Neuro exam & mental status
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
combined set
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
segments of the spinal cord
7 cervical vertebra, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, sacral fused bones
difference between efferent and afferent
afferent: sensory info (dorsal root)
efferent: motor info (ventral root)
what are the parts and functions of both the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system?
CNS: spine, brain, brainstem
synthesizes information and produces output
PNS: autonomic (sympathetic + parasympathetic) involuntary, somatic voluntary
intakes and reacts to information
CN 1
olfactory, scent - close one nare at a time, patient identifies smell
CN 2
optic, visual acuity + visual fields - fundoscopy exam, swinging flashlight test
CN 3
Oculomotor, eye movement - H-test extraoccular movements, pupil constriction with bright light, convergence, alternate gaze between nose and finger
CN 4
trochlear, eye movement down and laterally (similar to CN3)
CN 5
trigeminal, mastication + facial sensation - clench teeth, palpate masseter and temporalis muscle, use sensory testing soft sharp dull for V1 (opthalmic above eyebrow), V2 (maxillary cheek), V3 (mandibular) aspects of face
CN 6
Abducens, lateral eye movement (similar to CN 3)
CN 7
facial expressions - smile with teeth + puff cheeks + close eyes tightly
CN 8
vestibulocochlear, hearing + balance - gross hearing test finger rub, Weber and Rinne tests if indicated
CN 9
glossopharyngeal, speech + swallowing + gag reflex - wide mouth say “ahh” and watch for uvula deviation and/or soft palate raise
CN 10
vagus nerve, parasympathetic innervation (similar to CN 9) - check uvula deviation
CN 11
spinal accessory nerve - sternocleidomastoid muscle strength turn head with resistance, shrug shoulders against resistance
CN 12
hypoglossal, tongue muscles - extend tongue, test lateral tongue strength resist against tongue in cheek, listen for speech difficulty
what is an upper motor neuron? how does it appear in physical examination?
-Cell bodies of upper motor neurons lie in the motor strip of the cerebral cortex
Exam- Characteristic upper motor neuron signs: increased muscle tone, hyperreflexia
what is an upper motor neuron? how does it appear in physical examination?
-Cell bodies of lower motor neurons reside in the anterior horns of the spinal cord, so they are also called anterior horn cells
Exam- Characteristic lower motor neuron signs: decreased muscle tone, hyporeflexia, fasciculations and atrophy
components of a mental status exam
A&Ox4, graphesthesia, and stereognosis
components of cognitive evaluation
orientation (A&Ox4), attention/focus, memory (short/long term), calculation, abstract thinking, constructional ability (drawing)
difference between roots and ramus
roots (either motor OR sensory) combine to the spinal nerve ramus (both sensory + motor)
cerebrum
largest part of the brain
surface of brain, consists of frontal lobe (executive function/thinking), motor cortex, sensory cortex, parietal lobe (perception), occipital lobe (vision), temporal lobe (memory)
cerebellum
balance, coordination, muscle tone
walking/standing
brainstem
consists of midbrain, pons, and medulla - responsible for automatic life functions (breathing, sleep, regulation, etc.)
basal ganglia
motor movements, connects motor cortex to upper brainstem - important in movement disorders!
limbic system
long term memory, olfaction, motivation, emotion, behavior
What are the locations their associated dermatomes for testing light/pain sensation in the UE/LE?
UE:
dorsal web space of thumb and index finger (C6)
pad of long finger (C7)
pad of little finger (C8)
LE:
medial aspect of foot (L4)
great toe web space (L5)
lateral aspect of foot (S1)

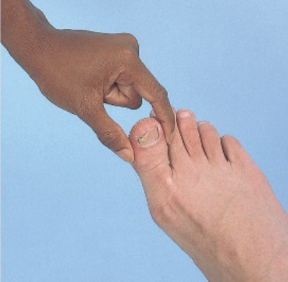
Steps for testing proprioception?
Grasping digit from their lateral sides: IP joint of great toe & MCP joint of long finger
Have patient close their eyes
Have patient identify direction in which you are moving digit (up or down)
Test bilaterally
*be sure to stabilize wrist for hand
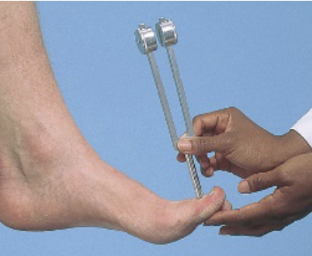
Steps for testing vibration?
Using 128 hz tuning fork
Set on bony prominence: DIP of long finger & IP joint of big toe
Have patient close their eyes
Ask if buzzing/not buzzing, ask when buzzing stops
Test bilaterally
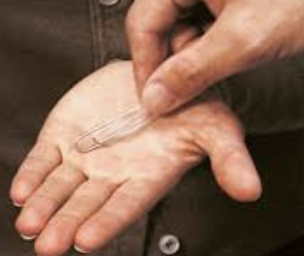
Stereognosis
ability to identify an object by feeling - with patient’s eye closed, place familiar object in their palm and ask them to identify, repeat bilaterally
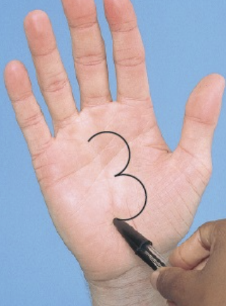
Graphethesia
number identification - with patient’s eye closed, with blunt end of pen/reflex hammer, draw large number in the patient’s palm and ask them to identify, repeat bilaterally
Rapid-alternating movements - What are the steps/purpose?
Testing coordination, rhythm/speed
*you can show patient how to perform, but then stop and watch patient
UE: have patient flip their hands over and back as fast as they can and stop. Do left, then right, then both at the same time
LE: toe taps for as fast as possible, can brace patient’s ankle. One side at a time
*their is typically less coordination in the feet vs. hand
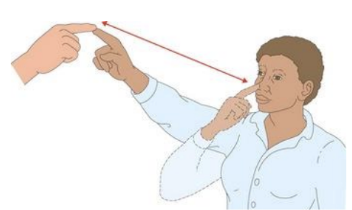
Finger-to-nose test - What are the steps/purpose?
*be far enough to where patient must fully extend their arm
with eyes open, have patient alternative touching your index finger and their nose
move your finger continuously and have patient continue alternating touching your index finger and their nose
with your finger unmoving directly in front of patient, have them touch your finger then have them close their eyes and repeat
watching for: end point tremor, dysmetria: problems with coordination/point passing
Heel-to-shin test steps?
seated: have patient place their heel on their knee and move down shin to foot & back up
repeat with eyes closed
test can also be performed with patient supine
Gait testing includes?
casual walk: observe posture, stance, balance, swinging of the arms, movement of legs
heel walking/toe walking: watch for sinking in each step, testing strength
heel-to-toe in straight line (tandem walking): may reveal ataxia, which is cerebellar dysfunction, loss of muscle control
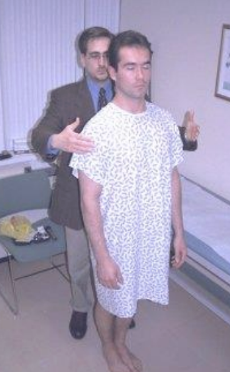
Romberg test - what are the steps?
position sense test
with patient standing and feet together, arms to their side
then have patient close their eyes and watch for excessive postural sway or loss of balance *be sure to spot patient
if positive: could indicate proprioceptive deficit (sensory ataxia)
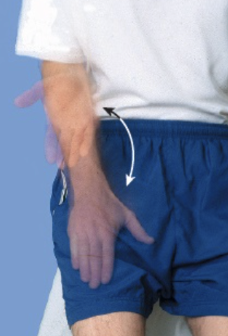
Pronator drift - steps?
motor function test
patient can be seated or standing
have patient hold both arms forward, parallel to ground, palms up
have patient close their eyes and watch to see if arms drift
have patient keep their eyes closed while you tap the arms briskly downwards
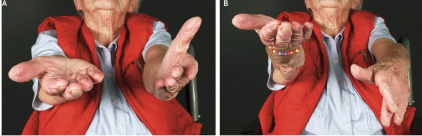
Grading scale for deep tendon reflexes
0: no response
1+ sluggish or diminished
2+ active or expected responses
3+ brisk or more than expected
4+ hyperactive, may elicit clonus
‘normal’ can vary from person to person, can be between 1+-3+, always compare side to side
Spinal nerve innervation associated with each reflex location
bicep - musculocutaneous nerve (C5)
brachioradialis - radial nerve (C6)
triceps - radial nerve (C7)
patellar - femoral nerve (L4)
achilles - tibial nerve (S1)
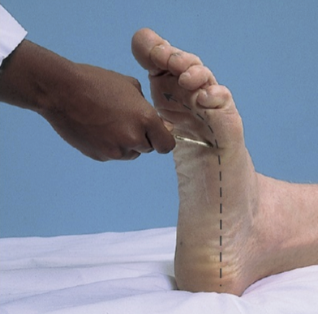
Babinski (Plantar response) reflex assessment/significance
a type of superficial reflex: motor response when skin is stroked
use blunt edge of reflex hammer or pen to trace path from heel curved out to big toe
extended great toe when there is pressure applied to the lateral/distal plantar surface of the foot
plantar flexion of big toe is normal
document: plantar response is extensor/flexor, upgoing/downgoing toes
NOT Babinski positive
dorsiflexion of the big toe indicates positive CNS lesion affecting the corticospinal tract
What are the tests for meningeal inflammation? What are the steps?
Kernig
patient supine
flex one of the patient’s legs at the hip and knee
straighten the knee
check for pain or resistance to knee extension
Brudzinski
patient supine
place your hands behind the patient’s head and passively flex their neck forward until the chin touches the chest
check if knees and hips flex in response to the head movements/if patient is in pain
Clonus definition & purpose?
Greek for violent, confused motion. A repetitive contraction of a muscle when attempting to hold a stretched state
Purpose: indicates possible damage in CNS that could be temporary, an acute change or chronic
Method for eliciting clonus
Patient in relaxed supine position
Support the patient's lower leg.
Slightly flex the patient's leg at the knee.
Gently move the ankle in dorsiflexion and plantarflexion a few times.
Quickly dorsiflex the ankle upwards.
Hold the ankle in dorsiflexion.
Look for oscillations against the pressure. If you feel and see oscillations, you've recorded a positive clonus sign.
Decorticate
abnormal extensor response; jaws are clenched, and the neck is extended
Decerebrate posturing
abnormal flexor response; upper arms are flexed tight to the sides with elbows, wrists, and fingers flexed
Flaccidity
no response on one side suggests a corticospinal tract lesion
Spasticity
increased tone that is velocity-dependent and worsens at the extremes of range of motion. Resistance increases with more rapid movement
Hemiplegia
paralysis of one side of the body
Paraplegia
paralysis of the legs
Delirium
multifactorial syndrome; an acute confusional state marked by sudden onset; fluctuating course, inattention, and changing levels of consciousness (at times)
Dementia
major cognitive disorder causing decline in at least two cognitive domains (loss of memory, attention, language, executive function) that is severe enough to impact social/occupational functioning
Depression
characterized by at least 2 weeks of depressed/irritable mood causing insomnia or hypersomnia, decreased self esteem, low energy, poor concentration, changes in appetite, feeling slowed or restless
Stupor
state of near-unconsciousness
The stuporous patient arouses only after painful stimuli. Verbal responses are slow or even absent. The patient lapses into an unresponsive state when the stimulus ceases
Lethargy
appearance of drowsiness. state of sluggishness, tiredness, or lack of energy, often accompanied by a decreased interest in activities
Coma
deep state of prolonged unconsciousness, unresponsive to external stimuli, no evidence of inner need
Areflexia
muscles do not respond to stimuli
Hyperreflexia
increased muscle tone
Hyporeflexia
decreased muscle tone
paresthesia
irritative phenomena '“pins and needles” sensation
receptive
Wernicke aphasia; with impaired comprehension with fluent speech
Expressive aphasia
Broca aphasia; nonfluent speech slow and broken, with few words and laborious effort
Vertigo
a spinning sensation within the patient or of the surroundings