Internal Bacteria Structure
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Describe the plasma membrane structure of bacteria
composed of phospholipids, imbedded proteins for transport and signal transduction, and markers
fluid/moving
may have hopanoid to decrease membrane fluidity and permeability
What is hopanoid?
similar to cholesterol in eukaryotes
decreases membrane fluidity and permeability in bacteria
What macronutrients do bacteria require?
CHNOPS
carbon
hydrogen
nitrogen
oxygen
phosphorous
sulfur
PICK MI
potassium
calcium
magnesium
iron
Describe basic bacterial nutrient uptake
only take in dissolved molecule
uptake is specific and efficient
most often move nutrients against concentration gradient to store (requires ATP)
What are the types of active transport that bacteria use?
primary, secondary, group translocation
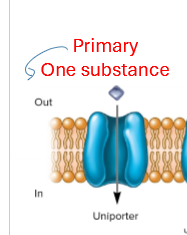
Describe primary transport
one substance transported through uniporter
hydrolosis of ATP for energy
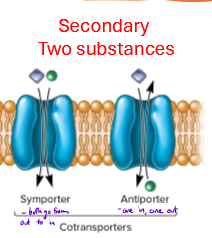
Describe secondary transport
two substances transported through cotransporters
use ion gradient of one of the substances to power
Describe ABC transporter (ATP Binding Cassette)
primary active transport
solute binds to solute binding protein on PM
transporter undergoes conformation change that allows solute through
requires ATP hydrolysis
Describe Group Translocation
active transport
molecule chemically modified as it enters
ex. PTS System
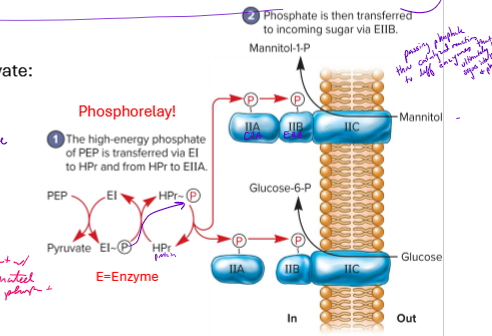
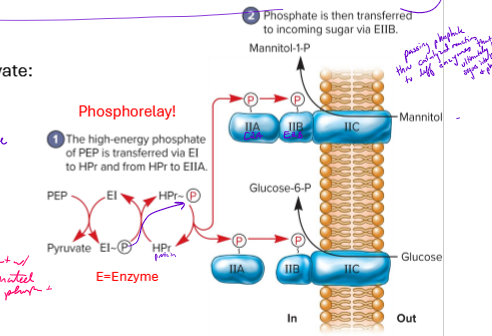
Explain the PTS System (Phosphoenolpyruvate: Sugar Phosphotransferase System)
example of group translocation (active transport)
imports a variety of sugars
phosphate donated from PEP to Enzymes, which passes it to a protein
phosphate then transferred to different enzymes
enzymes bring sugars into cell and phosphoralyte the sugars
What special requirement do bacteria have to intake iron?
use siderophores to intake insoluble iron
Describe siderophores
compound secreted by bacteria that grab iron and release it to the cell or ABC transporter
can be a virulence factor by stealing iron from host (allows bacteria to grow better)
What are the key cytoskeleton proteins in eukaryotes?
actin
intermediate filaments
tubulin
Describe MreB and what eukaryotic structure it’s homologous to
bacterial cytoskeleton protein
similar role to actin, homologous structure
provides shape to cell
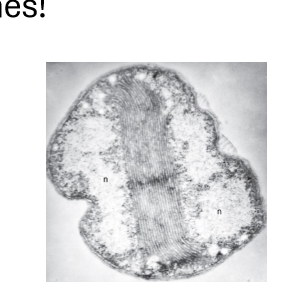
Describe Intracytoplasmic membranes
internal membrane structures within cytoplasm of some bacteria
may connect to plasma membrane and would have a higher concentration of electron transport proteins
Often in bacteria that are photosynthetic or nitrifying
What are thylakoids?
cyanobacteria internal membranes containing photocenters; type of intracytoplasmic membrane
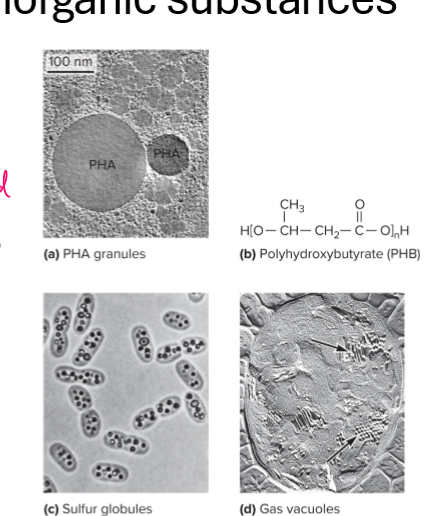

What are inclusions? Provide two examples
aggregates of organic/inorganic substances
stored/concentrated for later date, often because would be toxic otherwise
ex. Sulfur globules stored in inclusions as byproduct of anaerobic respiration in photosynthetic bacteria
ex. Gas vacuole protein bound structures store gas to allow bouyancy in aquatic bacteria
Describe Carboxysomes
type of inclusion
in CO2 fixing bacteria
fix CA to CO2 then convert to sugar
for efficiency; make all the sugar in one palce
Describe magnetosomes
type of inclusion
used by aquatic bacteria to orient to Earth’s magnetic filed
Briefly describe bacteria ribosomes, including subunit size
70s total (30s and 50s subunits)
made of rRNA and proteins
Describe eukaryotic cytosol ribosomes size
80S total, 40s and 60s subunits
Describe eukaryotic mitochondria/chloroplast ribosomes size
70s
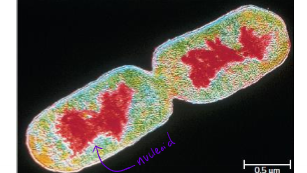
What are nucleoids?
unique regions within bacteria with DNA that has no membrane
usually circular chromosomal DNA
bacteria usually monoploid, but be polyploid (multiple copies)
500-1000 genes, compacted into macrodomains for space
Describe Nucleoid associated proteins (NAPs)
proteins that help bacterial chromosomes bend and fold, stiffen, or link
important for packaging before replication
Describe plasmids
extrachromosal DNA in bacteria
<30 genes, don’t have essential genes for growth, replication, etc. just fun stuff like AR
transfered between organisms
usually replicate independtely
called episomes when integrated into chromosome
Describe episomes
type of plasmid that’s integrated into chromosomes and replicates with it
<30 non-essential genes
transferred between organisms