Physical Properties
1/156
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Graciously from Alexis
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
what are optical properties
properties related to the light interacting with the optical aspects of an object and recognized by a sensor (observer)
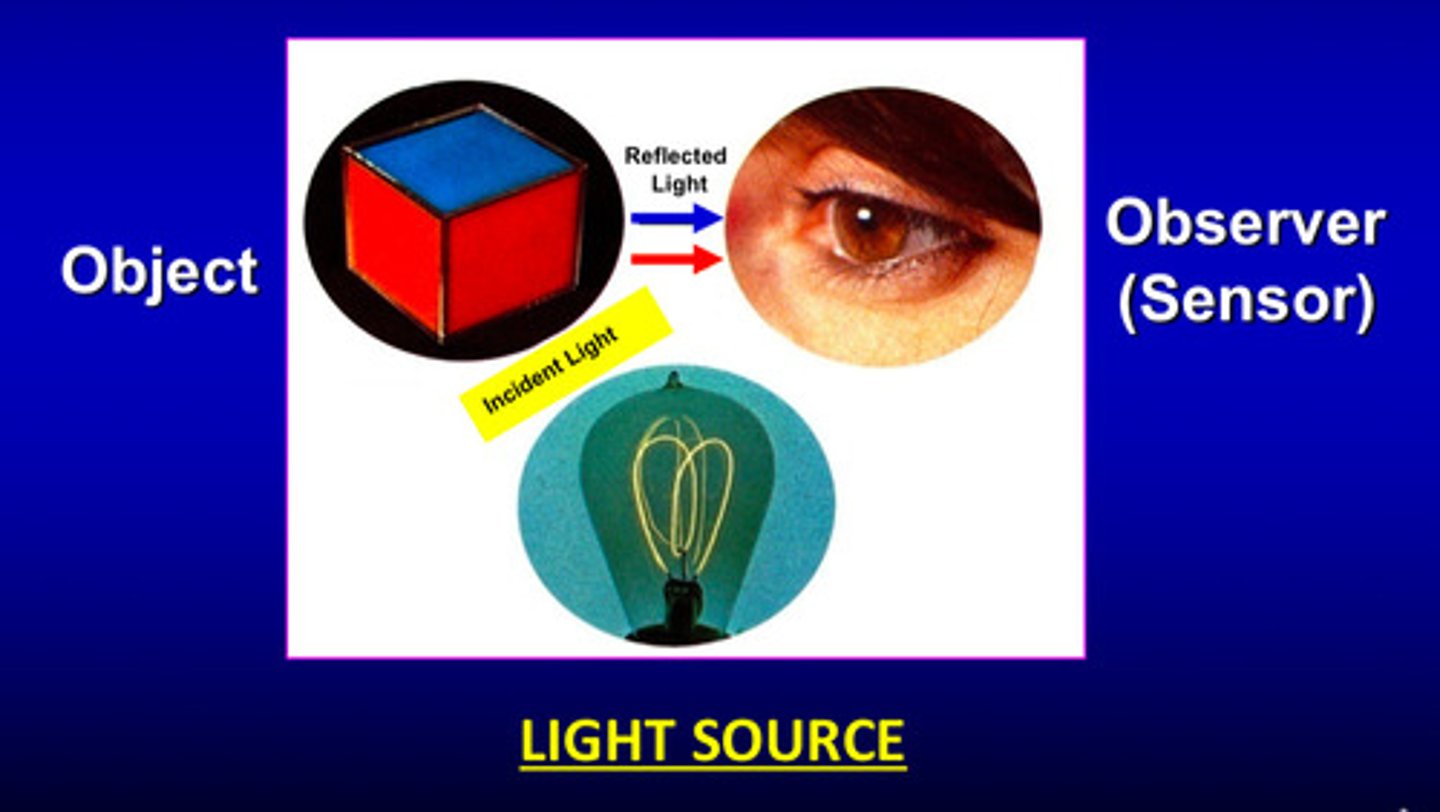
what is incident light
light emitted from a source that strikes an object
what is reflected light
light that bounces off an object and that the observer perceives
what are 2 sources of light?
artificial or natural
what is perception of the color of an object determined by
the radiation from the light source as modified by the object and received by the human visual system
color is the result of what kind of response to what kind of stimulus?
the result of a physiological response to a physical stimulus in human beings
what 2 things determine appearance properties
1) reflected light intensity
2) combined intensities of the wavelengths present in incident and reflected light
what are the 3 dimensions of color
1) hue (the color itself)
2) value (brightness)
3) chroma (intensity of the color)
what is light?
electromagnetic radiation (or photon) that can be detected by the human eye
red light has ________ wavelength and ________ energy
longer wavelength and lower energy
blue light has _________ wavelength and ________ energy
shorter wavelength and higher energy
what are the 6 colors and corresponding wavelengths of the visible light spectrum
1) violet: 400-450 nm
2) blue: 450-495 nm
3) green: 495-570 nm
4) yellow: 570-590 nm
5) orange: 590-620 nm
6) red: 620-700 nm
the spectrum is __________ and there are no _______ __________ between one color and the next that can be detected by the human eye
continuous; there are no clear boundaries between one color and the next
what is the range of the visible spectrum
400 nm (violet) - 700 nm (red)
the hue or the dominant wavelength is the wavelength in ______
nm (nanometers)
what is the visible spectrum
the wavelengths of visible light which can be perceived by the human eye
what does hue describe
the dominant color of an object
hue is the visual quality that distinguishes what
one color family from another
what are the 3 major bands of color on the visible light spectrum
red, green, and blue
why are the RGB primary (additive colors) significant
RGB color model is based on principle of additive color mixing; colors are created by combining light of these 3 primary colors in varying intensities
what are tristimulus values
set of 3 numerical values that represent the color of an object based on the human visual system's response to light; these values correspond to the 3 primary colors in sensitivities of the human eye: red, blue, green
what is the dominant wavelength of grass
green; 550 ish nm
what are 2 other terms for chroma
excitation purity or saturation
chroma is only present when?
when there is hue
chroma depends on the _______ or ________ of the hue
concentration or strength
the higher the chroma —> the _____ _______ the color
the more intense the color
value or luminance reflectance is a measure of what
relative lightness OR darkness of a color
the luminous reflectance of a color permits an object to be classified as equivalent to what
to a member of a series of achromatic objects
what are achromatic objects
objects that reflect or transmit light without selectively absorbing specific wavelengths of visible light; no distinct hue and typically appear as shades of black, white, gray
what is the range of achromatic objects
black to white for light-diffusing objects and from black (complete absorption) to perfectly clear/colorless for complete reflection or transmitting objects
what does value or luminance reflectance reflect?
the subjective brightness perception of a color
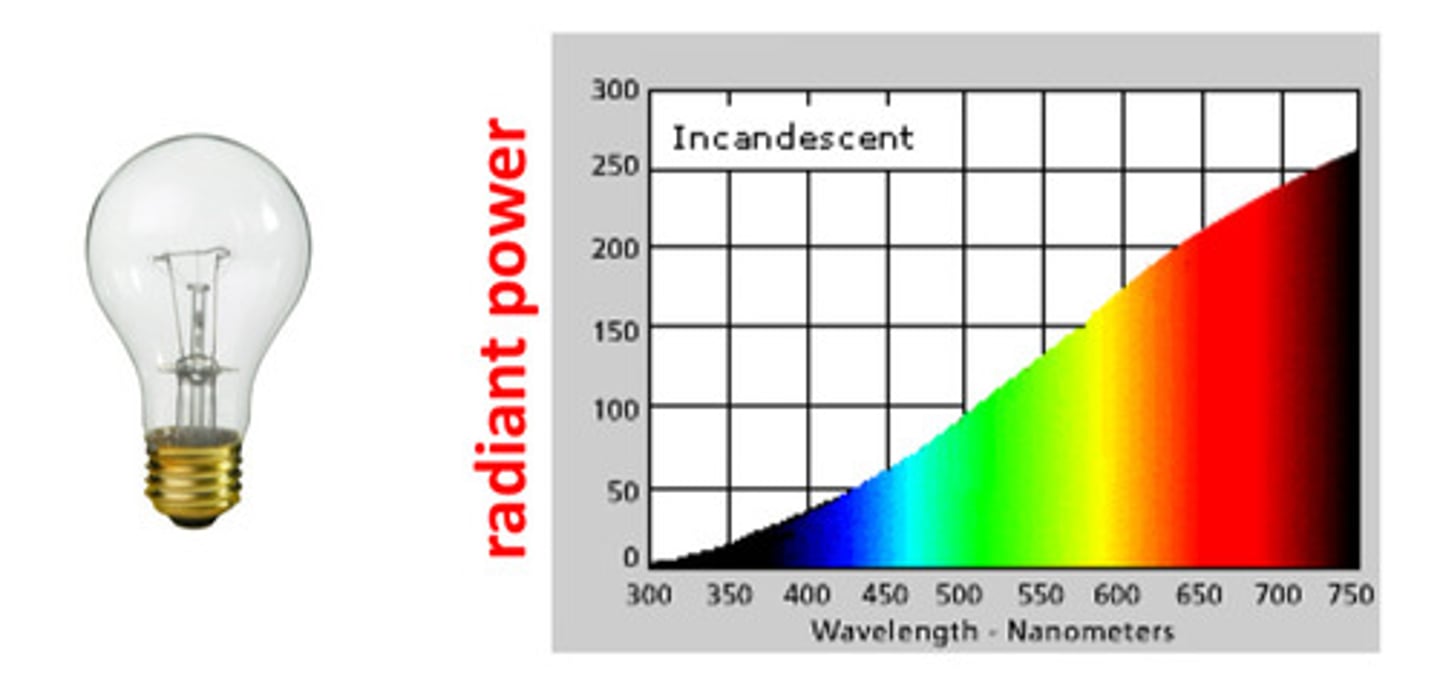
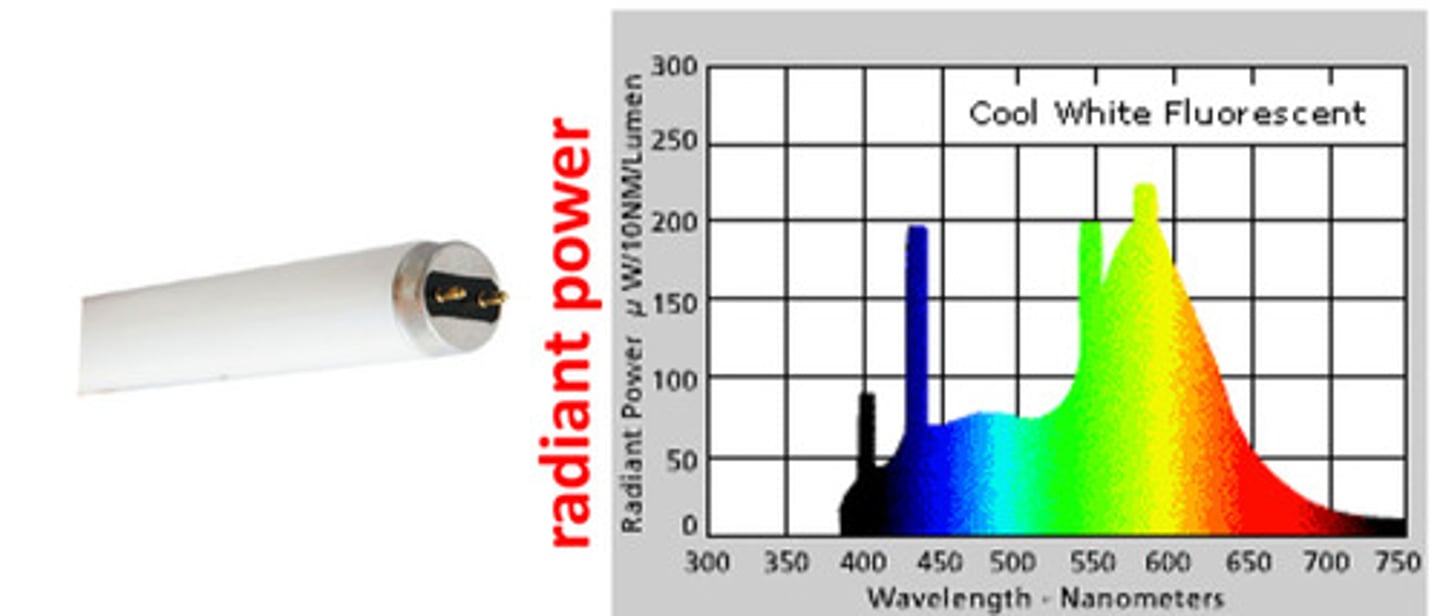
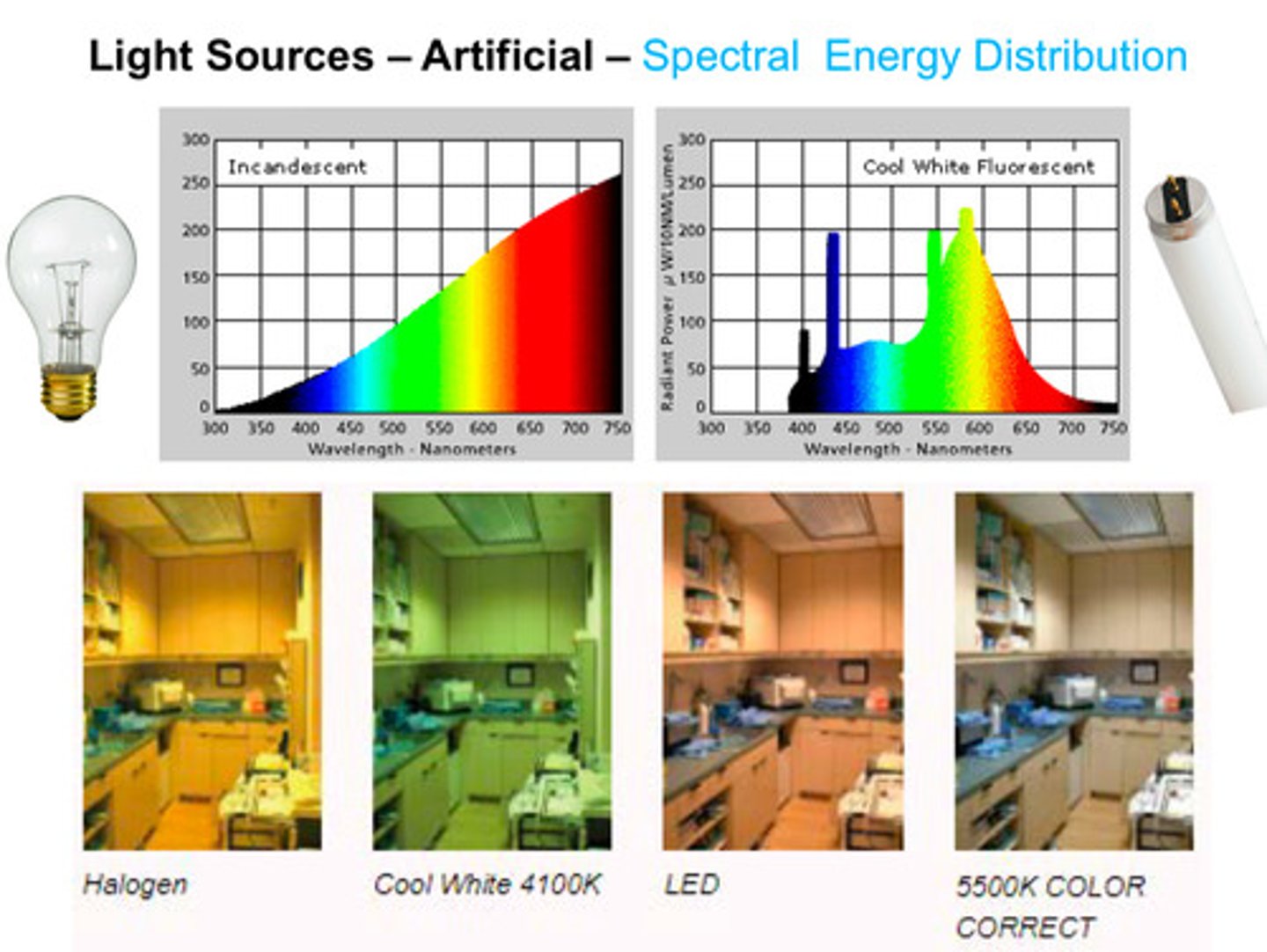
what is spectral energy distribution
a pictorial representation of the radiant power emitted by a light source at each wavelength or band of wavelengths in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum (300 to 750 nm)
radiant power of incandescent light
radiant power of cool white fluorescent light
examples of artificial light sources and how they look
what is metamerism
a phenomenon that occurs when colors change when viewed in different light sources
what are colors that match under one light source called
metamers
general explanation of metamerism
under some lights, the color pairs appear to match, but under other lights, they would be different
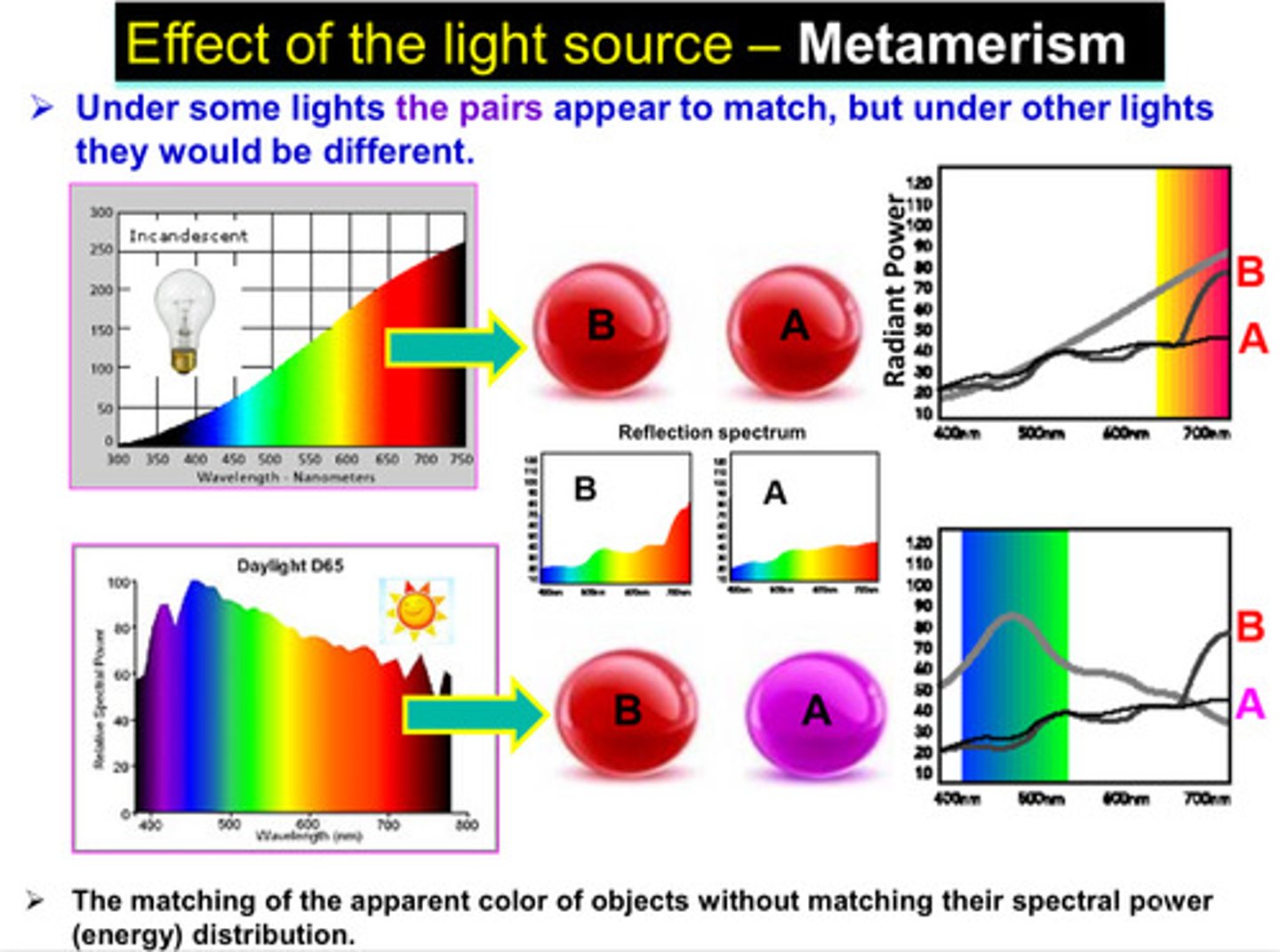
metameric colors are color stimuli of identical tristimulus values under a particular light source but with ?
but with different spectral energy distributions
what 3 things contribute to metamerism
1) spectral energy distribution of the light source
2) material reflectance
3) human vision response
because of metamerism, shade matching should be done in conditions where ?
where patient's activity will occur mostly
what is the best light source for shade matching
natural diffuse light
what is the worst light source for shade matching
harsh/direct dental chair light
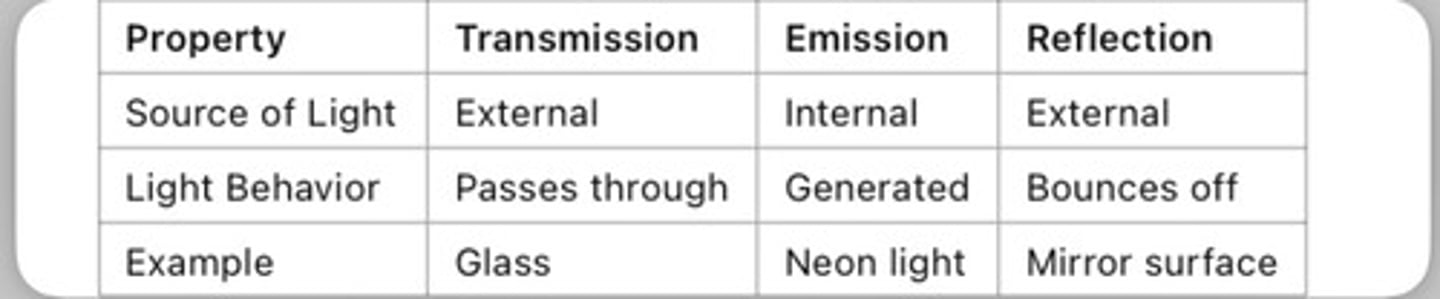
what are optical effects caused by
light given off via transmitted, emitted, or reflected reactions
comparison of transmitted, emitted, and reflected lights
complete reflection: white color
complete absorption: black color
selective reflection/absorption: colored but will appear the color that it reflects bc absorbed wavelengths are usually converted into other forms of energy and are not visible to us
what determines the appearance properties of objects?
the combined intensities of the wavelengths present in incident and reflected light
what is opalescence
optical phenomenon characterized by a milky/pearly appearance seen in some materials when light scatters through them; this occurs when particles in a medium are small enough to scatter shorter wavelengths of visible light (like violet or blue) while allowing longer wavelengths (like red and yellow) to pass through, creating a bluish/iridescent appearance when viewed against light and the transmitted light that passes through may appear red/orange
what is the tyndall effect
the scattering of light by particles in a colloid or very fine suspension that favors the scattering of shorter wavelengths; opalescence is a specific visual manifestation of the tyndall effect
what happens in direct light in the tyndall effect
shorter wavelengths (blue and violet) are reflected/scattered (by dentin or porcelain) and the longer wavelengths (red and yellow) are absorbed
what happens in transillumination (light passing through a medium and being observed from opposite side) in the tyndall effect
longer wavelengths are reflected at the surface and the shorter wavelengths are absorbed
opalescent materials (such as enamel and dentin) can _______ and ______ shorter wavelengths of light
scatter and reflect shorter wavelengths of light
an opalescent object will appear what color in transmitted light?
yellowish-red
an opalescent object will appear what color in the reflected light perpendicular to the transmitted light?
blue
what is fluorescence
the emission of visible light by substances or minerals that have absorbed light (UV) or other electromagnetic radiation
the wavelength of the emitted light in fluorescence usually is ________ than that of exciting radiation
longer (this is because emission occurs as the energy is released and will be at a lower energy)
what is exciting radiation
electromagnetic radiation (usually UV, visible, or near-infrared light) that provides energy to a system and raises it to a higher energy state —> the system becomes unstable in this excited state and will release the absorbed energy (ex: fluorescence)
the most striking examples of human teeth fluorescence occur when the absorbed radiation is in the _____, and thus invisible to the human eye, and the emitted light is in the _______ region - blue
UV; visible region
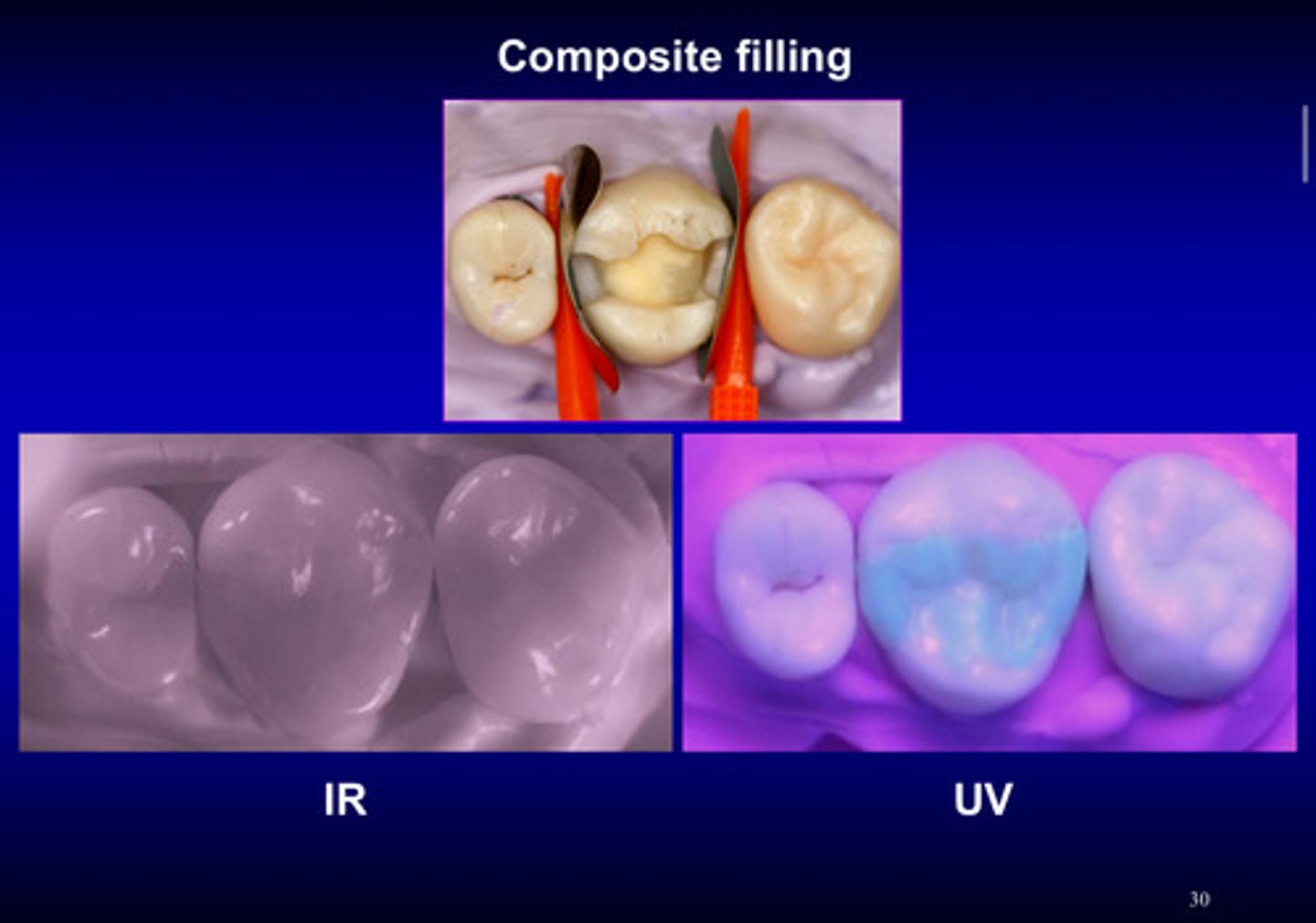
what kind of oxides such as cerium oxide are added to the dental porcelain and composite that cause them to look blue under UV lights
rare earth oxides
why does surface texture matter in the perception of the color of an object
a rough surface will look dull due to scattering light in many directions
what does transparency mean
light will fully pass through an object
what does translucency mean
light will pass through a little but will also be dispersed
what does opacity mean
light will not pass through at all
what is translucency as a property
it is the property of a material that indicates the degree of light transmission or disperses the light
what is opacity as a property
it is the property of the material that prevents the passage of light or light is totally reflected
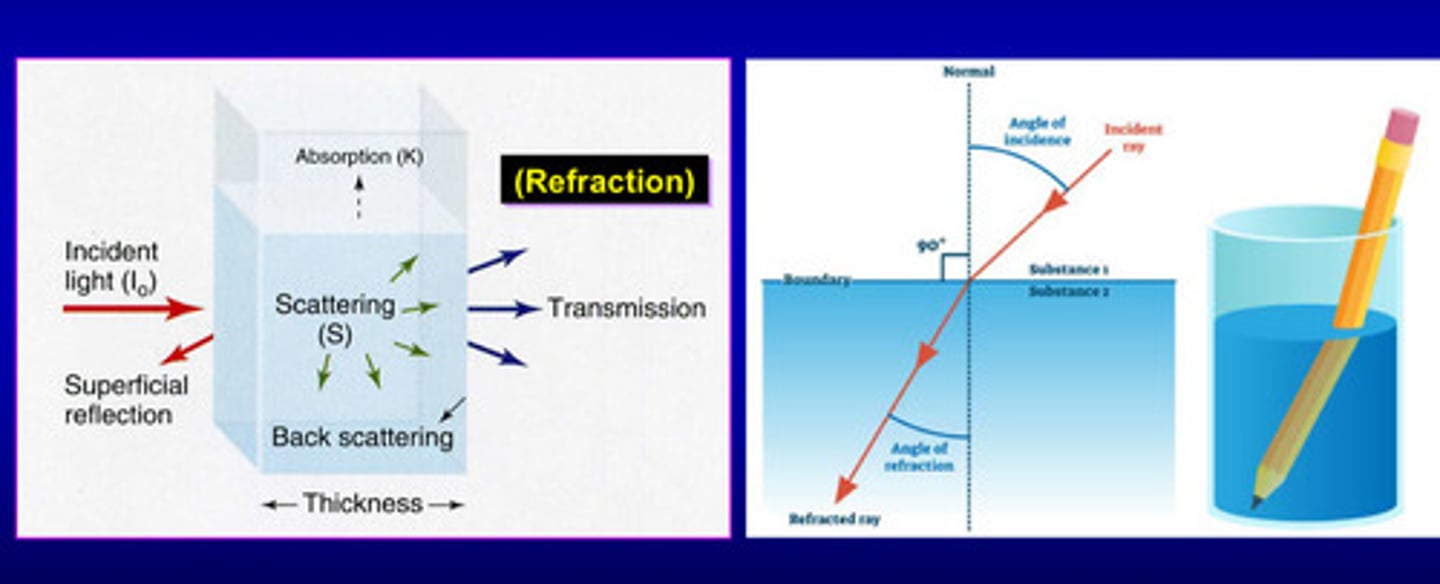
what is the refraction of light
the bending or change in direction of light when it travels from one medium to another
what is the index of refraction
the speed of light in vacuum / the speed of light in medium (n = c/v)
the amount of bending of light depends on the change in ___
the index of refraction
what is the clinical application of the index of refraction
dentists should control the IR component of restorative materials to match the translucent appearance of tooth structure
materials with low refractive indices allow light to pass through with minimal bending, making them appear?
transparent
materials with high refractive indices scatter or absorb more light, making them appear more?
more opaque or translucent
when light enters a medium, it ______ from its speed in air and may change ____________
slows; may change direction
indices of refraction of various materials
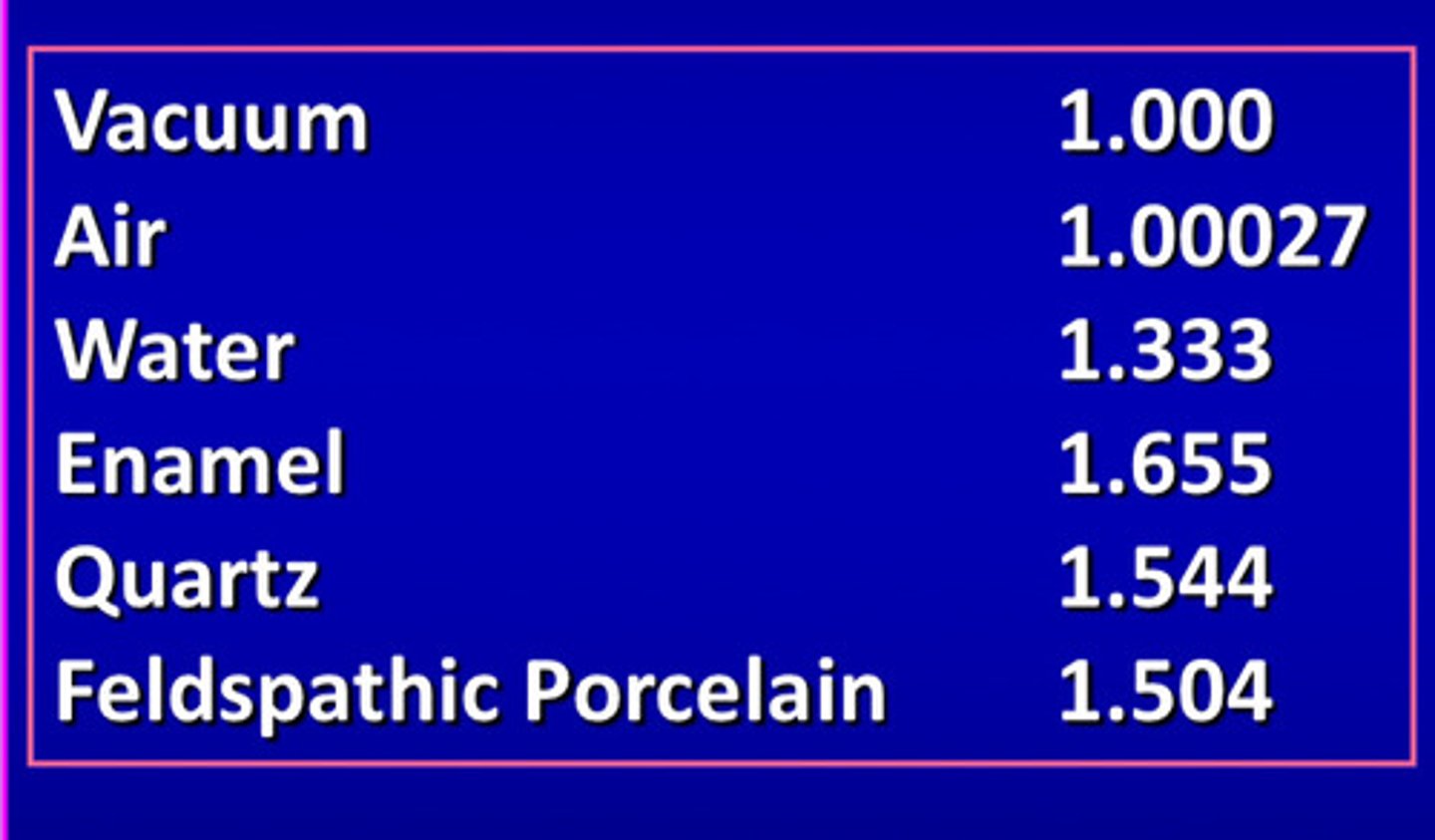
white opacity on teeth are created by differences in what
differences in the refractive index (for example enamel has IR of 1.65 but composite has IR of 1.6)
a perfect match in the IR results in what
a translucent solid
what might white lines on teeth indicate (4)
1) gaps
2) discontinuous voids
3) micro fractures in the tooth substance
4) micro fracture in the restorative materials
what is the munsell color system
color is compared with a large set of color tabs and is then identified by its hue, value, and chroma (HV/C)
shade guides used in clinic are designed to match which classical shade guide
VITA classical shade guide
A1-A4 on the shade guide are what colors
reddish brown
B1-B4 on the shade guide are what colors
reddish yellow
C1-C4 on the shade guide are what colors
gray
D2-D4 on the shade guide are what colors
reddish gray
to measure color of teeth, you may use __________ technique
instrumental
what is the function of instrumental technique
it evaluates the chromaticity and illuminance of light sources or objects by reflected or transmitted light
what is a relevant instrumental technique
CIELab Method: uses 3 coordinates to define color to find the color difference metric (deltaE)
- L (lightness): 0 (black) to 100 (white)
- a (green-red axis): +a (red) to -a (green)
- b (blue-yellow axis): +b (yellow) to -b (blue)
- delta E: 0 (perfect color match), < or equal to 1 (not noticeable to human eye), >3 (noticeable difference)
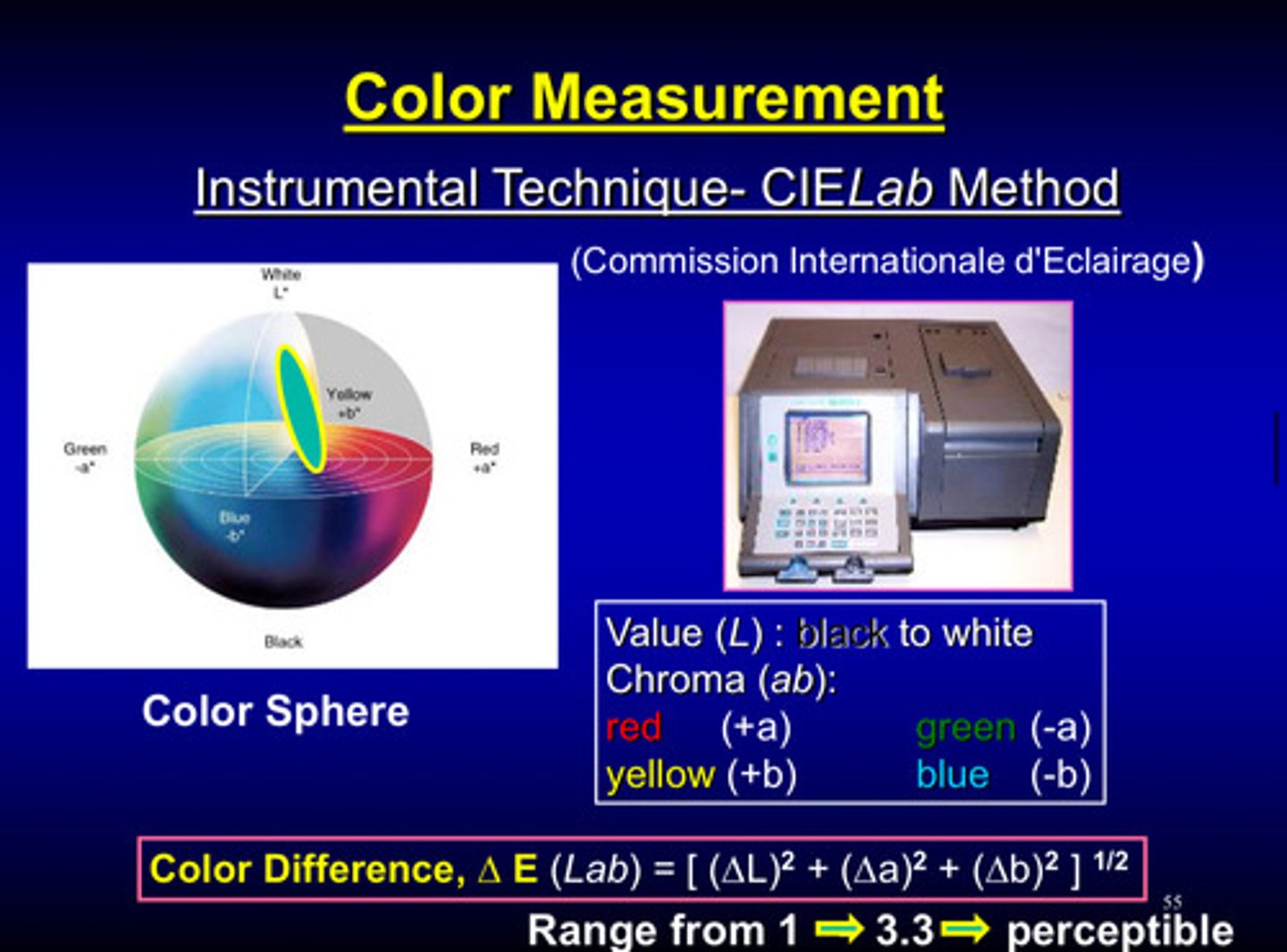
how does the CIELab Method work
1) the sample is illuminated with a standard light source
2) a color measurement device captures the light reflected or transmitted by the sample
3) the instrument converts the spectral data into L, a, and b values on mathematical models
4) the measured color can be compared to target standard using the calculate deltaE, which represents the difference between 2 colors
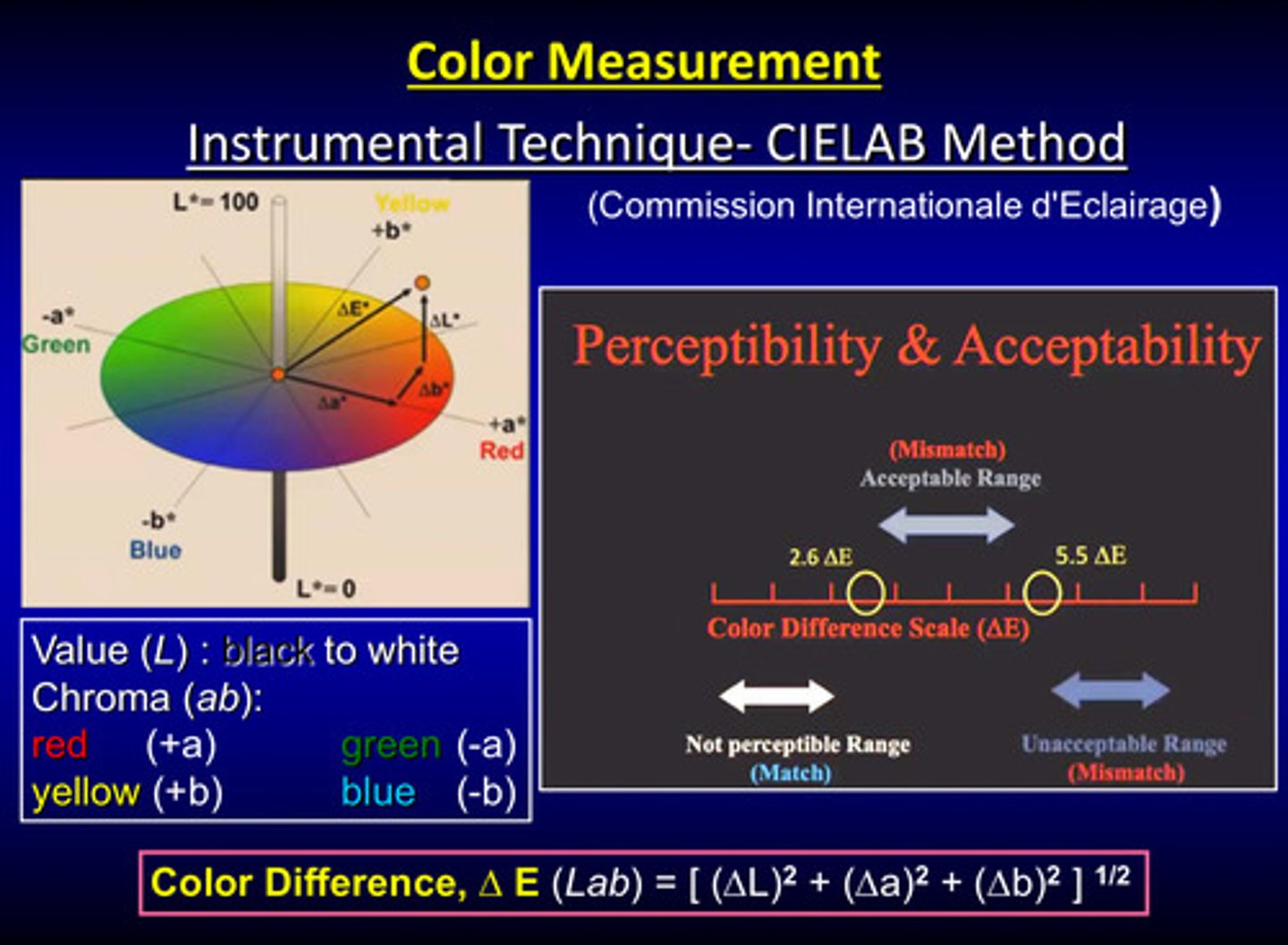
what are the perceptibility and acceptability ranges of the CIELab Method
no perceptible color difference (match): 0-2.6 deltaE
perceptible and acceptable color difference (mismatch): 2.6-5.5 deltaE
perceptible and unacceptable color difference (mismatch): 5.5+ deltaE
what are thermal properties related to
related to the thermal changes of the materials during manufacturing
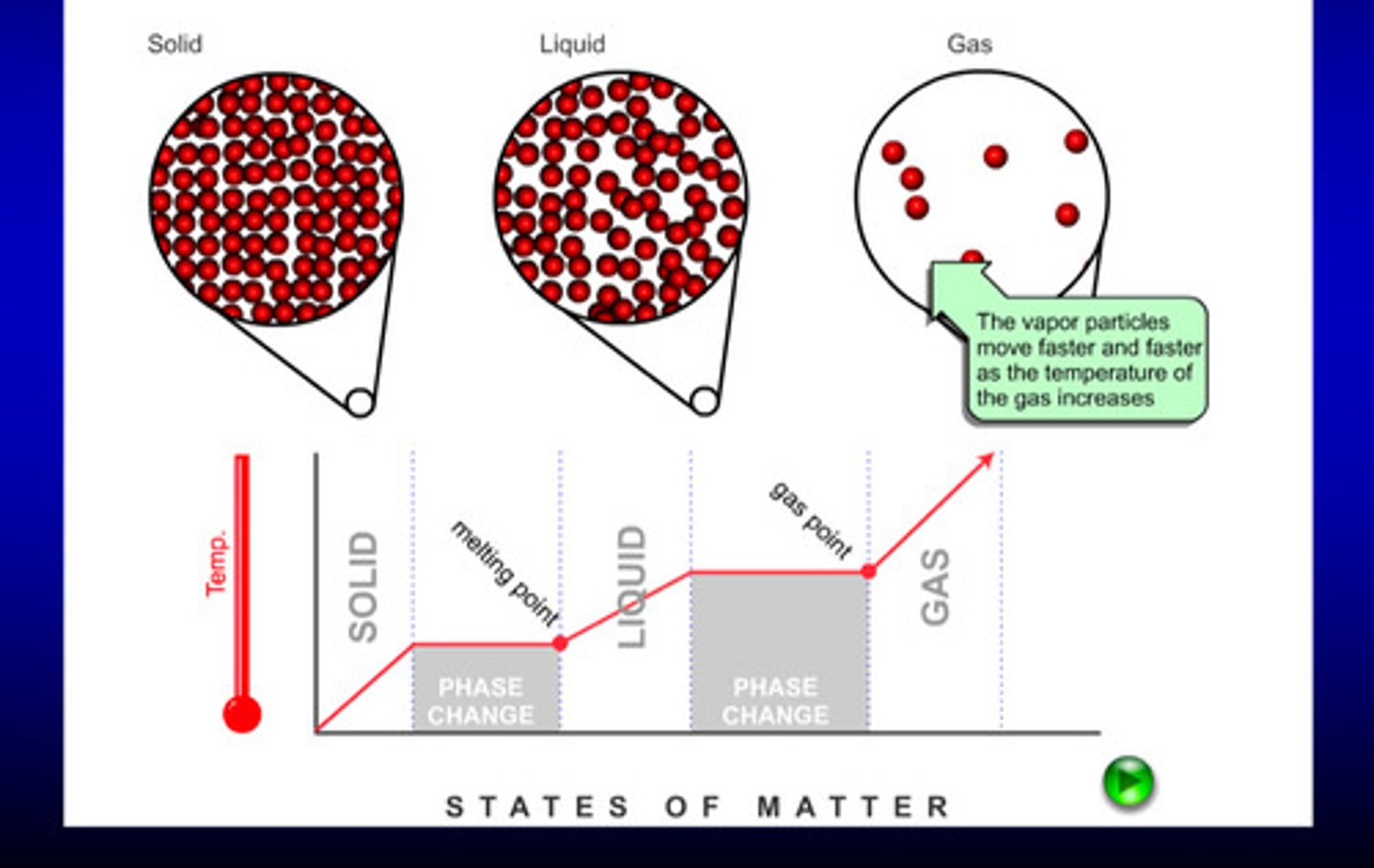
what are the 3 states of matter
solid, liquid, gas
states of matter table
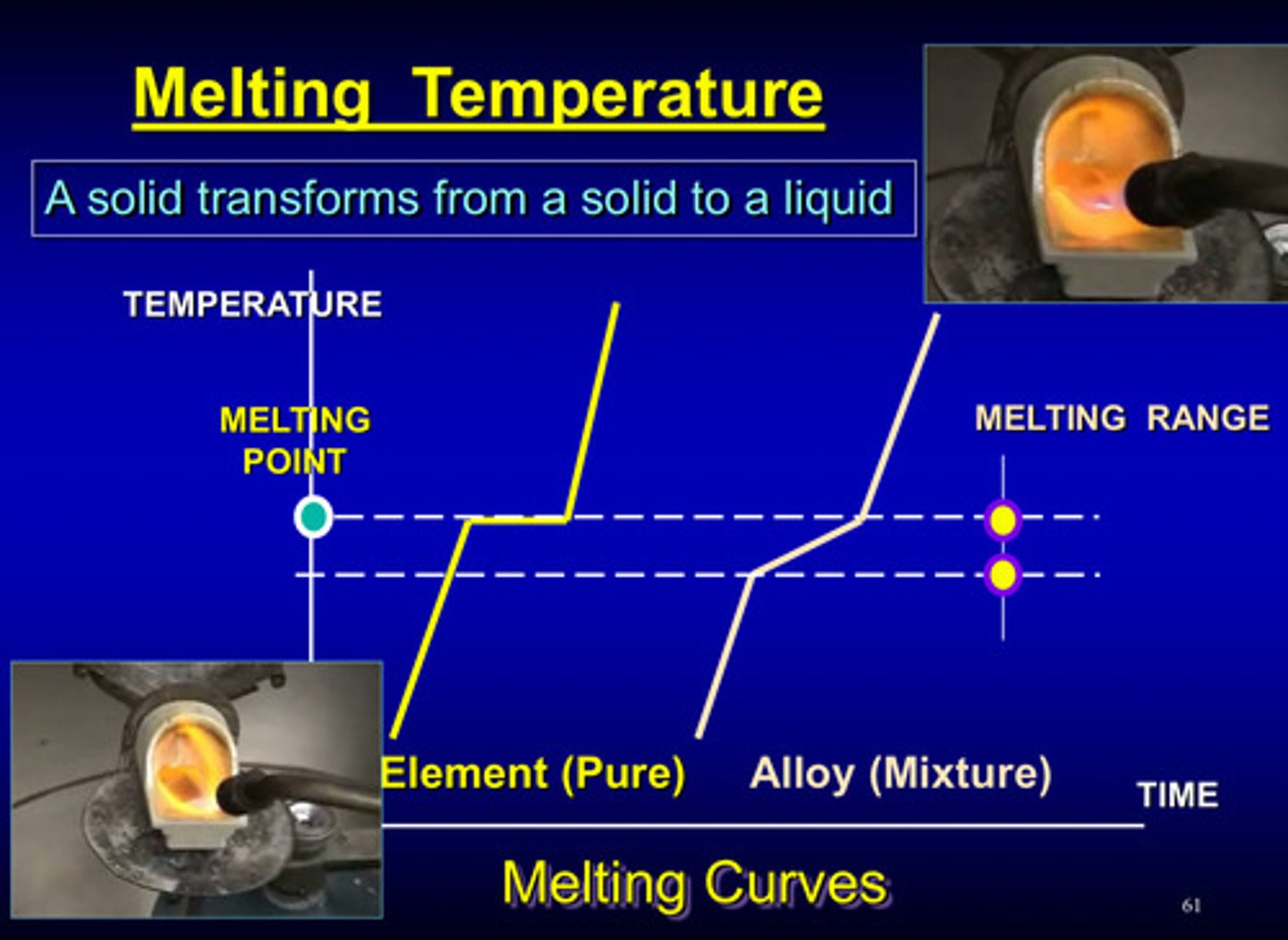
what is the melting temperature
the temperature in which a solid transforms from a solid to a liquid
a pure element most likely has one melting/freezing _______
one melting point
an alloy (mixture) most likely has a melting/freezing _______
melting range
melting curve picture
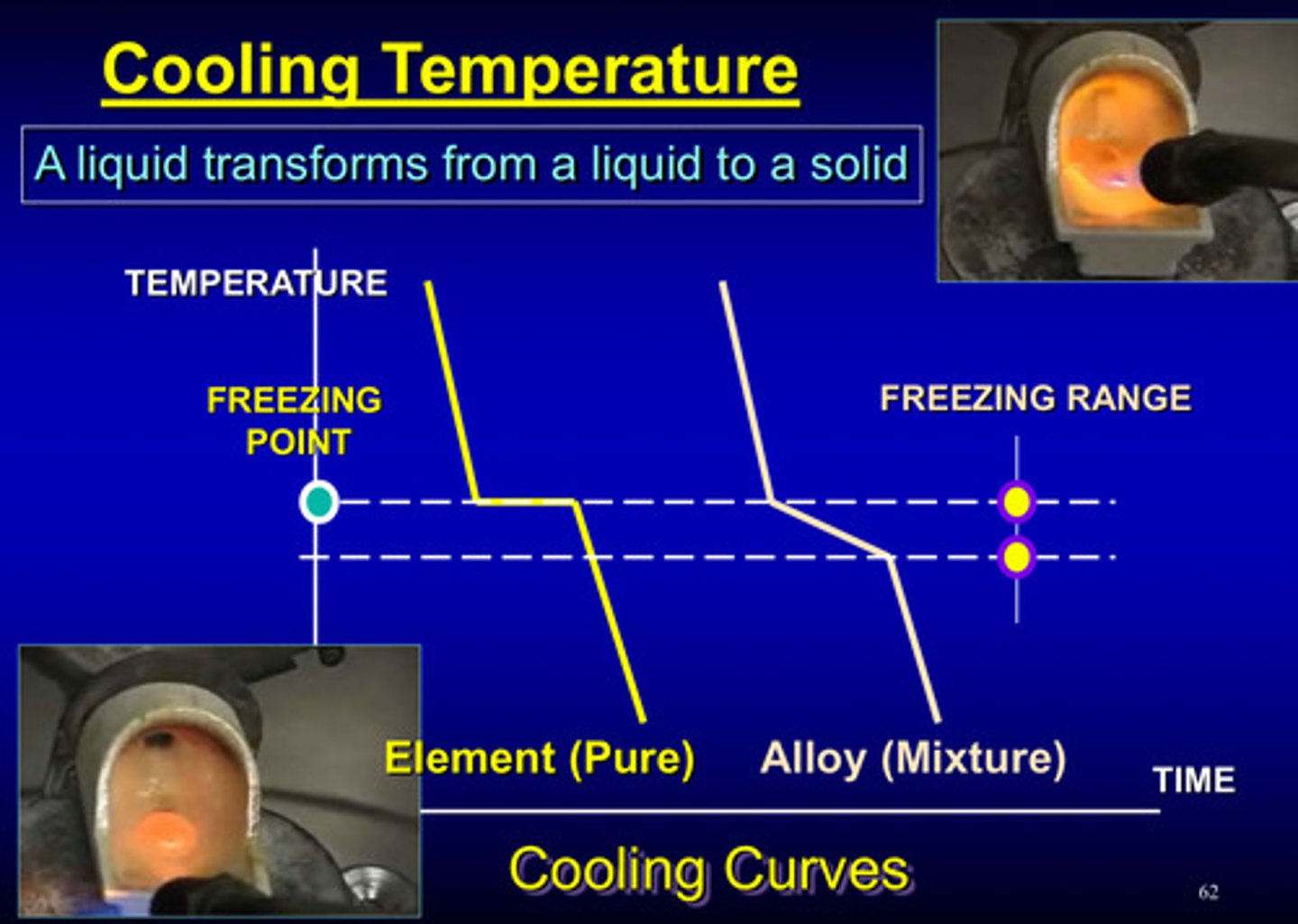
what is the cooling temperature
the temperature at which a liquid transforms from a liquid to a solid
cooling curve picture
what are the importances in dentistry of melting temperature
1) casting alloy melting temperatures determine types of investments and flame source
2) porcelain addition and staining requires close observance of firing temperatures to avoid melting of metal substrate
what is latent heat
the heat/energy required for a material to undergo a change of phase or state rather than to increase its temperature
latent heat is retained for what?
for maintaining the kinetic molecular motion of molecules in the liquid and gas state
there is ___ temperature change in latent heat
NO
in other words, latent heat is the heat input required to change what
to change from a solid to liquid or liquid to gas