CPI Test 2
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Bones that make up the foot
medial, intermediate, and lateral cuneiform
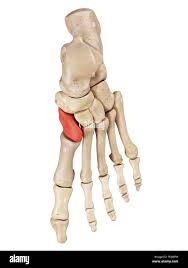
medial cuneiform
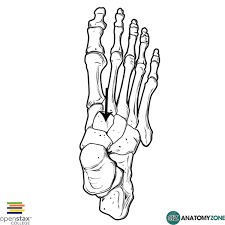
intermediate cuneiform
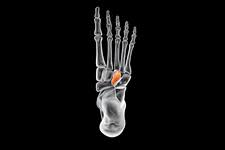
lateral cuneiform
Bones that make up the ankle
calcaneus, talus, navicular, and cuboid
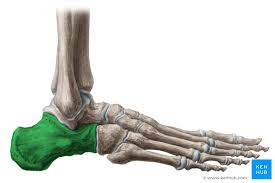
calcaneus
talus
navicular
cuboid
bones that make up the lower leg
tibia and fibula
tibia
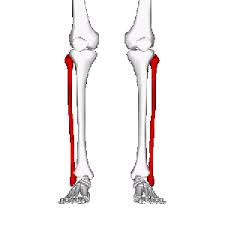
fibula
lower leg muscles
anterior tibialis, posterior tibialis, gastrocnemius, soleus, peroneal muscle group
makes up the peroneal muscle group
longus, brevis, and tertius
quadricep muscles
vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, rectus femoris, sartorius
hamstring muscles
biceps femoris, semimembranosus, semitendinosus
which muscle does the Achilles originate from?
soleus
what is the other important structure of the foot not listed?
plantar fascia
function of the bursa of the knee
protect the tendon from rubbing on the bones
ligaments in the knee
anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), medial collateral ligament (MCL), and lateral collateral ligament (LCL)
bones that make up the shoulder joint
humerus, scapula, and clavicle
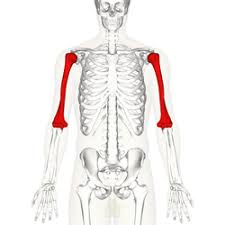
humerus
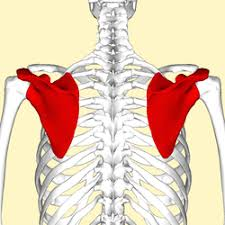
scapula
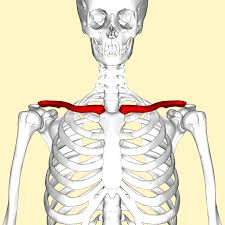
clavicle
muscles that make up the rotator cuff
supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis
action of the biceps
flexion
action of the triceps
extension
action of the rotator cuff
internal and external rotation
six motions of the wrist
flexion, extension, radial deviation, ulnar deviation, supination, and pronation
additional motion of the wrist
adduction/abduction of 1st finger
which upper extremity injury is graded on a scale of I-IV
AC joint (acromioclavicular) sprain
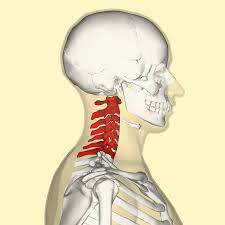
cervical segment
vertebrae and intervertebral discs in the cervical segment
7 vertebrae (C1-C7) and 6 intervertebral discs
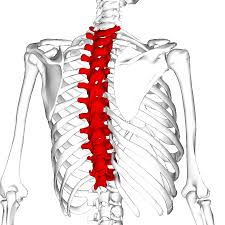
thoracic segment
vertebrae and intervertebral discs in the thoracic segment
12 vertebrae (T1-T12) and 12 intervertebral discs
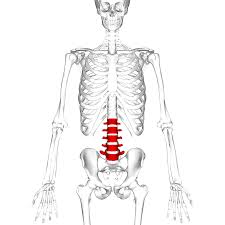
lumbar segment
vertebrae and intervertebral discs in the lumbar segment
5 vertebrae (L1-L5) and 5 intervertebral discs
type of curvature in the cervical segment
lordotic curvature
type of curvature in the thoracic segment
kyphotic curvature
type of curvature in the lumbar segment
lordotic curvature
total amount of invertebral discs and amount of layers in each
23 total, 2 layers
anatomy of invertebral discs
annulus fibrosis and nucleus pulposus
annulus fibrosis
outer/thicker layer
nucleus pulposus
inner/jelly-like layer
anatomy of rib cage
12 sets total with intercostal muscles
types of ribs
true, false, and floating
true ribs
(1-7) connect to sternum
false ribs
(8-12) connect to cartilage of 7th rib
floating ribs
(11-12) doesn’t connect to anything
abdominal muscles
rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, internal & external oblique
rectus abdominis
6-pack, trunk flexion
transverse abdominis
used majority of the time
internal & external oblique
trunk rotation
mTBI
mild traumatic brain injury
common symptoms of a concussion
headache, nausea, dizziness
emergency symptoms of a concussion
vomiting blood, unequal pupil size, loss of consciousness
buldging discs
outer annulus fibrosis pushes into joint space
herniated discs
nucleus pulposa forces its way completely through the annulus fibrosis
“catch all” term for athletic pubalgia
sports hernia
stage 1: return to play from concussion
very slow, controlled cardio
stage 2: return to play from concussion
elliptical
stage 3: return to play from concussion
light jog, weight lifting, and agility work
stage 4: return to play from concussion
running, sport-specific movements, ½ practice with little to no contact
stage 5: return to play from concussion
full practice with contact
what can cause return to play protocols to stop, stall, or start over?
physical stimulus, mental stimulus, and medications
empathy
understanding/appreciating what someone is feeling or experiencing
sympathy
feeling bad for someone; trying to experience what the affected person is experiencing
4 lengths of injury
short-term, long-term, chronic, and terminating
short-term reaction to injury
shock or relief
short-term reaction to rehab
impatient or optimistic
short-term reaction to return
eagerness or anticipation
long-term reaction to injury
fear or anger
long-term reaction to rehab
loss of vigor or irrational thoughts
long-term reaction to return
acknowledgement
chronic reaction to injury
anger or frustration
chronic reaction to rehab
dependence/independence or apprehensive
chronic reaction to return
confident or skeptical
terminal reaction to injury
isolation or grief process
terminal reaction to rehab
loss of athletic identity
terminal reaction to return
closure or renewal
two types of injury prone athletes
the “risk taker'“ and the reserved personality
why should a scared athlete not return to play?
may lead to further injury
overtraining
can cause anxiety which them amplifies non-athletic issues
burnout
physical/emotional exhaustion due to lack of rest
how can goal setting be a method of prevention for overtraining and burnout?
keeps focus on healthy goals and promotes healthy mindsets