OCR A 6.1.1 Aromatic Compounds
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
benzene
cyclic planar molecule
C6H6
benzene structure
each C bonded to 2 C and 1 H
final lone e- in p orbital
adjacent p orbital e- overlaps sideways above and below plane
overlapping p orbitals create pi bons which spread all of 6 C atoms in ring structure
e- in the system r delocalised
benzene bond length
due to delocalised e- structure
al C-C bonds have same bond length
benzene skeletal formula
kekule skeletal formula
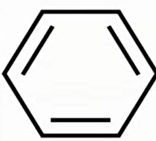
why kekule model is wrong
using x-ray diffraction all of benzene’s C-C bond length are 0.139nm
enthalpy change of hydrogenation is less exothermic for benzene than model
benzene is less reactive as it requires a catalyst for chlorination to occur, but alkenes don’t
kekule has 3 pi bonds which overlap in 1 direction
but benzene has pi system where orbitals overlap in both direction with 6 electrons in pi bond
arene
aromatic compounds that contain benzene ring
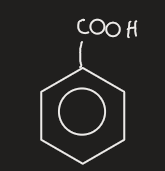
benzoic acid
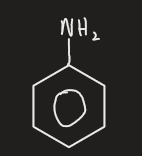
phenyl amine
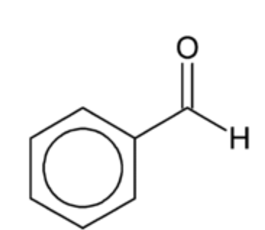
benzaldehyde
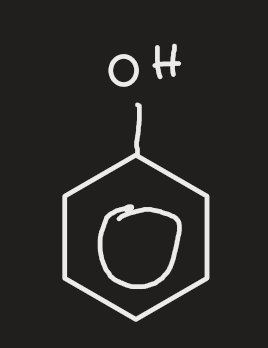
phenol
naming benzene rules
grp that is attached first is n1
when benzene attached to alkyl chain w. func grp or with more than 6 C phenyl prefix used
reactions of arenes
undergo electrophilic substitution
-has high e- density due to delcoalised ring of e-: attract electrophiles
why arenes don’t undergo electrophilic addition
stable
would disrupt stable ring of electrons
instead electrophilic substitution occurs where grp on benzene ring subd for electrophile
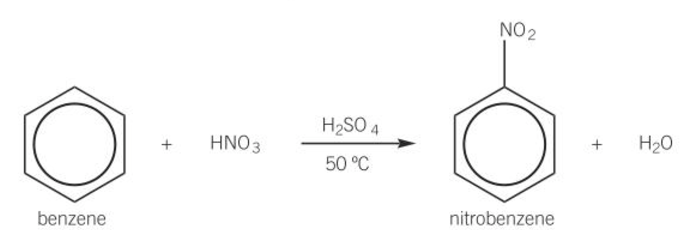
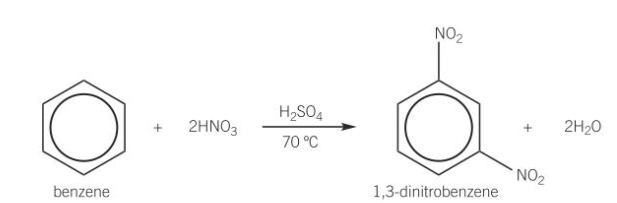
benzene nitration conditions
catalysed by sulfuric acid
heat to 50 using water bath
benzene nitration equation
benzene nitration production of electrophile
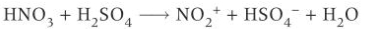
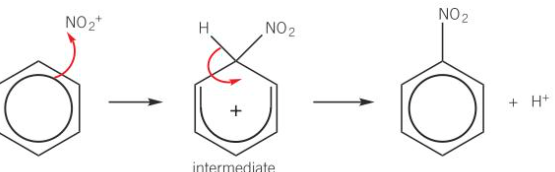
benzene nitration mechanism
NO2+ electrophile accepts pair of e- from benzene ring
dative covalent bond formed
intermediate is unstable positively charged ring
e- in C-H bond move to reform delocalised e- ring
nitrobenzene and H+ formed
benzene nitration regeneration of catalyst
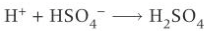
what happens if nitration of benzene happens in temp <50
further sub reactions may occur
leading to dinitrobenzene
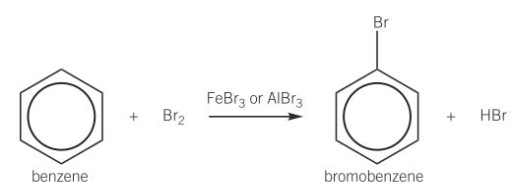
halogenation of benzene conditons
doesn’t react unless halogen carrier (catalyst) present
eg: FeCl3, AlBr3
generated in situ from metal and halogen
halogenation of benzene equation
halogenation of benzene production of electrophile
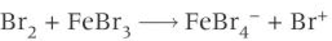
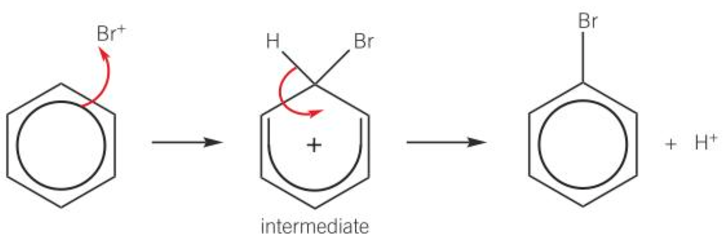
halogenation of benzene mechanism
Br+ electrophile accepts pair of e- from benzene ring
dative covalent bond formed
intermediate is unstable positively charged ring
e- in C-H bond move to reform delocalised e- ring
bromobenzene and H+ formed
halogenation of benzene reproduction of catalyst
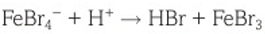
halogen carrier for chlorination

halogen carrier for bromination
friedel crafts acylation
as benzene is too stable to react with
adding acyl grp makes easier to modify it further
acylation of benzene conditions
acyl chloride or acid anhydride
anhydrous - prevent reaction of AlCl3
60 for 30 mins under reflux
acylation of benzene production of electrophile
AlCl3 accepts pair of e- away from acyl grp
polarisation increases and carbocation forms
strong electrophile made

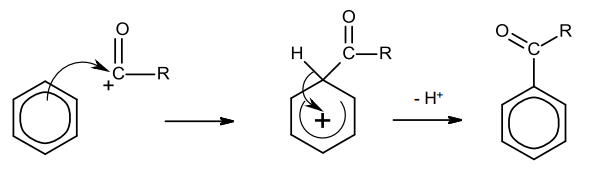
acylation of benzene mechanism
delocalised e- in benzene ring attracted to electrophile
2 e- move to form bond
breaks ring and +ve charge forms
-ive AlCl4- attracted to +ve charged ring
1 of Cl atoms break away to form bond with H
acylation of benzene regeneration of catalyst
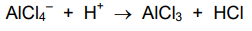
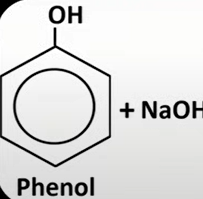
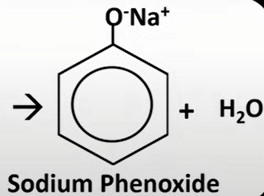
phenol
have hydroxide grp attached to benzene grp
c with OH grp is 1
phenol reactivity
more reactive than benzene
due to e- density in ring is higher
polarises electrophile
more susceptible to electrophilic attacks
due to OH grp; e in O becomes part of pi ring
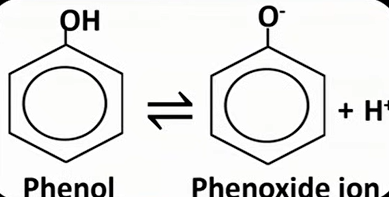
phenol property
weak acid; partially dissociate
form H+ ion and phenoxide ion
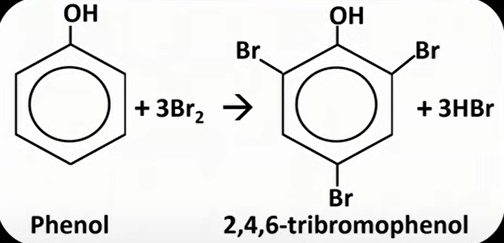
phenol + Br water
phenol + dilute nitric acid
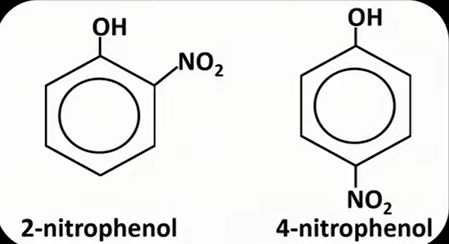
activation
some groups can activate benzene ring by donating a lone pair of e- into pi system of benzene (NH2, OH)
aromatic ring reacts more readily w/ electrophile
therefor in presence of these extended groups the aromatic compound can react more readily with other electrophile and mutli-substituted product can form
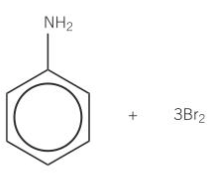
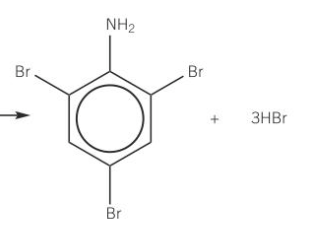
why can Br react with phenyl amine w/out halogen carrier catalyst
NH2 group has activated benzene group already
benzene can polarise the Br molecule
deactivation
some groups can deactivate benzene ring
so aromatic ring can react less readily w/ electrophile
also need halogen carrier catalyst when extended group are present with aromatic compounds
directing effect table