CAPE Bio (P2) - Cell Structure and Functions
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
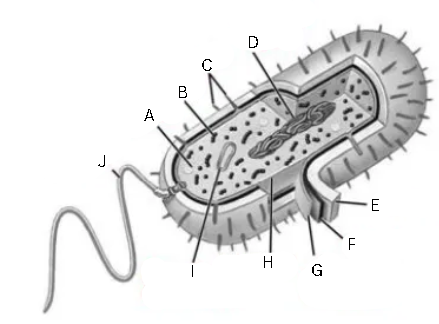
Label and identify this diagram
General structure of a prokaryotic cell
A - food granule
B - ribosome
C - pili
D - nucleoid region
E - capsule
F - cell wall
G - plasma membrane
H - cytoplasm
I - plasmid
J - flagellum
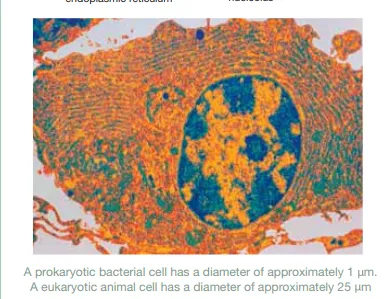
Identify this image
Electron micrograph of a prokaryote
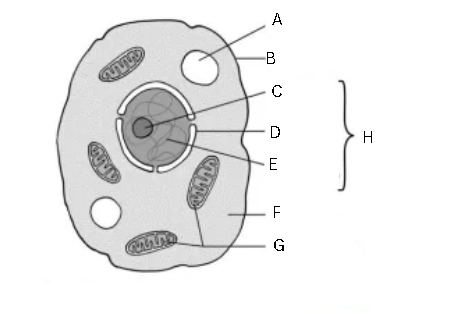
Label and identify this image
General structure of animal cell
A - vacuole
B - cell membrane
C - nucleolus
D - nuclear membrane
E - chromatin
F - cytoplasm
G - mitochondria
H - nucleus
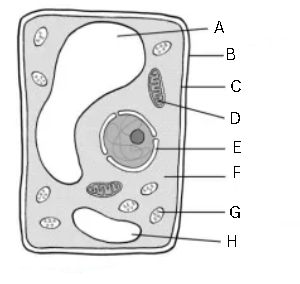
Label and identify this image
General structure of a plant cell
A - vacuole
B - cell wall
C - cell membrane
D - mitochondrion
E - nucleus
F - cytoplasm
G - chloroplast
H - vacuole
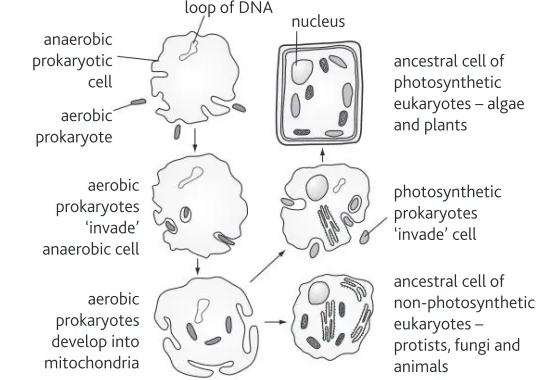
Identify this image
Endosymbiosis
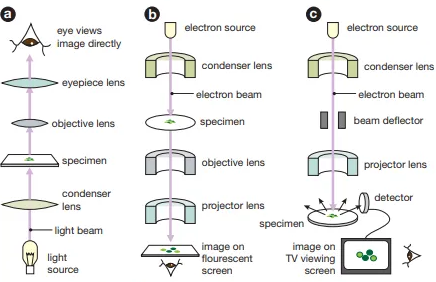
Label this image
a - light microscope
b - transmission electron microscope
c - scanning electron microscope
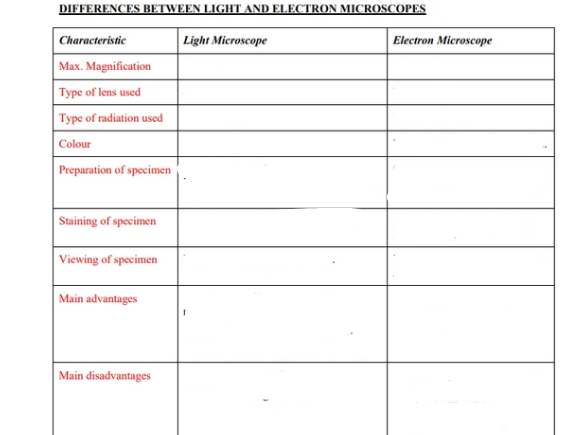
Complete this table
A - x1400, x300,000
B - Glass, Electromagnets
C - Visible light, Electron beams
D - Image will appear in color, Black and white
E - Both living and non-living tissues can be used, Only non-living and dehydrated cells are used
F - Cells absorb colored stains, Cells absorb heavy metals
G - By eye or projection on a screen, Fall onto fluorescent screen
H - Affordable; Slides are multi-use; Low-risk of distortion, Higher resolution; Higher magnification
I - Lower resolution; Lower magnification, Expensive; Requires expertise; Specimen deteriorates during viewing; High risk of distortion
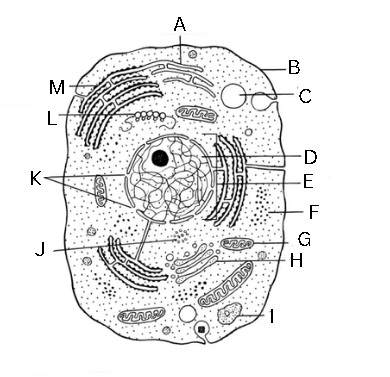
Identify and label this diagram
A - smooth endoplasmic reticulum
B - plasma membrane
C- vacuole
D - chromatin
E - nucleus
F - ribosomes
G - mitochondrion
H - Golgi body
I - lysosome
J - centriole
K - nuclear pore
L - polyribosome
M - rough endoplasmic reticulum
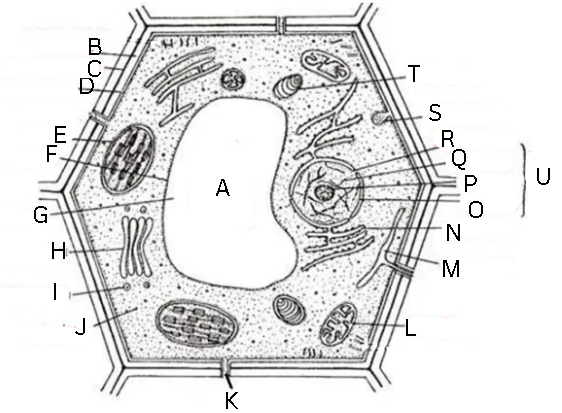
Identify and label this diagram
A - central vacuole
B - cell wall
C - middle lamella
D - cell membrane
E - chloroplast
F - tonoplast
G - cell sap
H - Golgi body
I - Golgi vesicle
J - cytoplasm
K - plasmodesmata
L - mitochondrion
M - smooth endoplasmic reticulum
N - rough ednoplasmic reticulum
O - nuclear envelope
P - nucleolus
Q - chromatin
R - nuclear pore
S - pinosome
T - amyloplast
U - nucleus
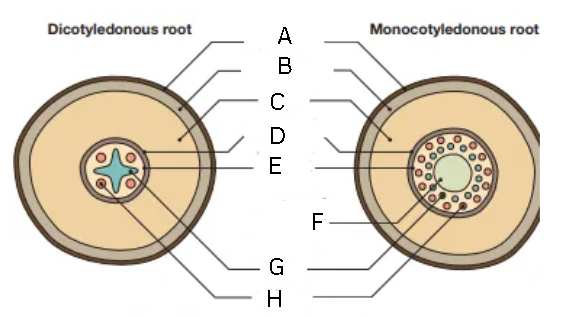
Label this diagram
A - epidermis
B - exodermis
C - cortex
D - endodermis
F - vascular cylinder
G - core of parenchyma cells
H - xylem
I - phloem