Compounding (copy)
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Compounding USP Chapters summary
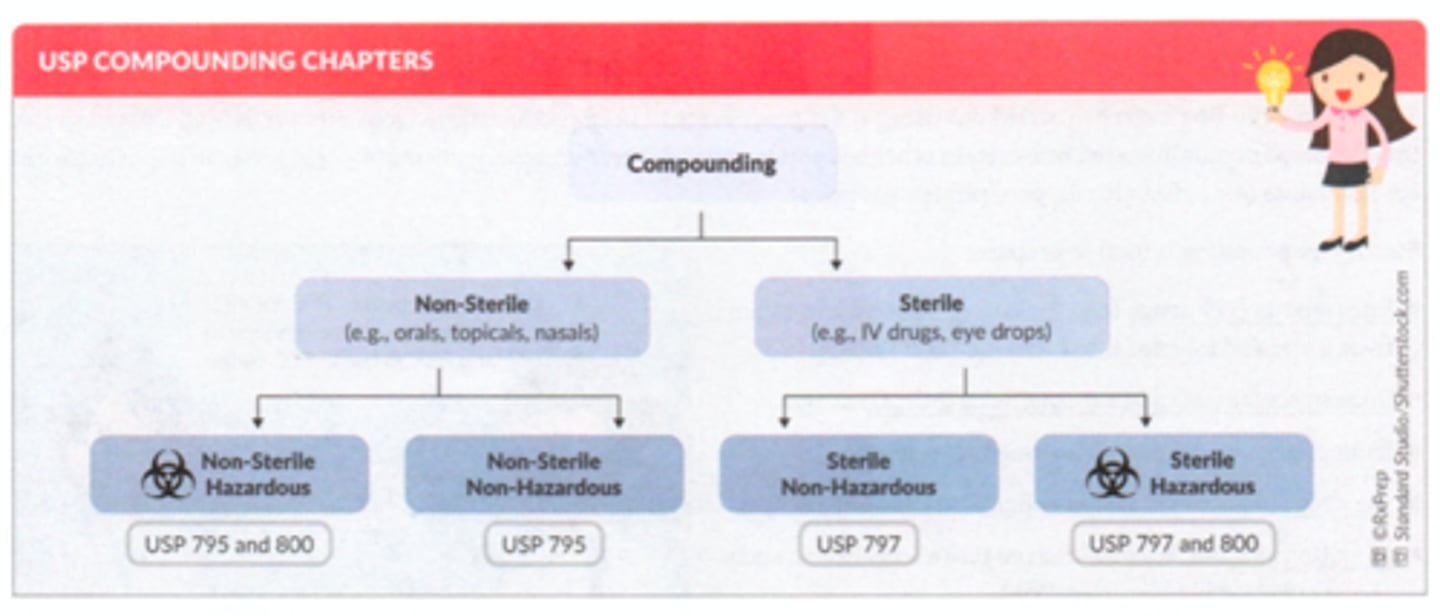
USP terminology
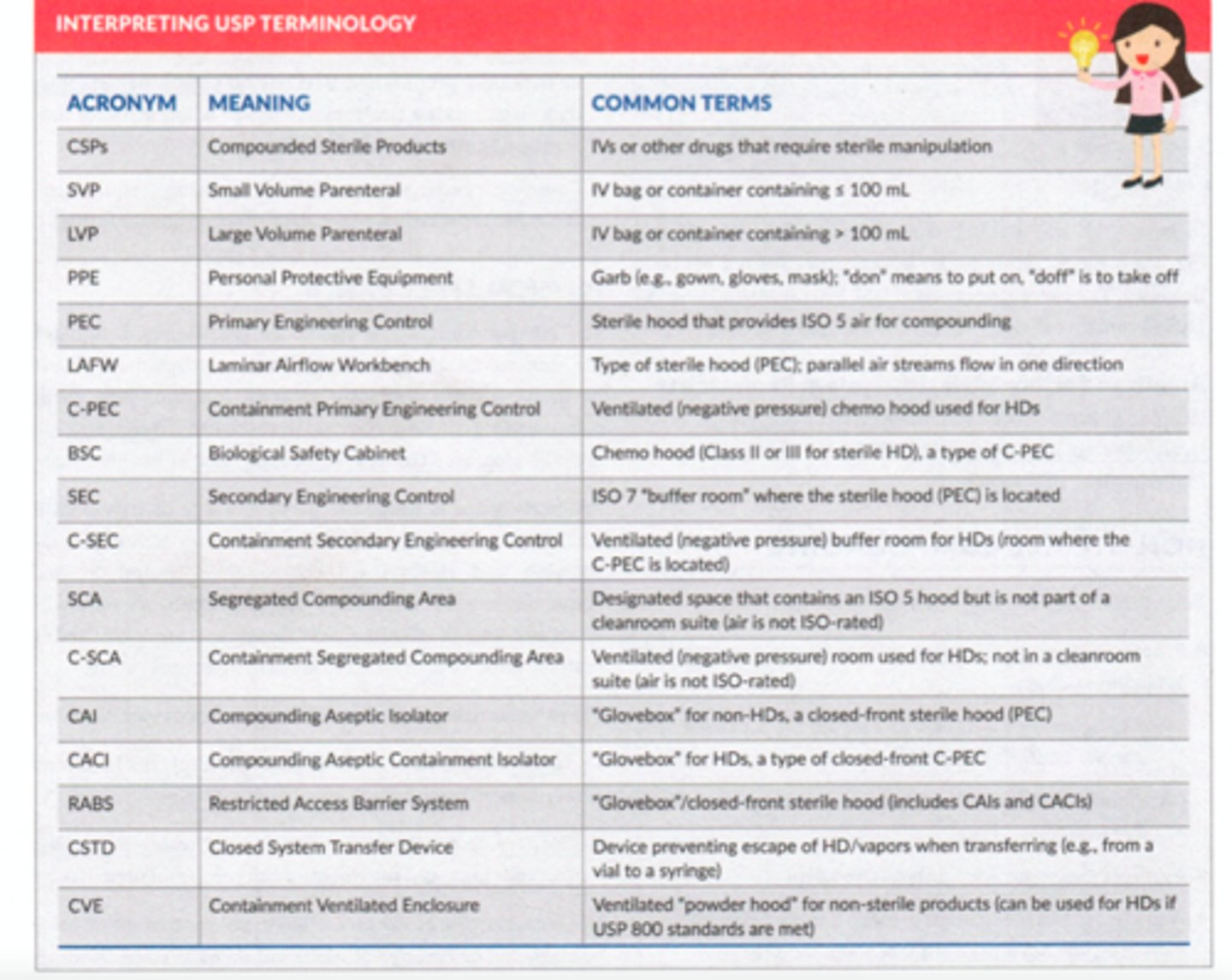
Air quality and HEPA filters
inside PEC (sterile hood) = iso 5
outside hood in SEC = iso 7
ante room for hand washing, etc:
- iso 8 if non-hazardous sterile + positive pressure
- iso 7 if opens up to hazardous sterile + negative pressure
Techniques to maintain sterility in PEC (hood)

What air pressure must a hazardous room have?
negative
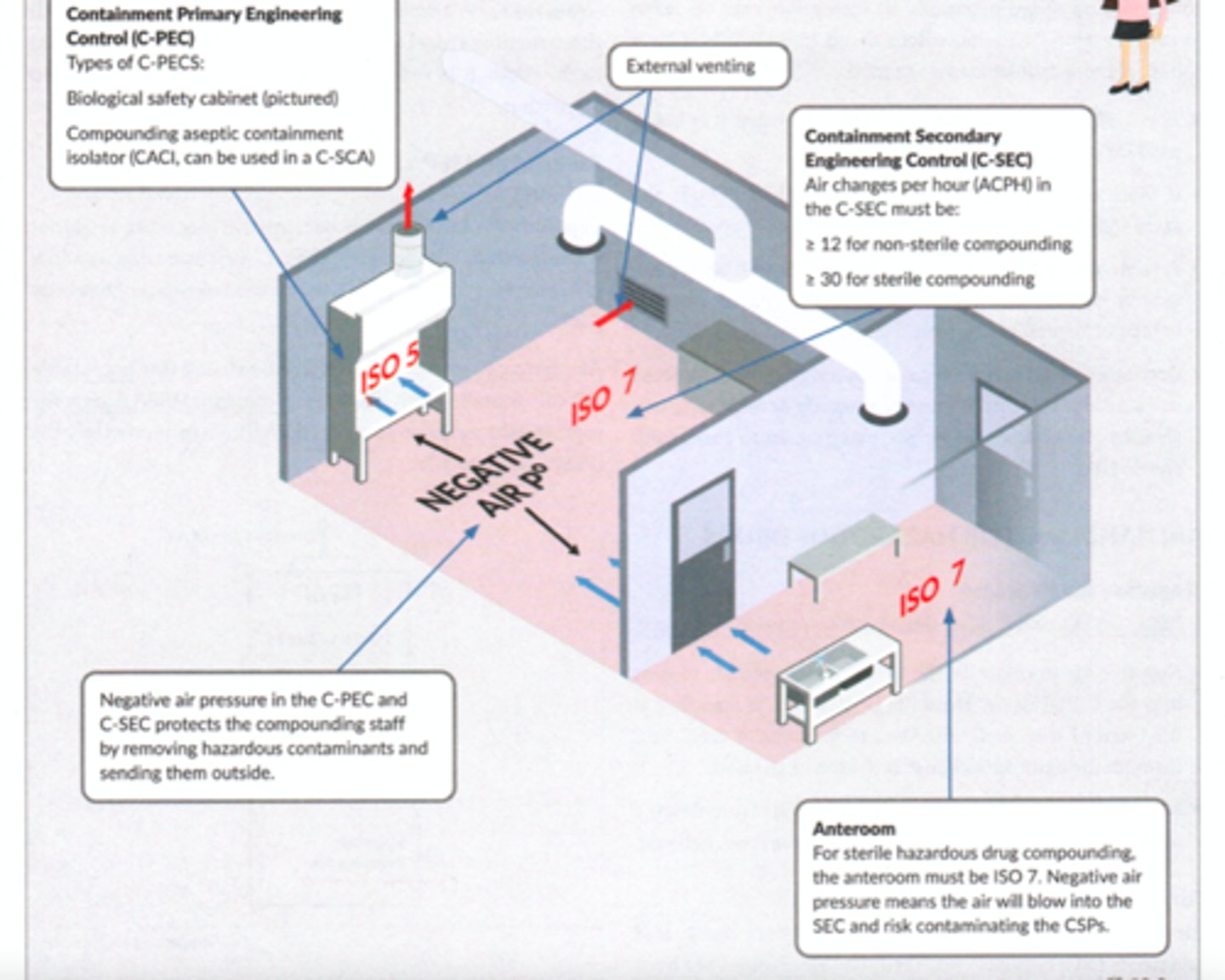
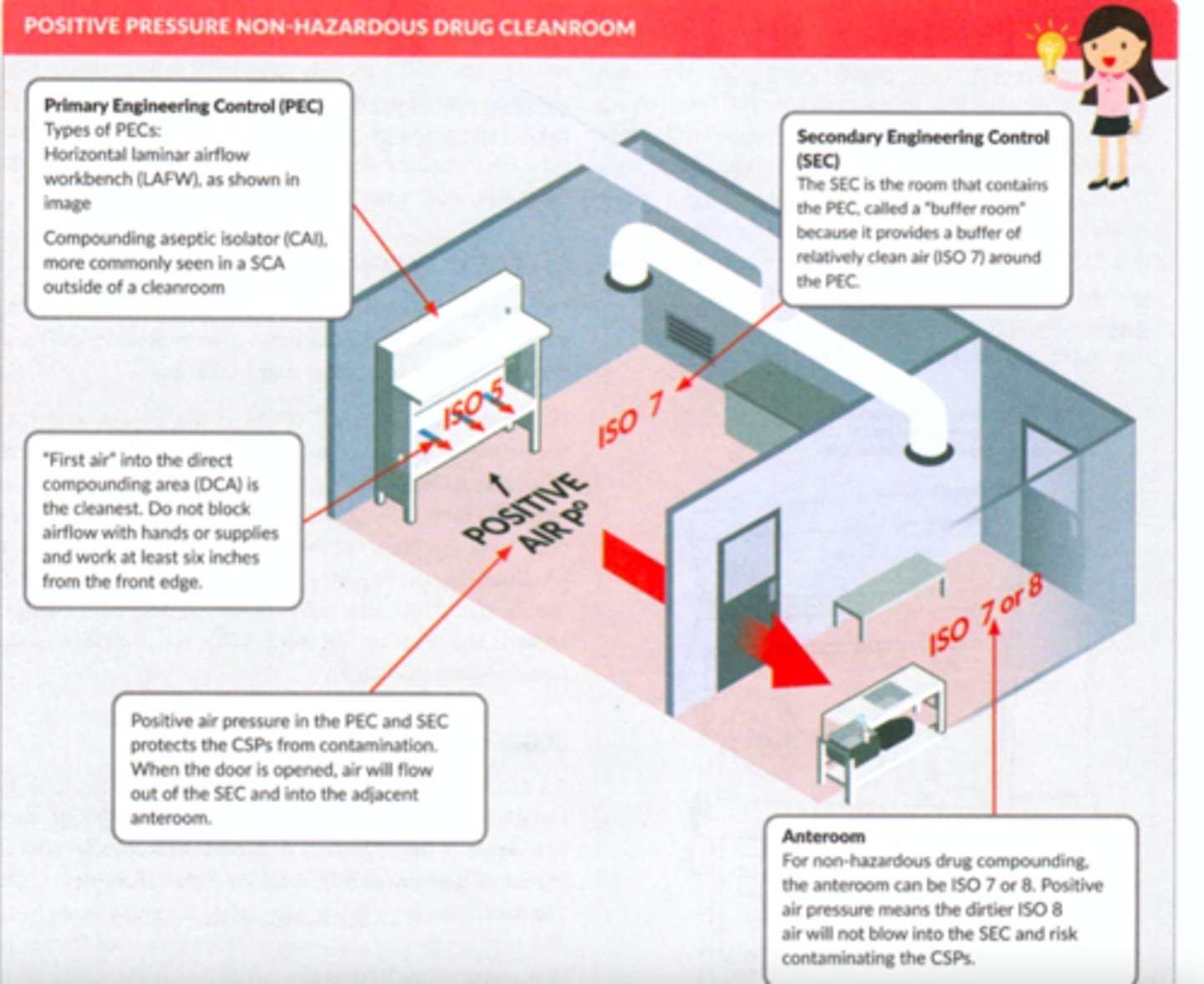
What air pressure must a non-hazardous room have?
positive
Hazardous Drugs (NIOSH)

What temp should the SEC room be?
20 C/68F or cooler
check QD
What temp should a refrigerator be?
2 - 8°C
check BID
What temp should a freezer be?
-25 to -10°C if vaccines
- 50 to - 15 C if no vaccines
check BID
How often does air sampling need to be done?
every 6 months by a person certified in air sampling, or by a qualified compounding staff member.
How long is a media fill test incubated?
14d
Surface Sampling red flags
TAKE ACTION IF:
- > 3 CFUs in iOS 5 area
- > 5 CFUs in iOS 7 are
- > 100 in iOS 8 area
How often should air flow be checked?
QD
Hazardous drug compounding good cleaning steps
1) deactivate/decontaminate
2) clean (germicidal detergent)
3) disinfect (70% IPA)
bleach or peroxide can be used to both deactivate & decontaminate
How often should surface sampling be done in a hazardous room?
at least every 6 months to ensure that hazardous residue is adequately contained
Non-Sterile Hazardous Drugs Garbing
- Double gloves
- a gown
- a mask
- disposable pad to protect the work surface
Sterile Hazardous Drugs Garbing
- head cover
- face mask
- beard cover if applicable
- 2 shoe covers
- impermeable chemo gown
- two pairs chemo gloves (ASTM D6978)
- full face piece respirator or face shield with goggles
Sterile Compounding Garbing Steps
1) remove rings, etc
2) hair cover, face mask, show cover (2 pairs if HD)
3) wash hands
4) gown
5) gloves
Minimum weighable quantity (MWQ)
sensitivity requirement / 0.05
Mortars and Pesles
Glass : liquids
Wedgewood: crystals and hard powders
Porcelain: powders & gummy consistencies
In what case would a steel spatula not be appropriate?
not be used if making a mixture that contains metallic ions
Binders
allow the contents of a tablet to stick together while permitting the contents to be released once ingested.
They can provide stability and strength.
Diluents and Fillers
Diluents (to make something more dilute)
fillers (to bulk up a small amount)
they add size to very small dosages.
Tabs/Caps:
- lactorse
- starches
- Ca salts
- cellulose
Topicals: petrolatum
Disintegrants
Facilitates the breakup of a tablet after oral administration
Ex:
- alginic acid
- cellulose
- polacrillin K
- starges
(meds need to be dissolved when reach small intestine for absorption)
Sweeteners
Non-Caloric/artificial:
- aspartame
- sucralose
Others:
- glycerin
- dextrose
- mannitol, sorbitol, xylitol
- stevia
Lubricants
prevent ingredients from sticking to each other and to equipment
Ex: magnesium sterate
Preservatives
slow or prevent microorganism growth
Ex:
- chlorhexidine
- povidone iodine
- Sodium benzoate/benzoic acid, benzalkonium chloride
- Sorbic acid/potassium sorbate
- Methyl/ethyl/propyl parabens
- EDTA
- Thimerosal
- Cetylpyridinium chloride
**DO NOT USE IN NEONATES*
In what population can preservatives NOT be used in?
neonates
Buffers
keep the pH within a certain range, which can improve stability and solubility and decrease irritation to sensitive tissues in the body
Ionized compounds are more polar, which makes them more water-soluble.
acids maintain acidic pH
NaOH ex of buffer to maintain alkaline
Na/K phosphate ex buffer to maintain neutral
Hydrophillic solvents
- water
- sterile water
- alcohols ex: bonzyl peroxide is solvent and perservative, IPA 70% disinfects surfaces
- polyethylene glycol (when linked to a protein drug (pegylated), such as PEG-filgrastim, it increases the half-life)
Hydrophobic Solvents
Oils and fats
Ex:
- mineral oil (Baby Oil)
What is an emollient?
A fatty material used to lubricate and keep other substances on the skin
Ointments
0-20% water
Ex:
- petrolatum
- Polybase
- Aquaphor
- Aquabase
Creams
Most creams are water-in-oil or oil-in-water emulsions.
Ex:
- lipoderm
- eucerin
- cetaphil
Lotions
Lotions can be aqueous or hydroalcoholic, with a small amount of alcohol addedto solubilize ingredients, or to hasten evaporation of the solvent from the skin.
Ex: versabase
Gels
Semisolid suspensions of very small particles usually in a water base
Ex: paloxamers
- PLO gel ( liquid at fridge, gel at RT)
Suppository bases
made of various fats and glycols
have to stay intact for insertion, and melt once inserted.
Ex:
- Polybase
- hydrogenated vegetable oils (palm, coconut)
- gelatin
Adsorbents
To keep powders dry, to prevent hydrolysis reactions.
Ex:
- MgOH
- Mg Carbonate
- Keolin
Anti-Foaming agents
Breaks up and inhibits the formation of foams.
Ex: simethicone
Regular Coatings
Prevent degradation due to oxygen, light, moisture, mask unpalatable taste.
Ex:
- shellac
- gelatin
- gluten
Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers are a type of surfactant (Reduce the surface tension between two liquids to allow to mix)
Ex:
- Acacia
- PEG
Enteric-Coating
acid-resistant (enteric-coated) protective layer to prevent dissolution in the stomach.
used when drugs would be destroyed by stomach acid
(usually dissolve in stomach)
Ex: Cellulose acetate phthalate
Gelling/Thickening Agents
Increases the viscosity of a substance; can stabilize the mixture.
Ex:
- gelatin, cellulose, betonite (clay)
- Agar
- alginates
- various gums [guar, xanthan, acacia (a natural gum)]
- carbomer
- starches
- poloxamer (pluronic) gels
Humectant
Prevents preparations from becoming dry and brittle
Ex:
- glycerin
- glycerol
- propylene glycol
- PEG
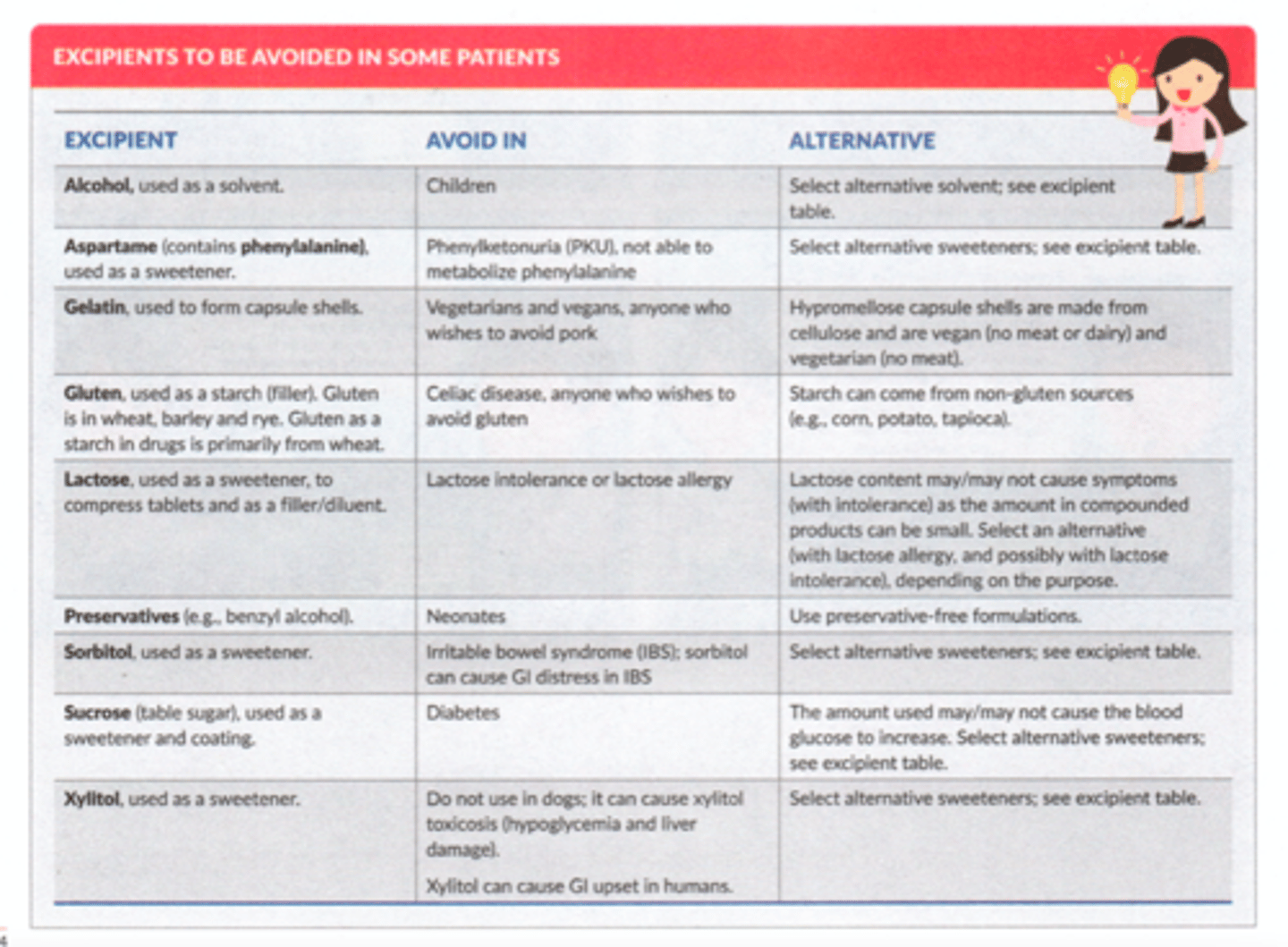
Excipients to be avoided in some pts
- alcohol in children
- aspartame in PKU
- gelatin in vegetarians/vegans or pork avoider (religious)
- gluten in celiac disease
- lactose if lactose allergy/intolerance
- preservatives in neonates
- sorbitol in IBS
- sucrose in DM
- xylitol in dogs
Solutions
homogeneous mixtures : solute dissolved in a solvent
Ex:
- syrups
- elixirs
- tinctures
- spirits
Suspensions
Heterogeneous mixtures: solid dispersed in a liquid.
A wetting agent/levigating agent is a type of surfactant used to incorporate an insoluble drug into a liquid, which makes a suspension.
redispersed easily by shaking.
Emulsions
heterogeneous: liquid dispersed in a liquid oil in water or water in oil
emulsifier is a type of surfactant that is used to reduce the surface tension between two liquids (e.g., oil and water). The emulsifier allows the two phases to come closer together.
hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) number will help choose emulsifier
Precipitation/Sedimentation
when the dispersed phase settles (clumps) together. The process of a solid settling on the bottom of a container is sedimentation.
can happen with suspensions and emulsions, and less commonly with solutions. Shake or gently roll to re-disperse.
Use of Suppositories

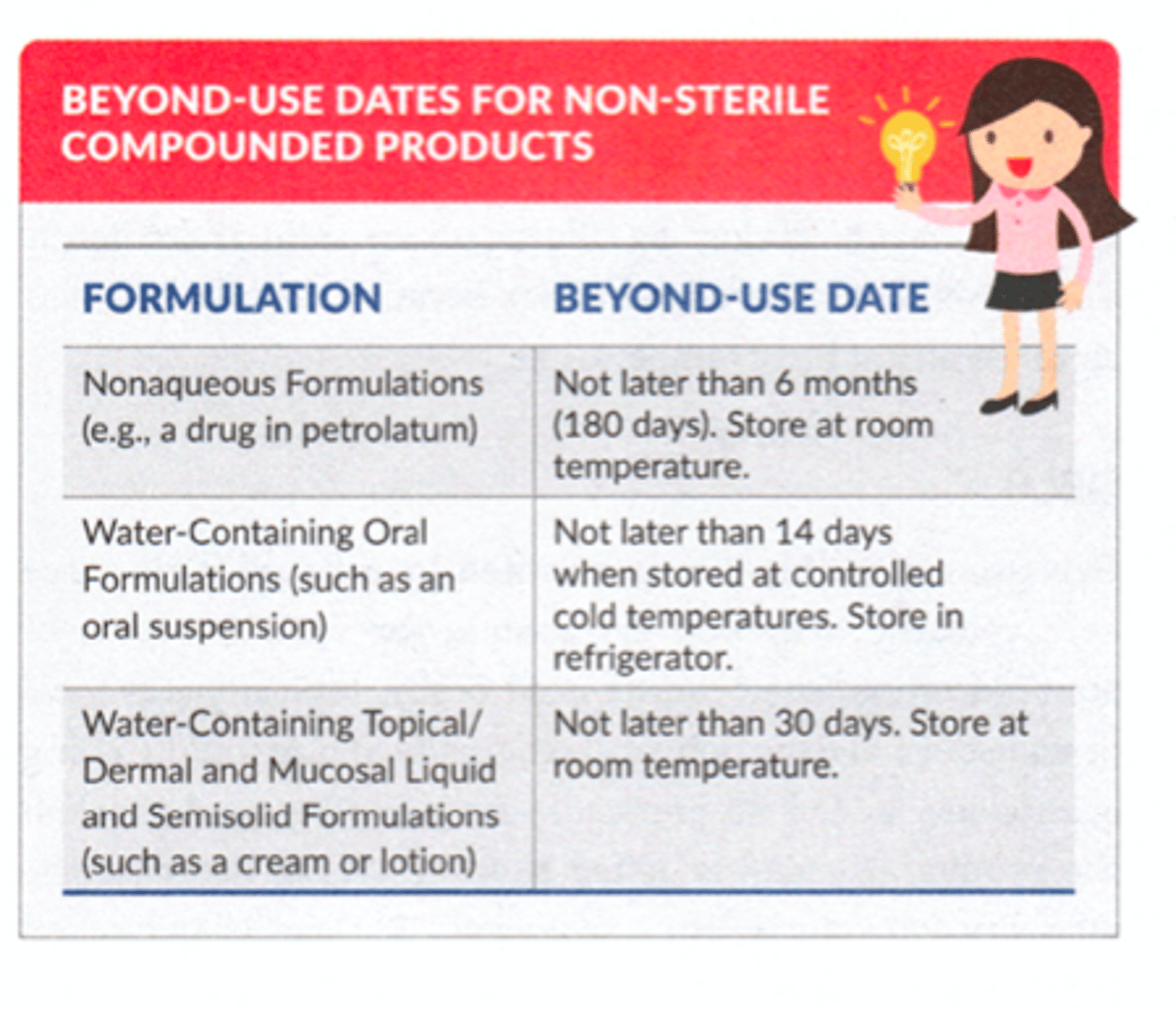
Non-Sterile BUDs
What must be used when working with an ampule for a sterile compound?
A filter needle or filter straw will be required to remove the glass.
What must be done to vials with powder in a sterile compound?
reconstituted by adding sterile water for injection, bacteriostatic water for injection or a diluent supplied by the manufacturer.
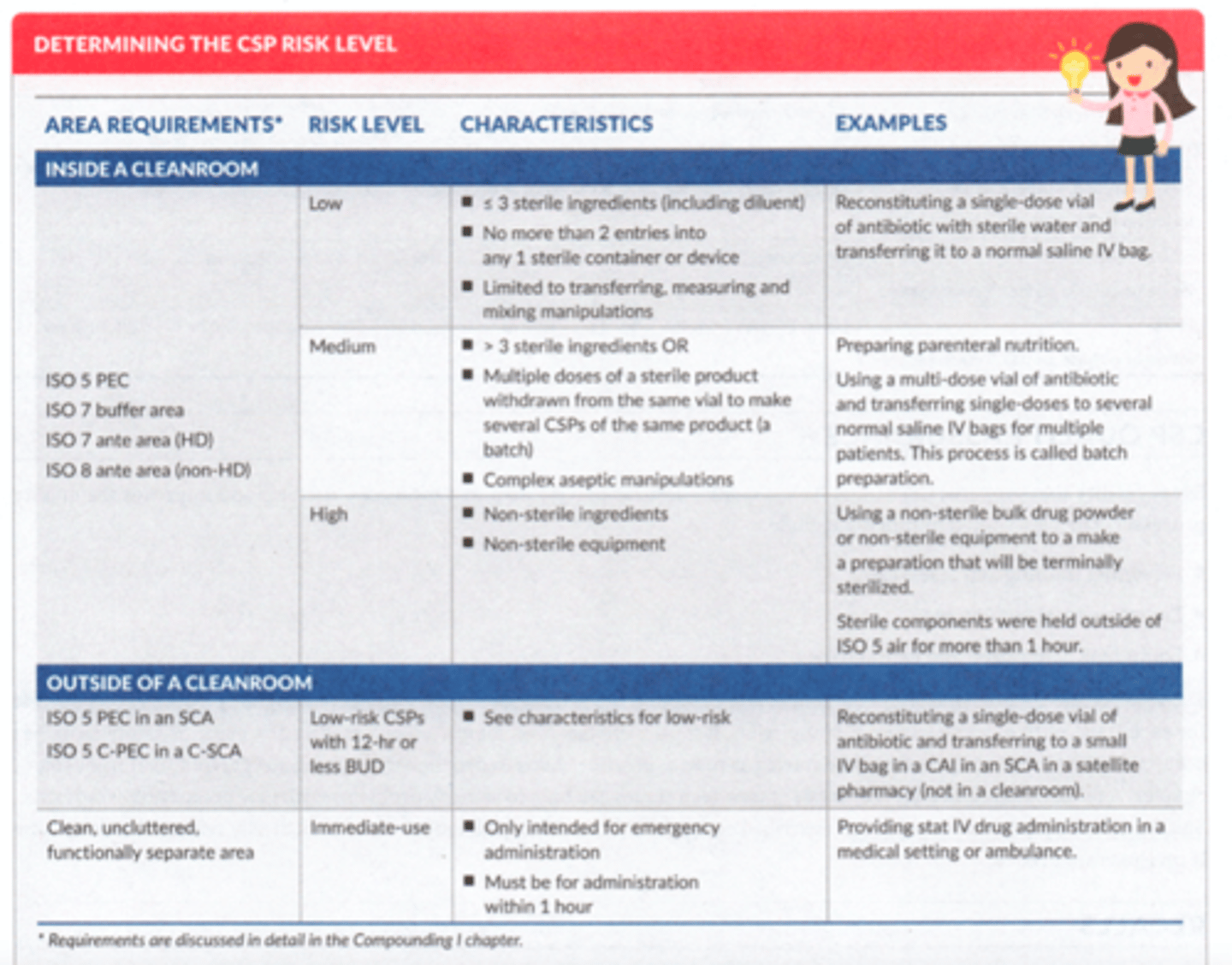
Determining CSP Risk Level
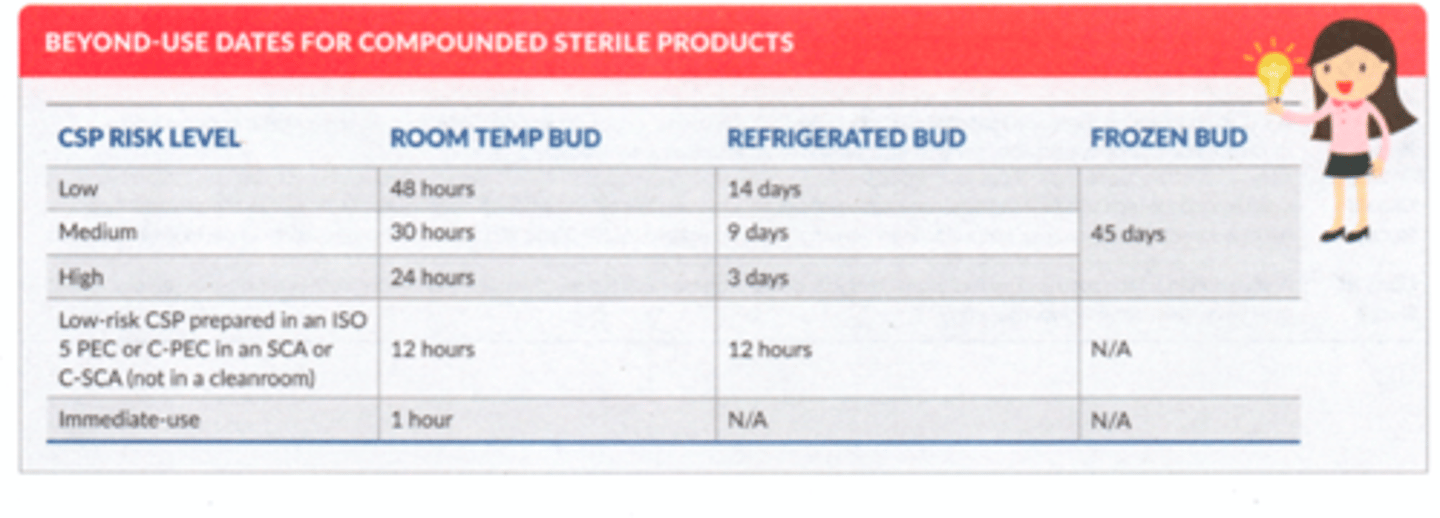
Sterile BUDs
What is Oxidation?
loss of electrons
(when oxidation occurs, so does reduction aka gaining of electrons of the atom that took them)
What meds are at increased risk of oxidation?
Meds w/ hydroxyl OH group bonded to aromatic ring
- catecholamines: Epi, NE, DA
- phenolics: phenylephrine
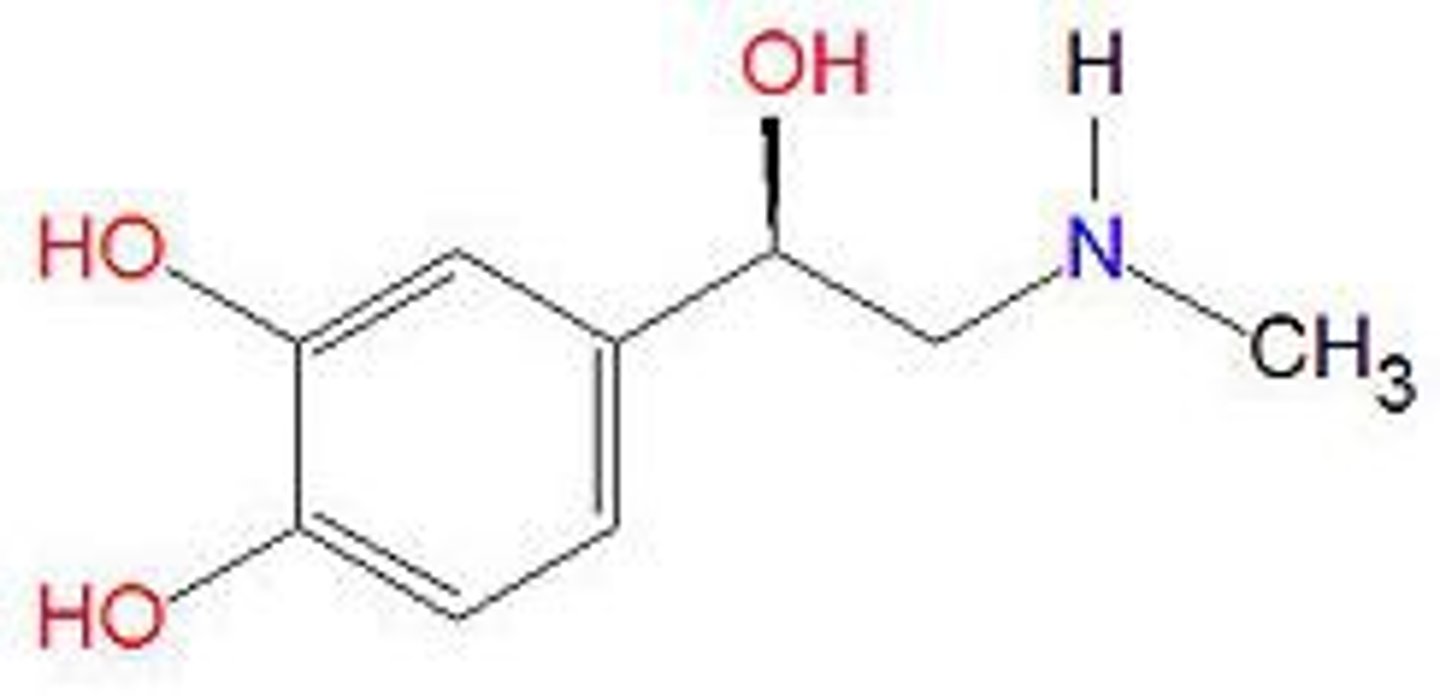
How fo you precent oxidation of a compound?
- light protection (amber glass or UV-protective sleeve)
- temperature control with refrigeration
- add chelating agents to prevent run (ex: EDTA)
- add antioxidants (Vit C ascorbic acid, Vit E tocopherols)
- control pH w/ buffer
What is hydrolysis?
the chemical breakdown of a compound due to reaction with water
What compounds/meds are more likely to undergo hydrolysis?
Meds w/:
- esters: carbonyl + O-R (ASA)
- amines: carbonyl + N
- lactams: beta lactams
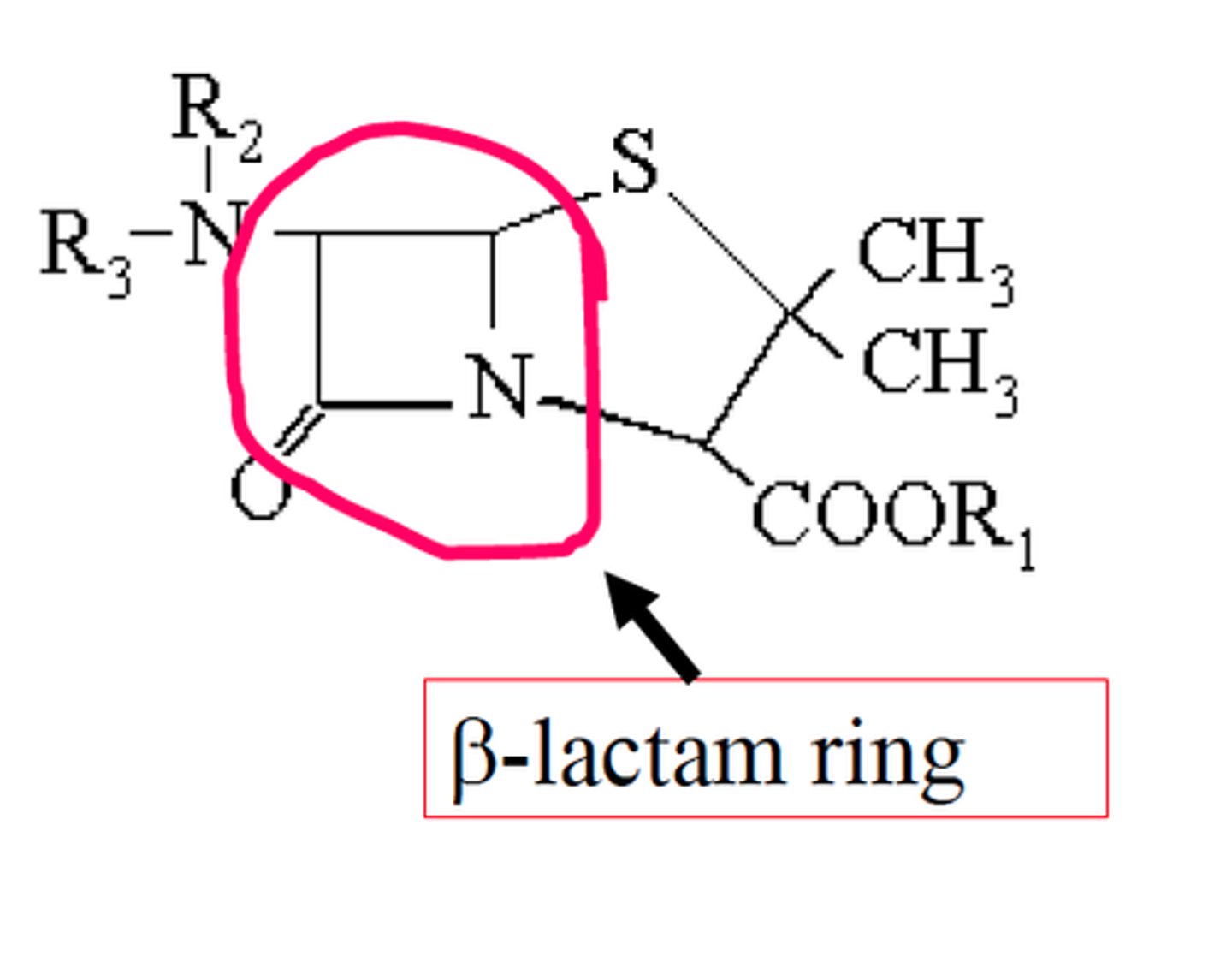
What can be done to prevent hydrolysis?
- light protection (amber glass or UV-protective sleeve)
- add desiccants to absorb moisture
- store as lyophilized/freeze-dried powder
- add chelating agents to prevent run (ex: EDTA)
- add hygroscopic/water-absorbing salt
- make into a prodrug that --> active agent via hydrolysis (like ASA that acetylsalicylic acid --> salicylic acid))
- control temp: occurs at higher rate at higher temp
- maintain pH w/buffer
What is the effect of hypertonic solutions on RBCs?
water moves out of RBCs (they shrink)
often given as an attempt to dilute a solute concentration in the blood, but this can cause RBCs to shriven to the point of dysfunction --> these solutions are restricted to the pharmacy
What is the effect of hypotonic solutions on RBCs?
water moves into RBCs (they swell)
this can lead to hemolysis and RBC bursting that can be fatal
What is it called when the melting point of combined ingredients is lower than them individually?
Eutectic