AQA Chemistry Paper 1
1/270
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
271 Terms
C1 Atomic Structure
What are atoms?
Atoms are the particles that make up everything
What is an element?
An element is a substance in which all the atoms are the same
Where are elements shown?
Elements are shown in the Periodic table
How many elements are there?
There are around 118 elements
What is a compound?
A compound is a substance that contain two or more elements chemically combined
Describe the properties of compounds
The properties of compounds are usually different to the elements that they are made from
What is a mixture?
A mixture is a substance with different elements or compounds not chemically combined
Give an example of a mixture
An example of a mixture is sand and water as they are not chemically combined and can be separated by physical means
What is a molecule?
A molecule is a substance that has any elements chemically joined
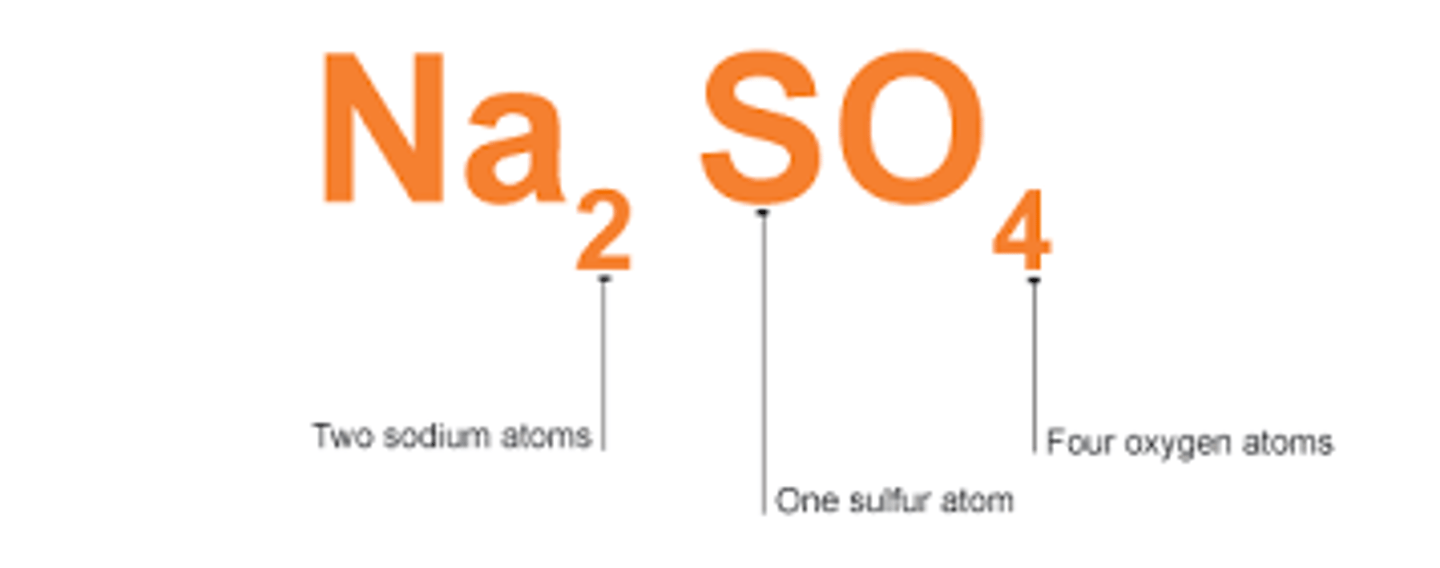
What does a chemical formula tell you about a molecule?
A chemical formula tells the elements in a molecule and the number of atoms of each element
How is a chemical formula presented?
Each element symbol starts with a capital letter, if there is a second letter it is in lower case
Give an example of a chemical formula
What are state symbols?
State symbols show the physical state of the substance solid (s), liquid (l), gas (g), or dissolved in water (aq)
Name three properties of Metals
-Strong
-Good conductors of heat and electricity
-High melting and boiling points
Name three properties of Non-Metals
-Weak
-Bad conductors of heat and electricity
-Low melting and boiling points
State the four different ways of separating mixtures
Four different ways of separating mixtures are filtration, crystallisation, distillation or chromatography
Describe the process of filtration
Pour your mixture onto the filter paper, the liquid simply passes through the filter paper into the flask. The insoluble solid cannot pass through and so it stays on the paper
Describe the process of crystallisation
Use the method of filtration to filter off any excess soluble solid. Evaporate the mixture then transfer the hot mixture onto a dish. Crystals are formed when the mixture has cooled
Describe the process of simple distillation
First we evaporate the mixture by heating it, the dissolved solid then vaporises. These vapours condense in the condenser, the dissolved solid then flows into the beaker and liquid stays in the flask
Describe the process of chromatography
Take a strip of filter paper and draw a line on the bottom of the paper. Put a small drop of ink on the line, take a jar full of water up to the line and put the filter paper in. As the water moves up we see different colours on the paper these are the dyes in the ink
What were the early ideas of the structure of atoms?
Early ideas of the structure of atoms stated that they are tiny spheres that cannot be divided
What is the plum pudding model?
The plum pudding model is what scientists suggested is the structure of atoms is after the discovery of the electron
Describe the plum pudding model
The plum pudding model suggested that an atom is a ball of positive charge with negative electrons in embedded in it
Describe how Rutherford carried out the gold foil experiment
Rutherford took a piece of gold foil, he then fired tiny positive alpha particles at the gold foil
What did Rutherford observe in the experiment?
Rutherford observed that most of the particles when straight through the gold foil and sometimes the alpha particles bounce back of the gold foil
What did Rutherford discover from these observations?
Rutherford discovered that atoms are mainly empty space as most of the alpha particles went straight through the gold atoms and that the nucleus of the atom is very small as only a small number of alpha particles bounce back
Describe the structure of the nuclear model
The nuclear model states that most of an atom is empty space, in the centre is the nucleus which contains protons and neutrons around the edge we find electrons
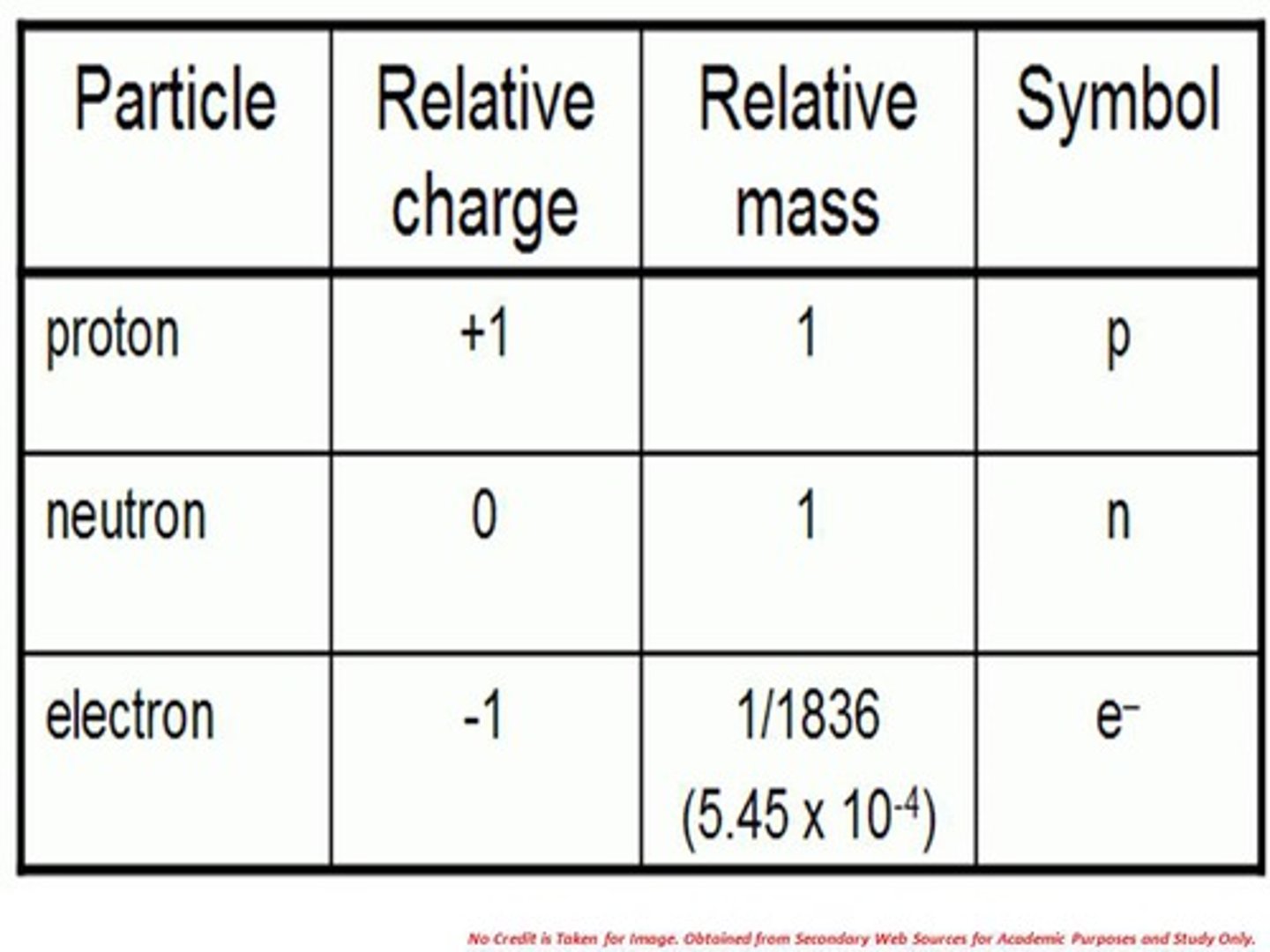
What is the Relative mass and the relative charge of protons, neutrons and electrons?
Why do atoms have the same number of protons as electrons?
Because atoms have have no overall charge
What is an Ion?
An ion is a charged particle, it is possible to get positive or negative ions
What is an Isotope?
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes
What is the mass number of an element?
The mass number is the number on the top of an element it is the number of proton and neutrons combined
What is the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number is the number on the bottom it is number of protons in an atom, which is the same as the number of electrons
How many electrons can you fit in the first, second and third shells?
Shell 1 : 2 electrons
Shell 2 : 8 electrons
Shell 3 : 8 electrons
What is an Electronic structure?
A set of number to show the arrangement of electrons in their shells, eg. [2,6]
C2 The periodic table
What did John Newlands periodic table look like?
He arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic mass, he saw that every eighth element reacted in a similar way
What did Dmitri Mendeleev's periodic table look like?
He arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic mass, he switched the order of some elements to the fitted in the patterns of other elements. He left gaps for undiscovered elements
What does the modern periodic table look like?
Elements are arranged in order of atomic number, the elements are organised in groups and periods which have the similar properties
Why are elements in the periodic table grouped the way they are?
Elements with similar chemical properties are grouped together in groups
Why do elements in a group have similar chemical properties?
Elements in a group have similar chemical properties because they all have the same number of electrons in their outer energy level therefore react similarly
What are the names of group 1, 2, 7 and 0?
Group 1: alkali metals
Group 2: alkaline earth metals
Group 7: halogens
Group 0: noble gases
Where are the metals and non-metals located on the periodic table?
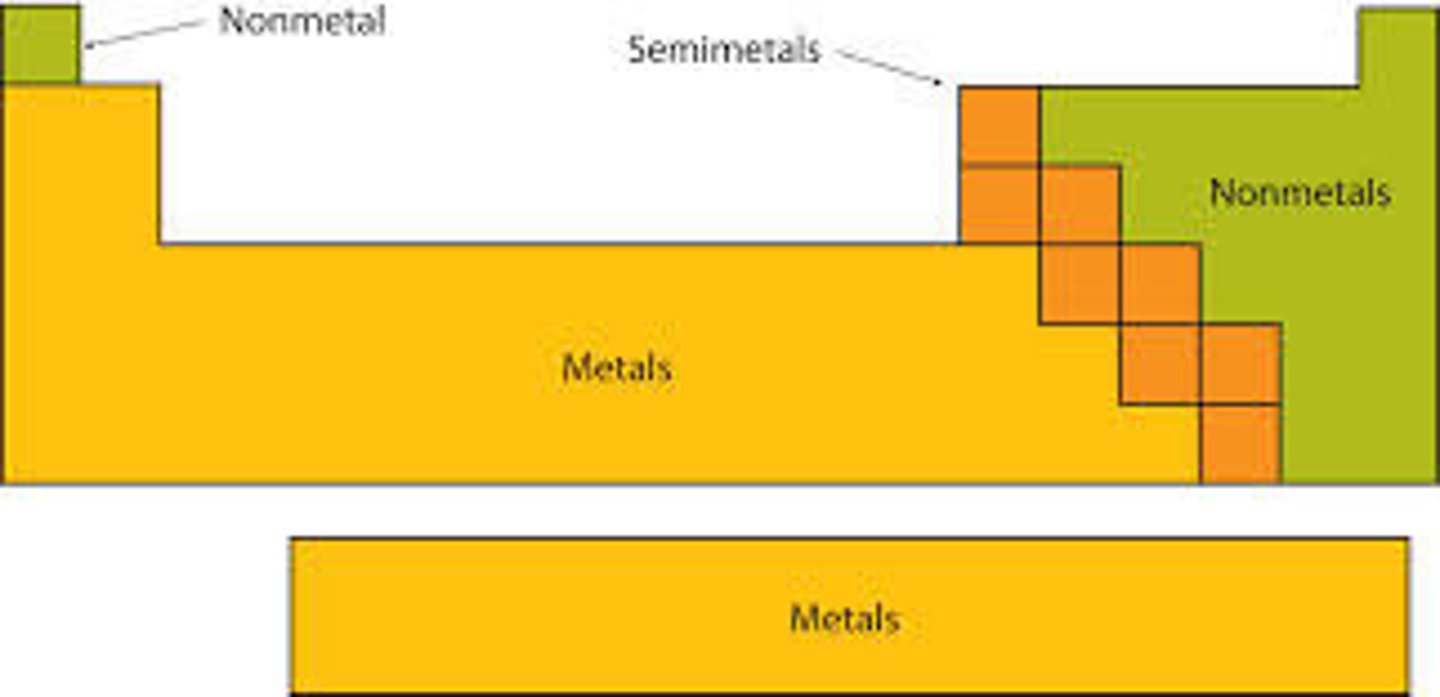
What happens to metals when they react?
When metals react they lose electrons to achieve a full outer energy level
What ions do metals from group 1 and 2 form?
Group 1 form 1+ ions
Group 2 form 2+ ions
Name the elements in Group 1
Lithium, Sodium, Potassium,
Rubidium, Cesium, Francium
Describe the reaction of a group 1 metal and oxygen in terms of electrons
In the reaction one group 1 metal transfers its outer electron to the oxygen another group 1 metal does the same, now all the atoms have a full outer energy level. The metals have a 1+ charge and the oxygen has a 2- charge
Describe the reaction of a group 1 metal and chlorine in terms of electrons
In the reaction a group 1 metal transfers its outer electron to the chlorine, now both atoms have a full outer energy level. The metals have a 1+ charge and the chlorine has a 1- charge
What is the word equation for the reaction of group 1 metals and water?
Metal + Water →
Metal Hydroxide + Hydrogen
Describe the reaction of the first three group 1 metals and water
When water reacts with lithium the reaction is fast and there is fizzing. When it reacts with sodium the reaction is very fast and gas is produced. When it reacts with potassium the reaction is extremely fast and there is a small flame. In all the reactions the water turns alkaline
Describe the correlation of the reactivity of a group 1 metal and it's location in the table
Group 1 metals react faster as you move down the column
Why are group 1 metals more reactive as we move down the group?
As we move down the group the outer electron is less attracted to the nucleus and easier to lose because it has a greater distance between the positive nucleus
Name some properties group 1 metals
Group 1 metals have low melting points and a low density, they are soft metals and react very rapidly
What elements are in group 7?
Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine, Astatine
How do group 7 elements achieve full outer shells?
Group 7 elements need 1 electron to fill their outer shell so they just share an electron with another group 7 element, this is known as covalent bonding
Describe the correlation of the melting and boiling point of a group 7 element and it's location in the table
Group 7 elements have a higher melting and boiling point as you move down the column
What is formed when group 7 elements react with non-metal atoms?
Group 7 elements form covalent compounds when they react with other non-metal atoms so the electrons are shared
What is formed when group 7 elements react with metals?
Group 7 elements form ionic compounds when they react with metals so the electrons are transferred
When a group 7 element reacts with a metal what charges does the group 7 element have?
When a group 7 element reacts with a metal the group 7 element gains and electron and forms a 1- ion
Describe the correlation of the reactivity of a group 7 element and it's location in the table
Group 7 elements have a lower reactivity as you move down the column
Why is it harder for an element at the bottom of the group to gain an electron that an element at the top of the group?
An element at the top has less distance between the nucleus and the outer energy level so it gains electrons easier, an element at the bottom has a greater distance between the nucleus and the outer energy level so it is harder to gain electrons
Explain what happens in a displacement reaction
A more reactive halogen can displace a less reactive halogen from an aqueous solution of its salt
Give an example of a displacement reaction
Sodium Bromide + Fluorine → Sodium + Bromine Fluoride
What elements are in group 0?
Helium, Neon, Argon, Krypton, Xenon, Radon
Why are group 0 elements unreactive?
Group 0 elements have full outer shells and so they don't need to react to fill up their shells
Describe the correlation of the melting and boiling point of a group 0 element and it's location in the table
Group 0 elements have a lower melting and boiling point as you move down the column
Where are transition metals located?
Transition metals are located in the centre of the periodic table
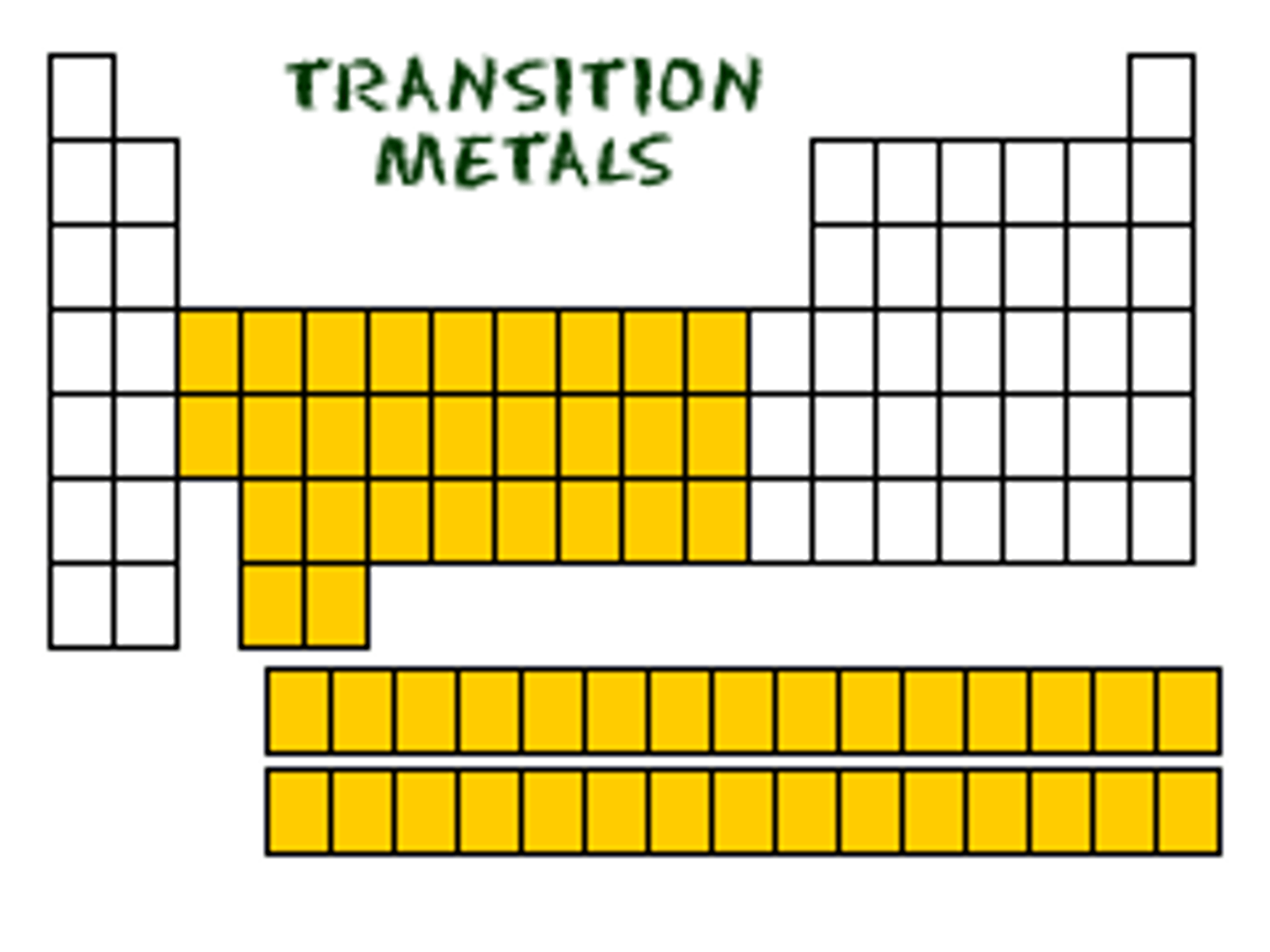
Name some properties of transition elements
Transition metals are hard and strong and have a high density and melting point, they are good conductors of heat and electricity. They for coloured compounds and can be used as catalysts
C3 Structure and bonding
What are the three states of matter?
The three states of matter are solids, liquids and gases
What is the particle theory?
The particle theory describes the movement and arrangement of particles
Describe the particles in a solid
The particles in a solid are packed closely together in a fixed arrangement, they vibrate constantly
Describe the particles in a liquid
The particles in a liquid are close together in a changing, random arrangement, they can move around
Describe the particles in a gas
The particles in a gas are much further apart in a random arrangement, they move very quickly
When does a solid become a liquid?
A solid turns into a liquid when it reaches it's melting point. As the temperature increases the particles vibrate faster until the forces between them breaks and a liquid is formed
When does a liquid become a gas?
A liquid turns into a gas when it reaches it's boiling point. As the temperature increases the particles move around faster, at the boiling point bubbles of gas form and rise to the surface and a gas is formed
How are the forces between particles affected by melting and boiling points?
Substances with higher and melting and boiling points have stronger forces between the particles
How do elements form compounds?
Elements form compounds by gaining or losing electrons or by sharing electrons
In ionic bonding what two types of element react?
In ionic bonding a metal reacts with a non-metal
How are full outer energy levels achieved in ionic bonding?
Electrons from the metal is transferred to the non-metals to give both elements full outer shells
How do ionic compounds achieve full outer shells?
Ionic compounds transfer electrons to achieve full outer shells
What ions do Group 1, 2, 3, 5, 6 and 7 elements form?
Group 1/ 1+
Group 2/ 2+
Group 3/ 3+
Group 5/ 3-
Group 6/ 2-
Group 7/ 1-
Describe the structure of an ionic compound
Ionic compounds form a giant ionic lattice where every positive ion is surrounded by a negative ions
What are ionic compounds held together by?
Ionic compounds are held together by strong electrostatic forces
What are the properties of ionic compounds
The properties of ionic compounds are that they can transfer electrons when they react, they have high melting and boiling points and can conduct electricity when they are not solids
Why do ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points?
Tonic compounds have high melting and boiling points because the strong electrostatic forces require a lot of heat energy to break
Why can't ionic compounds conduct electricity when they are solids?
Ionic compounds can't conduct electricity when they are solids because the ions cannot move, they are locked in place by strong electrostatic forces
Why can ionic compounds conduct electricity when they are liquids or dissolved in water?
Ionic compounds can conduct electricity when they are liquids or dissolved in water because the ions can now move and carry the charge
In covalent bonding what two types of element react?
In covalent bonding happens between two non-metals
How are full outer energy levels achieved in covalent bonding?
In covalent bonding full outer energy levels are achieved by two non-metals sharing electrons
What are the properties of covalent molecules
The properties covalent molecules are that they share electrons when they react, they have a low melting and boiling points and cannot conduct electricity
Why do Covalent Molecules have a low melting and boiling point?
Covalent Molecules have a low melting and boiling point because the bond between the molecules is weak and so it doesn't need a lot of energy to break the intermolecular forces
Why can't Covalent Molecules conduct electricity ?
Covalent Molecules can't conduct electricity because they don't have an overall electric charge
What state are giant covalent molecules at room temperature?
Giant covalent molecules are solids at room tempreature
Do giant covalent molecules have high or low melting and boiling points?
Giant covalent molecules have high melting and boiling points because they have millions of strong covalent bonds
Name three giant covalent molecules
Three giant covalent molecules are diamond, silicon dioxide and graphite
What element is diamond formed from?
Diamond is formed from the element carbon
How many bonds does Carbon form?
Carbon forms 4 bonds
Describe the structure of a diamond
Diamond has a giant molecular structure. Each carbon atom is covalently bonded to four other carbon atoms, diamonds contains many strong covalent bonds