A2 Physics Alternating Currents
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
what is period in terms of AC
time taken for one complete cycle of an alternating current
what is frequency in terms of AC
number of complete cycles per unit time
what is peak value in AC
the amplitude of the oscillating current or voltage
formula for representing a sinusoidally alternating current or voltage
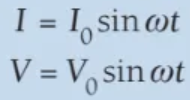
what is mean power in a resistive load half of
it is half of the maximum power for a sinusoidal alternating current
what is the difference between root mean squared and peak values
root mean squared would give the equivalent DC value that would give the same power dissipation
peak values is maximum amplitude of the wave
formula for root mean squared
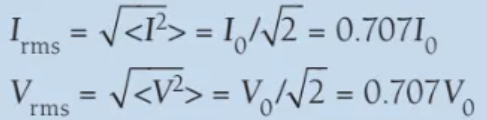
what is half-wave and full-wave rectification
rectification is converting an AC to DC
half-wave consists of the positive half-cycles
full-wave reverses the polarity the negative half-cycles to make it more efficient
what is the use of a single diode for the half-wave rectification
only allows movement only in one direction
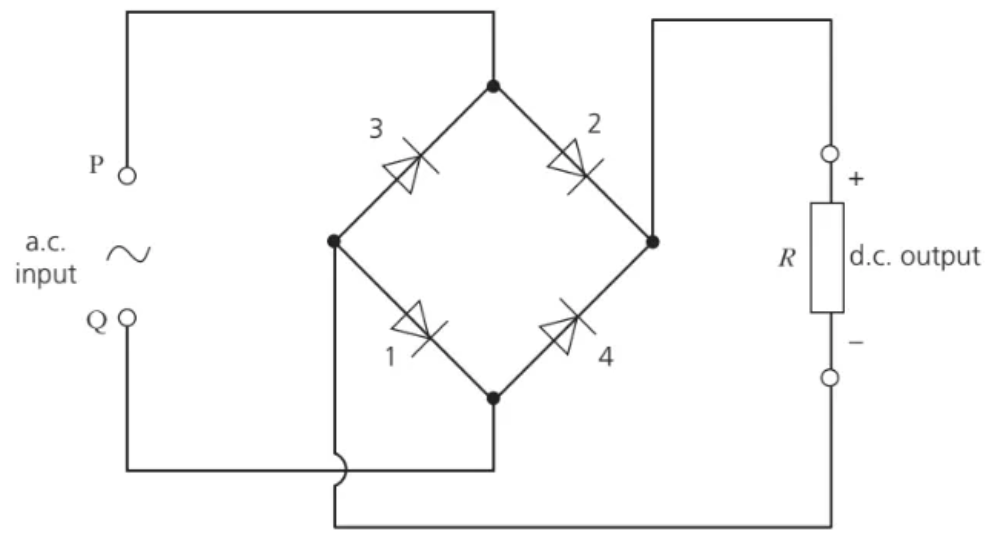
what is the use of four diodes (bridge rectifier) for the full-wave rectification
diodes switch on and off to allow current to flow from one end to another
In the diagram below, when P is positive, diodes 1 and 2 on opposite sides will conduct. When Q is positive, diodes 3 and 4 will conduct. Thus the resistor will always have its upper terminal positive and its lower terminal negative
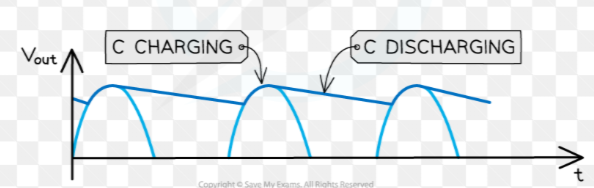
what is smoothing
reduction in the variation of the output voltage or current using capacitors
what does the capacitor do in smoothing
placed parallel to resistor
capacitor charges up input voltage and discharges gradually when voltage drops
how does a graph of smoothing look like