ResearchDsgnStats Exam1
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Advantages of EBM
Attempts to increase the likelihood of receiving interventions that are efficacious
Disadvantages of EBM
Many questions lack available evidence.
Characteristics of a Good Research Question- FINER
F - Feasibility
I - Interesting
N - Novel
E - Ethical
R - Relevant
N in FINER
N - Novel
Five Steps of Practicing EBM
1. Ask - develop your answerable questions
2. Acquire (Find) - Efficiently Find best Evidence
3. Appraise - Critically evaluate the evidence for validity and usefulness
4. Apply - use results of the appraisal in your clinical practice
5. Assess (Evaluate) - Evaluate your performance
Five Steps to Practicing EBM Highlighted Answer
Acquire (Find) - Efficiently find the best evidence
Why do you need to know how to practice EBM?
Keep up to date and to apply knowledge necessary for good clinical care
Stay current with relevant literature
Four PICO(T) Questions defined
Therapy - compare two or more interventions for condition
Etiology/Harm - looking for association between an exposure and an outcome
Diagnosis - comparing a new diagnostic test to the reference standard test
Prognosis - given a condition, does a certain factor portend a worse prognsis?
Four PICO(T) questions are...(highlighted word)
foreground questions
Background questions
STEM = What is, Why do, How does...
Statistical Estimation
General method of calculating confidence intervals
Point estimate +/- (critical value)(Standard Error)
Statistical Estimation and Confidence Interval
Increasing the sample size will decrease the width of a confidence interval
Type I (a) error
Rejecting the null when the null is true
When you randomly select a group of 500 people across the US to participate in a study, what is the group you have chosen called?
Sample
For a statistical test where the alpha is set at 0.05 for the level of significance, a p-value of 0.01 should be interpreted as confirmation that ___________.
Small p-values indicated strong evidence AGAINST the null hypothesis
Statistical vs Clinical Significance
Clinical significance - related to whether the finding are clinically or practically meaningful (i.e will they affect practice?)
Statistical significance means that the observed results are unlikely to have occurred due to chance alone, assuming the null hypothesis is true
When a research article is said to have clinical significance, it means the results of the study are unlikely due to chance
Prognosis and Harm/etiology do not have
RCT (random controlled trials)
P values and confidence levels
Confidence level is equivalent to 1 - alpha level. So significance level is 0.05, the corresponding confidence level is 95%. If the p-value is less than your significance (alpha) level, the hypothesis test is statistically significant
What chart is best used to represent proportions or relative quantities of values?
Pie graph
Central Limit Theorem
The distribution of sample means approximates a normal distribution as the sample size gets larger, regardless of the population's distribution
3 main tenants of Central Limit Theorem
1. The mean of all sample means will equal the population mean
2. The standard deviation of the sample means is equal to the standard error of the mean
3. As the sample size increases, the distribution of the sample means approaches the normal distribution (regardless of the underlying distribution of the variable)
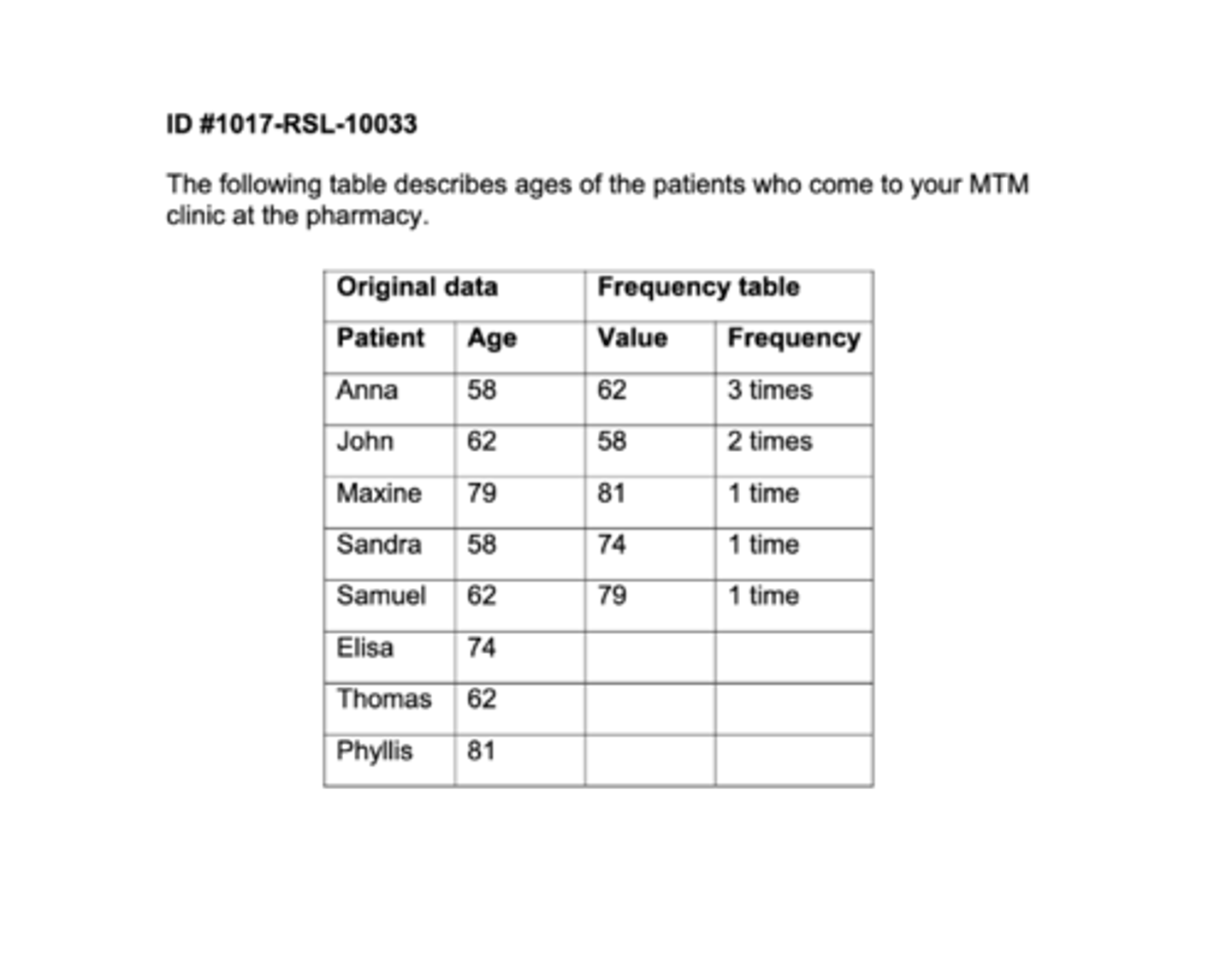
IQR for Data = 16.5
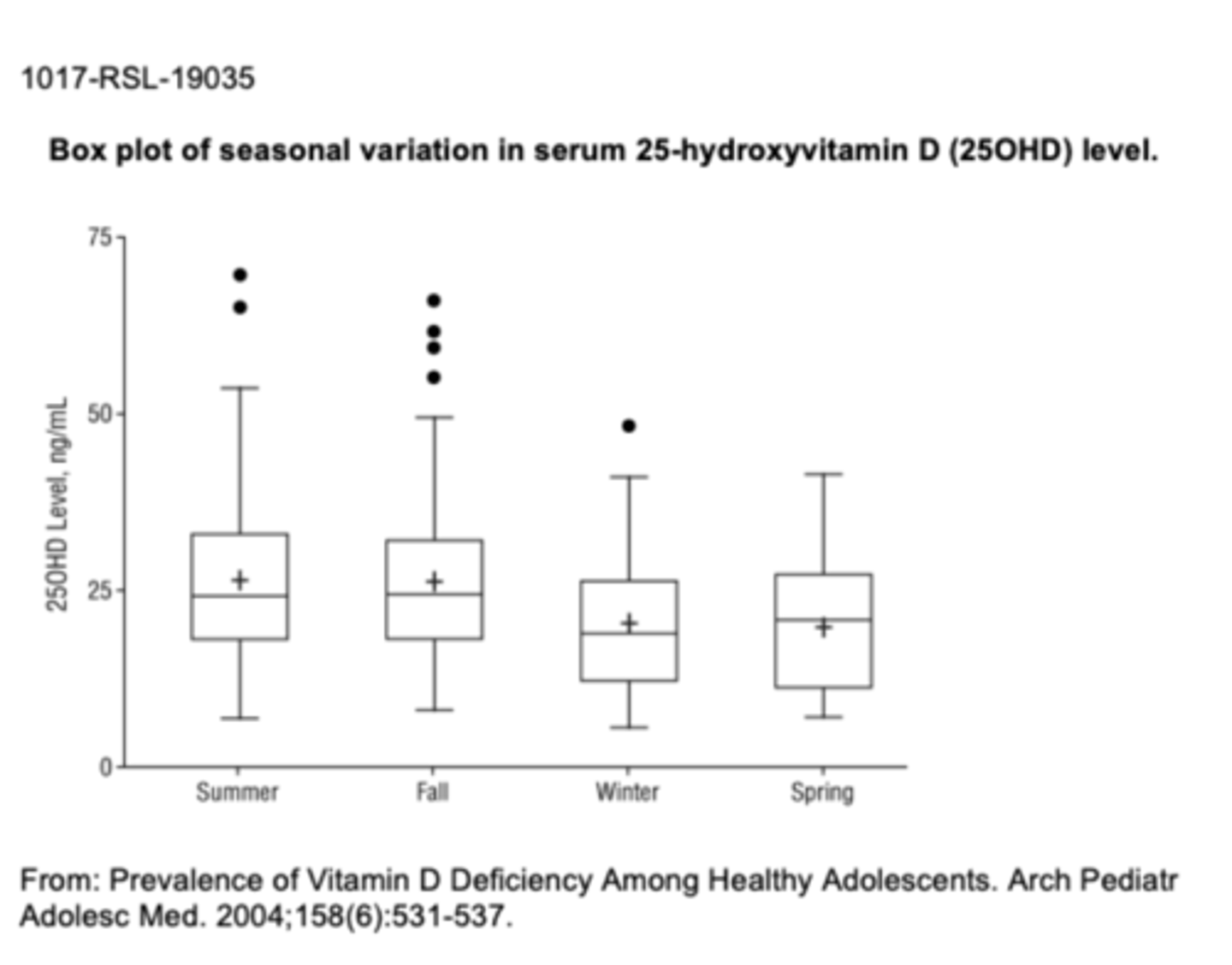
Minimum 250HD (vitamin D) level in ng/mL for healthy adolescents in Spring is ~10
Intervention in: On morning rounds in the Hem/Onc unit, a first year resident turns to you for consultation. She wants to discuss options for managing moderate nausea and vomiting that result following chemotherapy. She shares an experience a relative had taking ginger when prochlorperazine didn’t provide effective relief and asks for your input.
Intervention: ginger
Intervention in: In patients with recurrent furunculosis, do prophylactic antibiotics reduce the recurrence rate compared to ‘no treatment’?
Intervention: Prophylactic antibiotics
Which are clinical foreground questions?
•Is 15 minutes of exercise daily more effective than 45 minutes of exercise three times a week in reducing the risk of cardiovascular problems in middle-aged men?
Does fatigue contribute to depression in patients with cancer?
In patients presenting with chest pain, is high-sensitivity troponin more accurate than standard troponin in diagnosing myocardial infarction?