Intro to economics
1/115
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
What is economics?
the study of choices made about money, how and why it is produced, used, and traded by individuals and nations
What are two ways values are produced?
goods and services
What is a good?
items that are grown or manufactured
What is a service?
jobs or chores people do for other people. (doctor, waiter, plumber)
What are goods and services produced by?
producers
Who buys goods and services?
consumers
What kind of economics focuses on individual desicions?
microeconomics
What kind of economics focuses on whole economies?
macroeconomics
What are the two types of resources that countries use to produce goods?
natural resources and human resources
What kind of resources come from the earth?
natural resources (water, soil, air, trees)
What kind of resources are done by people and their abilites?
human resources (labor, skills, knowledge)
What is an example of a poor country?
Haiti
What is an example of a wealthy country?
The United States
What is scarcity?
a shortage of or total absence of a resource
What kind of decisions does scarcity force?
trade offs
What economic decision involves giving up one thing to get something else?
trade-off
What is given up in a trade-off?
opportunity cost
What is defined as something a person accepts as a payment for a good or service?
money or value
What are the three factors that decide the value of a price?
supply, demand, competition
What is the relationship between supply and demand?
when supply decreases, demand increases. when supply increases, demand decreases
What is supply?
the amount of a good or service available to consumers
What is controlled by supply?
producers
What is demand?
the amount of good or service consumers are willing to pay for
What is demand controlled by?
consumers
When will price be the highest?
when the supply of a good or service is low and the demand is high
When will the price be the lowest?
when the supply of the good or service is high and demand is low
When will the price decrease?
when the supply is low and the demand is low
when will the price increase?
when the supply is high and the demand is high
What is the balance between what consumers will pay and what producers charge?
market price or the “equilibrium point”
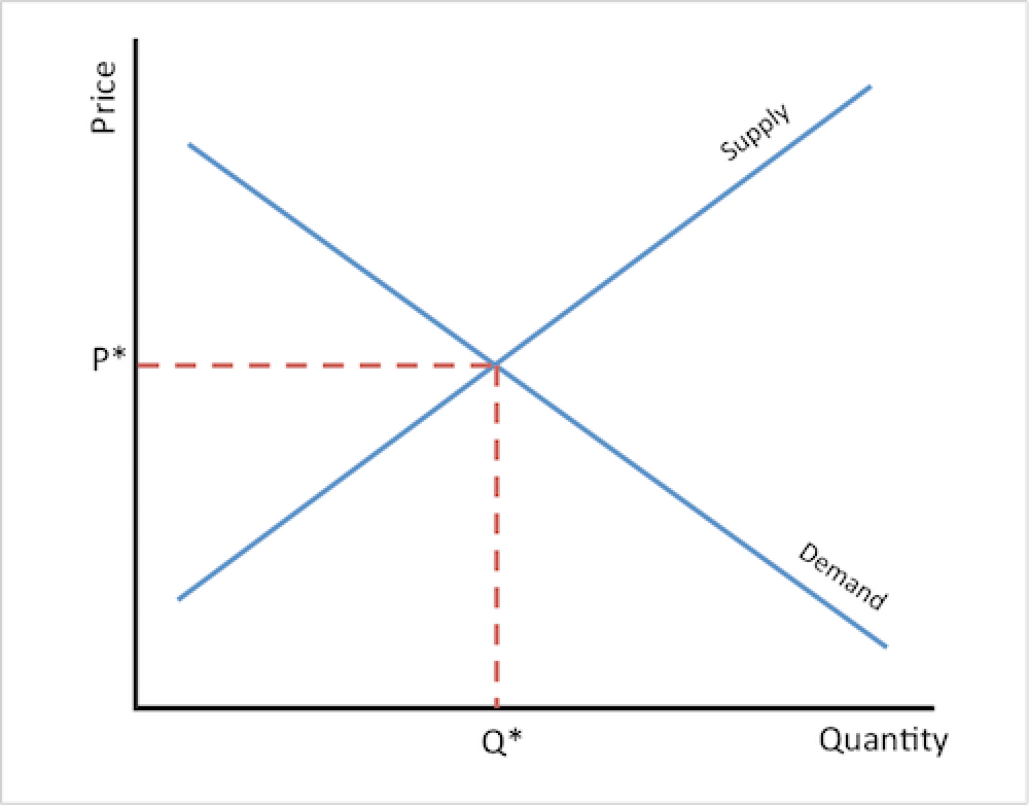
What is shown on the graph?
the equilibrium point
What is inelasticity?
the demand stays constant even though the price changes
What products exist for inelastic demand?
medicines and medical care
What are the effects of a shortage?
causes prices to rise
What are the effects of a surplus (overabundance)?
causes prices to fall
What do changes in price effect?
demand for complimentary items and substitute items
What are examples of complementary items?
sugar for tea and coffee
What is an example of a substitute item?
tea and coffee
What is does it mean when the supply curve shifts?
there is an increase or decrease in a number of sellers, or a technological breakthrough
What does it mean when the demand curve shifts?
increase in income, change in the number of buyers, or changes in prices of related goods
Why do producers sell a product at the least possible price?
to make a pre-determined profit and sell the most of that product
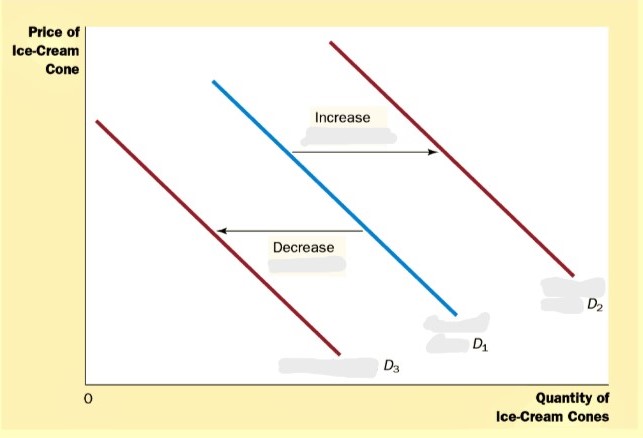
What curve is this?
demand curve
What does the demand curve represent?
consumer demand
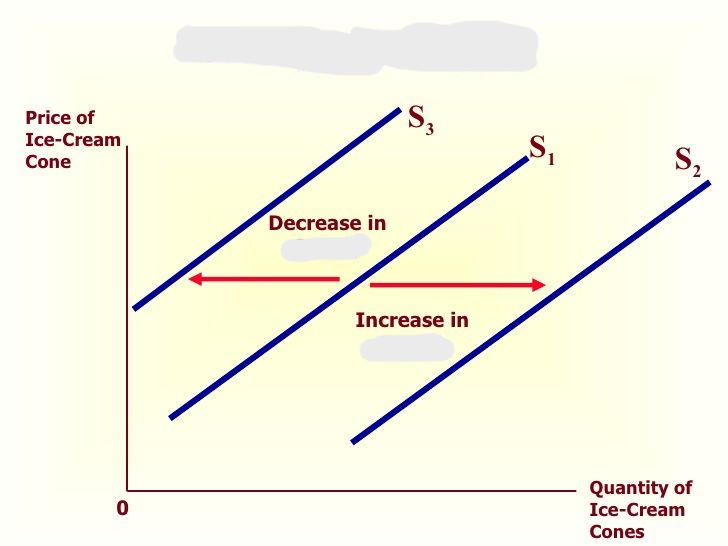
What curve is this?
supply curve
What does the supply curve represent?
amount supplied by a producer
What is competition'?
the rivalry between producers of a good or service
What are the effects of competition?
it forces producers to produce high quality products at a lower price
How is competition good for consumers?
most sellers use competitive pricing which helps consumers afford goods or services
What are the four factors of a good or service?
capital/capital goods, natural resources, labor, management
What are the machines, tools, and buildings used to produce goods/services?
capital goods
What is automation?
the act of implementing equipment with advanced technology
What do companies evaluate by measuring productivity?
output
What is productivity?
a measure of output from a production process
High productivity =
high output
high output =
more productivity for producers
What is used to supervise and plan production?
management
What is the law of diminishing returns?
at some point, the amount of extra output created by an increase in production begins to decrease
Who owns a business?
entreprenuers
What do entrepreneurs do?
risk their own money in hopes of receiving more money
What is the money remaining for a business after it has paid all of its bills and taxes?
profit
What is the total amount of money a business makes before it pays its bills and taxes?
gross income
True or false: profit is always lower than gross income
true
What is the selling of a good or service, from creating through final sale?
marketing
What does marketing include?
packaging, distribution, placement, advertising
What is one of the highest expenses when producing a good or service?
marketing is one of the most expensive
What part of marketing involves wholesalers and retailers
distribution
What are the business that buy goods directly from producers to store in a warehouse?
wholesalers
What are the stores that consumers buy products from?
retailers
What are the four functions of money?
medium of exchange, measure of value, standard of deferred payment, store of value
What does medium of exchange mean?
money is value used to buy goods and services
What does measure of value mean?
money defined by how much something is worth
What does standard of deferred payment mean?
money can be a credit that allows you to buy now and pay later
What does store of value mean?
money can be saved up and stored until needed
What is an economic system?
a system of production, resource allocation, and distribution of goods and services within a society
What are the four types of economic systems?
command economy, traditional economy, socialist economy, market economy
What is a command economy?
the government is the primary decision maker and controls production, found in communist countries
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a command economy?
advantages: low prices for consumers, everyone has a job
disadvantages: no competition means low quality goods
What is a traditional economy?
decisions are based upon tradition and tradition answers basic economic questions, commonly found in third world countries, no technology
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a traditional economy?
advantages: sense of community, lack of greed/crime
disadvantages: lacks modern technology, lack ability to handle obstacles
What are labor-intensive economies?
depend on the usage of workers to produce a good or service because they lack money to purchase machines, prone to error, more costly
What are capital-intensive economies?
use machines and technology to produce goods and services faster, better, and more profitably
What is a socialist economy?
economic system where the government owns the nation’s major industries, and individuals own smaller businesses, common in europe
What are the advantages and disadvantages of socialist economies?
advantages: stability among important national industries, lower price
disadvantages: options for going into business are limited, very high tax
What is a market economy?
economic system where economic decisions are determined by individual buyers and sellers, and the means of production are controlled by individuals, often called capitalism. there are government controls called taxes and regulations
What are the advantages and disadvantages of market economies?
advantages: high quality products at lowest possible price, opportunity to determine one’s worth and pursue a profit
disadvantages: little protection from high prices, no guarantee of employment for workers
What is a free enterprise system according to the United States?
people have the freedom to own property, people have the freedom to compete with others in business, people have the freedom to go into business and make a profit, people have the freedom to buy the best products at a low price
True or false: some countries are 100% communist, traditional, social, or capitalist
false
What does the US have for workers that most countries dont?
minimum wage
What is minimum wage in the US?
$7.25 per hour
What is the average wage in the US?
$17 per hour
What is the average wage in china and mexico?
$2.50 per hour
True or False: companies earn more profits by paying workers less in other countries
true
How did the US government attempt protect American businesses?
by placing a tariff/tax on imports from other countries
What is the NAFTA agreement?
North American Free Trade Agreement, gradually eliminated tariffs and trade barriers on products
What is the CAFTA agreement?
Central American Free Trade Agreement, a regional agreement between the US and five central American countries: Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica
What are the three business organizations producers choose from when establishing a business?
single/sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation
What us a sole proprietorship?
a business owned/operated by one person- the proprietor, 75% of businesses in the US
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a sole proprietorship?
advantages: owner sets up own hours, owner receives all profits
disadvantages: owner works long hours, owner has great personal financial risk
What is a partnership?
a business owned by two or more people, often used by doctors and attorneys, 7% of business in the US
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a partnership?
advantages: more capital to start business, workload is shared
disadvantages: disagreements among partners, financial risks
What are sole proprietorships and partnership mainly considred?
small businesses