GCSE Biology
1/278
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
279 Terms
Communicable diseases
Infectious (can be transmitted)
Non-communicable disease
Can’t be transmitted
Microbe/Microorganism
very small organism
Pathogen
A disease causing organism
Types of pathgogen
virus bacteria fungi protists
How does bacteria and viruses cause illness
they divide rapidly and release harmful toxins or they invade the cells and reproduce in it causing the cell to burst and die
how can a pathogen spread
water contact water droplets in air
Size of bacteria
1-5 micro metres (µm)
1 micro metre = 0.001
Size of viruses
0.02-0.3 micro metres
Size of Fungi
50+ micro metres
Size of protists
1+ micro metres
How they cause disease bacteria
multiply rapidly and release toxins
How they cause disease Viruses
by invading and killing cells
How they cause disease Fungi
They stop plants from photosynthesising
How they cause disease Protists
bites of infected insects
Examples of bacteria
Salmonella
cholera
Gonorrhoea
Examples of viruses
flu
covid
HIV/AIDS
Examples of fungi
rose black spot, ringworm
Examples of protists
maleria
Plasmodium
protists that causes malaria
A parasite
an organism that lives on another organism and cause harm.
Vector
An organism that carries a pathogen to another organism
Physical barriers
Skin
Nose
Trachea
Stomach acid
Lymphocytes
produce antibodies/antitoxins
Phagocytes
engulf pathogens
Role of white blood cells
producing antitoxins, ingesting microbes (non-specific response), producing antibodies
how vaccines work
pathogen enters body
causes immune system to respond
microbe had been made harmless
Lymphocytes produce antibodies
White blood cells remember antibodies
if body attacked by pathogen again it can make antibodies faster.
detecting plant diseases
growths, malformed stems leaves roots, areas of decay, visible pests
Identifying plant diseases
dna analysis
compare symptoms
test kits
plant defences Physical
Physically stops pathogens form getting in
eg bark , waxy cuticle
plant defences Chemical
Chemicals that the plant can secrete
these can be used in medicine
plant defences Mechanical
Ways the plant defends its self from being eaten
hairy stems thorns leaves that drop when touched.
Difference between virus and bacteria
virus- nonliving cannot be treated by antibiotics no cell wall smaller
bacteria- can be affected by antibiotics dont need host to reproduce can live outside a host
How does bacteria reproduce
1 cell splits into 2
how do viruses reproduce
replicate itself 1000s of times
What causes symptoms of disease
its the bodies way of trying to get rid of the pathogen
life cycle of plasmodium
Mosquito sucks blood containing the protists and passes it on the other people when it sucks their blood.
why are antibodies specific to one pathogen
each pathogen has antigens with unique shape so antibodies need to fit the same shape.
herd imuntiy
when the majority of the population is immune to a disease so there are less people who can transmit it meaning less people who are not immune get sick
how do aphids affect pkant growth
aphids suck the sap of plants from the phloem affecting the growth rate and killing the,
measles symptoms
fever red rash
cause brain damage and blindness
hiv and aids symptoms
flu like symptoms
HIV attacks the immune system until they cant fight certain diseases such as cancer
TMV symptoms
Mosaic pattern of plants
virus destroys cells
Measles transmission
inhalation form coughs and sneezes
HIV and AIDS transmission
blood saliva std
TMV transmission
contact between plants
Salmonella transmission
raw eggs meat poultry
risk factors for cardiovascular diseases
smoking excessive drinking no exercise poor diet
photosynthisis equation
co2+water → glucose+o2
Lactic acid
makes muscles hurt is toxic, oxygen is used to get rid of it
AEROBIC 1
releases lots of energy, uses o2, produces co2 and h2o, long time, low intensity, C6H12O6+O2→CO2+H20,
ANAEROBIC
Releases less energy, short time, high intensity, glucose to lactic acid, happens in muscle cells
ALVIOLI ADAPTATIONS
THIN CELL WALLS, LARGE SURFACE AREA
OXYGEN DEBT
The amount of oxygen required to remove the lactic acid, and replace the body's reserves of oxygen
LIMITING FACTORS
A FACTOR THAT LIMITS PHOTOSYNTHESIS
PRODUCTS OF RESPIRATION
water and co2
What are enzymes
Enzymes are catalysts. They speed up useful chemical reactions in the body.
Enzymes need a specific pH and temperature to work. If they are not in this environment they will
denature. this means that the active site changes and it no longer fits the substrate
Starch is broken down into
sugars
Protiens is broken down into
amino acids
Lipids are broken down into
glycerol and fatty acids
Lipids is broken down by
Lipase
Proteins is broken down by
Protease
Starch is broken down by
Amylase
Where is bile produced
in the liver
where is bile stored
in the gallbladder
Where is bile released
in the small intestine
what does bile do
It neutralises the stomach acid acid emulsifies fats
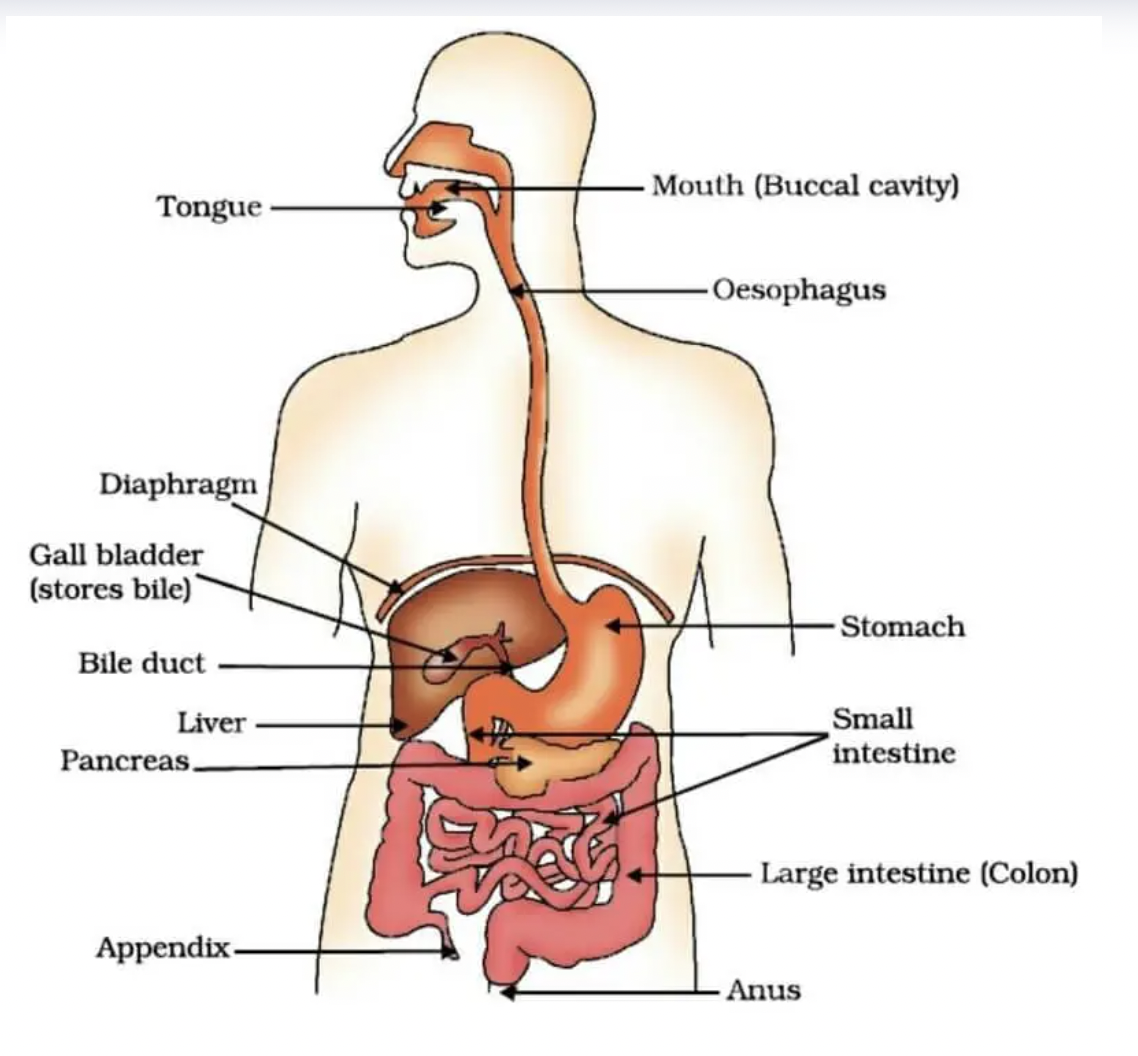
Salivary glands
Produce amylase in saliva
Oesophagus
Muscle that transports food to stomach
Liver
Bile is produced here
Stomach
Pummels food
Produced protease
Produced hydrochloric acid-To kill bacteria and give right pH for protease
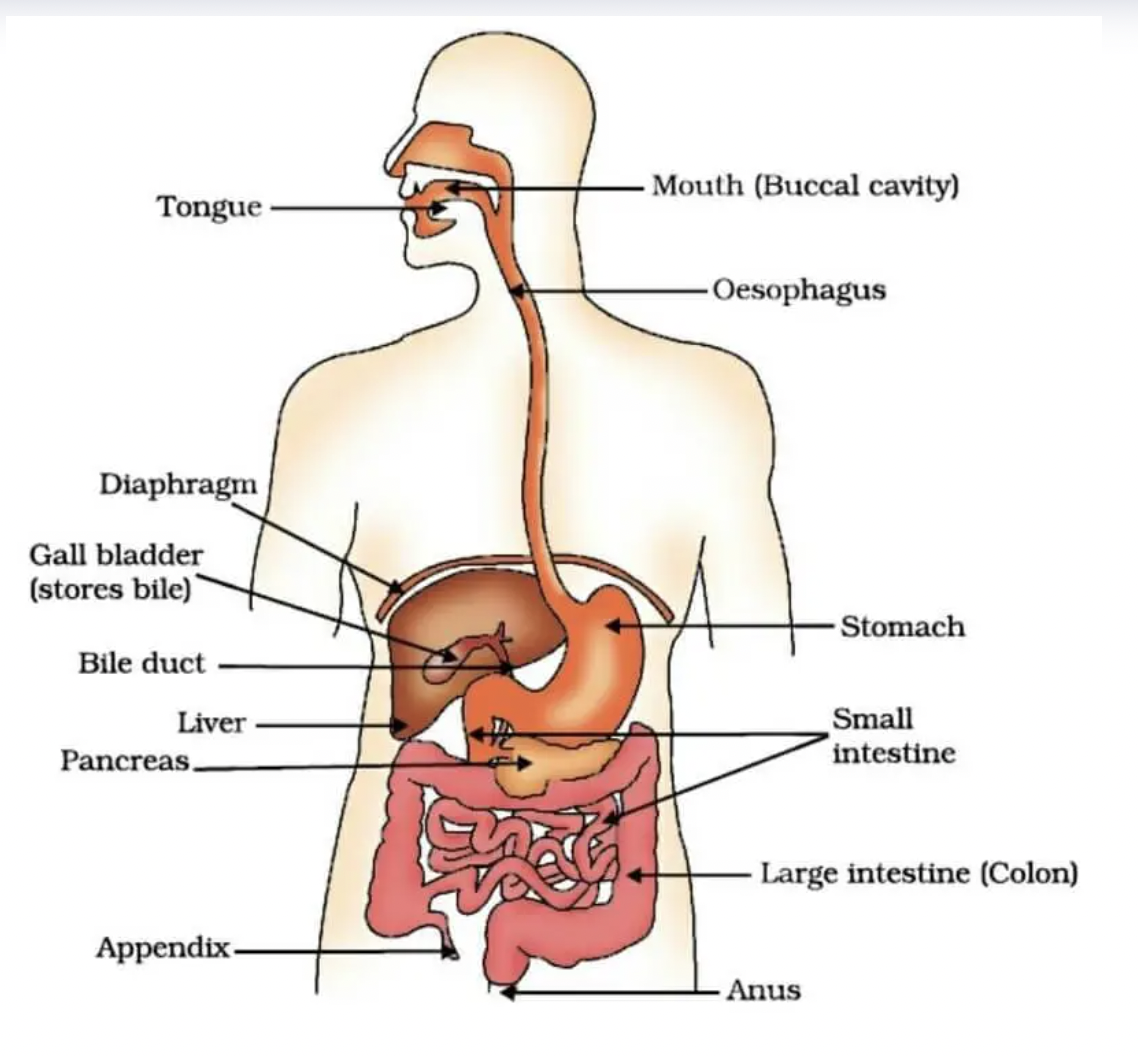
Gallbladder
Bile is stored
Pancreas
Makes Protease, amylase, lipase
Large intestine
excess water is absorbed
small intestine
digested food is absorbed into the blood
Test for sugars
Benedict’s test Positive-Blue to green to yellow to red
Test for starch
iodine Positive- Orange to black or blue
Test for Proteins
biuret Positive- Blue to purple
Test for lipids
Sudan 3 Positive- Red layer
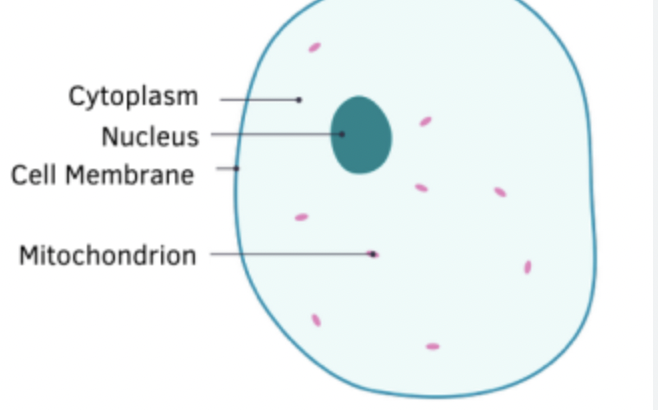
Animal cell
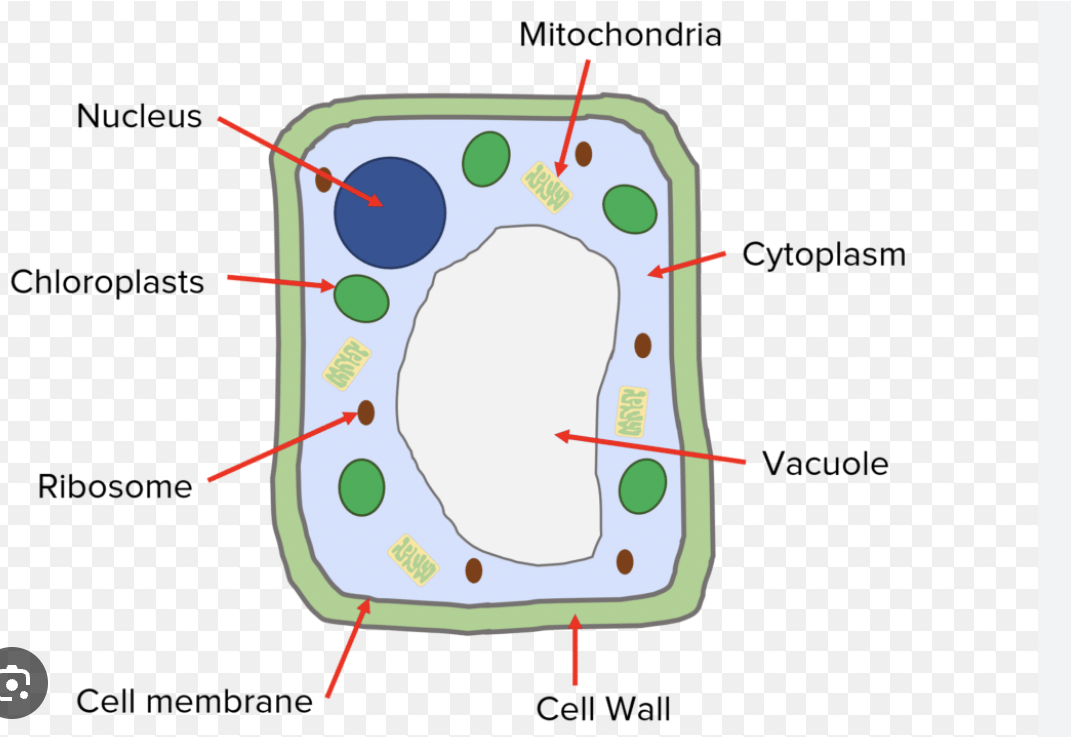
Plant cell
magnification
image size/ real size
How to prepare slide
add drop of water to slide, cut onion, separate the layers epidermal tissue, place tissue into water, add drop of iodine, place cover slip,
Order of size
cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
Diffusion
is the spreading out of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
Diffusion happens in
gasses and solutions
Osmosis
is the movement of water molecules across a semi permeable membrane from high to low concentration
Potato osmosis experiment
cut up potato into cylinders, measure mass of potatoes, put potatoes in varying sugar solutions, leave for 24 hours, measure mass, drawn water in by osmosis = bigger mass, water drawn out by osmosis = smaller mass, calculate percentage change.
percentage change
Final value - Original/ original x 100
Active transport
When substances are absorbed against the concentration gradient from low to high concentration
surface area to volume ratios
volume= length x width x height, area = length x width, put into ratio, simplify
how gills work
water enters fish through mouth, passes out through gills, o2 diffues from water into blood, co2 diffues from blood into water, each gill has gill filaments, have large surface area, lot of cappileries,
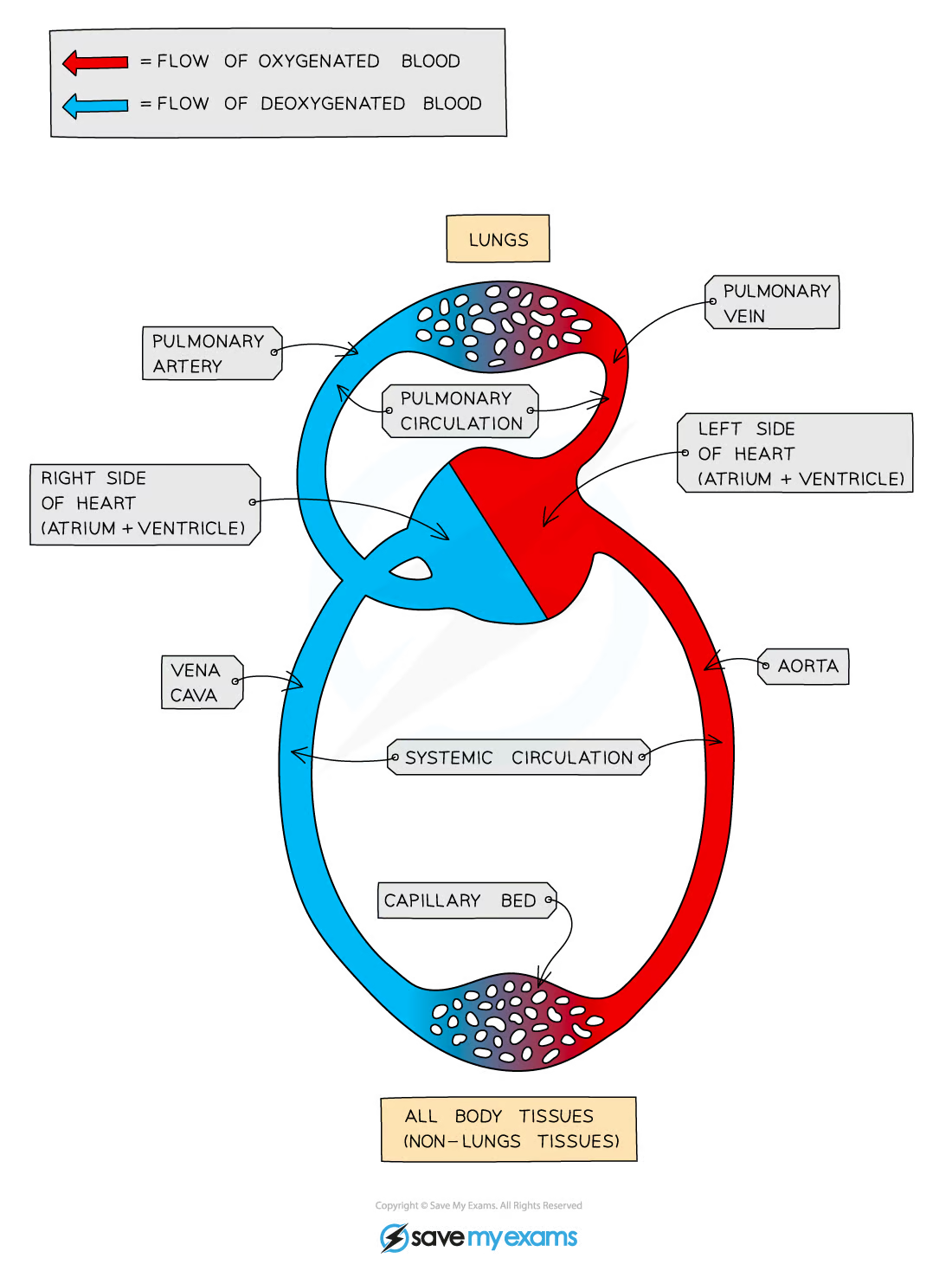
curculatory system
Heart
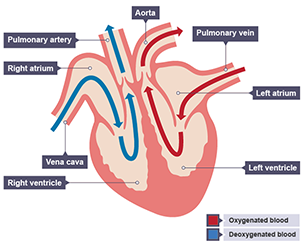
Arteires carry
blood away from the heart
Cappileries are involved
with the exchange of materials
Viens carry
blood to the heart
Arteries info
high pressure, walls are strong and elastic, thick walls,