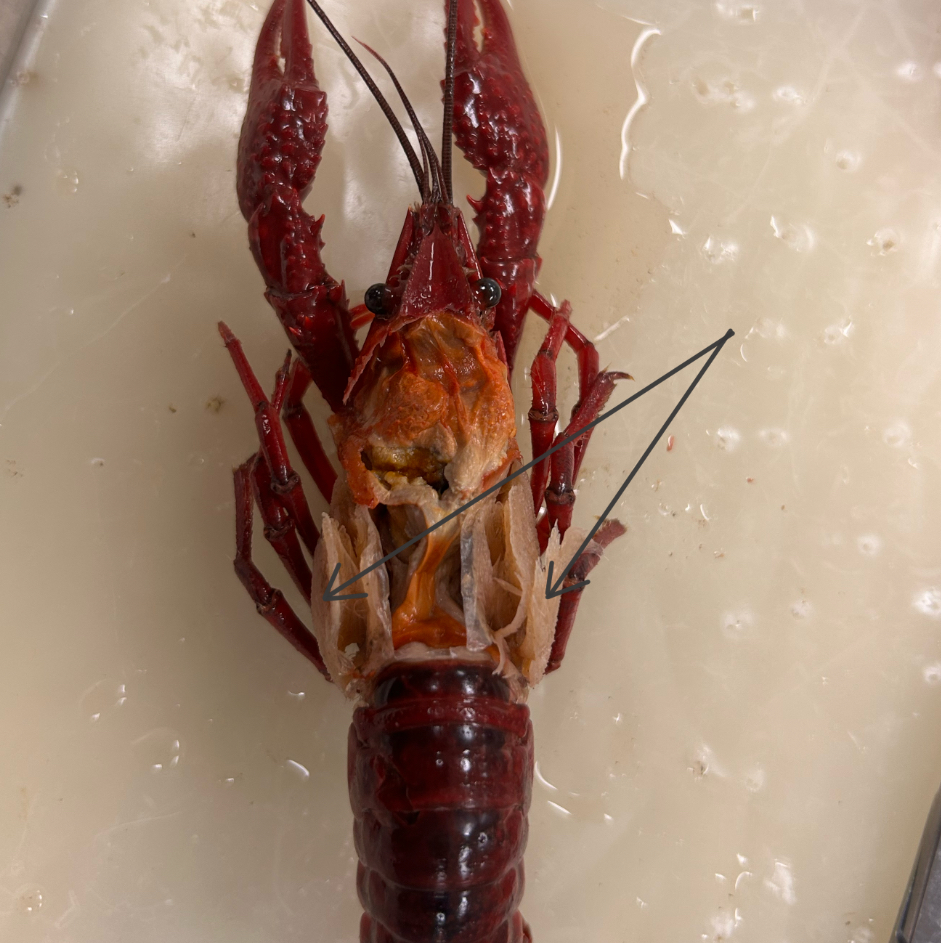

Identify this structure (2)
Gills
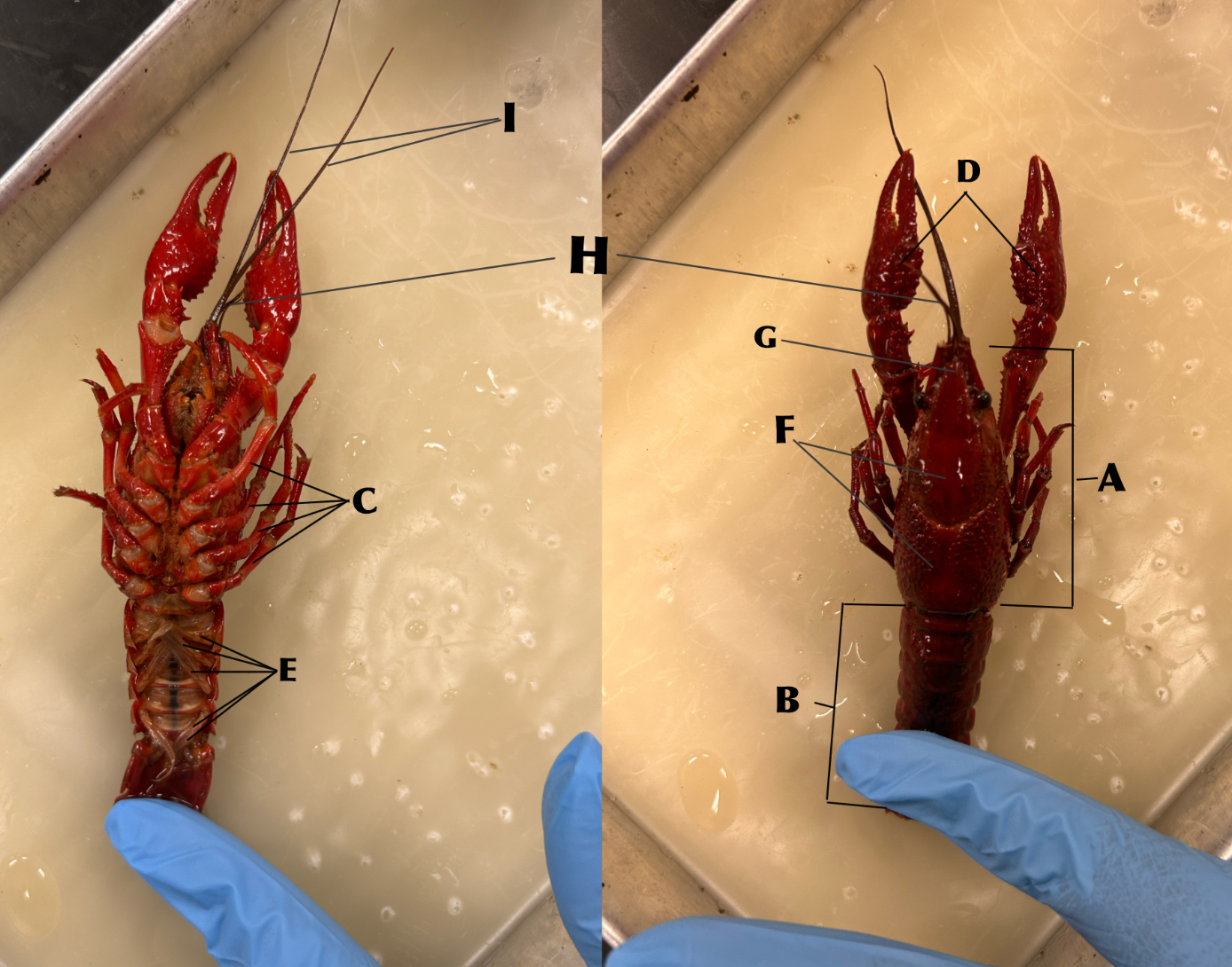

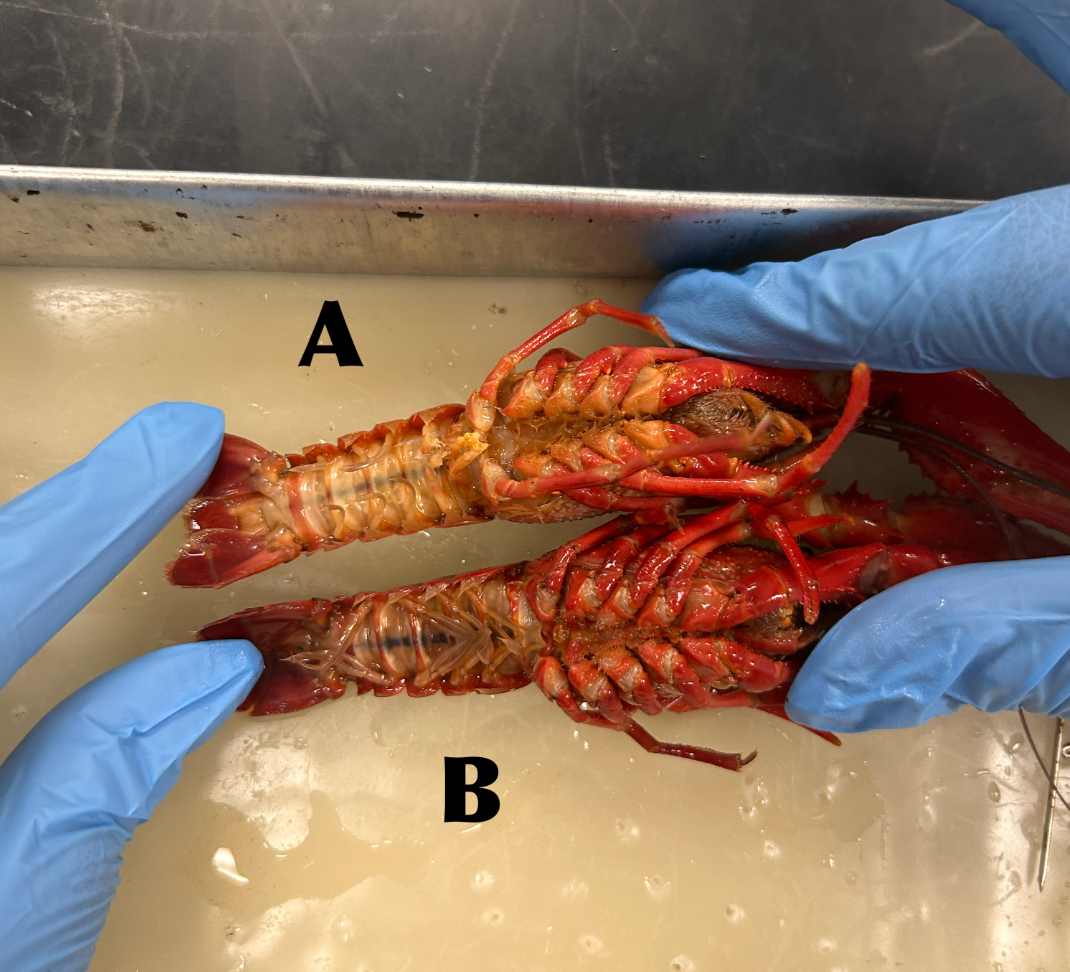
What is B
Abdomen
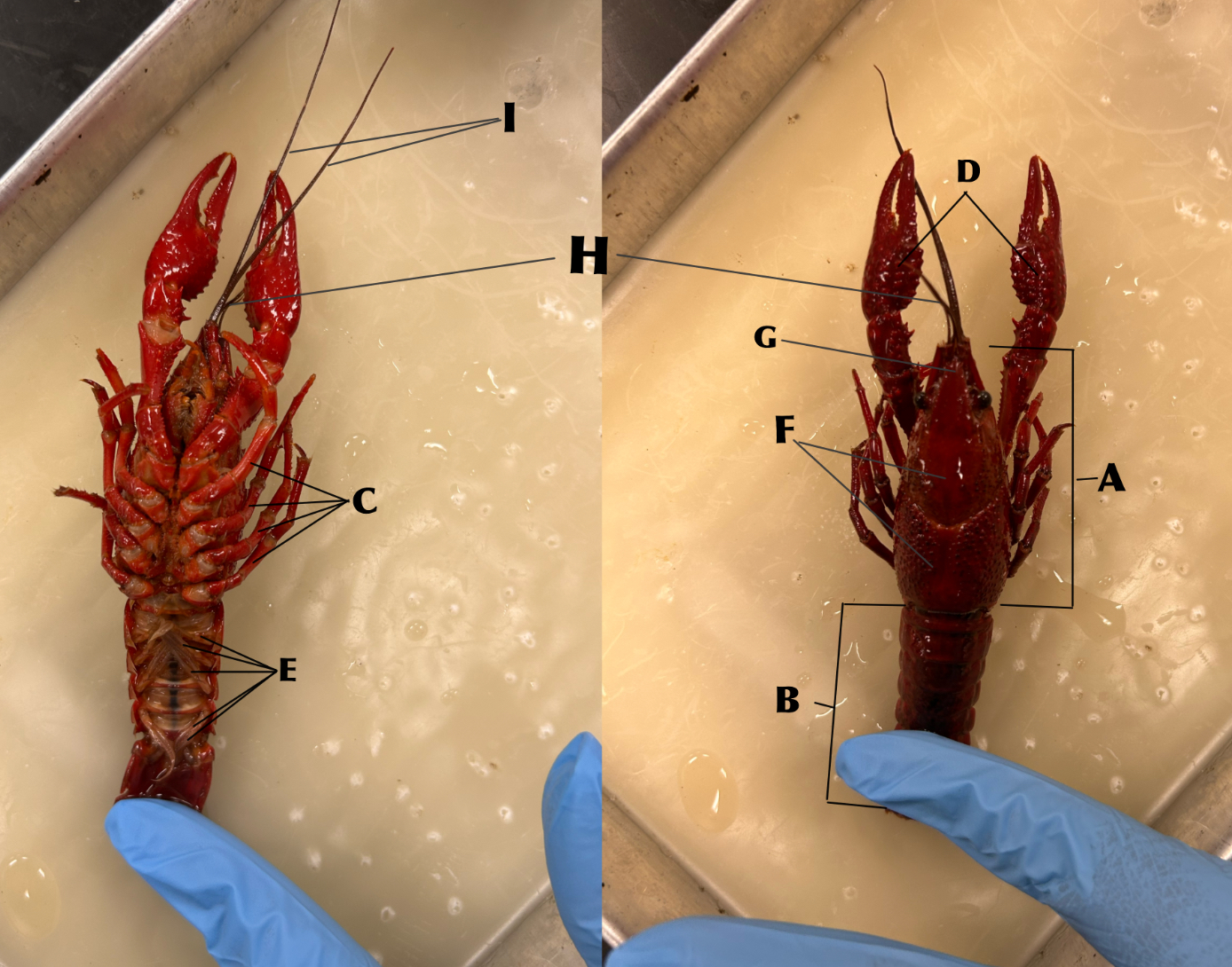

What is C
Walking legs (locomotion)
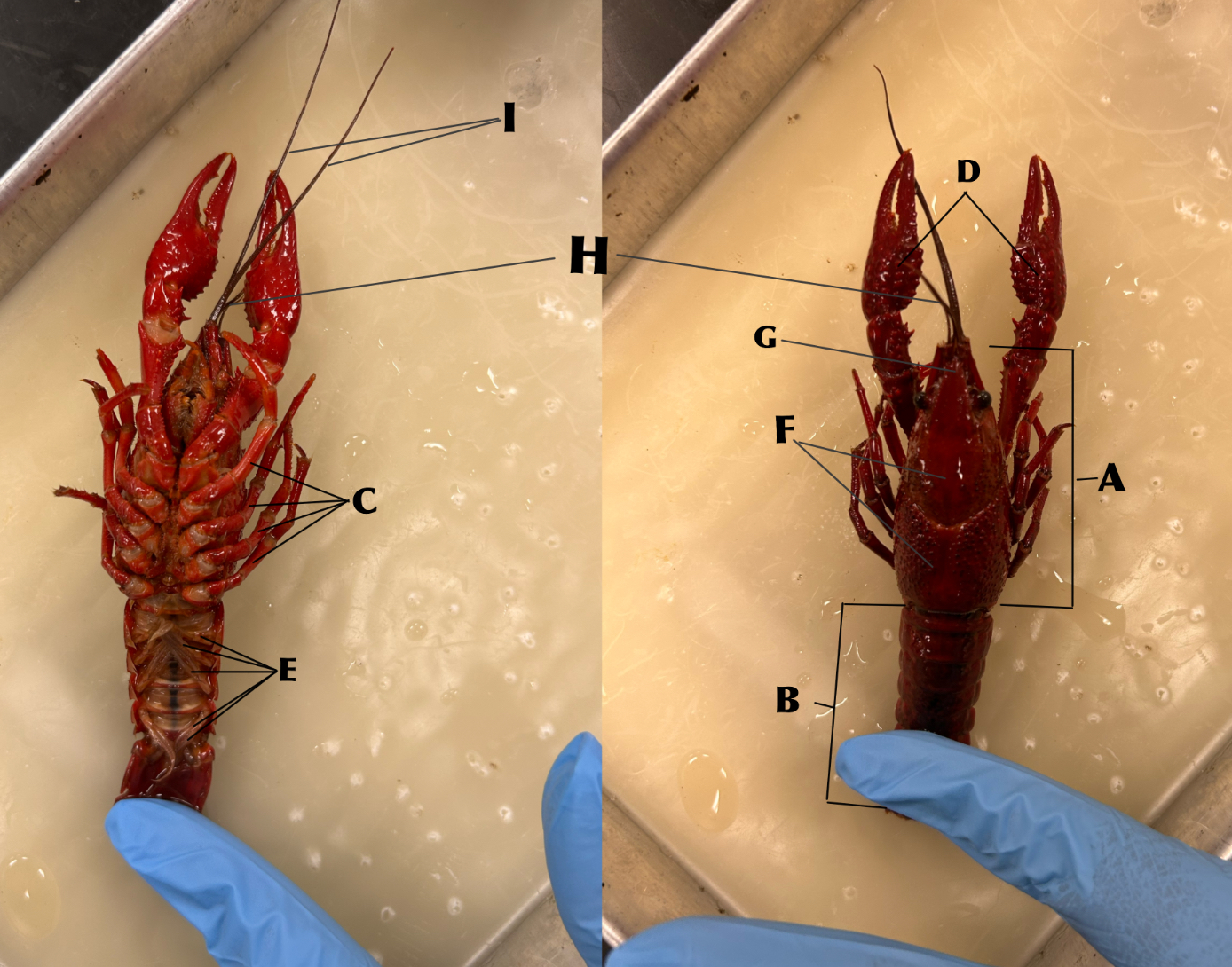

What is D
Chelipeds (defense)
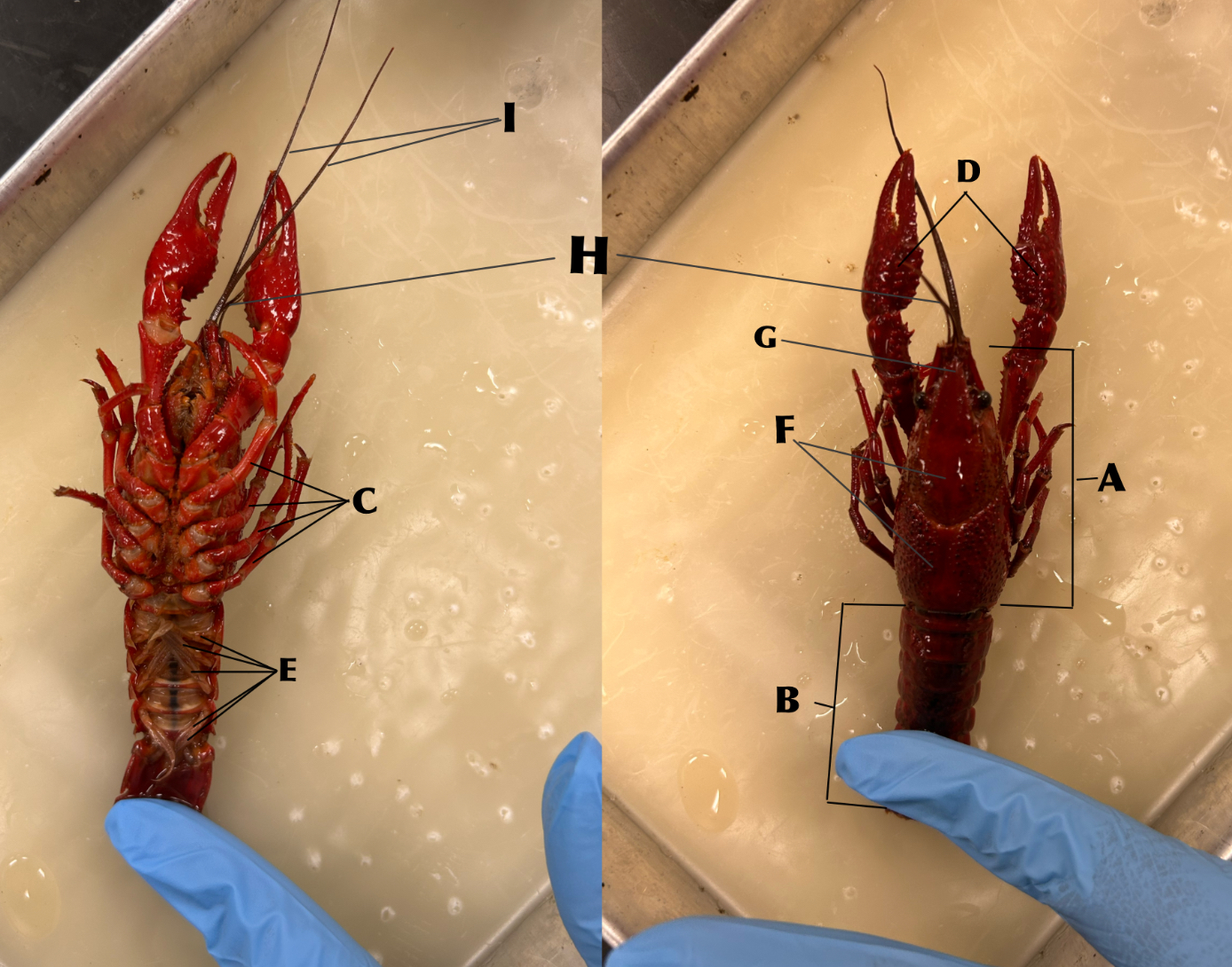

What is E
Swimmerets (creates water currents and function in reproduction)
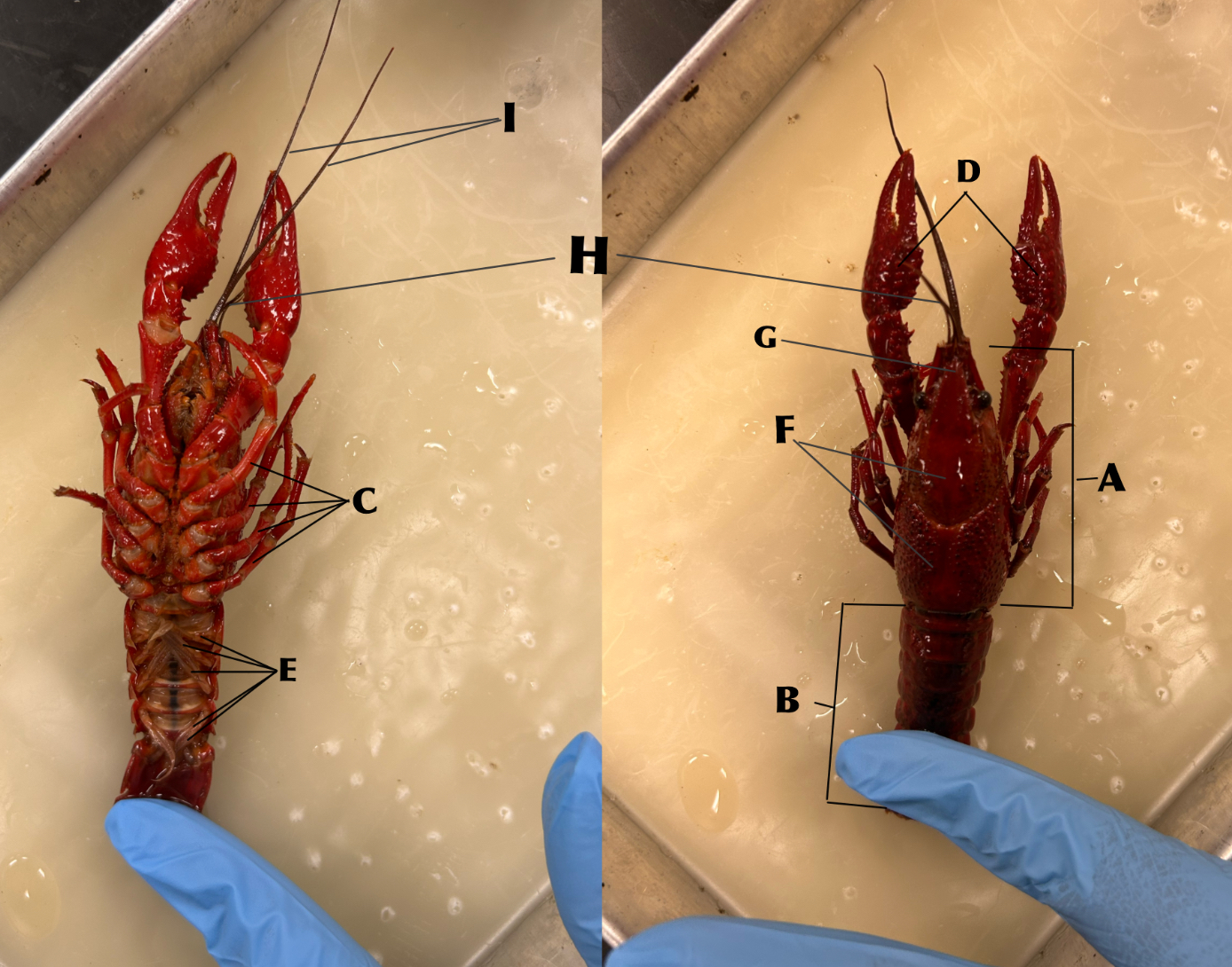

What is F
Carapace
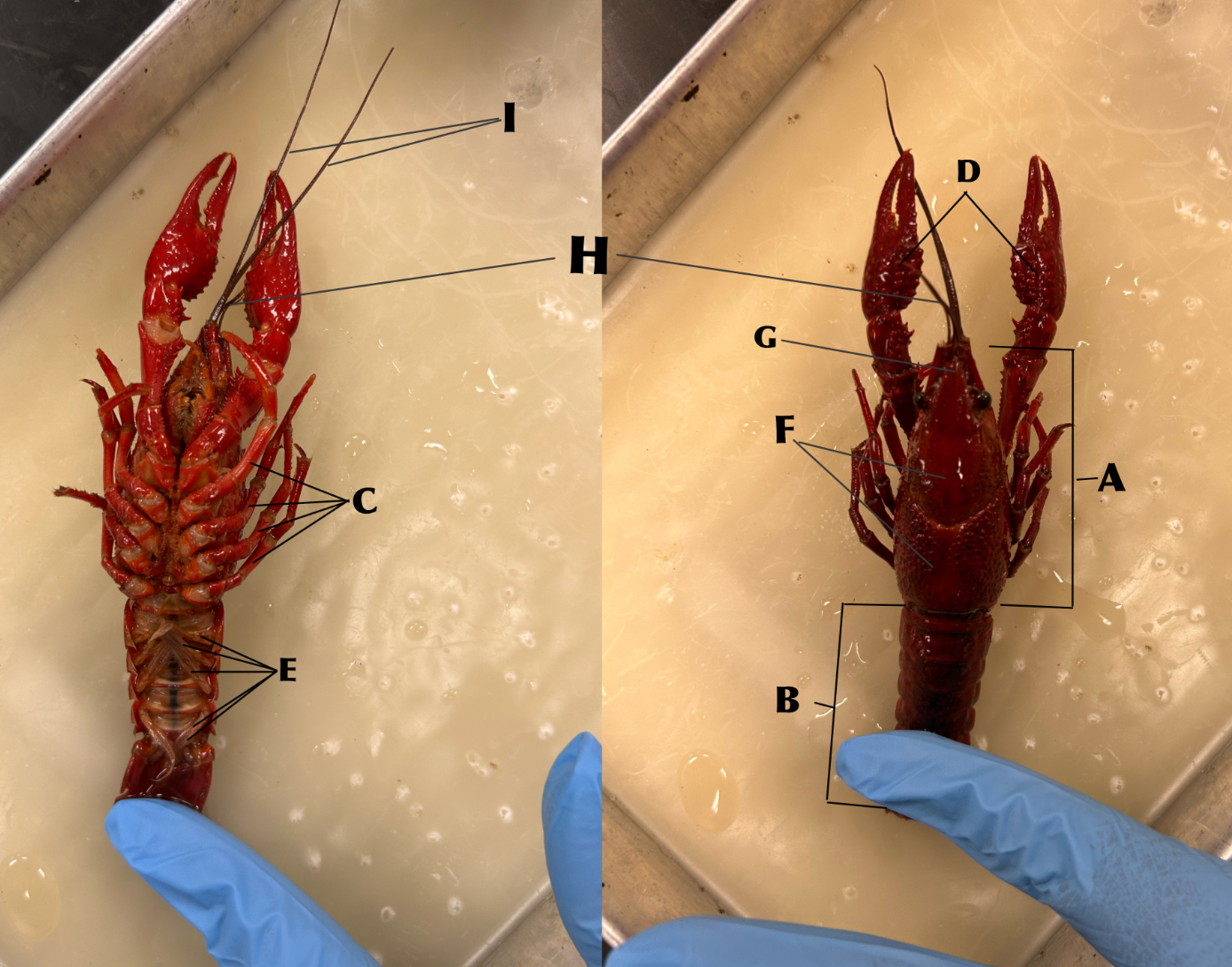

What is G
Rostrum
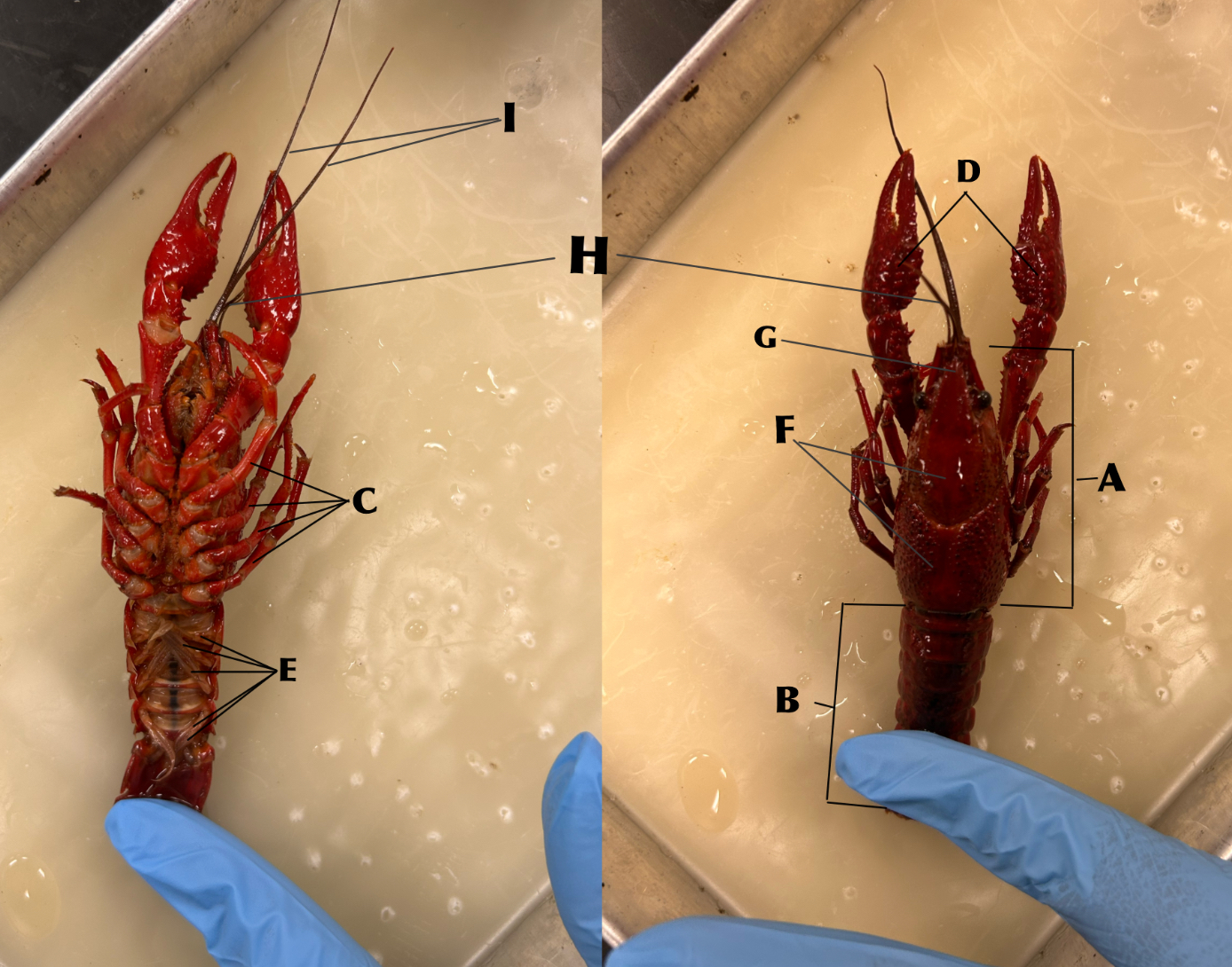

What is H
Antennules (organs of balance, touch, taste)

What is I
Antennae (organs of touch, taste, and smell)
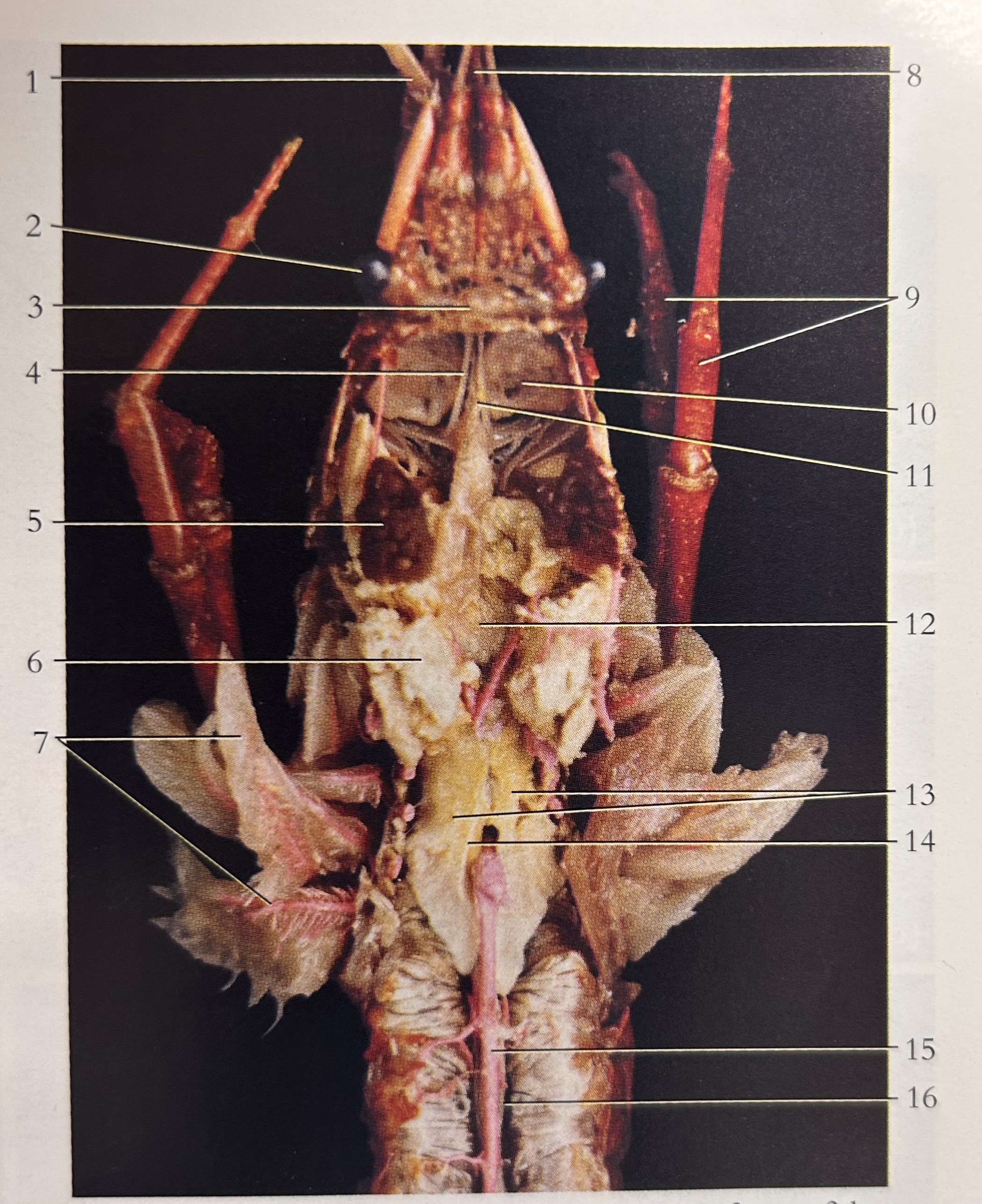
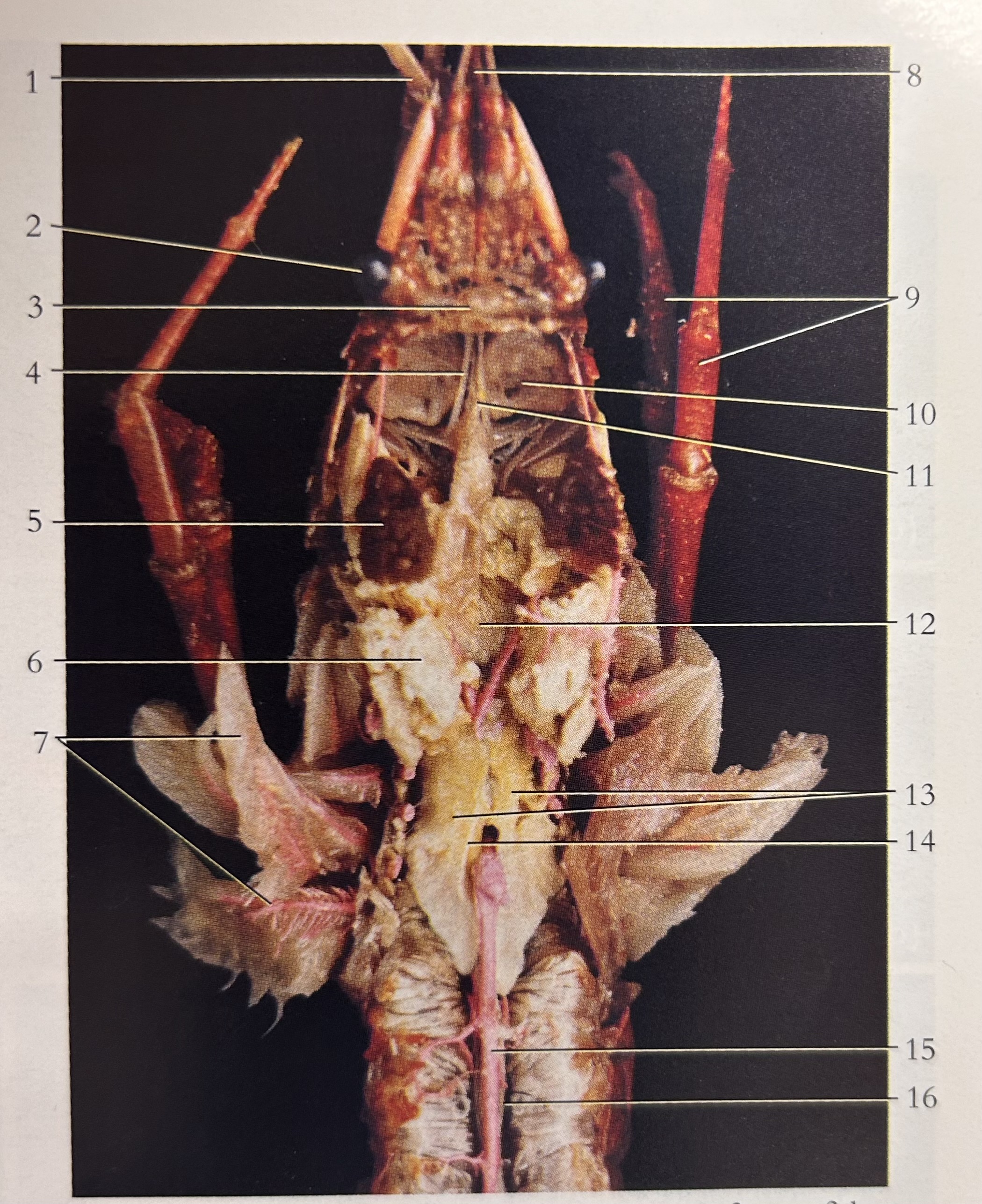
What is 16
Intestine
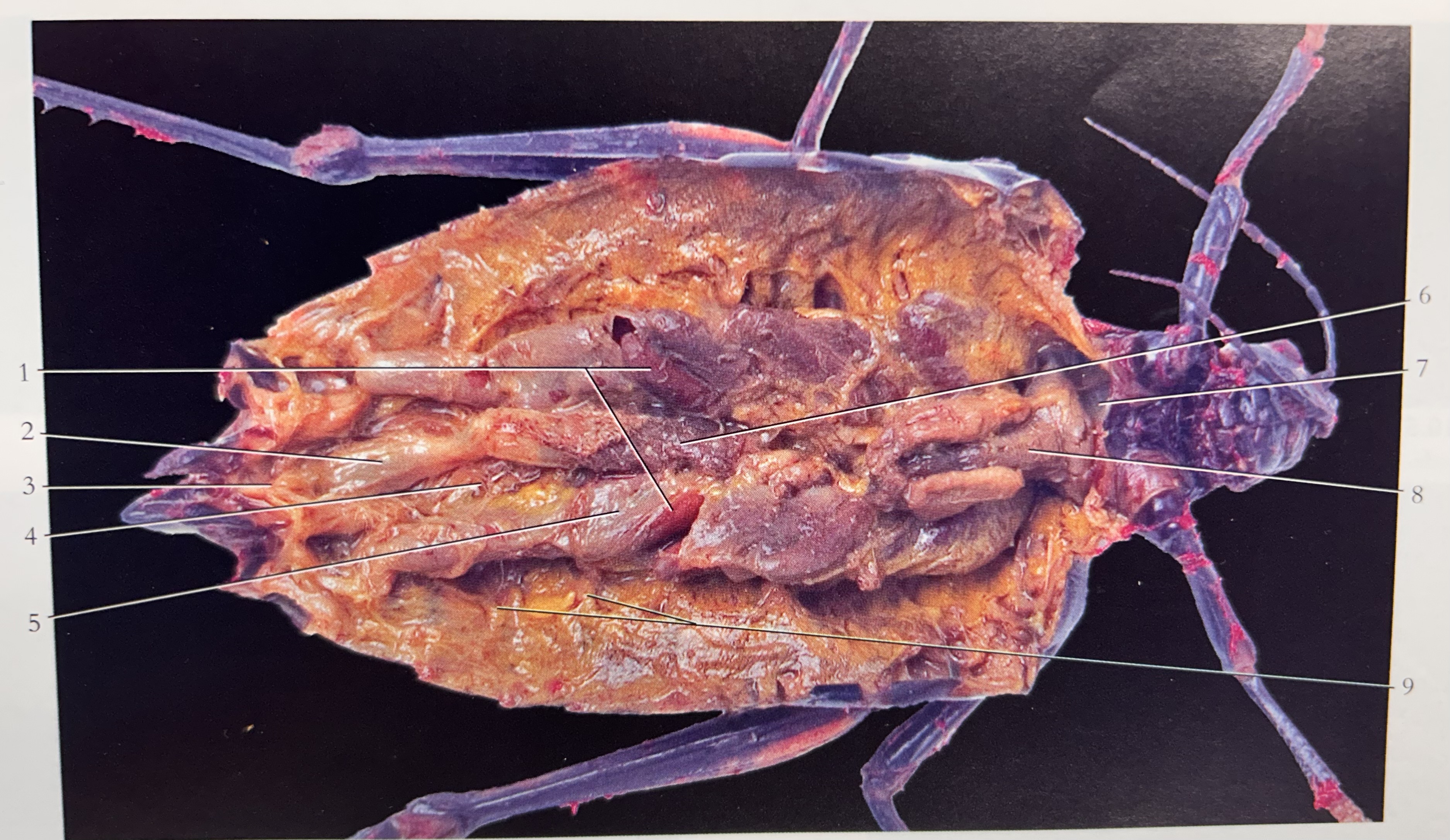
What is 1
Gastric cecae
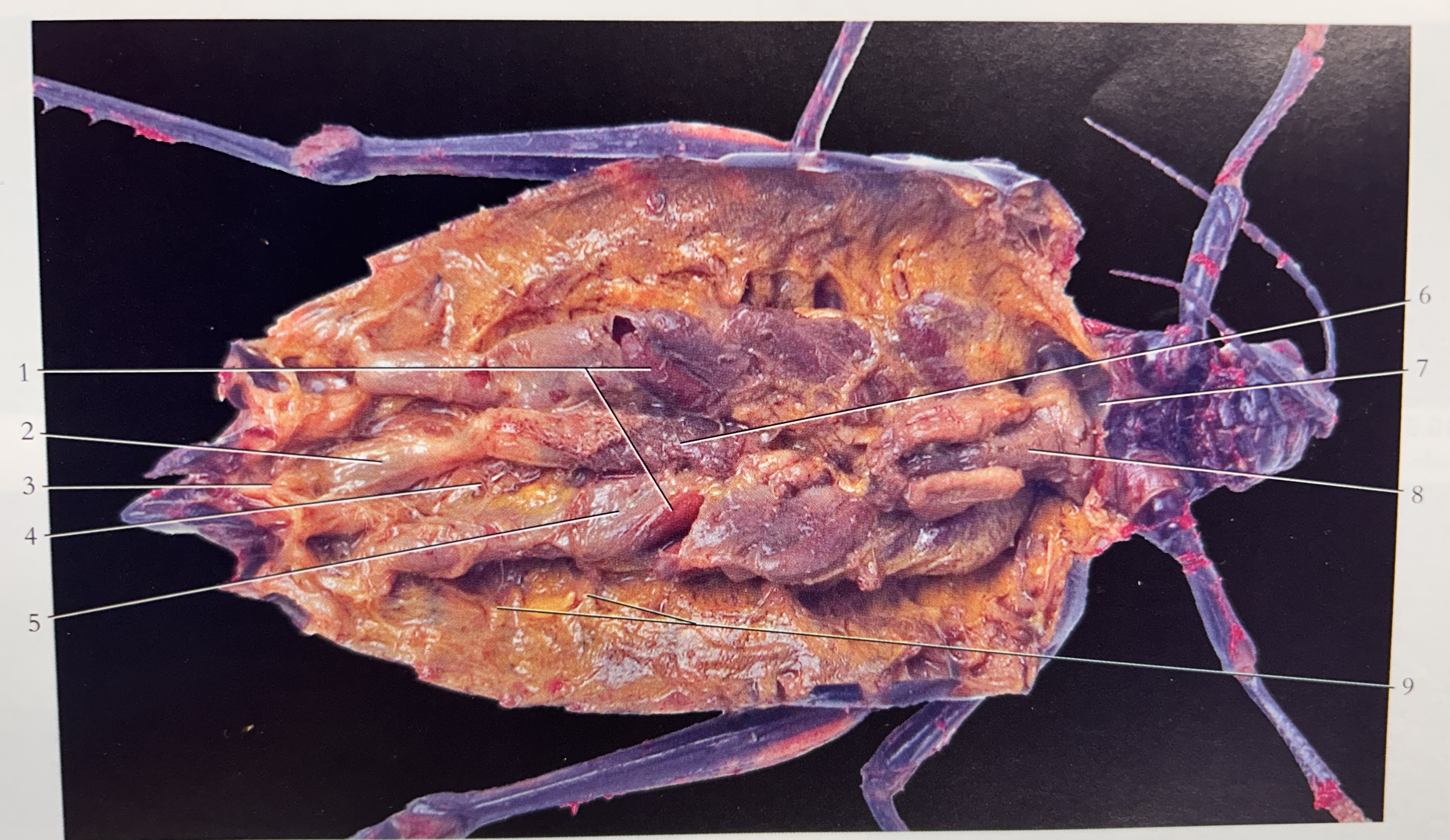
What is 8
Crop
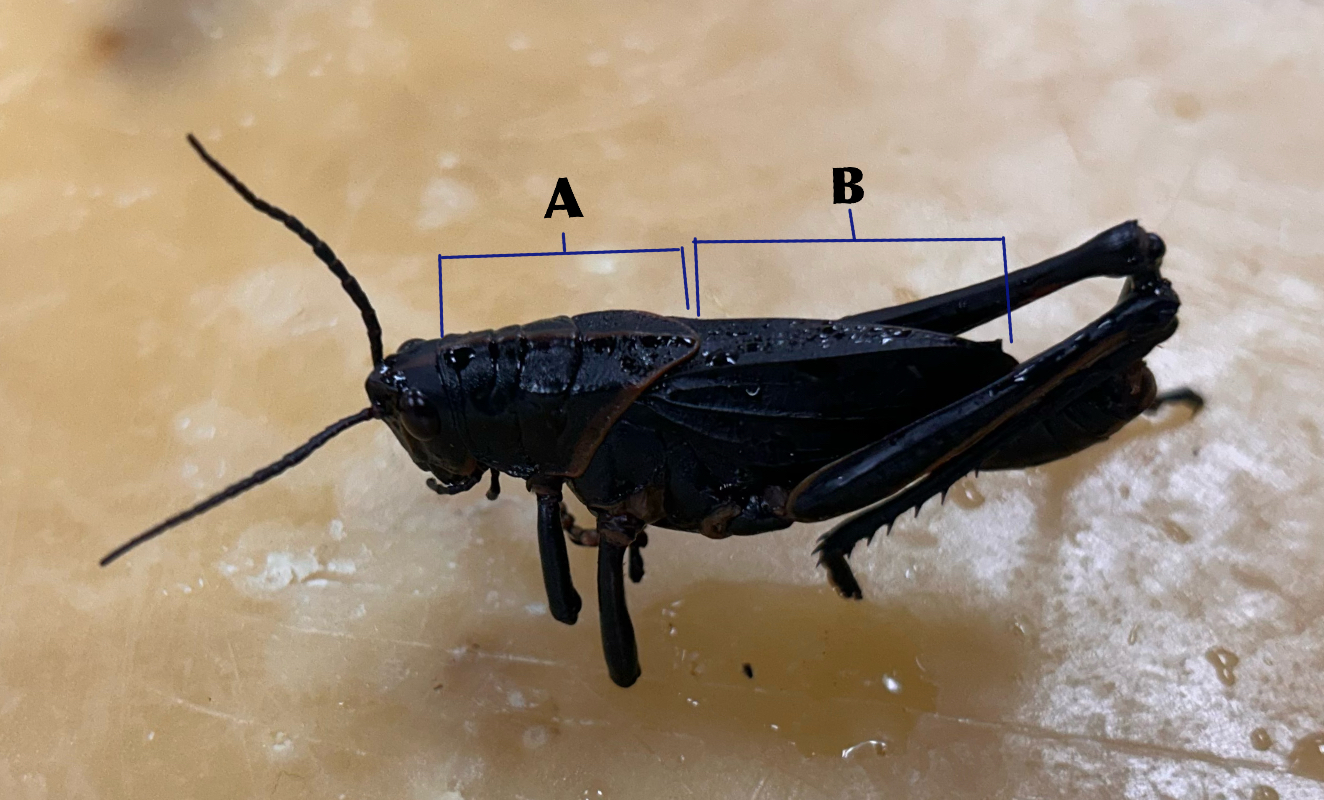
What is A
Thorax
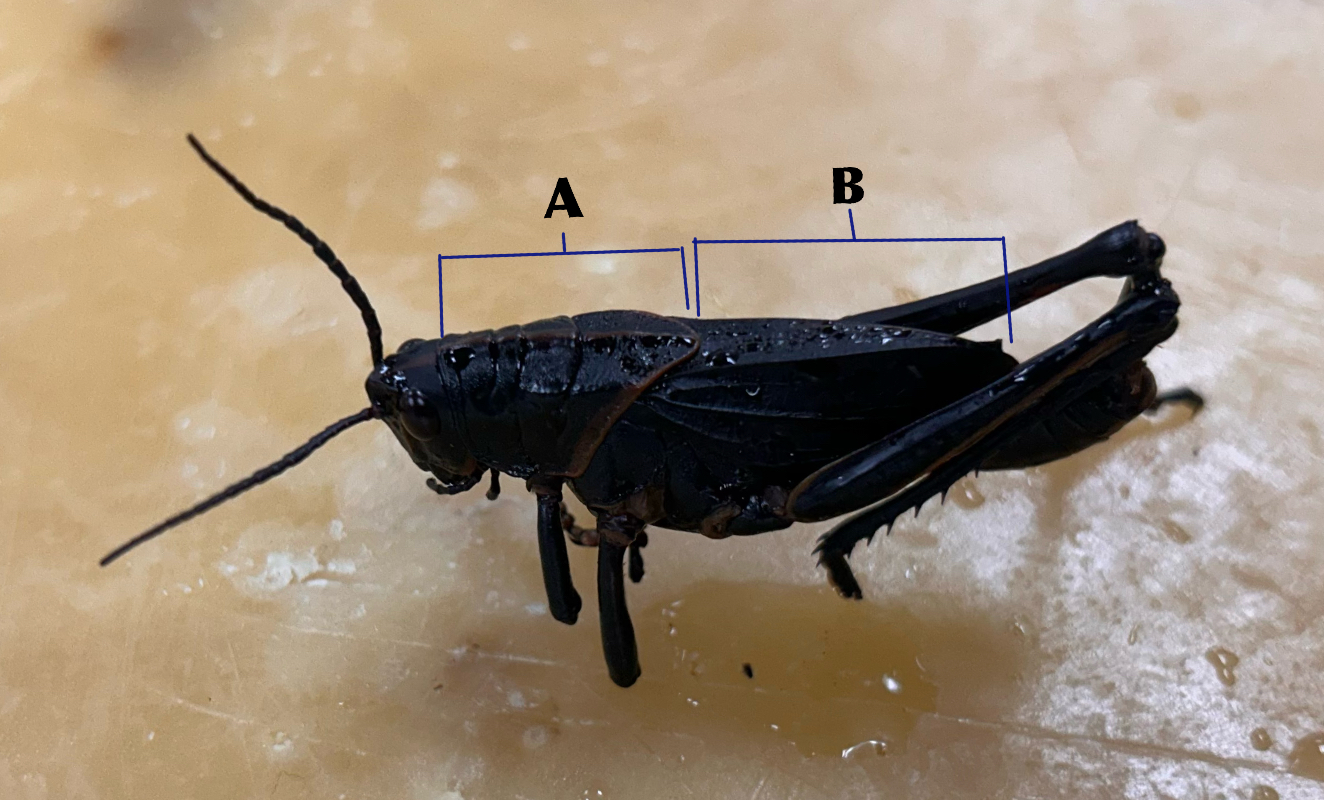
What is B
Abdomen
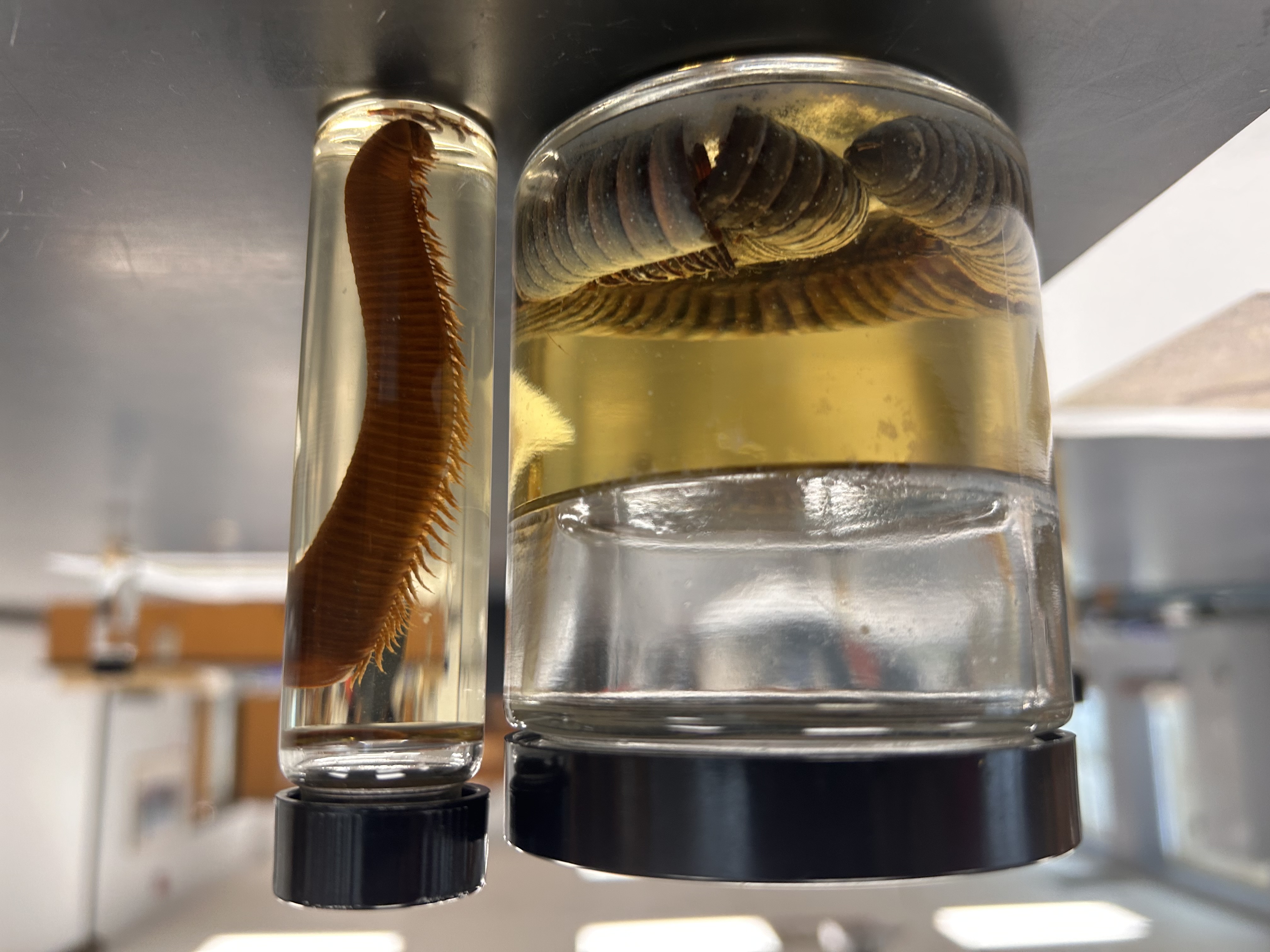

Identify the Species and what Subphylum and Class
Millipedes
Subphylum Myriapoda
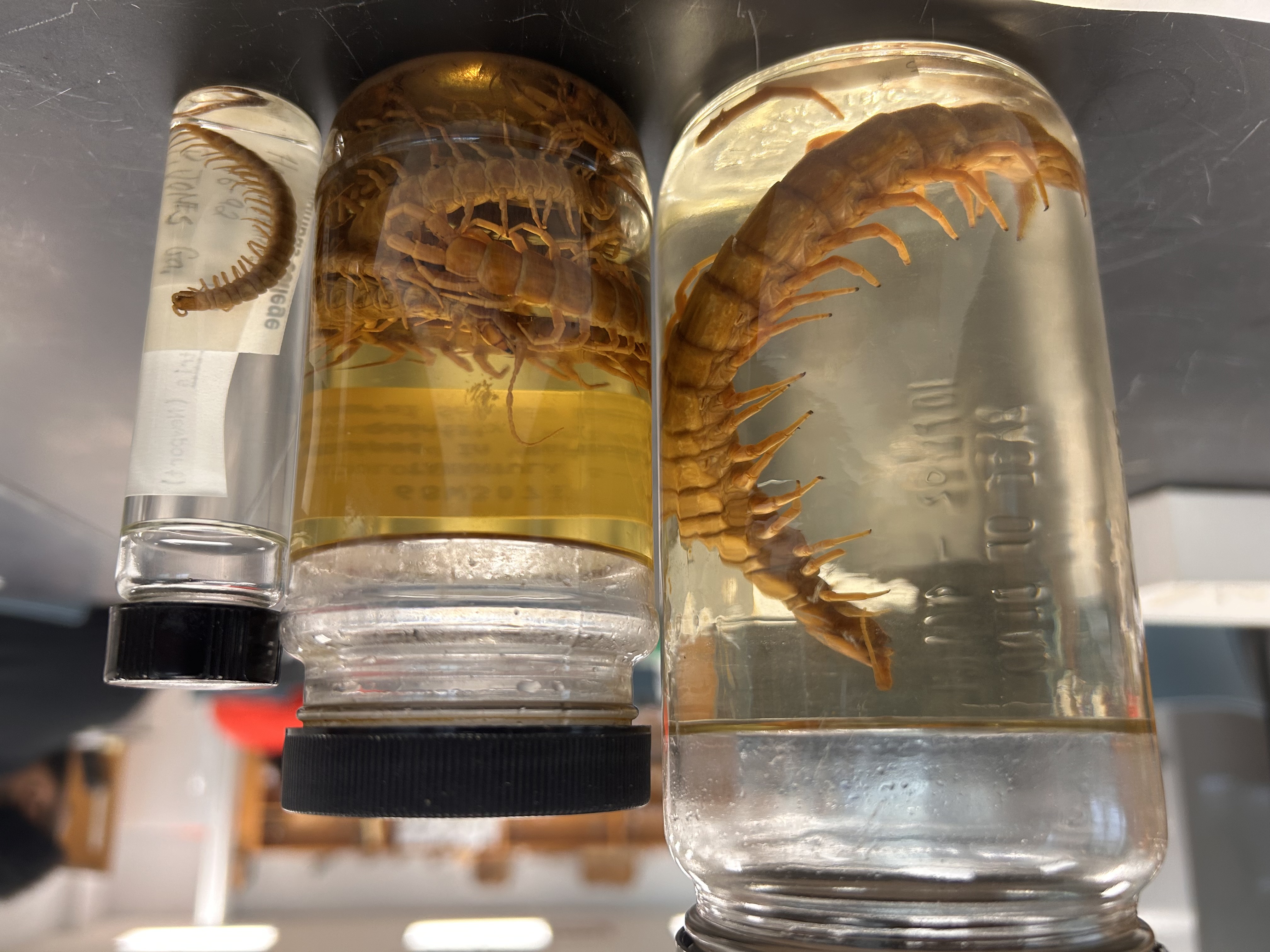

Identify the Species and what Subphylum and Class
Centipedes
Subphylum Myriapoda
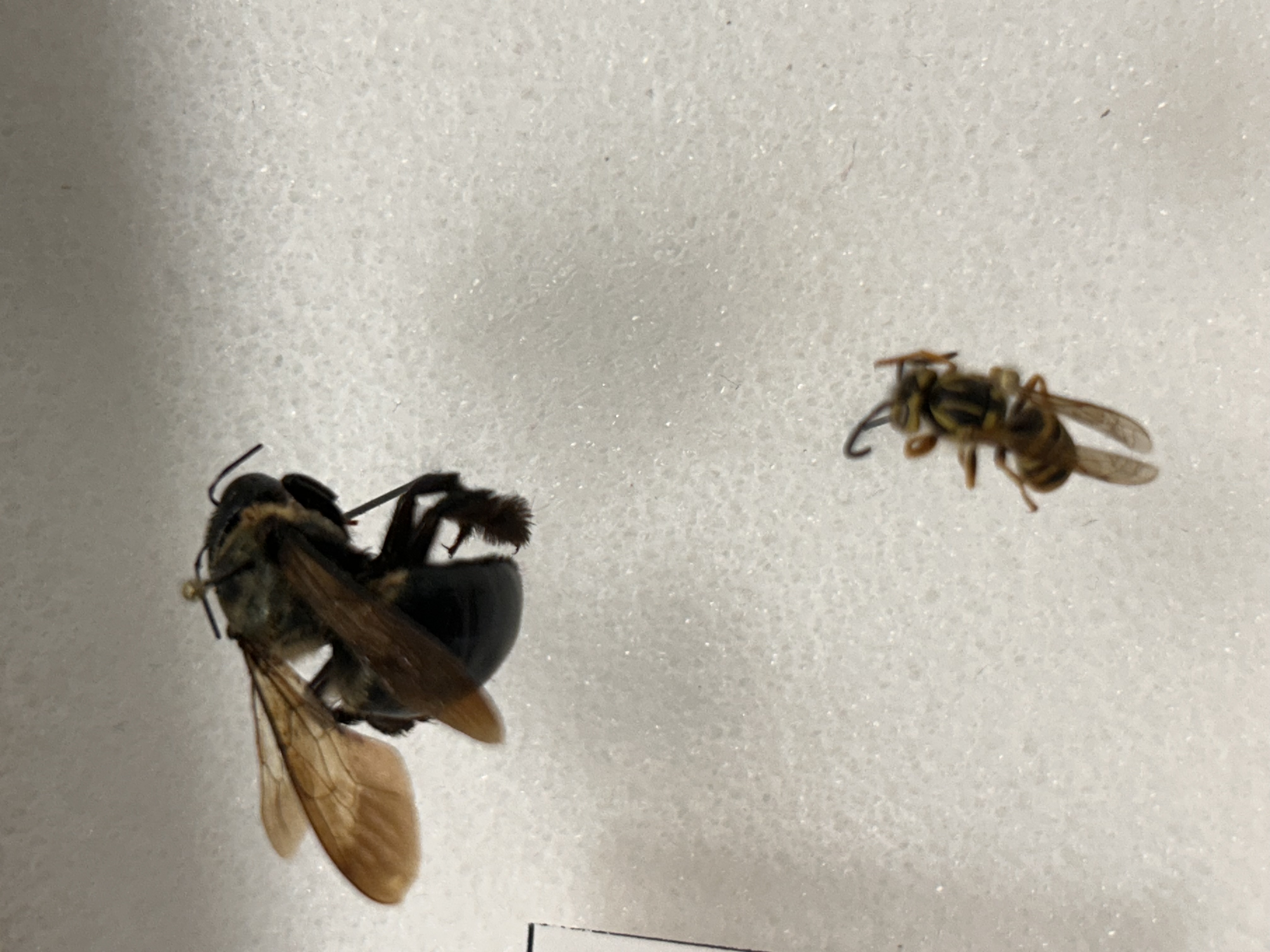

What Order and Class do these organisms belong to
Order Hymenoptera, Class Insecta
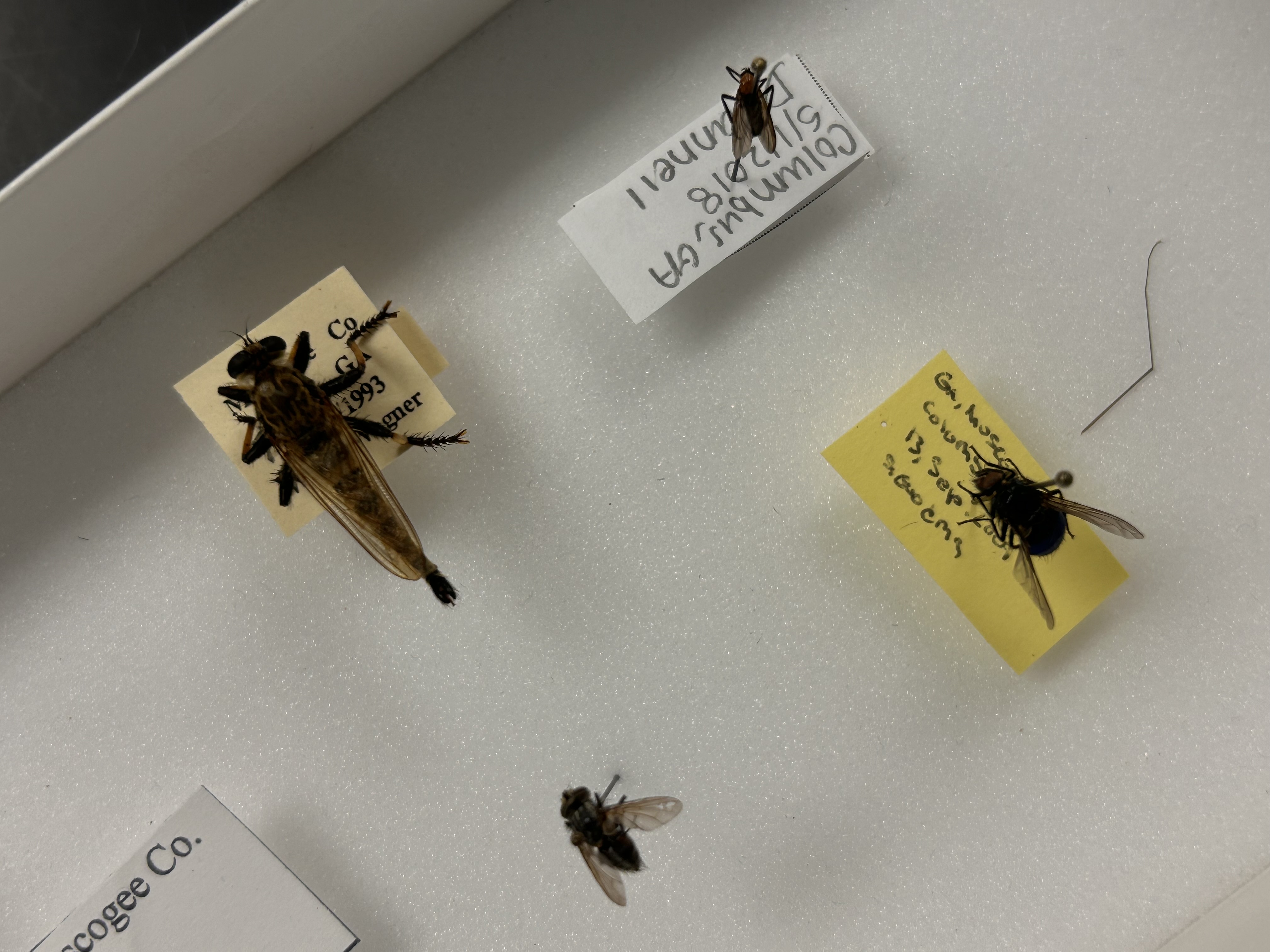

What Order and Class do these organisms belong to
Order Diptera, Class Insecta
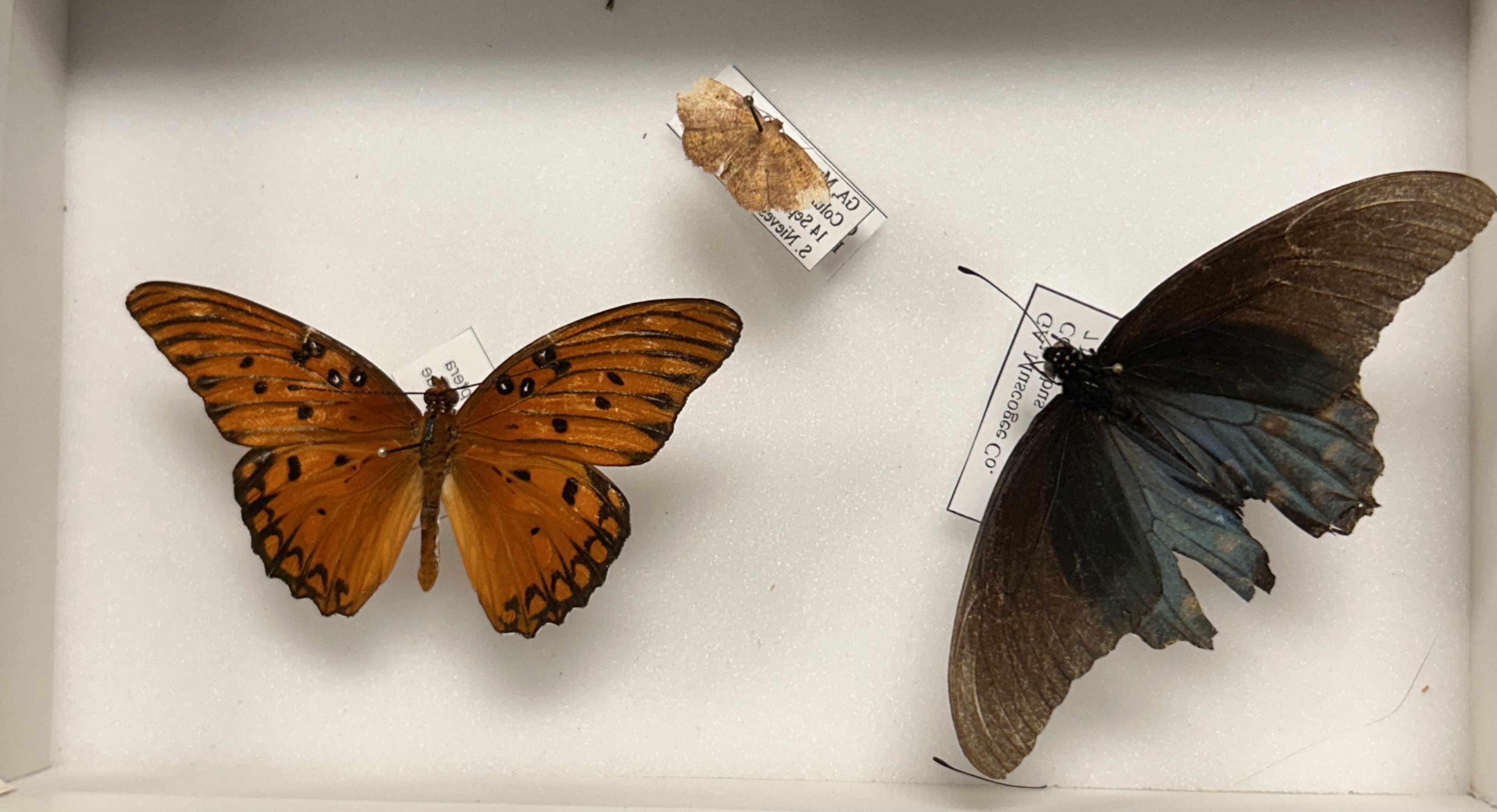

What Order and Class do these organisms belong to
Order Lepidoptera, Class Insecta
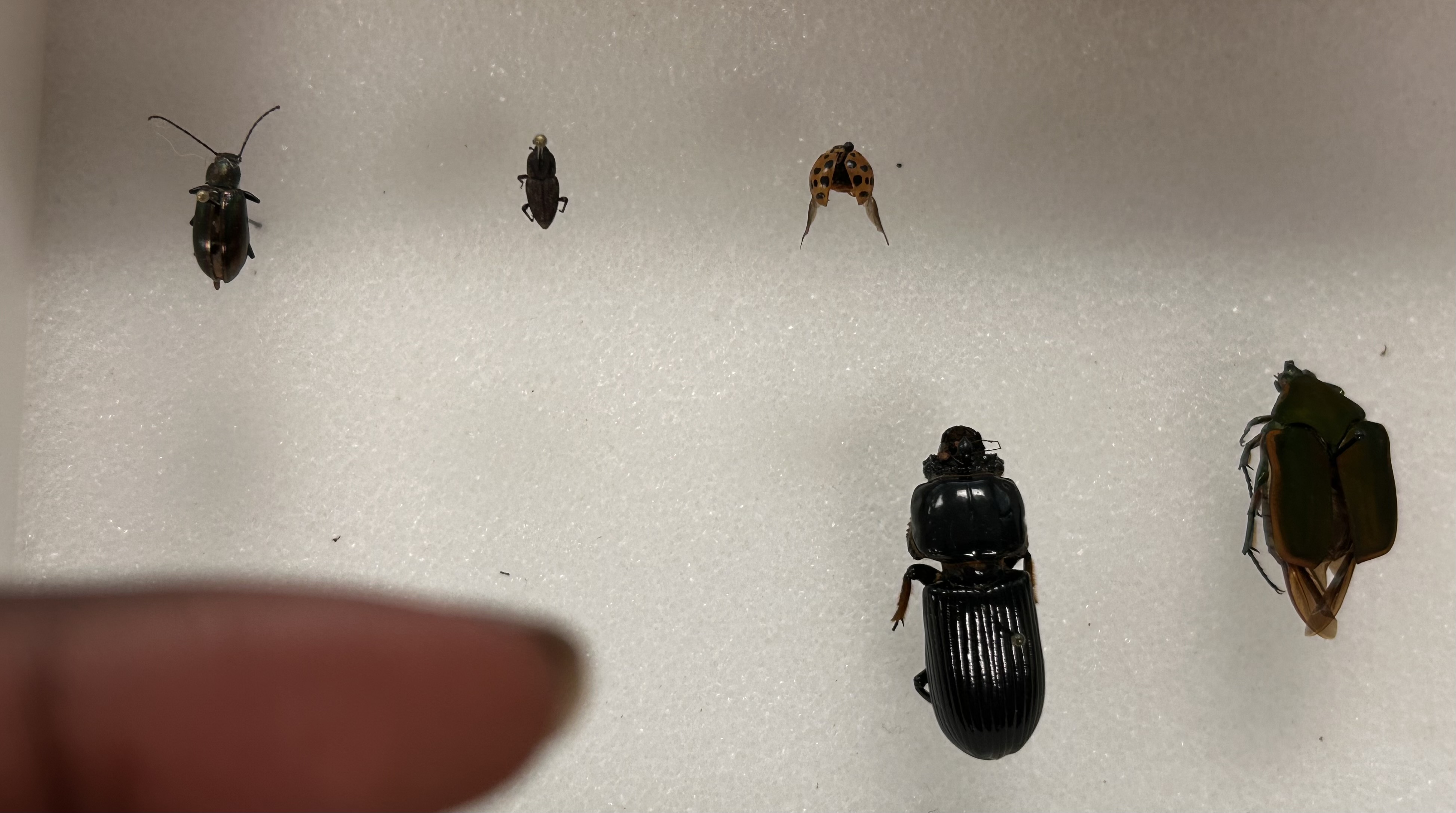

What Order and Class do these organisms belong to
Order Cloptera, class Insecta
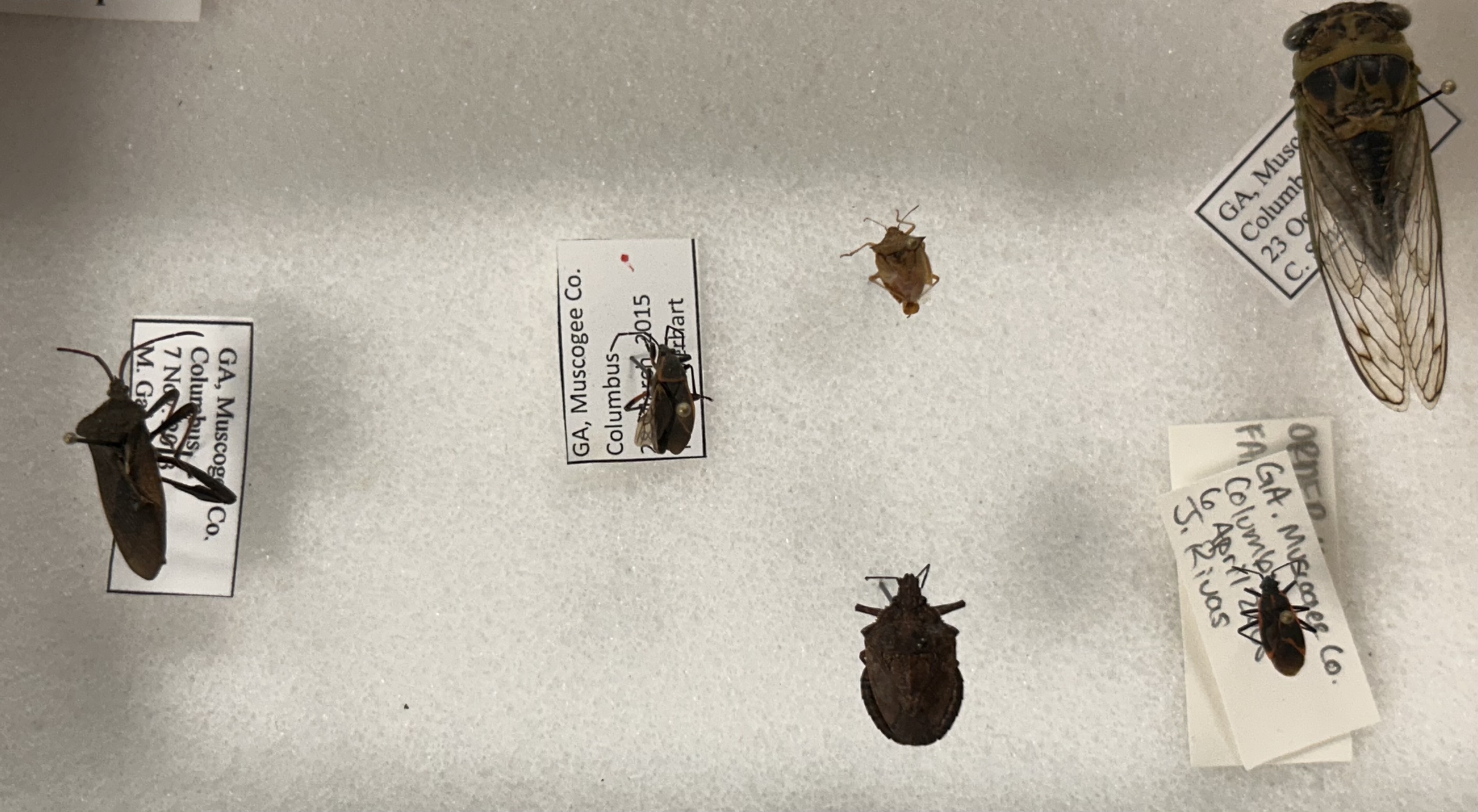

What Order and Class do these organisms belong to
Order Hemiptera, Class Insecta

What Order and Class do these organisms belong to
Order Orthopotera, Class Insecta
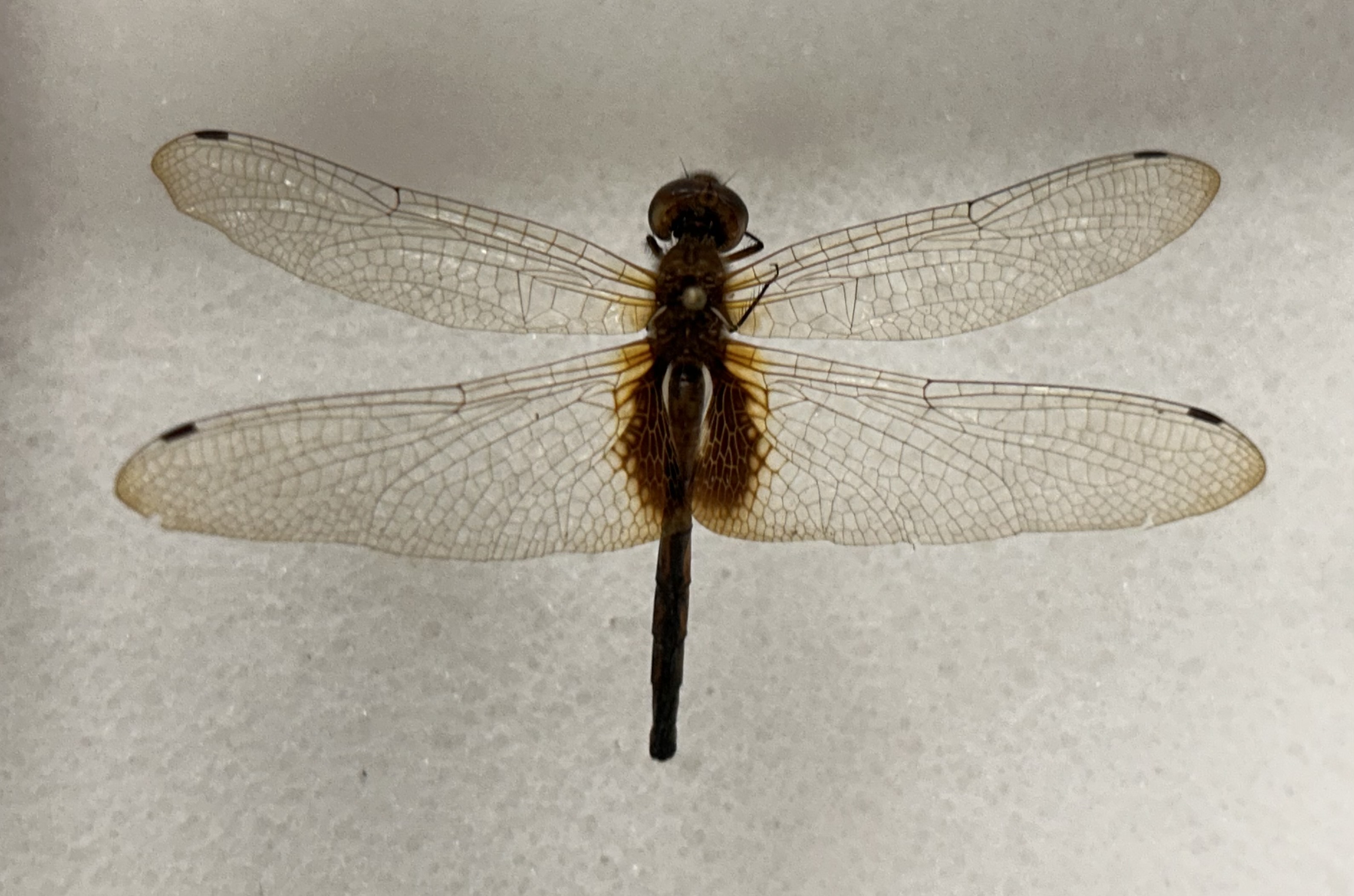

What Order and Class do these organisms belong to
Order Odonata
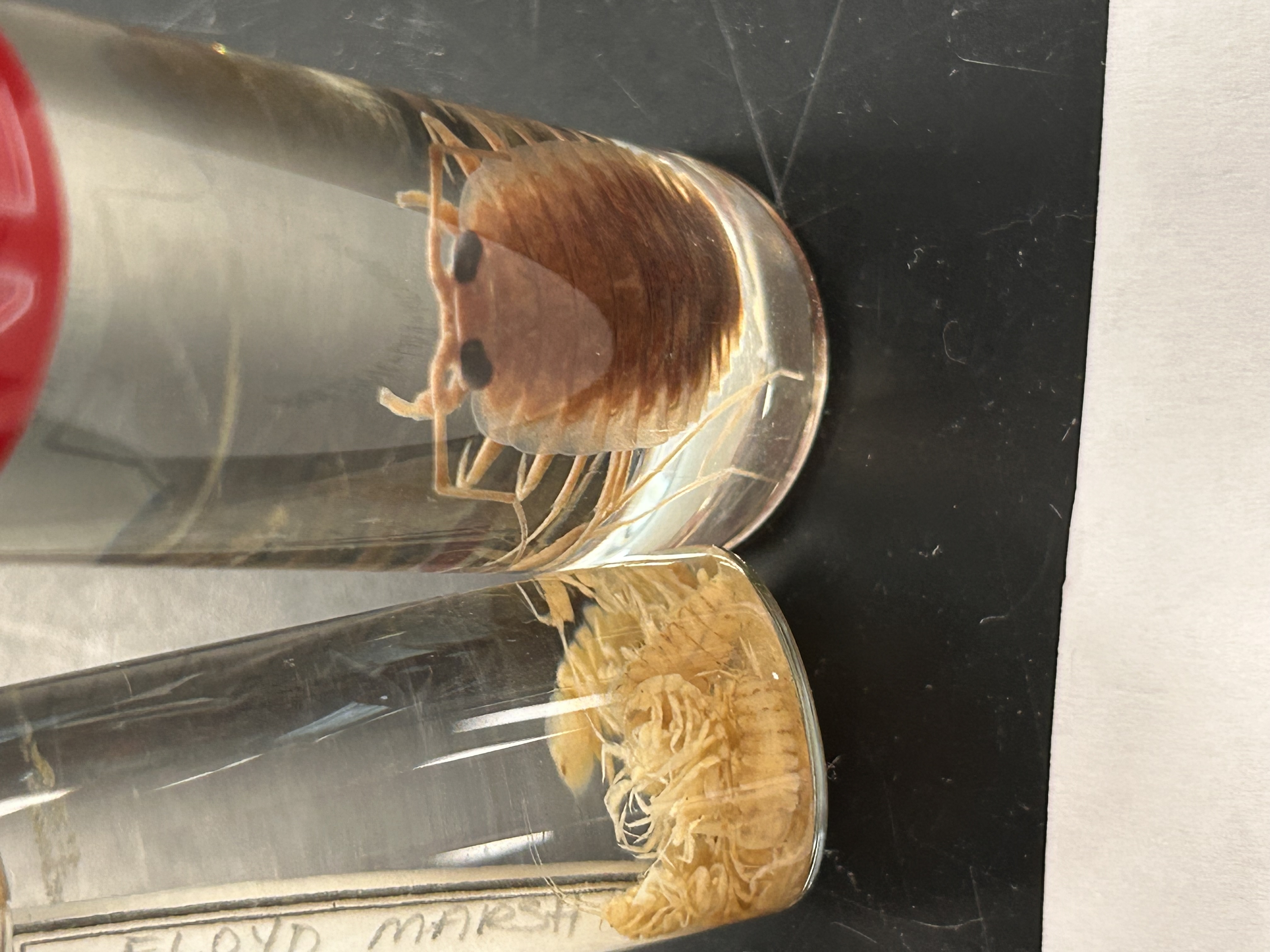

What Order and Class do these organisms belong to
Order Isopoda, Class Malacostraca
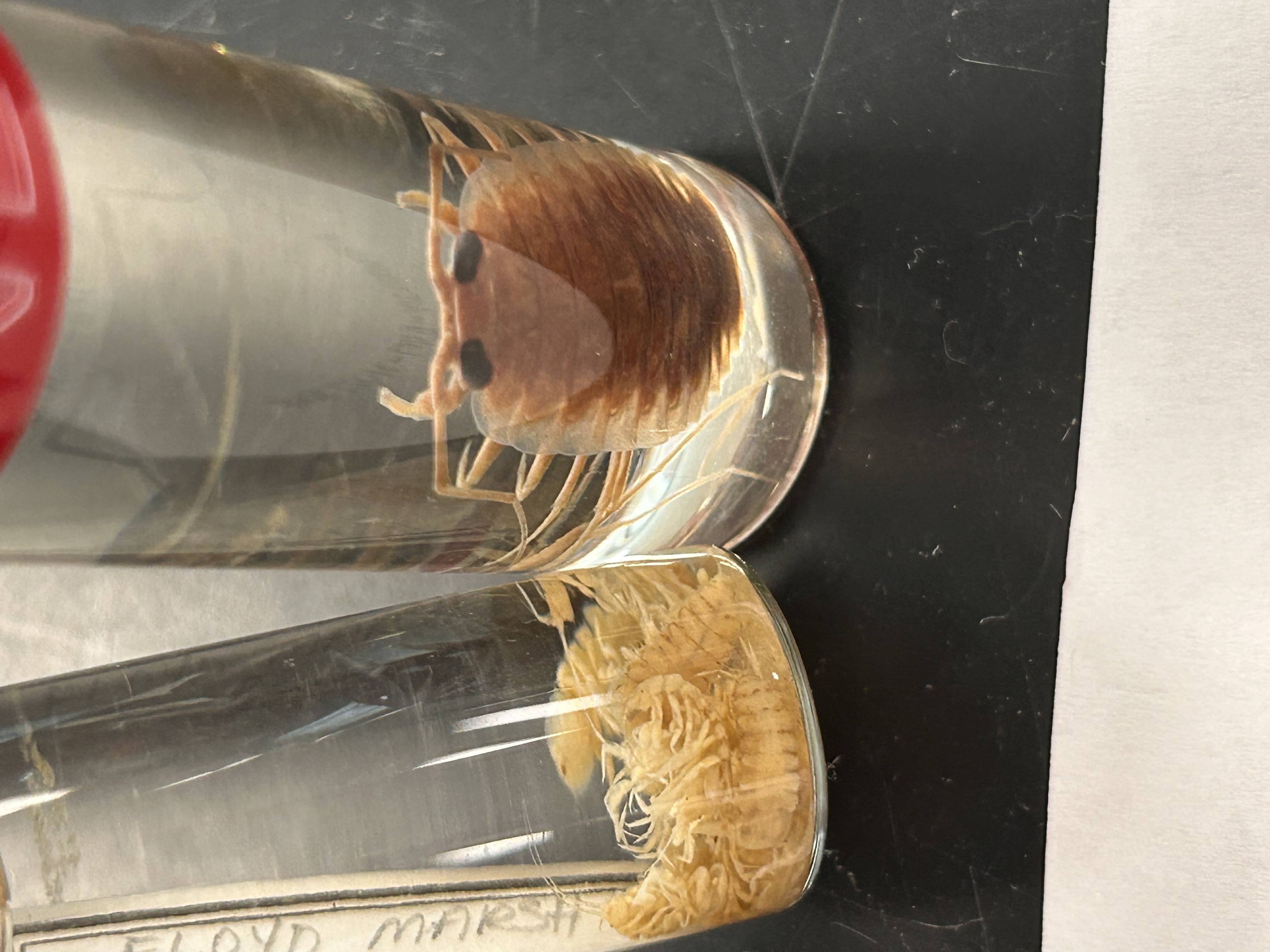

What Order and Class do these organisms belong to
Order Isopoda, Class Malacostraca
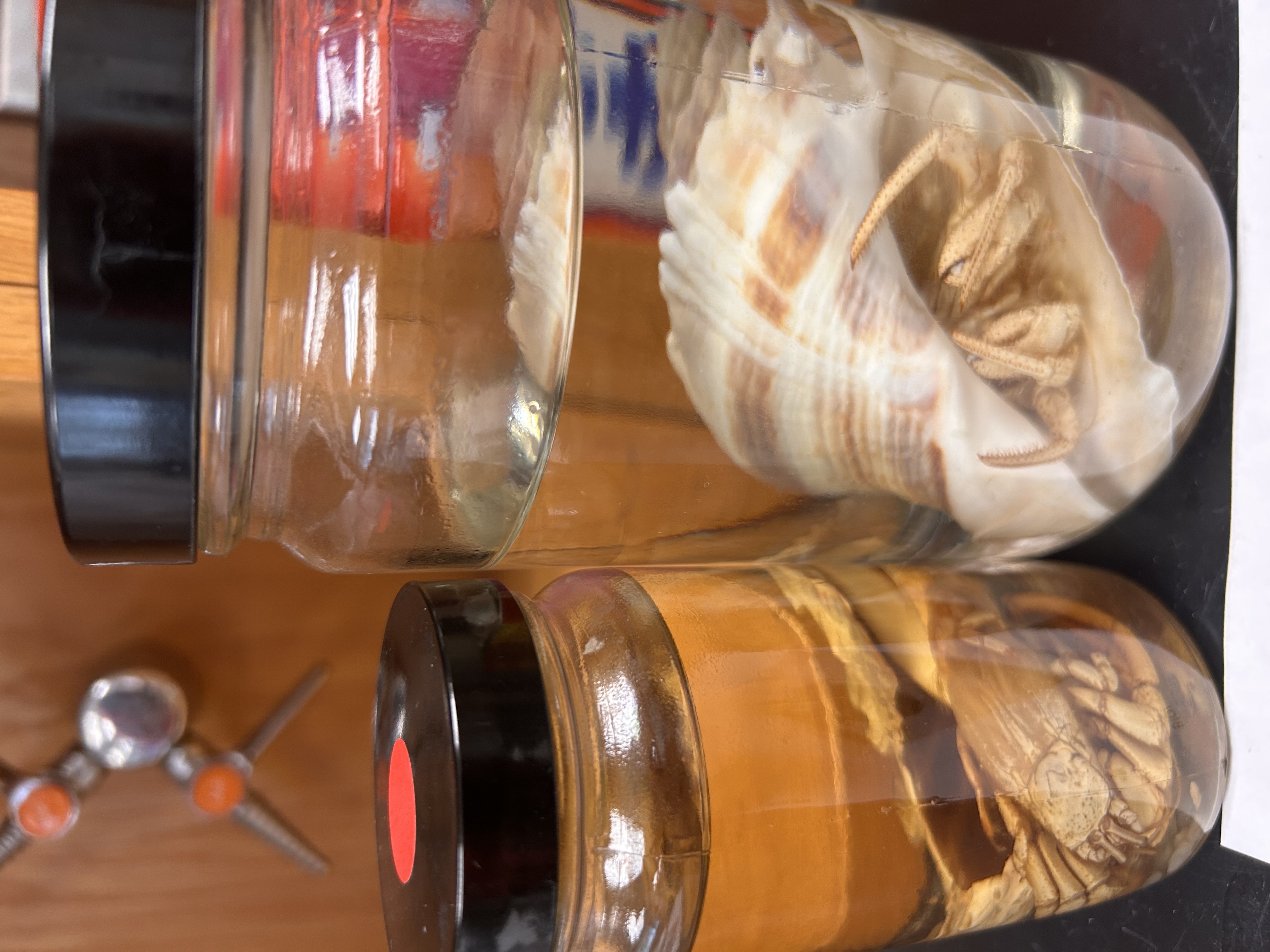

What Order and Class do these organisms belong to
Order Decapoda, Class Malacostraca