Biology topic 5
1/128
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
Ecology
The study of living things in their environment
Ecosystem
A self-sustaining life-supporting environment (with biotic and abiotic factors)
Habitat
The place where an organism lives
Population
Group of organisms of the same species
Community
All the populations of different species
Niche
Role of an organism in the community
Abiotic factors
Non-living elements of the habitat that affect survival
Biotic factors
Living elements of the habitat that affect survival
Anthropogenic
Factors arising from human activity that affect survival
Biosphere
Global ecosystem, all organisms on earth
Biomes
Major ecosystems on earth
Succession
The process by which communities of organisms colonise an area and then over time are replaced by other usually more varied communities
Primary succession
Succession on inorganic surface devoid of any vegetation
Stage 1 of succession
pioneer species eg. Lichens and mosses
Help break down rock surface
Rock grains and dead organic matter form soil
Stage 2 succession
intermediate species
Establish root systems in soil
Soil system develops (more water and nutrients retained) allowing other plants to survive
Stage 3 succession
climax community
Remains unchanged unless conditions change
Dominant species influence rest of community
Secondary succession
Development of an ecosystem from existing soil that has been cleared of vegetation
Deflected succession
A community that is kept stable by human activity which prevents succession from running its course
heterotrophic nutrition
get food from somewhere else e.g. fungi, animals
autotrophic nutrition
make their own food e.g. plants, algae, some bacteria
phototrophs
make food using solar energy e.g. plants
chemotrophs
make food using chemical reactions e.g. sulphur bacteria use chemosynthesis
photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O —> C6H12O6 + 6O2
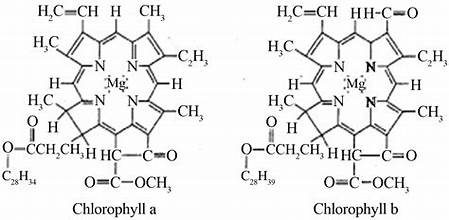
chlorophyll
one of several photosynthetic pigments
chlorophyll a and b
hydrophilic head - Mg2+ at centre of porphyrin ring
hydrophobic tail - hydrocarbon chain anchors molecules into chloroplast membrane
carotenoids
red, orange, yellow pigments
hydrophobic
membrane attached
assist chlorophyll by passing light on to them = accessory pigment
outer membrane of chloroplast
allows free passage of CO2, O2 and H2O
inner membrane of chloroplast
contains many transporter proteins
thylakoid membrane
interconnected flat fluid-filled sacs of membrane
membrane contains photosynthetic pigments
light-dependent reaction occurs across thylakoid membrane
granum
stack(s) of thylakoids
stroma
fluid surrounding thylakoids
light independent reaction occurs here
starch granule in chloroplasts
storage of photosynthetic products
DNA loop in chloroplasts
chloroplast DNA coding for some proteins
functions of the light dependent reaction
production of ATP to supply energy for synthesis of carbohydrates
production of NADPH to supply H+ ions for synthesis of carbohydrates
ATP
adenosine triphosphate - transport of chemical energy
how does ATP release energy?
when it is hydrolysed to form ADP and Pi
NADPH
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
coenzyme
functions as reducing agent by carrying hydrogen
photosystem 1
P700 - reaction centre is chlorophyll a
photosystem 2
P680 - reaction centre is chlorophyll a
diagram of light dependent reaction
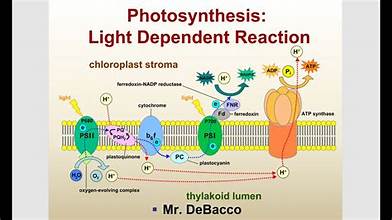
light dependent reaction steps 1-4 in detail
PS 2’s P680 reaction centre emits 2 excited electrons when light hits it which pass to an electron acceptor which is reduced
the electrons lost from PS 2 are replaced by the photolysis of H2O which produces 2H+ ions, 2 free electrons and 1/2O2
electrons then pass to a series of electron carriers along an electron transport chain. each carrier becomes reduced, then oxidised as it passes the electrons on
each electron carrier has a lower energy level than the last so as the electrons pass on energy is released which is used to synthesise ATP in a reaction called photophosphorylation
light dependent reaction steps 5-7 in detail
PS 1’s P700 reaction centre also emits 2 excited electrons. these are replaced by the two electrons from the PS 2 electron transport chain
electrons emitted from PS 1 are captured by an electron acceptor and pass down another chain of electron carriers
the 2 electrons combine with H+ from H2O to reduce NADP+ to NADPH
chemiosmosis
Movement of ions across a semi permeable membrane, down their electrochemical gradient
occurs as H+ ions move across the thylakoid membrane
function of the light independent reaction
to use NADPH and ATP to reduce CO2 to produce glucose in a series of reactions called the Cavlin cycle
Calvin cycle diagram
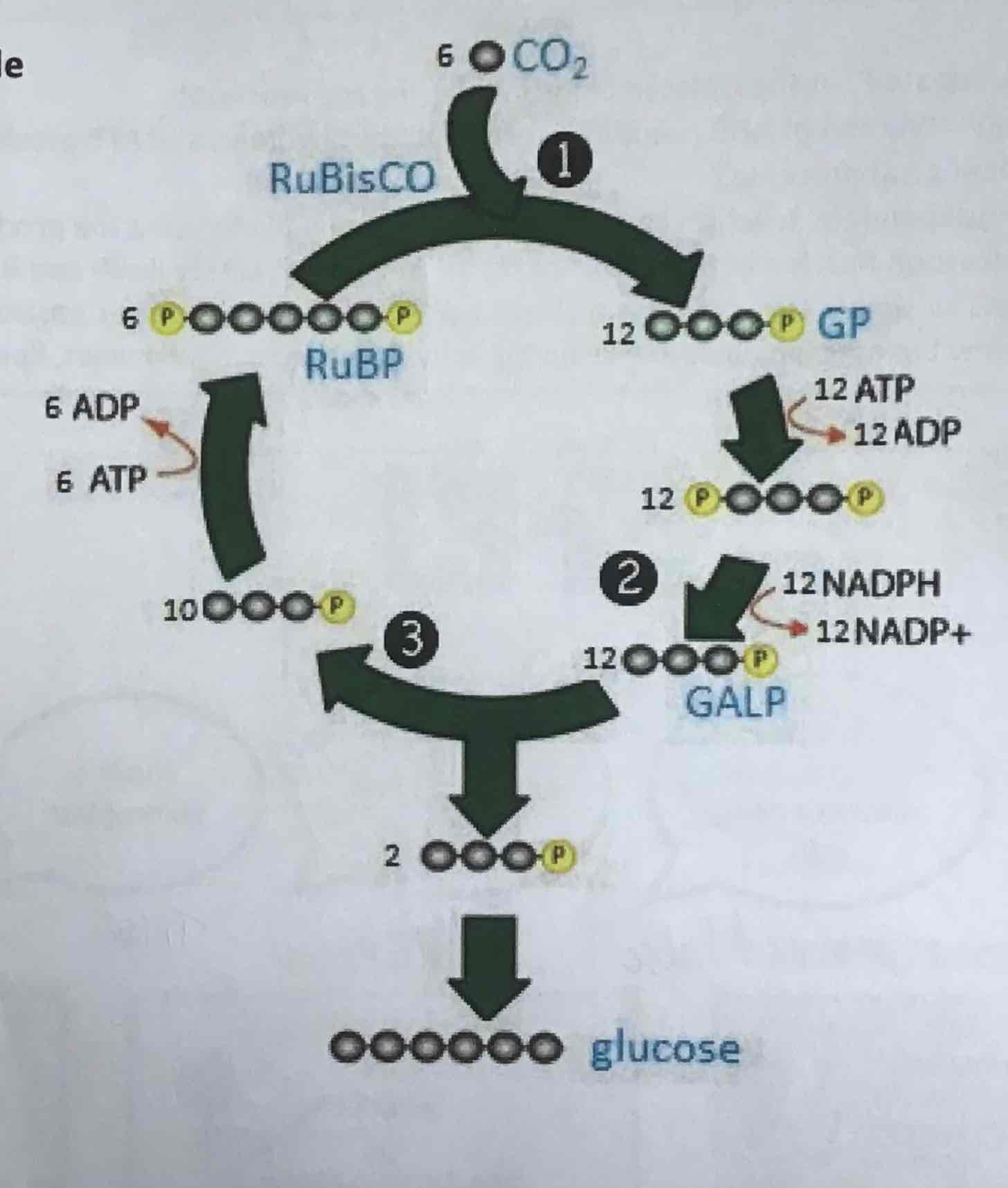
step 1 of the Calvin cycle : CO2 fixation
CO2 combine with RuBP to form 2x GP
catalysed by enzyme RuBisCO
step 2 of Calvin Cycle: reduction
GP is reduced to form GALP
hydrogen for reduction is from NADPH
energy for reduction is from ATP
step 3 of Calvin Cycle: regeneration of RuBP
GALP uses ATP to resynthesise RuBP
glucose is produced (cycle completed 6 times per glucose molecule)
primary consumer
herbivores - eat photosynthetic material
secondary consumer
carnivores - feed on herbivores
tertiary consumer
top carnivores - feed on herbivores and other carnivores - aren’t eaten by anything
autotrophs
photosynthetic or chemosynthetic organisms
heterotrophs
consumers of other organisms
omnivores
feed on photosynthetic organisms and animals
trophic level
feeding level
food chain
diagram showing a simple linear feeding relationship
food web
diagram showing complex feeding relationships (often representing all organisms in an ecosystem)
detritivores
primary consumers that feed on dead organic matter
decomposers / saprotrophs
bacteria and fungi that feed on dead organic matter and faeces; recyclers of nutrients; use external digestion
on average, how much energy is lost between trophic levels?
about 90%
limiting factors to photosynthesis
light intensity
H2O from soil
temperature
CO2 from air
gross primary productivity (GPP)
the rate at which energy is incorporated into organic molecules
net primary productivity (NPP)
the rate at which energy is incorporated into organic molecules that make up new biomass
NPP equation
NPP = GPP - respiration
secondary productivity
the rate at which energy is used to make new consumer biomass
secondary productivity equation
energy consumed = energy lost in respiration + energy lost in waste + energy in biomass
factors that affect how much energy is lost in respiration
SA/vol ratio
time spent foraging for food
temperature of environment
digestibility of food
temperature records as evidence for climate change
data from more than 1000 weather stations around the globe
precise records begin in 1880
overall trend is increasing temperature
paleoclimatology
the study of changes in climate taken on the scale of the entire history of Earth
use of ice cores for evidence of climate change
drilled from ice sheets and glaciers
encloses small bubbles of air that contain a sample of the atmosphere at that time
older ice is further down
concentration of gases can be measured and can be interpreted for temperature
in warmer climates more 18O in polar ice than usual
peat bogs
substrate made of dead organic matter
acidic, cool and anaerobic/anoxic
forms in layers - age can be determined by carbon dating
how do anaerobic conditions reduce decomposition?
low (or no) oxygen, decomposing bacteria and fungi cant respire so die
digestive enzymes not present
acidic pH reduces enzyme activity
pollen in peat bogs as evidence for climate change
pollen is resistant to decomposition
different plant species grow best in different conditions
plants can be identified and climate at the time can be interpreted
insect records in peat bogs as evidence for climate change
exoskeleton preserved in peat bogs
populations respond faster than plants to climate change
thrive in particular climate conditions
dendrochronology
the dating of tree wrings to the year they were formed in order to analyse climatic conditions during different periods in history
atmosphere
a layer of gases surrounding a planet
how does the atmosphere sustain life?
oxygen for respiration
carbon dioxide for photosynthesis
ozone layer absorbs UV light reducing genetic damage
maintains stable temperature
greenhouse effect
short wavelength solar radiation passes through the atmosphere
some radiation is absorbed, warming the Earth
some longer wavelength infrared radiation is reflected off the Earth
most longer wavelength IR radiation escapes to outer space allowing the Earth to cool
some longer wavelength IR radiation is absorbed by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, warming the earth and lower atmosphere
global warming
enhanced effect due to an increased level of greenhouse gases
source of carbon dioxide
combustion of fossil fuels
respiration
source of methane
anaerobic bacteria in marshes and rice paddies
anaerobic bacteria in guts of ruminants e.g. cows
decomposition of organic material
leakage from gas pipes and coal mines
source of nitrous oxide
combustion of fossil fuels
denitrifying bacteria acting on nitrates and nitrites
sources of CFCs
coolants
propellants
source of ozone
reaction product of car exhaust pollutants and sunlight
scientific theory
comprehensive explanation of some aspect of nature that is supported by a vast body of evidence and upon which predictions can be made
extrapolation
an estimate outside the recorded or observed range
factors to take into account to predict future CO2 concentration
price of fossil fuel
Kyoto protocol
development of clean technology
amount of photosynthesis
increase in word population
climate models
quantitative methods to simulate the interactions of the different factors to project future climate
limitations of climate models
limited data
limited knowledge on how climate works
limited computing resources
not all factors considered
changing factors or new factors
how flora and fauna are adapting to climate change
changes in distribution
changes in development
changes in life cycle
alien species
non-native species that can reduce biodiversity through disease, competition or predation
coral bleaching
loss of the photosynthetic symbiont
increase in temperature below optimum
as temperature increases, rate of reaction increases
more collision of substrate and enzyme due to higher kinetic energy
enzyme optimum temperature
highest rate of reaction
effect of temperature increase on enzymes above optimum
as temperature increases, rate of reaction decreases
secondary and tertiary bonds break due to high vibration of molecules
enzyme denature
active site change shape
no binding of substrate
phenology
study of periodic plant and animal life cycles and how these are influenced by seasonal climate
how natural selection works
features encoded by genes
natural variation due to alleles increasing the gene pool of the population
selection pressure gives some individuals an advantage
these are more likely to survive, reproduce and pass on their alleles
chromosome mutation
a change in the structure of a chromosome
e.g. duplication, inversion, deletion, insertion, translocation
gene mutation
change in the DNA base sequence in genes
evolution
a change in allele frequency in a population over time