DNA STRUCTURE + REPLICATION
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
DNA
information storage molecule. double helix, consisting of 2 very long strands of nucleotides, hydrogen bonded together (nucleotides = monomer, DNA = polymer)
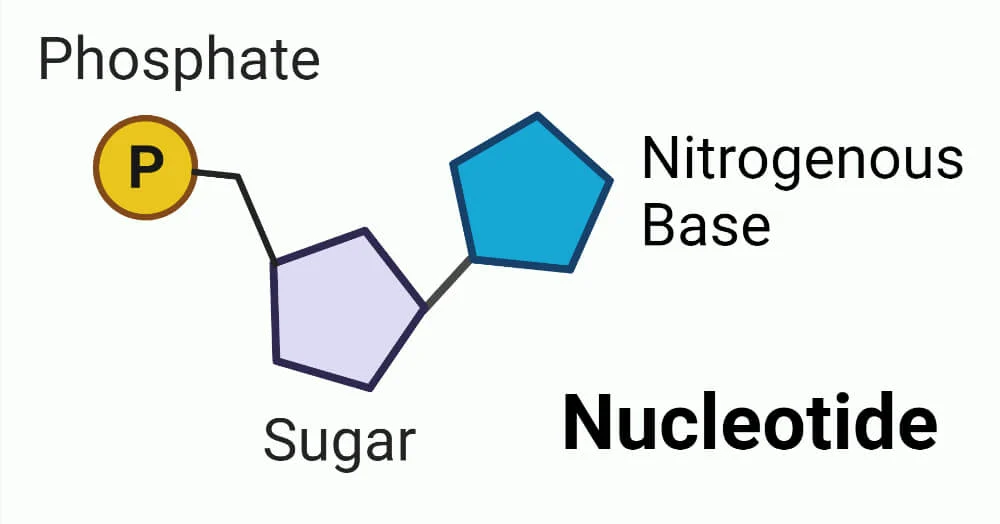
nucleotide
monomer of DNA. each one has a phosphate, a 5 carbon sugar, and one of 4 possible nitrogenous bases

sugar phosphate back bone
nucleotides on a single strand are connected by covalent bonds between the phosphate on one and the sugar on the nucleotide above/below it. establishes the order of the bases on a single strand
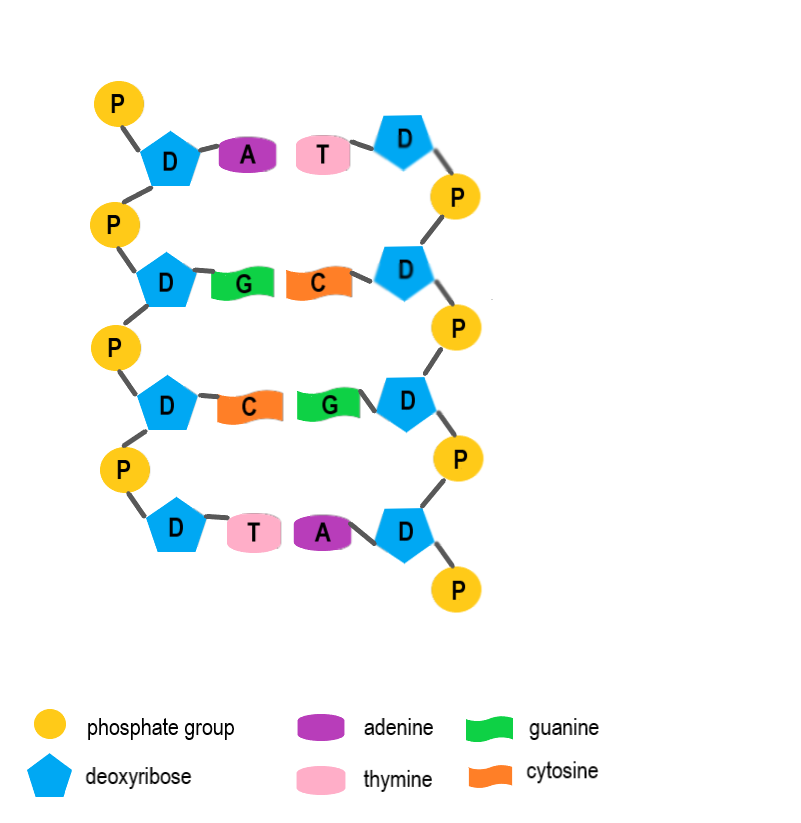
strands
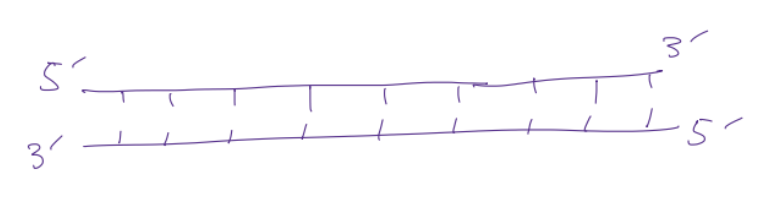
double helix, run opposite directions (anti parallel). ends that have a phosphate are called 5’, ends with sugars are called 3’. ends provide info that help the cell know which direction to read the DNA in
sequence
on a single strand, can be any combo/order of basses. allows us to write any words/info
A goes with
T
T goes with
A
C goes with
G
G goes with
C
5’ and 3’ strands are
anti-parellel, going opposite ways
DNA binding proteins
protiens that bind specific short DNA sequences (different proteins copy, read, or repair DNA after binding)
chromosome
a single, long, continuous double stranded DNA polymer
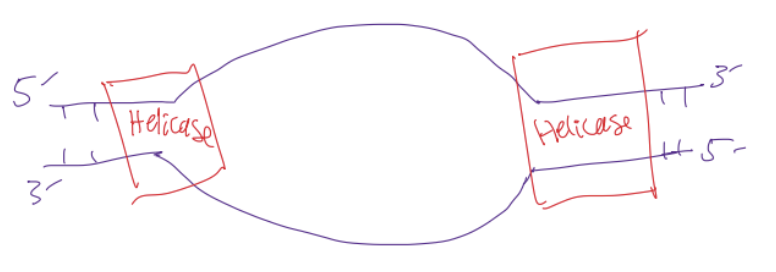
helicase
protein that unzips the hydrogen bonds between complementary strands
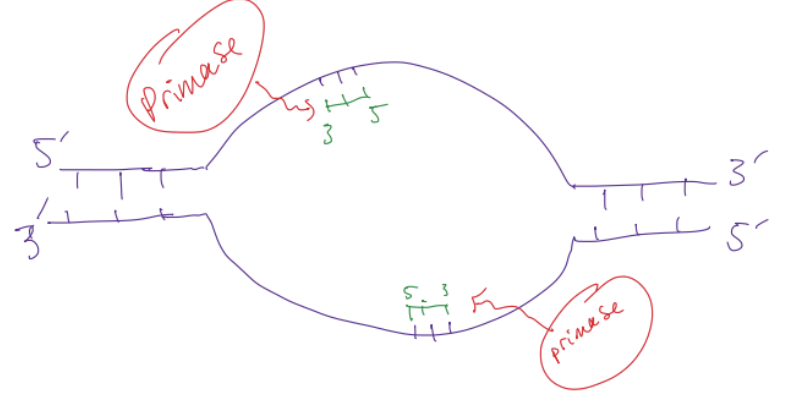
primase
protein that adds primers to both original strands
primer
short nucleotide strand that complements an original strand
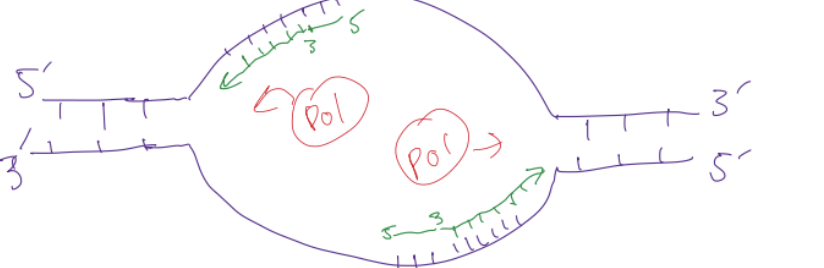
DNA polymerase
reads along a template strand toward the 5 end, adds new nucleotides and extends the 3 end of the primer, linking sugar to phosphate to sugar. this new strand base pairs with the old strand
new primer
primers are added and extended to back gaps
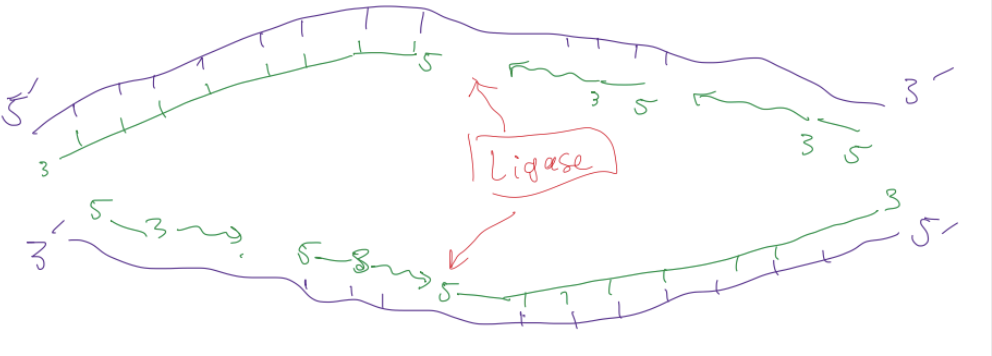
ligase
protien that links up all the partial strands onto long continuous new one