Chapter 13: Gastrointestinal System
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
How long is the alimentary tract?
8 m long; extending from mouth to anus
Where is the digestive tract in relation to the diaphragm?
below
What accessory digestive glands secrete digestive juices into the digestive system?
salivary glands, liver, pancreas
What does the circular sphincter muscle at the end of the esophagus help with?
prevent gastric acid from moving up into the esophagus
What is a muscle that connects tthe stomach to the proximal duodenum?
pyloric canal
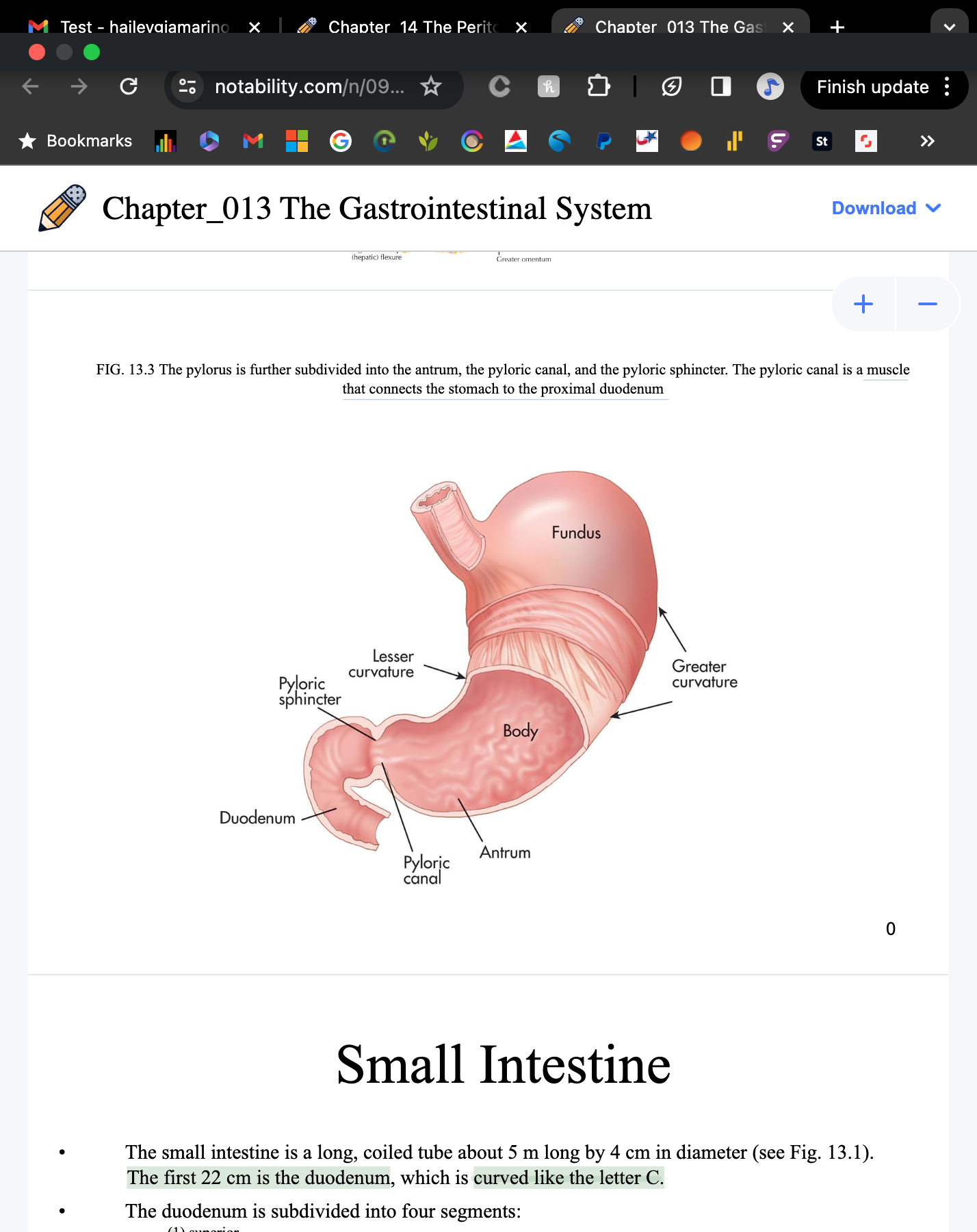
How long is the small intestine?
5 m long and 4 cm diameter
What is the first 22 cm of the small intestine called and is curved like the letter C?
duodenum
4 segments of the duodenum?
superior, descending, transverse, ascending
What is the duodenum called as it turns downward?
jejunum
How long is the jejunum?
2 m
What is the lower part of the small intestine?
ileum
What marks the entry into the large intestine and prevents food from reentering the small intestine?
ileocecal orifice
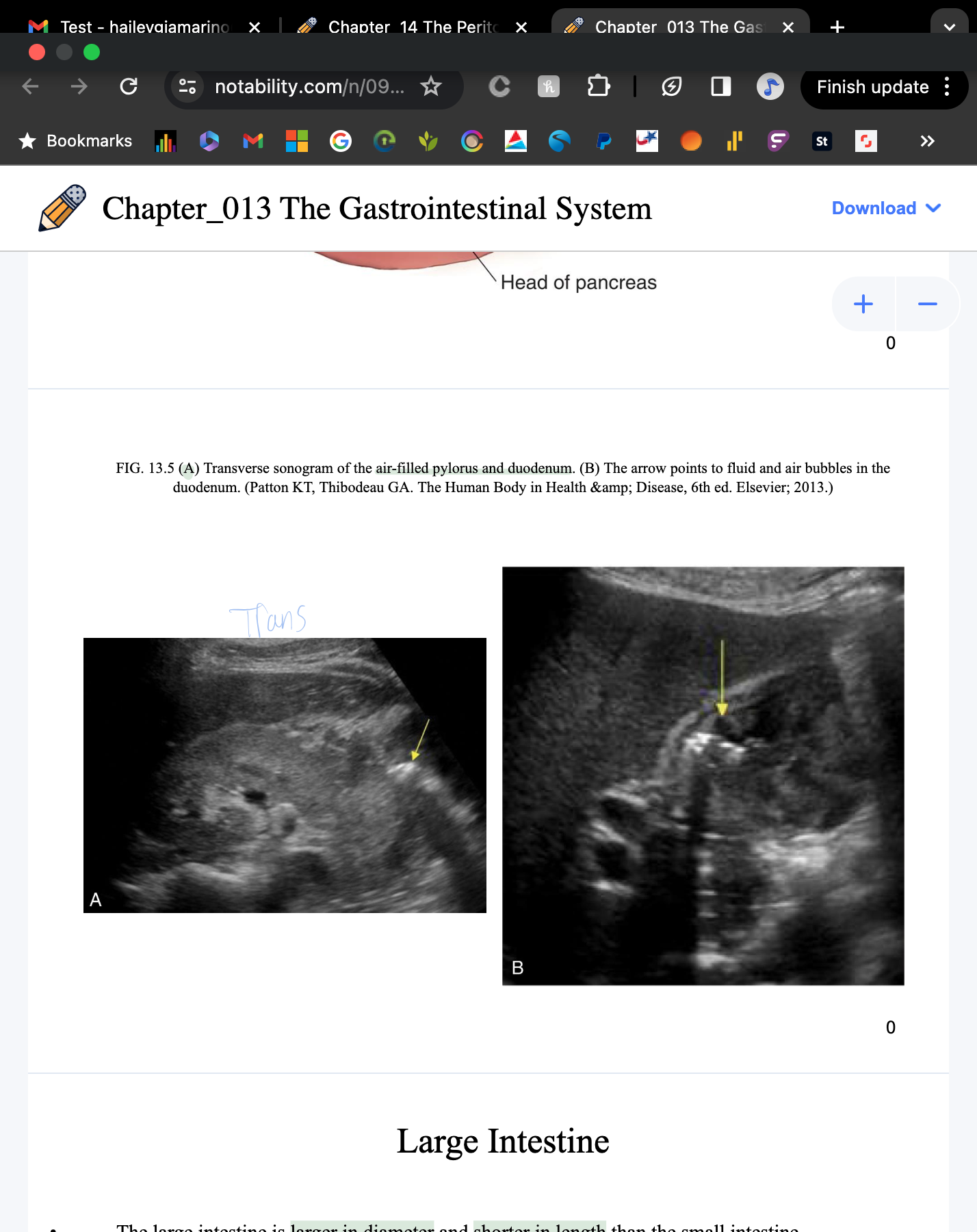
Trans air-filled pylorus and duodenum
How does the large intesttine compare to the small intestine?
larger in diameter and shorter in length
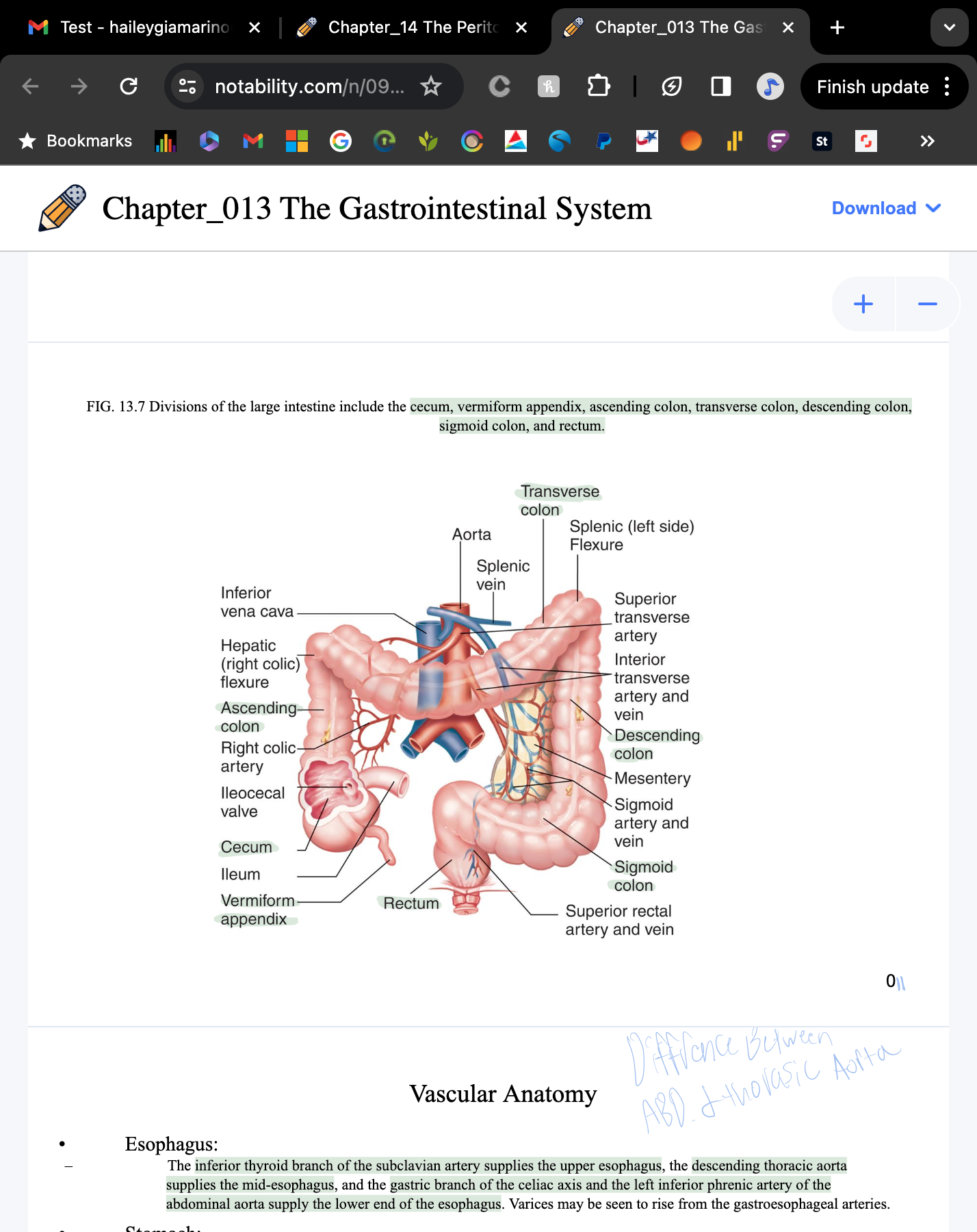
Parts of the large intestine?
cecum and vermiform appendix, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum
What are small pouches caused by sacculation which give the colon its segmented appearance?
haustra
how long is the rectum?
12 cm long, terminating at the anus
What does the mucosa of the large intestine lack and not produce?
lacks villi and produces no digestive enzymes
What artery supplies the upper esophagus?
inferior thyroid branch of the subclavian artery
What vessel supplies the mid-esophagus?
descendoing thoracic aorta
What vessel supplies the lower end of the esophagus?
gastric branch of the celiac axis and left inferior phrenic artery of abdominal aorta
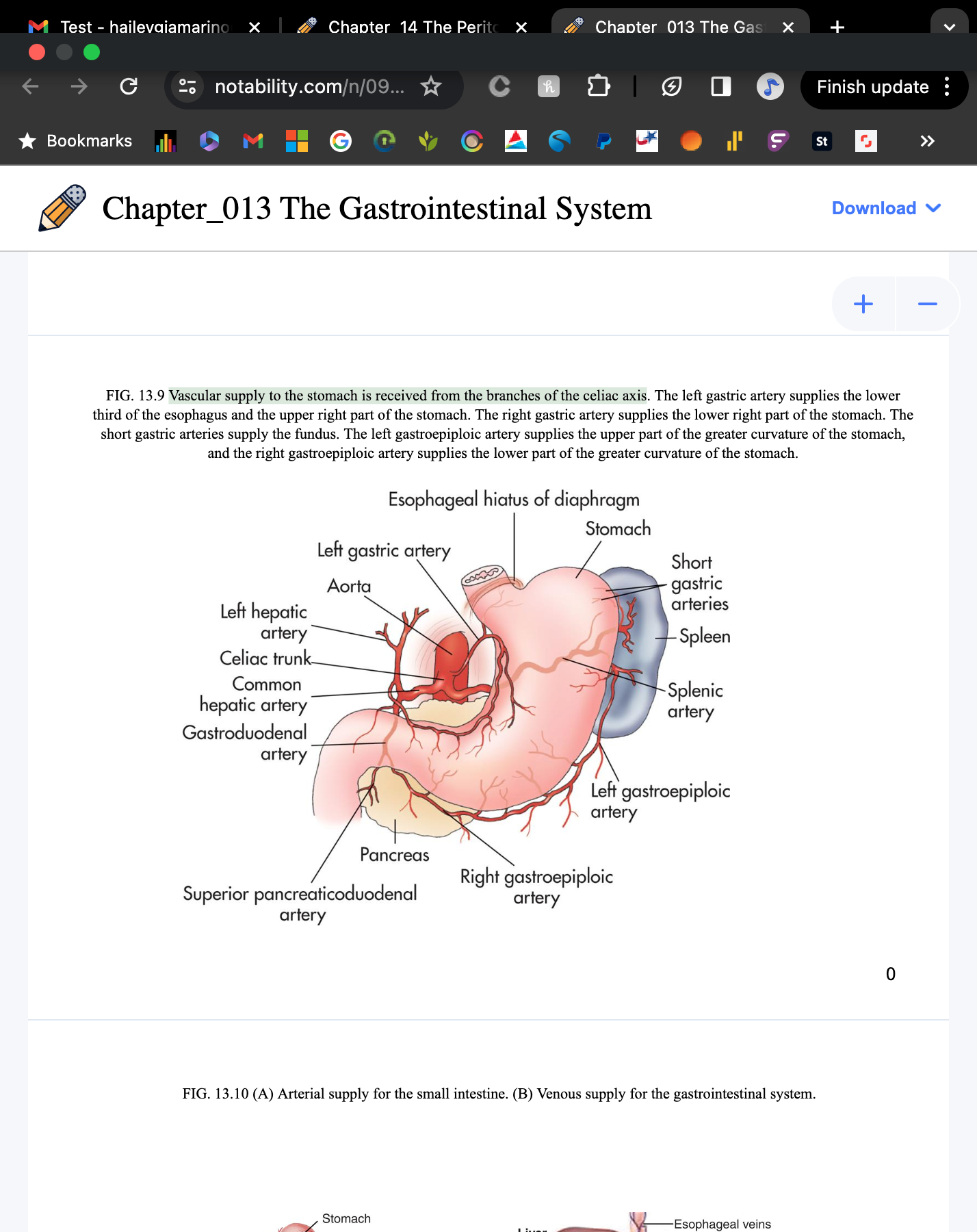
Where is vascular supply to the stomach received from?
branches of the celiac axis
What are the primary functions of the GI tract?
digestion and absorption
What is defecation?
undigested and unabsorbed food is eliminated from the GI tract
What is food converted to over a 3-4 hour period in the stomach?
chyme
What is a strong band of muscle that relaxes when necessary to release food from the stomach?
pyloric sphincter
What is released by the stomach mucosa that stimulates the gastric glands to secrete?
gastrin
Where does most digestion occur?
duodenum
What are other GI hormones?
cholecystokinin and secretin
When is cholecystokinin released?
by the presence of fat in the intestine and regulates gallbladder contraction and gastric emptying
Why might visualizing the GI tract be difficult?
intraluminal air produces an echogenic shadow which prevents the sound beam from penetrating structures posteriorly
What are the 5 layers of the bowel?
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, serosa, mesothelium
What is seen as a bull’s eye structure anterior to the aorta, posterior to the left lobe of the liver and inferior to the hemidiaphragm in LONG?
gastroesophageal junction
What should you do if a patient has a cystic mass in the left upper quadrant?
determine whether the mass is the fluid-filled stomach or another mass from adjacent organs; give carbonated drink to see bubbles in the stomach
Can you visualize the small bowel with sonography?
no
What is the remnant of what was originally the apex of the cecum?
vermiform appendix
What is located on the abdominal wall under McBurney’s point?
vermiform appendix
What is the size of the appendix?
2-20 cm in length
Where is the appendix found?
retained in position by a fold of the peritoneum that forms a mesentery for the appendix
Does the appendix have any known physiological significance?
no
What is the normal wall thickness of the colon?
4 mm
What aer the 5 layers of the colon?
2 mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria, subserosal fatty tissue
What indicates distention of the colon?
lower bowel larger than 5 cm; the entire halo should measure less than 2 cm
What pathology are embryologic mistakes?
duplication cysts
What are differential considerations for duplication cysts?
mesenteric or omental cyst
pancreatic cyst or pseudocyst
enteric cyst
renal cyst
splenic cyst
congenital cyst of the left lobe of the liver
gastric distention
What is an intragastric mass composed of accumulated ingested material?
gastric bezoar
What are the 3 types of gastric bezoars?
trichobezoars (hairballs in young women), phytobezoars (vegetable matter), concretions (inorganic materials; sand, salt)
What is a small, tumor like growth that projects from a mucous membrane surface?
polyp
What is the most common tumor of the stomach?
leiomyoma
What are leiomyoma’s associated with?
cholelithiasis, peptic ulcer disease, adenocarcinoma, leiomyosarcoma
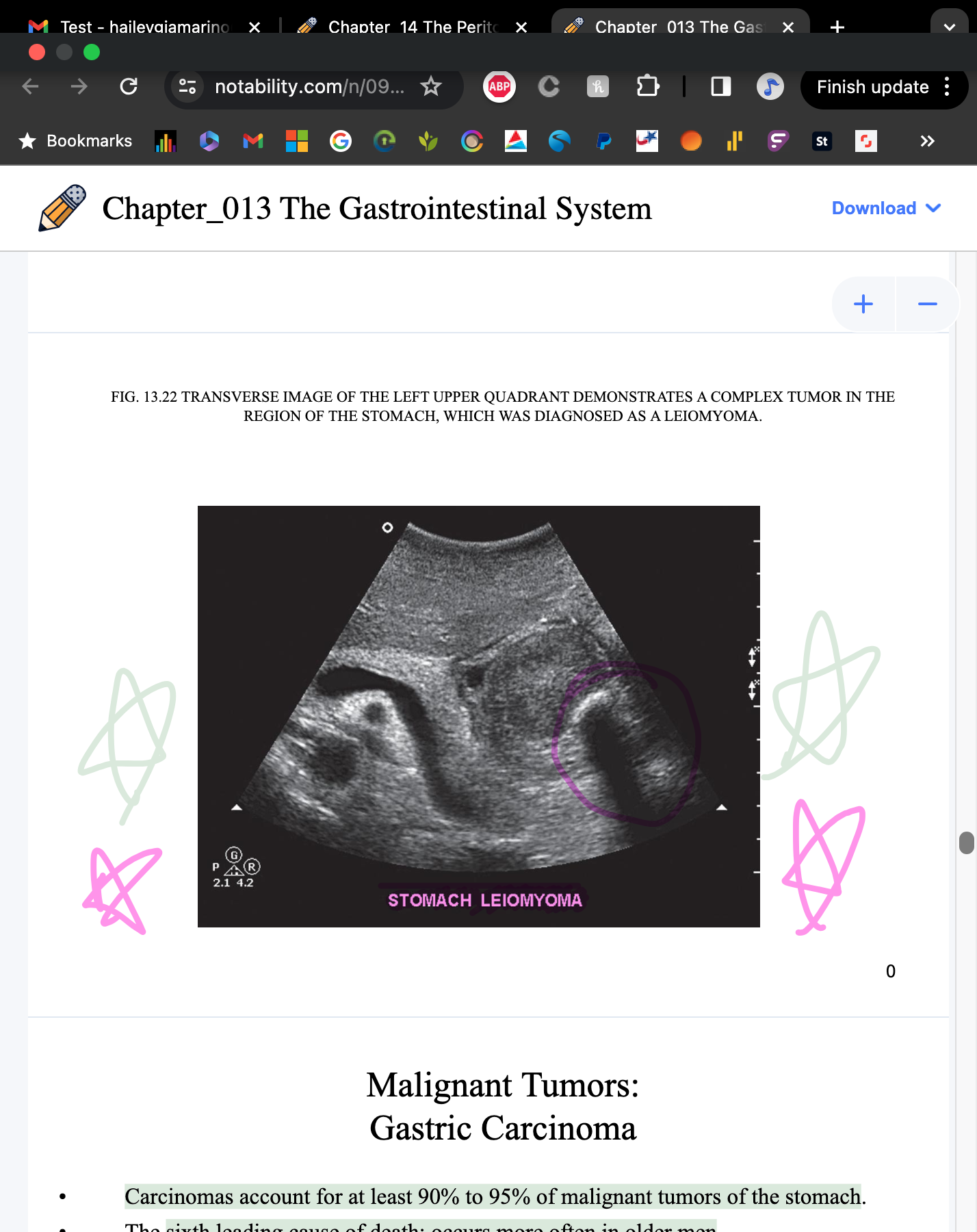
What accounts for at least 90-95% of malignant tumors of the stomach?
gastric carcinomas
What is the 6th leading cause of death that occurs most often in older men?
gastric carcinomas
What findings indicate gastric carcinoma?
target or pseudokidney sign
What makes up 3% of stomach tumors?
lymphoma
What is the 2nd most common malignant tumor (1-5% of tumors)?
leiomyosarcoma gastric sarcoma
What occurs in the 5th to 6th decades of life?
leiomyosarcoma gastric sarcoma
What tumor is rare to the stomach?
metastatic disease
What can be mistaken for a soft-tissue mass on x-ray in 6% of patients?
fluid filled dilated loops of the small bowel from obstruction
What is the result of luminal obstruction and inflammation?
acute appendicitis
What is McBurney’s sign?
pain and rebound ttenderness usually localized over the right lower quadrant
Who is at high risk of having acute appendicitis and being misdiagnosed?
women ages 20-40
How can the appendix occasionally be visualized?
gradual compression sonography
What is the maximal appendix measurement?
6 mm
What is a gross enlargement of the appendix from accumulation of mucoid substance within the lumen?
mucocele
What percentage of mucocele cases are asymtomatic?
25%
What is a pouchlike herniation through the muscular wall of a tubular organ that occurs in the stomach, the small intestine, and the colon?
diverticulum
How long is a meckel diverticulitis?
3-6 cm long and may have a greater lumen diameter than that tof the ileum
What is the most common tumor of the GI tract in children under 10?
lymphoma
What cancer is resistive and not responsive to chemotherapy or radiation?
leiomyosarcoma