Lecture 1: RNA structure and function
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
2 jobs of tRNAs
carrying amino acids to ribosomes and translating mRNA code via their anticodon
Ribonuclease (RNAse) (what they do and 3 functions)
enzymes made of RNA that break down other RNA molecules. Functions in getting rid of unwanted RNAs, refining RNA molecules, and serving as defense against RNA viruses
In what two ways may RNAses function?
by breaking down RNAs molecules starting at one end or by working in the middle of an RNA molecule
An RNA can protect itself from RNAse attack by doing what?
forming complexes with proteins or by adding certain chemical groups to either of its ends.
t/f all living things contain RNAses
true
When making a protein — holds mRNA in place —- carry amino acids and the —- bonds amino acids together
small ribosomal subunit; tRNAs; large ribosomal subunit
t/f all living things that have been studied contain rRNA
true
An early version of — may have helped organize proteins in cells when proteins first emerged on earth
SRP (signal recognition particle)
What does bicoid RNA do in fruit fly development?
it tells fruit fly embryos exactly where to make the head
Virus
collection of genetic material inside a protein shell. Debatable as to whether or not they are alive. Unable to produce on their own ( they must hijack cellular machinery like ribosomes to copy themselves)
Viruses carry genetic info as — or —
DNA or RNA
— viruses usually evolve faster. Why?
RNA; RNA is less stable and more mutation prone
—- is a component of the strongest nanomotor on earth which does what?
pRNA; packs genetic info into a virus’s protein shell
Capsid
outer protein shell of a virus
pRNA
packaging RNA. gathers tiger with ATPase motors and uses energy from ATP to form a ring that acts like a gear in a powerful motor to stuff viral genetic info into the capsid
Two main steps of RNAi in bacteria
detection of invading viral RNA via specially evolved RNAs and proteins and chop them up and then another set of RNAs pick up chopped viral RNA in order to use it to identify other viral mRNA and chop them up before they are translated
RNA “computers”
theoretical RNA treatment in which RNA riboswitches detect a molecule present only in infected cells and switch shape into a form that activates cell death, killing the diseased cell
The arrival of —- in multicellular life-forms likely sped up evolution
alternative splicing
Base pairs that may be found in RNA from strongest to weakest
GC, AU, GU
In a double stranded piece of RNA made of just AU base pairs, what would maximize its strength?
if the base pairs were arranged in a zipper like pattern
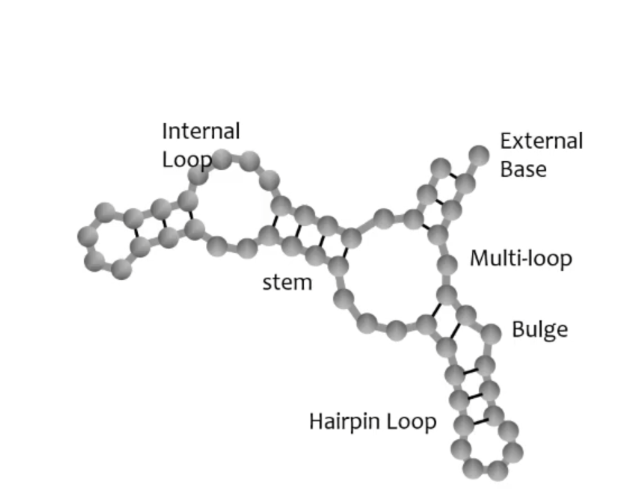
Common elements of RNA secondary structure
stem, loop and bulge
An RNA loop is most stable (boosted ) if there is a — at the —--
G at the 5’ ends of the loop
A riboswitch is a — that can do what?
RNA that can adopt two different stable structures
A riboswitch may not be completely made of —- pairs (it would not be able to switch shape).
GC pairs
Stable RNA fold has (minimal or maximal) free energy
minimal
Genomes be made of what different molecules?
DNA or RNA
For which organisms may genomes be made of RNA?
viruses
May genomes be made of protein?
no
What molecules may have enzymatic activity?
RNA or proteins
Which type of RNA was the first that led to life?
self-replicating RNA
How may RNAi be useful as a research tool?
is may be used to inactivate genes one at a time to identify their function
Components of RNA nucleotide
ribose, phosphate, and a nitrogenous base
RNA is (more or less ) stable than DNA
less
t/f DNA can form more shapes than RNA
false
Show the difference in Watson-crick base pairing and Hoogsteen base pairing of AT and GC
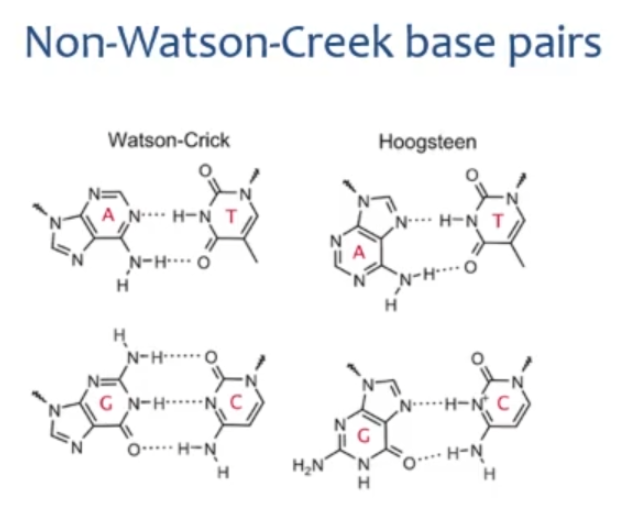
Hoogsteen pairing may allow RNAs to form a —- with DNA
triple helix
RNA has a lot of —--- bases not found in DNA
unusual
Most common unusual base in RNA
pseudouridine
Unusual bases are formed from —- of RNAs and the are most common in what type of RNAs?
post-transcriptional modification; tRNAs (and other noncoding RNAs)
Why do RNAs have lots of unusual bases?
they may stabilize RNA scondary/tertiary structure and/or affect function
There are around — RNA modifications known
100
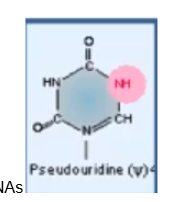
Pseudouridine
most common RNA modification. Common in tRNAs
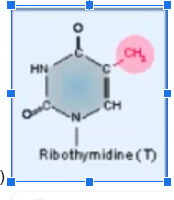
Ribothymidine
RNA modification in which uracil is methylated (creates thymine in RNA strand)
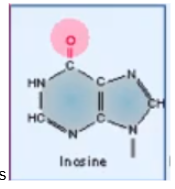
Inosine
RNA modification that is important to protein synthesis
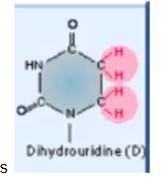
Dihydrouridine
one of the more common RNA modification
Primary structure of RNA
sequence of the RNA
Secondary structure of RNA
RNA structure formed by canonical base-pairing (loops and stems)
Tertiary structures of RNA
3D structure of RNA
—- and —- are both essential for RNA function
specific sequence and 3D structure
Label the structures of this RNA
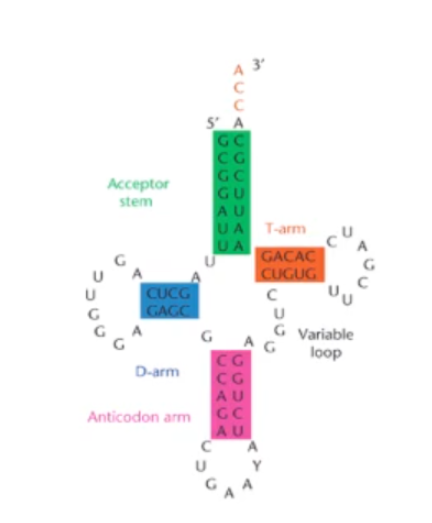
Label the structures of this RNA
Secondary structures are generally more — than tertiary
stable
Canonical base pairs of RNA
GC, AU, GU
Stable secondary structure of RNA minimize —--
free energy
How is the Gibbs free energy approximated in RNAs?
approximated as the sum of contributions from secondary structures
Sequences of ncRNAs are (more or less) conserved than their secondary structures
less
In what type of RNA is sequence more conserved than other RNAs and why?
mRNAs as their sequence holds the code for making proteins
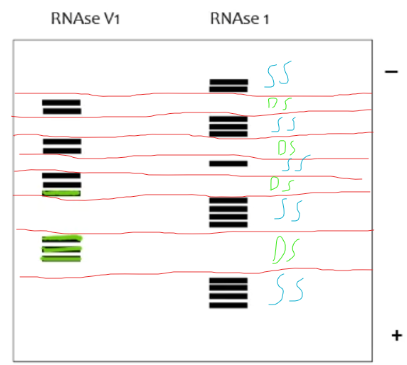
RNAse digestion assay
RNA secondary structure assay in which the an RNA molecule that is labeled at the 5’ or 3’ end is partially digested by endonucleases (RNAse) at either the double stranded or single stranded areas (depending on the nucleases used) of the molecule. When you run the ss digested RNAs and the ds digested RNAs on a gel, you can tell which areas of the RNA are double stranded and which areas are single stranded
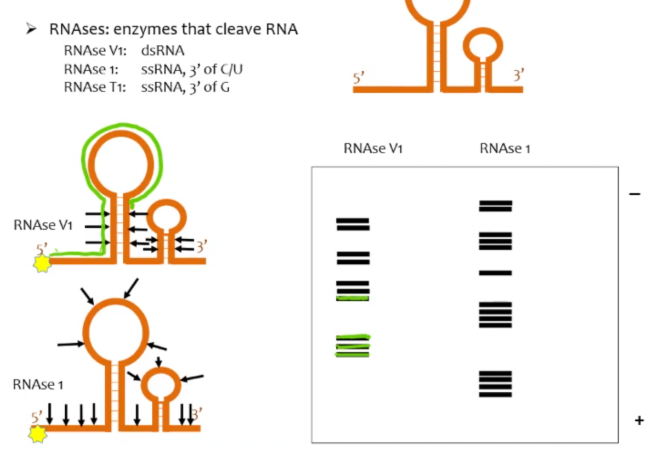
In a RNAse digestion assay, if digested by an endonuclease that targets dsRNA, what would gaps vs bands indicate on the gel?
gaps on the gel indicate single stranded regions of the RNA while areas with groups of bands indicate areas with dsRNA
In a RNAse digestion assay, if digested by an endonuclease that targets ssRNA, what would gaps vs bands indicate on the gel?
gaps on the gel indicate double stranded regions of the RNA while areas with groups of bands indicate areas with ssRNA
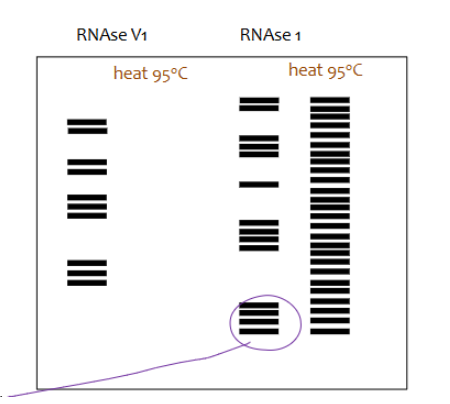
What happens if RNA is heated to 95 degrees C and an RNAse digestion assay is done on it?
there will be no bands on the gel associated with the RNA digested by ds digesting endonuclease but there will be lots of bands on the gel associated with the RNA digested by ss digesting endonuclease. This will tell nothing about the RNAs native secondary structure.
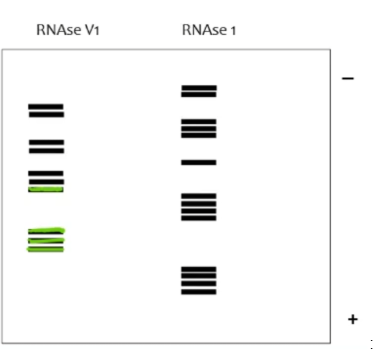
On this RNAse digestion assay gel, label which areas of the RNA are ssRNA and which are dsRNA (RNAseV1 targets dsRNA while RNAse1 targets ssRNA)
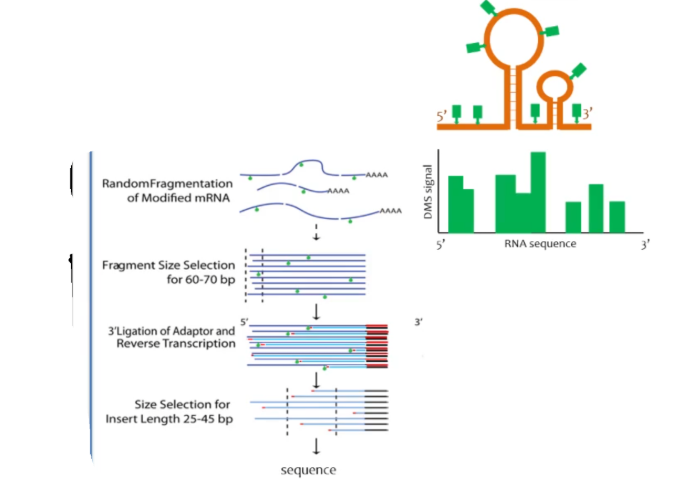
DMS-seq assay
RNA secondary structure assay. DMS is used to modify A and C in ssRNA. The modified RNA is randomly fragmented and fragments are the selected for a certain size (ideally there should only be 1-2 modified As or Cs on the fragments, usually 60-70 bp). A 3’ ligation adapter is attached so that a primer may be attached and reverse transcription can occur. During reverse transcription, DNA is synthesized up to the point of the modified A or C on the sequence. Size select again for a smaller size of fragment (a size ideal for sequencing). The strand is then sequenced. Reveals areas that are single-stranded vs double stranded on a RNA.
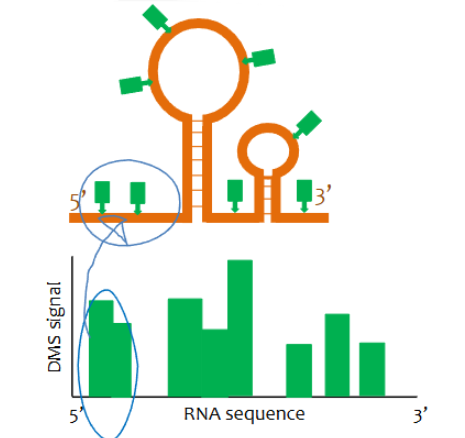
When reading a DMS-seq signal graph, what areas indicate ssRNA vs dsRNA
areas of high signal indicate ssRNA as DNA may only modify A’s and C’s in ssRNA. Low signal areas indicate dsRNA
What secondary structure assays for RNA may be done genome wide?
DMS-seq and SHAPE-seq
t/f DMS seq may be used to check if an RNA folds the same in vitro as in vivo
true, b/c DMS-seq may be used both in vivo and in vitro
Advantage of DMS-seq
it may be done in vitro and in vivo and it can be done genome wide
SHAPE-seq assay
a SHAPE reagent modifies the 2’ OH in ribose of accessible (ss) RNA. works more or less the same as DMS-seq but is more accurate as it labels all 2’ hydroxyl groups of ssRNA.
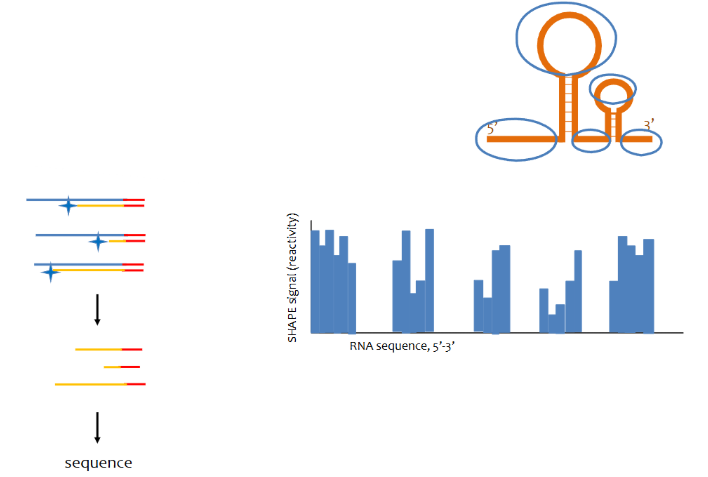
t/f SHAPE-seq can provide nucleotide level resolution while DMS-seq cannot (explain the answer)
true, SHAPE-seq labels all 2’ hydroxyl groups of ssRNA ribonucleotides while DMS-seq only labels A and C.
2 advantages of SHAPE-seq over DMS
nucleotide level resolution and signal strength of certain bases may be able to suggest things about structure of the RNA (lower signal can suggest that a ssRNA nucleotide is “buried” in the molecule)
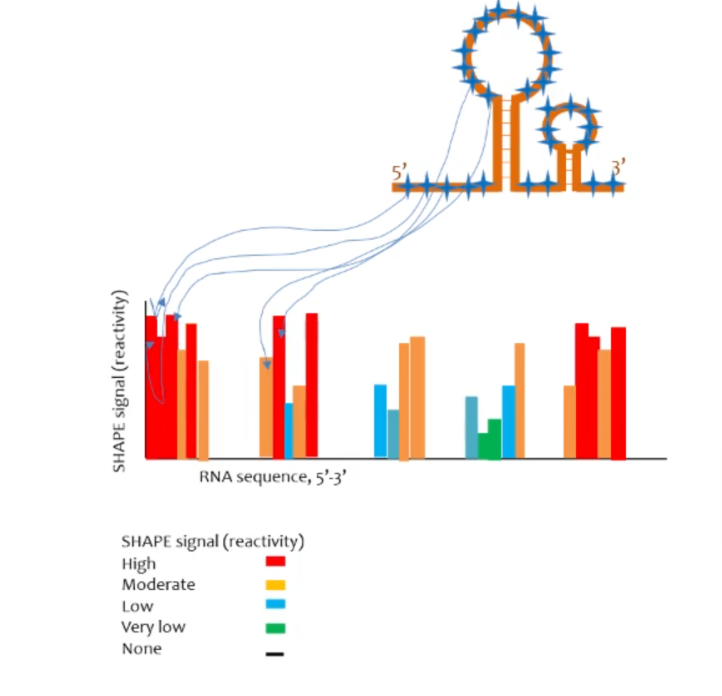
Is SHAPE-seq high throughput? What about DMS-seq?
both are high throughput
What is the most accurate method for assessing RNA secondary structure
SHAPE-seq
Most common RNA double helix form
A form
Most common DNA double helix form
B form
A helix form
primary form of RNA helices (even if RNA is hybridized with DNA). shorter and wider caused by extra repulsion from extra OH groups in RNA
3d structure of RNAs may be stabilized by what interactions
H-bonds, stacking interactions, sometimes metal ions, Base-pairing between distant nucleotides (watson-crick and/or hoogsteen base pairing), and interactions between 2’ OH
Label these common RNA 3d structures
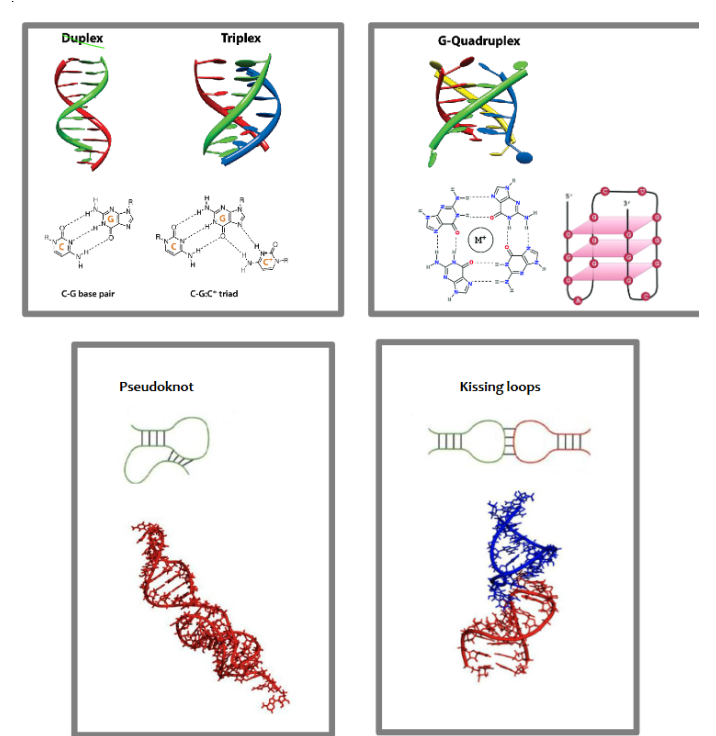
What allows for RNA triplex formation
hoogsteen base pairing in addition to watson-crick base pairing
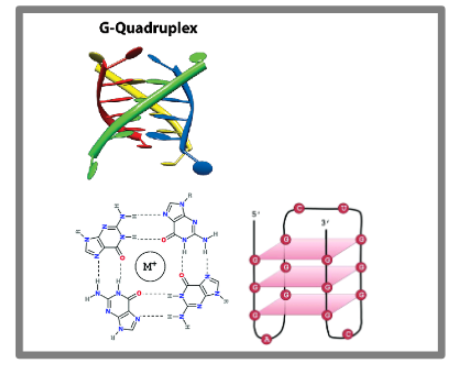
G-quadruplex
RNA tertiary structure that is 4 stranded helix stabilized by a metal ion and in which every second nucleotide is a G. may also occur in DNA.
t/f 95% of RNA is translated into proteins
false, 95% of RNA are NOT translated into proteins
RNAs are diverse in —-, —-, and —-
size, function , and expression levels
ncRNAs involved in translation
rRNAs, tRNAs, and tmRNA (bacteria only)
About —% of RNA in the cell are rRNA
80
About —% of RNA in the cell is tRNA
15
Non-coding RNAs involved in RNA processing
snRNAs, snoRNAs, RNAse P, and gRNAs
ncRNA involved in DNA replication
telomerase RNA and Y RNA
ncRNAs involved in protein targeting
4.5S RNA (bacteria) and 7SL RNA
Signal recognition particle (SRP)
complex of RNA and a number of different proteins which delivers nascent proteins with the ribosome to the ER (in eukaryotes) if they are to be secreted or to the plasma membrane (in bacteria).
Eukaryotic SRP is composed of — RNA and —-
7SL; several proteins
Ribozymes
RNAs that can catalyze reaction
Natural ribozymes are involved in what reactions?
peptide bond formation, phosphodiesterase bond cleavage and RNA ligation
Artificial ribozymes are involved in what reactions?
RNA phosphorylation, RNA aminoacylation, glycosidic bond formation and others…
Artificial ribozymes are usually (more or less) active than natural ribozymes
less
Hammerhead ribozyme
ribozyme which cleaves RNA at specific sites by recognizing substrate RNA via base pairing
529 packaging motor
most powerful molecular motor in nature responsible for packaging viral genetic info into a capsid. Made up of pRNA.
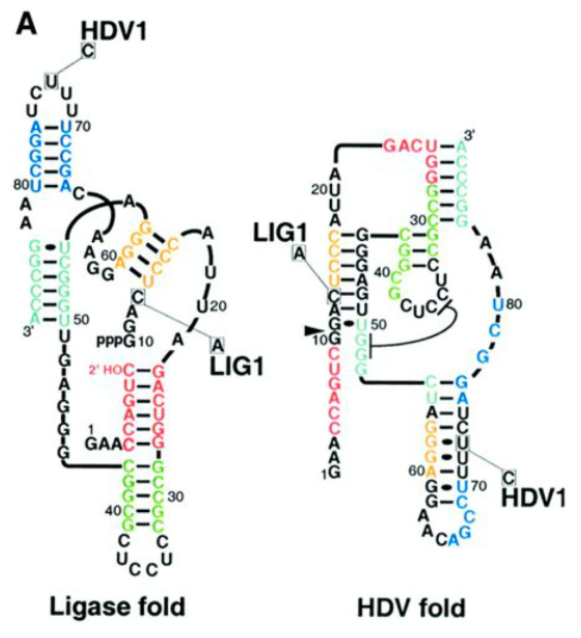
HDV1
a synthetic RNA molecule that has different functions based on how it folds. One structure ligates while the other cleaves
Riboswitch
RNAs that can switch their conformation based on environmental conditions
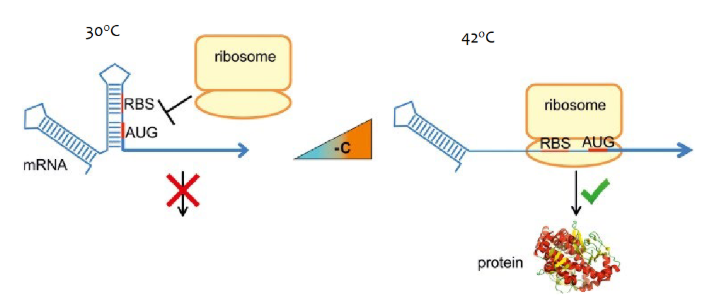
Bacterial RNA thermometer
mRNAs in bacteria that produce proteins to protect the bacteria from higher temp are riboswitches with two stem loops. The second stem loop denatures at higher temperatures allowing the ribosome to bind and the protein to be made.
Aptamers
RNAs that recognize and bind specific ligands
Natural aptamer example
guanine binding aptamer in guanine riboswitch of bacteria