Unit 7 - Equilibrium
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
At equilibrium concentrations …
stop changing
At equilibrium the rates of forward and reverse reactions are __
equal
If H2O is in (g) form instead of (l) do you include it in the eq constant expression?
YES because it’s in gas form, only disregard pure liquids and solids
What does LARGE eq constant mean?? k>>1
lots of product, little reactant
equilibrium lies to the RIGHT (products)
What does SMALL eq constant mean?? k<<1
lots of reactant, not much product
equilibrium lies to the LEFT (reactants)
if original chemical reaction has Kc=0.18.. if we multiply the coefficients by 2 what is the kc now?
0.18² = 0.0324
(don’t multiply by 2!! raise it to the power of 2!!)
if original chemical reaction has Kc=0.18.. if we flip the reaction what is the kc now?
1/0.18
(take the reciprocal! so.. 0.18/1 becomes 1/0.18)
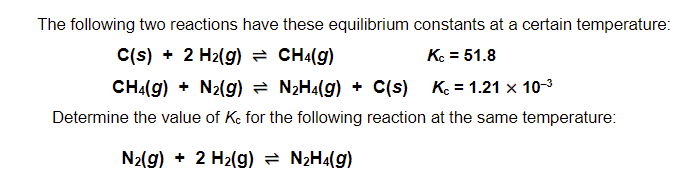
Two seperate reactions have their on Kc.. when we combine the reactions what do we do to the Kc? (add/multiply/subtract/divide)
If we add the reactions we have to multiple their kc’s (equilibrium constants)
What is the effect of adding N(g) to the right of the reaction CH4(g) + 2H2S(g) ←→ CS2(g) +4H2(g)
nothing! nitrogen considered inert gas when added just because it’s not involved in the reaction originally
when working with really small eq constants (10-5 and below) we can..
ignore the subtraction!
Ex
original: kc=[2x]2 [x] / [1-2x]2
do instead: kc= [2x]2 [x] / [1]2
![<p><strong>ignore the subtraction!</strong></p><p>Ex</p><p>original: kc=[2x]<sup>2 </sup>[x] / [1<strong>-2x</strong>]<sup>2</sup></p><p>do instead: kc= [2x]<sup>2</sup> [x] / [1]<sup>2</sup></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0aeb80b5-cda2-40c1-b620-8c8af3447991.png)
is a saturated solution at equilibrium
YES
ksp and solubility expression when 1:1 ratio
x²
ksp and solubility expression when 1:2 ratio
4x³
ksp and solubility expression when 1:3 ratio
27x4
write the dissociation equation for Magnesium fluoride in water
MgF2(s) ←→Mg2+(aq) +2F-(aq)
MgF2 because Mg is 2+ and F is -1 so we gotta balance it out to make a 0 charge compound (so 2 F’s)
(water is absent from equation because compound is being dissolved in it)