Reproduction and Inheritance Exam Style Qs
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Describe an investigation to find out if leaves growing at the bottom of trees are greener than leaves growing at the top of trees.
Your answer should include experimental details and be written in full sentences and paragraphs. (6)
m1: choose leaves from top and bottom branch levels on each tree m2: same species controlled m3: repeat many trees m4: use chromatography to measure the rf values and the pigment of green trees m5: extract by heating with ethanol m6: also control same location/time of day
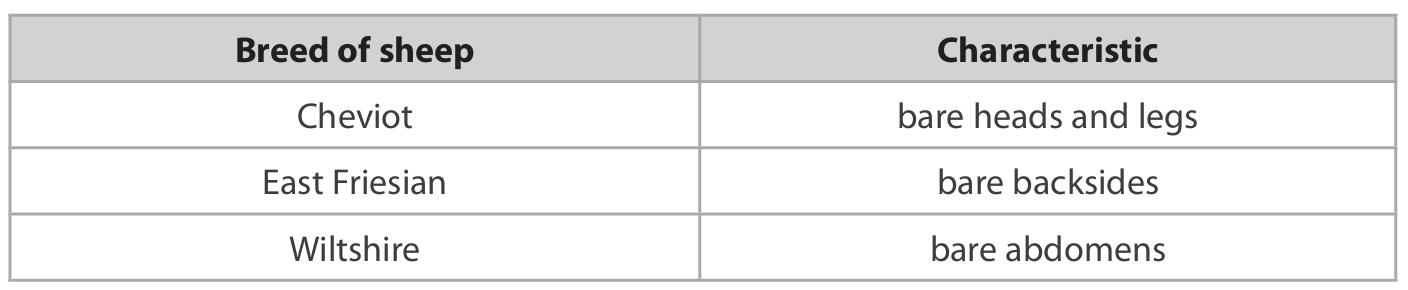
Describe how farmers could use selective breeding to develop sheep with bare legs and bare backsides. (4)
m1: choose Cheviot and East Friesian m2: parent sheep with bare backsides and parent sheep with bare legs m3: cross breed m4: select offspring with bare legs and bare backside m5: repeat for many generations
A student suggested that purple flowers are more likely to be visited by bees than white flowers.
Use your knowledge of natural selection to suggest how this might affect the number of purple and white flowers in the wild. (5)
m1: more purple pollen carried to other purple flowers m2: purple flower more likely to reproduce/purple allele is passed on in seeds m3: more purple flowers/less white flowers m5: carries on in generations
Describe how cell division by meiosis is different from cell division by mitosis. (4)
m1: mitosis produces 2 diploid cells which are m3: genetically identical whilst meiosis produces 4 haploid cells genetically different
m2: the haploid cells produced in meiosis have half the number of chromosomes
m4: meiosis produces gametes which take place in sex organs whilst mitosis occurs in almost every part of the human body
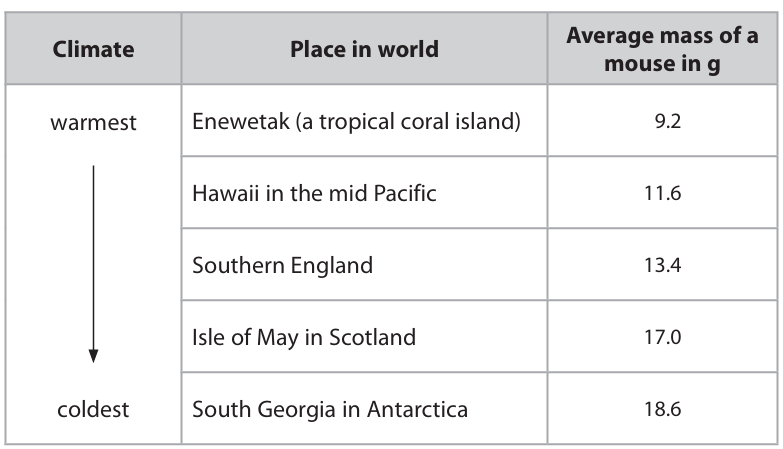
Use your understanding of natural selection to suggest why the mice in Antarctica have the biggest average mass. (5)
m1: the colder the place the bigger the mouse m2: due to mutation m3: bigger mice survive → survival of the fittest m4: reduces heat loss → insulation m5: smaller SA:V ratio to pass on allele/gene
The number of chromosomes in eggs and in sperm is less than the number of chromosomes in the body cells of animals.
Explain how the number of chromosomes in animals is maintained in their offspring (3)
m1: meiosis m2: haploid gametes m3: fuse to make a diploid
The flower in the diagram is insect-pollinated. An insect carrying pollen lands on the flower.
Describe the events that lead to seed formation. (5)
m1: stigma m2: pollen tube grows m3: into ovule m4: enters via micropyle m5: male gamete m6: fuses with m7: female gamete m8: ovule becomes seed m9: ovule wall becomes seed coat m10: ovary becomes fruit
Describe the features of an insect pollinated flower that help it to attract insects (3)
m1: large petals m2: brightly coloured
m3: scent m4: nectary
Describe the changes that take place in the uterus lining during the menstrual cycle (3)
m1: grows m2: maintained m3: breakdown m4: not broken down if pregnant → egg fertilised
Describe the role of oestrogen at puberty. (3)
m1: activates secondary sexual characteristics m2: start menstruation m3: hips widen m4: growth of breasts m5: growth of pubic hair m6: change distribution of fat
High levels of blood cholesterol can lead to narrowing of arteries. Suggest how this might affect the ability of the heart to function (5)
m1: less blood m2: less glucose m3: less oxygen
m4: more anaerobic respiration m5: lactic acid
m6: heart rate increases m7: increase in pressure m8: coronary artery m9: angina → reduced blood flow to heart muscles m10: heart attack and possibly death
An artery supplies the leg muscles with blood.
Explain what will happen to the muscle cells in the leg if cholesterol builds up in this artery. (5)
m1: less supply of oxygen m2: less aerobic respiration m3: more anaerobic respiration m4: more anaerobic respiration m5: less energy in the form of ATP m6: lactic acid produced m7: lowers pH and enzymes denature m8: muscle cells die
Explain three conditions needed for seeds to germinate (6)
oxygen for respiration
water/moisture activate enzymes → hydrolysis
optimum temperature for enzyme reaction
light activate plant growth regulators
The placenta supplies the embryo with nutrients during the gestation period.
Describe the role of the placenta in the development of the embryo. (4)
m1: diffusion m2: glucose/oxygen m3: respiration/energy/ATP m4: amino acids m5: protein synthesis m6: vitamins m7: remove carbon dioxide
Describe an experiment you could carry out to determine the energy content of a seed. (4)
m1: ignite seed m2: transfer under tube of water/use calorimeter m3: quick transfer/complete combustion m4: mass of water m5: mass increase of temperature m6: repeat