Memory and Cognition PSYC1011
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
1
New cards
Shallow processing
Encoding information in a superficial way, such as focusing on upper or lower case letters.
2
New cards
Deep processing
Encoding information in a meaningful way, such as connecting it to existing knowledge or generating new examples.
3
New cards
Retrieval practice
Testing yourself on the material to strengthen memory and improve recall.
4
New cards
Distributed practice
Spacing out study sessions over time to enhance learning and memory.
5
New cards
Elaboration
Thinking about the meaning of the material and making connections to other concepts or personal interests.
6
New cards
Inattentional blindness
Failing to see something that is right in front of you due to your attention being focused on a primary task.
7
New cards
Change blindness
Failing to notice changes in your environment, even when they are relatively large or obvious.
8
New cards
Feature integration theory
The idea that certain basic features are processed quickly and in parallel, while attention is needed to bind these features together into more complex objects.
9
New cards
Interleaved practice
Mixing up different types of practice problems or examples to encourage comparison and discrimination between concepts.
10
New cards
Memory palace
A mnemonic technique that involves associating information with specific locations in a familiar environment to aid in memory recall.
11
New cards
Sleep (study technique)
Getting sufficient sleep is important for memory consolidation and retention.
12
New cards
Flashbulb memory
A vivid and detailed memory of an emotionally significant event, often associated with strong emotions and high confidence in the accuracy of the memory.
13
New cards
Schemas
Organized knowledge or expectations about a particular domain or event that can influence memory and perception.
14
New cards
False memories
Memories that are distorted or fabricated due to suggestions, biases, or misleading information.
15
New cards
Source monitoring
The process of distinguishing between different sources of information, such as distinguishing between what was seen versus what was heard.
16
New cards
Retrograde amnesia
Inability to access old memories, typically more profound for recent memories.
17
New cards
Primitive Features
The idea that some basic features don’t need attention to be seen (visual pop-out)
18
New cards
When do primitive features require attention?
When you try to combine these features (conjunction features)
19
New cards
What is the binding process of feature integration theory?
Slow and serial, need to move attention from one item to the other in order to be aware of more complex objects.
20
New cards
Two ways we can manipulate attention to make it more likely people will see an unexpected object?
Spatial attention - moving attention around from place to place. OR Feature based attention - turning your attention to particular features
21
New cards
Simon & Levin
50% of people don’t notice they are talking to a different person
22
New cards
Desirable Difficulties and their effect
Elaboration = Deep encoding, testing yourself = retrieval, Distributed practice = Spacing effect
23
New cards
Why is interleaved practice good?
encourages comparison, contrasts and discrimination between concepts
24
New cards
Why is elaboration good for memory?
Concrete information is easier to visualise and remember
25
New cards
Why does memory palace work?
Hippocampus is thought to be involved in emotion and spatial navigation, which is in control of STM and LTM processing
26
New cards
Consolidation
The ‘stabilisation’ of memories that have been encoded.
If you start studying in the evening, and then continue after a good sleep, you will remember more than if you study the same topic in the morning and then the evening
If you start studying in the evening, and then continue after a good sleep, you will remember more than if you study the same topic in the morning and then the evening
27
New cards
reconstructive memory
The process of altering and reshaping memories over time, influenced by new information or experiences. It can lead to inaccuracies or false memories due to the brain's tendency to fill in gaps.
28
New cards
What did the Bartlett study show?
That memory is reconstructive and influenced by our pre-existing knowledge and schemas.
29
New cards
External source monitoring
Distinguishing between external sources
(what I saw vs. what someone told me)
(what I saw vs. what someone told me)
30
New cards
Internal source monitoring
Distinguishing between internal sources (what I thought vs what I said)
31
New cards
Reality monitoring
Distinguishing between internal and external sources
32
New cards
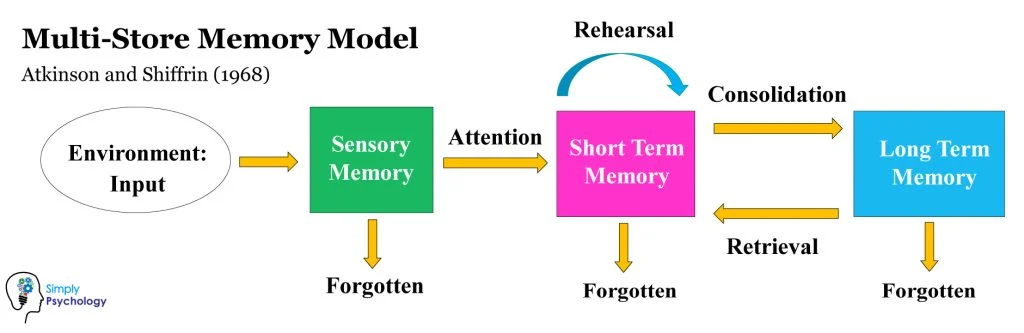
Multistore memory model
It consists of three main components: sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory.
1. Sensory Memory: This is the initial stage of memory where information from the environment is briefly registered. It has a large capacity but a very short duration (less than a second).
2. Short-Term Memory (STM): Also known as working memory, this is where information is temporarily held and actively processed. STM has a limited capacity (around 7 items) and a short duration (around 20-30 seconds) unless it is rehearsed or transferred to long-term memory.
3. Long-Term Memory (LTM): This is the stage where information is stored for a longer period of time, potentially indefinitely. LTM has a vast capacity and can store various types of information, including facts, skills, and experiences.
\
1. Sensory Memory: This is the initial stage of memory where information from the environment is briefly registered. It has a large capacity but a very short duration (less than a second).
2. Short-Term Memory (STM): Also known as working memory, this is where information is temporarily held and actively processed. STM has a limited capacity (around 7 items) and a short duration (around 20-30 seconds) unless it is rehearsed or transferred to long-term memory.
3. Long-Term Memory (LTM): This is the stage where information is stored for a longer period of time, potentially indefinitely. LTM has a vast capacity and can store various types of information, including facts, skills, and experiences.
\