2.3 Applying concepts underlying mendels laws of inheritance
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Inheritance
Refers to the principles regarding how traits are passed onto offspring
What does each gene for a train come in?
Varieties called alleles
Alleles
A specific copy of a gene
Example of allele
Green color of peas
Two alleles in a gene form a dominant trait must
Always be expressed or shown by the organism
dominant trait
A genetic trait is considered dominant if it is expressed in a person who has only one copy of the gene associated with the trait.
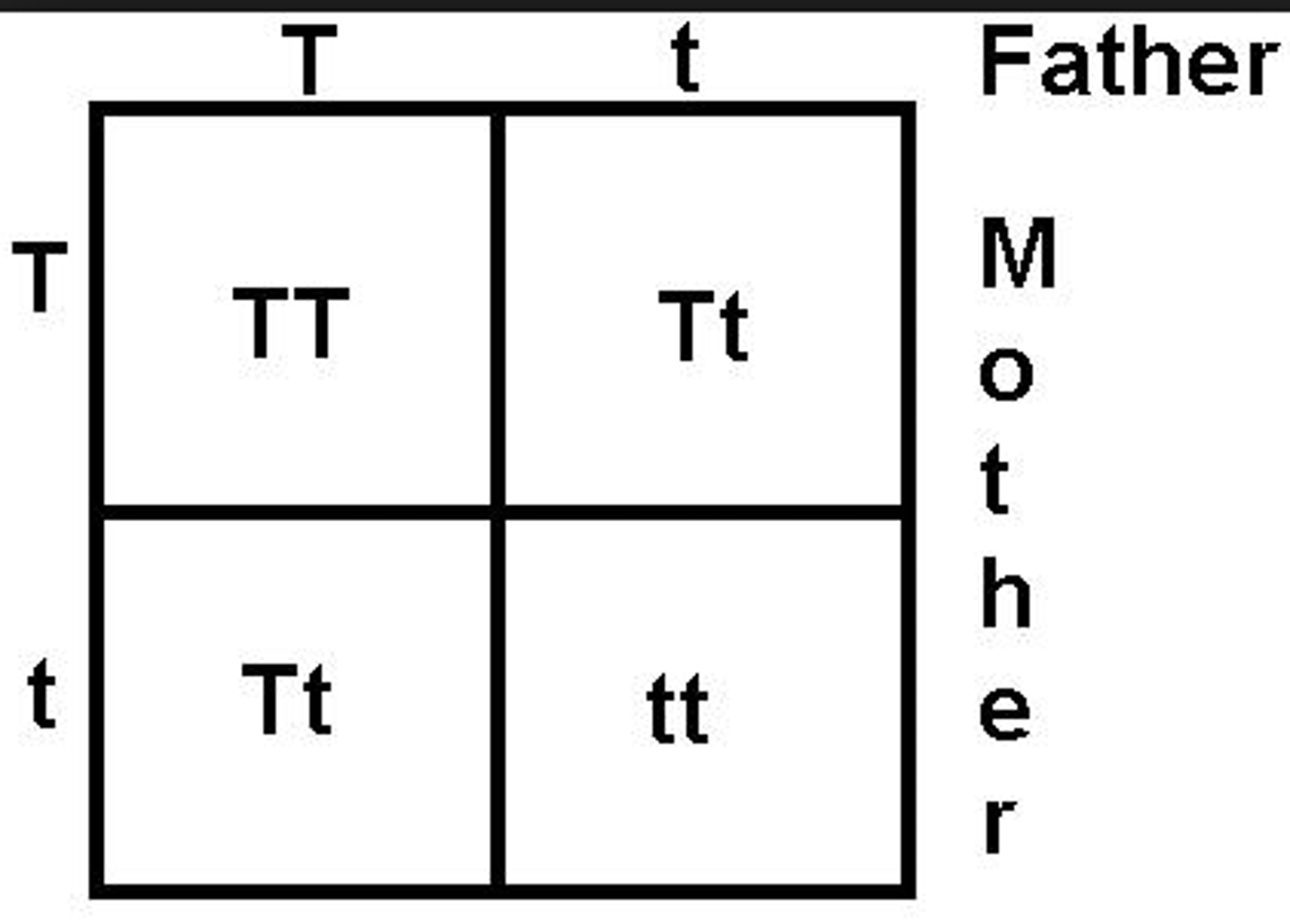
recessive trait
a genetic factor that is blocked by the presence of a dominant factor
Mendel's three laws
1. Law of Dominance
2. Law of Segregation
3. Law of Independent Assortment
How many chromosomes do humans have?
46 (23 pairs)
Combination of two alleles is called a
genotype
If a chromosome contains two alleles that are the same it is called a
Homozygous
if a chromosome contains two different alleles, that genotype is called
Heterozygous
What determines the phenotype
Alleles present in an organism
Phenotype
physical characteristics of an organism
How are inherited traits passed?
From parent through offspring through gametes
How many chromosomes does each gamete contain
23 chromosomes
What are not inherited from genome
Cultural influenced behavior
Punnet Squares are used to show
possible offspring genotypes and phenotypes
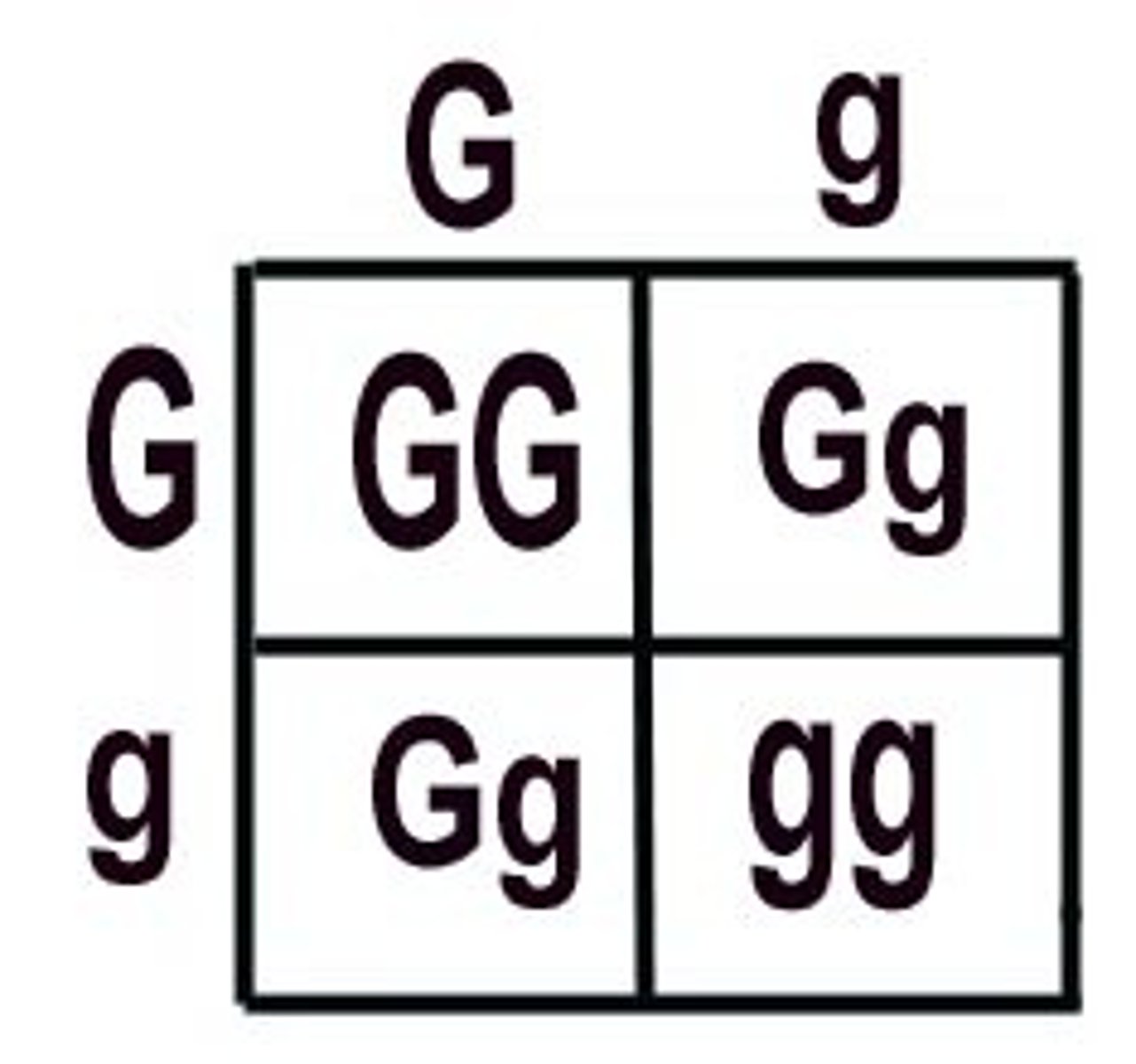
dihybrid cross
A cross between individuals that have different alleles for the same gene
The gametes that are produced by meiosis are
all genetically different
Why are cells from meiosis different
meiosis creates new combinations of genetic material in each of the four daughter cells.
Non-Mendelain Inheritance
Inheritance of traits that do not follow mendelial patterns of inheritance
When does Non-mendelian inheritance occur?
When there are factors other than dominant and recessive alleles in play