chem 107 8 4/3/25
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
chem 107 8 4/3/25
A cup of coffee with sugar represents a type of
homogeneous mixture called a solution.
• A solution consists of at least one substance—the solute—
evenly dispersed throughout a second substance—the
solvent.
• The components in a solution do not react with each other:
The sugar is still sugar.
• The solute is the substance present in the smaller
amount, and the solvent is the substance present in the
larger amount.
Solutions Are Mixtures (2 of 7)
A cup of coffee, though
dark brown in color, is
transparent; if held up to a
light, you can see through
the liquid.
• Once the sugar is
dissolved into the water, it
will not undissolve over
time.
• These properties provide
a quick way to determine
whether a substance is a
solution

Solutions Are Mixtures (3 of 7)
Particles are evenly distributed.
Components do not chemically react with each
other.
Aqueous solutions are transparent.
Components do not separate upon standing.
Concentration can be changed.
8.1 Solutions Are Mixtures (4 of 7)
States of Solutes and Solvents
• Solutions can be homogeneous mixtures of gases or solids.
• Air is a homogeneous mixture of gases. It is also a solution in which nitrogen
is the solvent and other gases are the solutes.
• Brass is a solution of solids where the solute is metal zinc in the solvent is
metal copper.
• The solute and solvent can be solid, liquid, or gas.
• Solutions in which water is the solvent are aqueous solutions.

Solutions Are Mixtures (5 of 7)
The Unique Behavior of Water
• Each water molecule can form up to four hydrogen bonds with
neighboring water molecules.
• These strong attractive forces give water some unique properties
not found in other solvents.
• Water has a high specific heat, allowing it to trap energy for longer
periods of time than many other substances.
• Water has a high boiling point and a low vapor pressure.
• Ice floats on liquid water: ice has a lower density than liquid water. As
water freezes, the molecules get farther apart to make optimal
hydrogen-bonding contacts. This is why ice has a lower density than
liquid water.
Colloids and Suspensions
Milk and cream are not transparent
liquids, so they are not solutions.
• Homogenized milk and cream are
colloids (or colloidal mixtures)
because of the proteins and fats
that do not dissolve.
• By definition, the particles in a
colloid must be between 1 and
1000 nanometers in diameter.
• Particles of this size remain
suspended in solution, so a colloid
does not separate over time.

Colloids and Suspensions
Muddy water will separate upon standing. If the diameter of the particles in a
mixture is greater than 1000 nanometers (1 micrometer), the mixture is a
suspension.
• Blood is also a suspension. Blood cells are larger than 1 micrometer and will
settle to the bottom of a test tube upon standing.
• Blood can be separated by centrifugation.

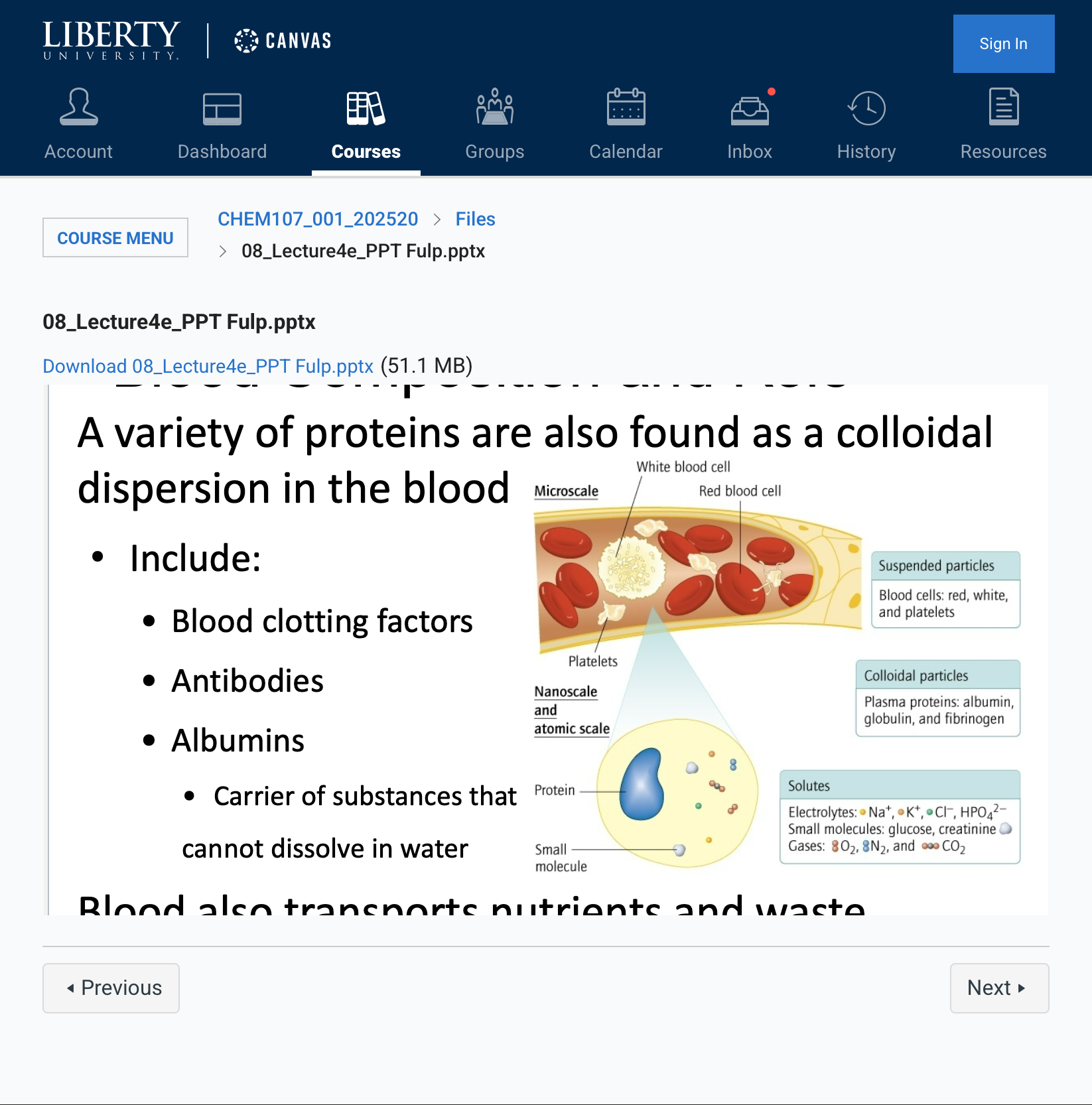
Blood Composition and Role
A variety of proteins are also found as a colloidal
dispersion in the blood
• Include:
• Blood clotting factors
• Antibodies
• Albumins
• Carrier of substances that
cannot dissolve in water
Blood also transports nutrients and waste
products
Formation of Solutions (1 of 8)
Recall like dissolves like that polar covalent compounds and
ionic compounds will dissolve in water because strong attractive
forces exist between them.
• Nonpolar covalent compounds are not soluble in the polar
molecules of water.
• Amphipathic molecules can interact with water through their
polar part, but these molecules typically do not form solutions.
• The dissolving process requires that individual solvent
particles surround the solute molecules and interact through
attractive forces.