f&vd quiz 4
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
dysphonia
altered quality, pitch, loudness, or increased effort
aphonia
loss of voice
vocal fatigue
client perceives an increase in phonatory effort over time that may be accompanied by decreased phonatory function
globus sensation
feeling like something is in your throat
fixed abduction or adduction
when the vocal cords are stuck and cannot move (abduction = open, adduction = closed)
dyspnea & what are 2 potential/primary causes
feeling out of breath due to interference of airflow due to…
vocal pathology
uncontrolled adduction or abduction obstructing the airway
odynophagia
pain when swallowing
sharp pain
pain at other times besides odynophagia
vocal fold bowing & two causes
inward curvature of vocal fold due to lost muscle bulk caused by aging or nerve damage
vocal fold paresis
weak vocal fold movement
organic voice disorders
due to detectable physical or biochemical changes within cells, tissues, or organs
lesion
damage or abnormal change in tissue
neoplasm
growth of new tissue, either benign or cancerous
two subtypes of organic voice disorders
structural and neurogenic
organic structural voice disorders
something is physically wrong with the vocal mechanism’s laryngeal or velar structure, due either to lesions in tissue or joint tissue
examples of potential causes of organic structural voice disorders
phonotrauma, medical conditions, birth defects, puberty, smoking
organic neurogenic voice disorders
problems with central or peripheral nervous system innervation due to larynx causing trouble with motor movement and muscle tone
examples of potential causes of organic neurogenic voice disorders
neurological diseases, infectious diseases, growths, tumors
velopharyngeal disfunction
insufficient velopharyngeal closure resulting in a leakage of air to the nasal cavity; causes resonance voice disorders
3 causes of VPD
velum deformed due to congenital disorder, doesn’t close due to neurological disorder, or velum is normal but client is not using habitual sufficient velopharyngeal closure
examples of things that cause medical trauma
surgeries, medical procedures, intubation damage, injury, burn, excessive emotional stress
functional voice disorders
vocal mechanism being used inappropriately even though the physical structure is normal
what do voice alterations due to changes in vocal fold vibration cause
changes in quality and pitch
what do voice alterations due to changes in airflow through vocal cords cause cause
changes in quality and loudness
5 categories of organic disorders
growths — neoplasms
lesions
potential or established disease
chronic congenital & acquired
related to development/changes across lifespan
3 types of voice issues — growths
vocal nodules
vocal polyps
vocal cysts
4 types of voice issues — lesions
laryngeal hemorrhage
reinke’s edema
contact ulcers
sulcus vocalis
2 types of voice issues — potential or established diseases
laryngeal leukoplakia
laryngeal cancer
two types of chronic congenital and & acquired voice issues
laryngeal papilloma
laryngeal web
5 types of voice issues related to development/lifespan
laryngeal ankylosis
presbyphonia
puberphonia
laryngomalacia
VPD
vocal nodules
white soft growth that becomes hard, thick and fibrous like a callous
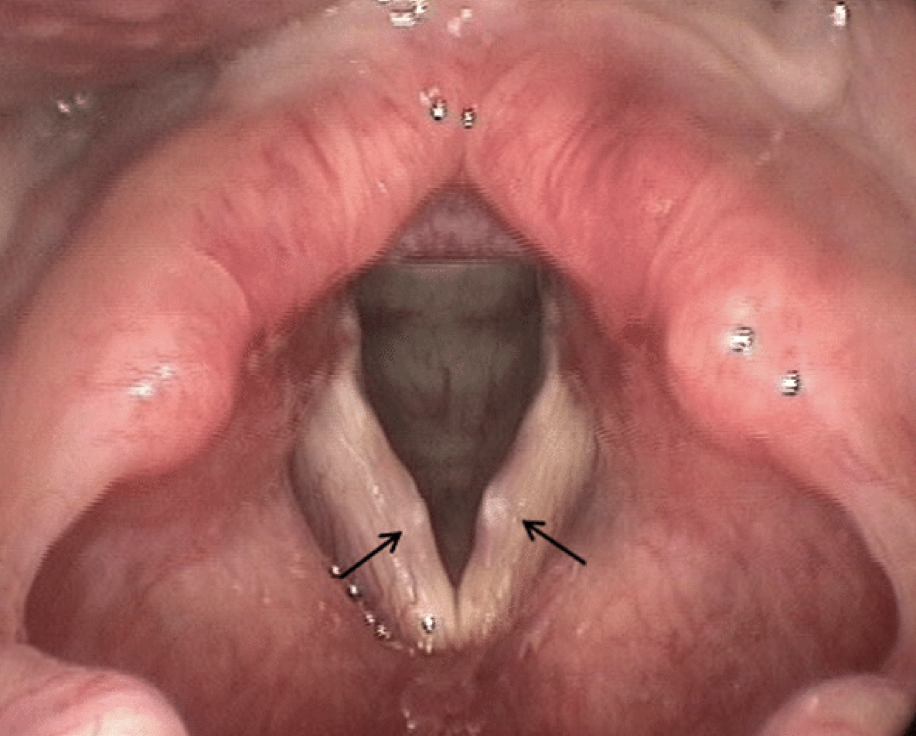
vocal polyps
blister filled with fluid or blood. can be directly on vocal fold usually at the midpoint (sessile), or attached by a separate piece of tissue (pedunculated)
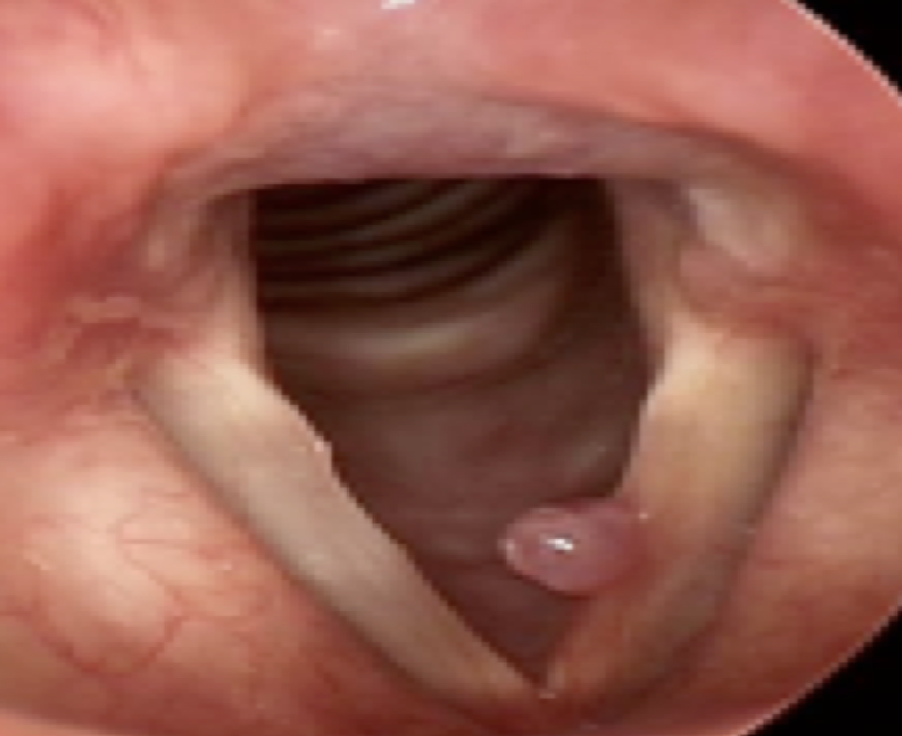
vocal cysts
blockage in the glandular duct causing retention of mucus or blood
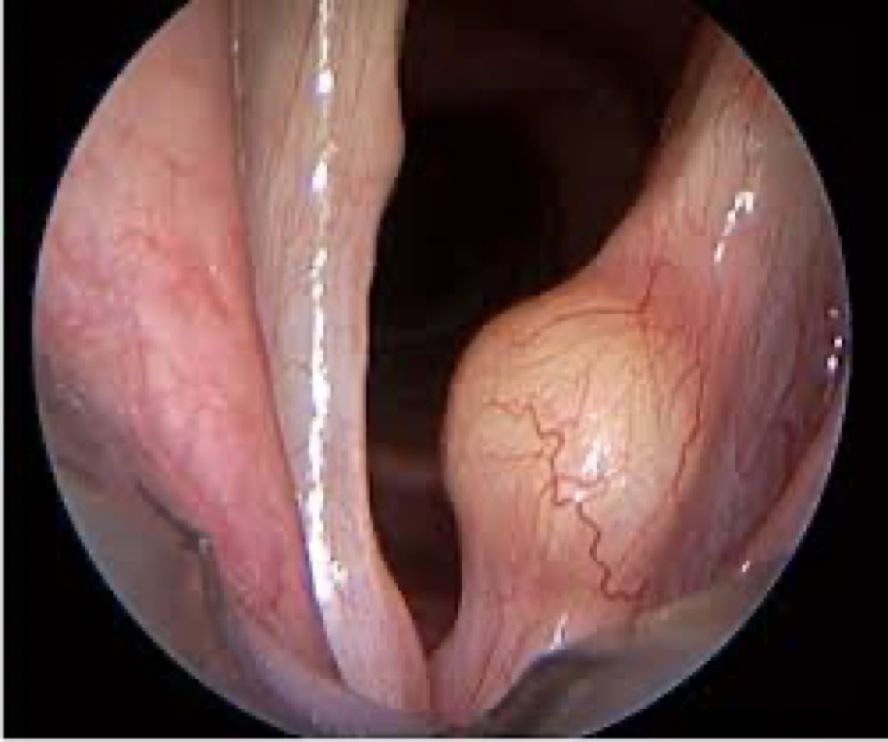
laryngeal hemorrhage
ruptured blood vessels in the submucosal layer of vocal folds (superficial lamina propria). often due to an acute event and increased risk if on blood thinners
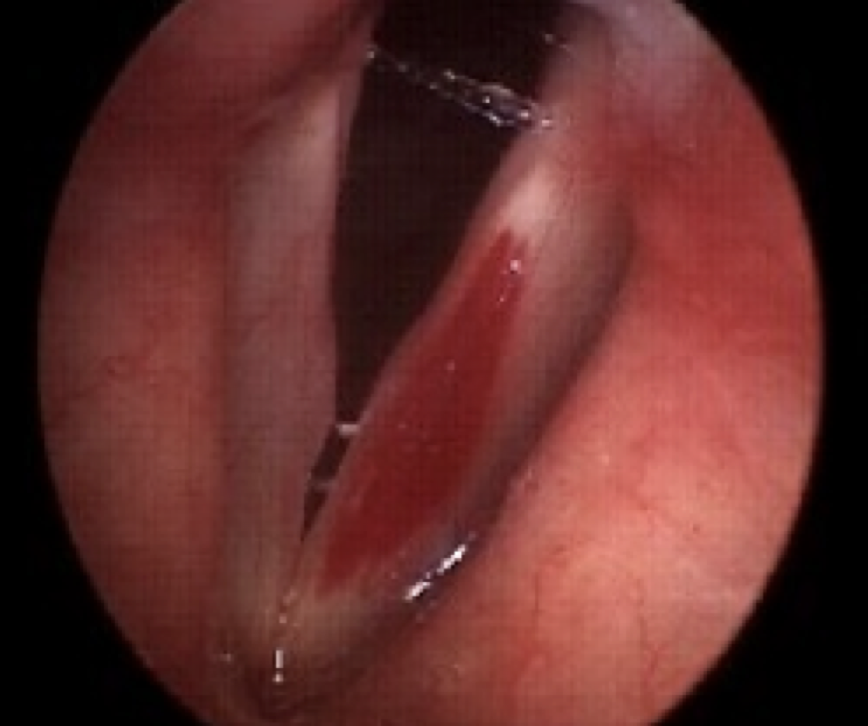
reinke’s edema & alternate names for it
aka polypoid corditis, or if extreme called polypoid degeneration; buildup of fluids or polyps in the superficial lamina propria, which causes edema or swelling of the vocal folds
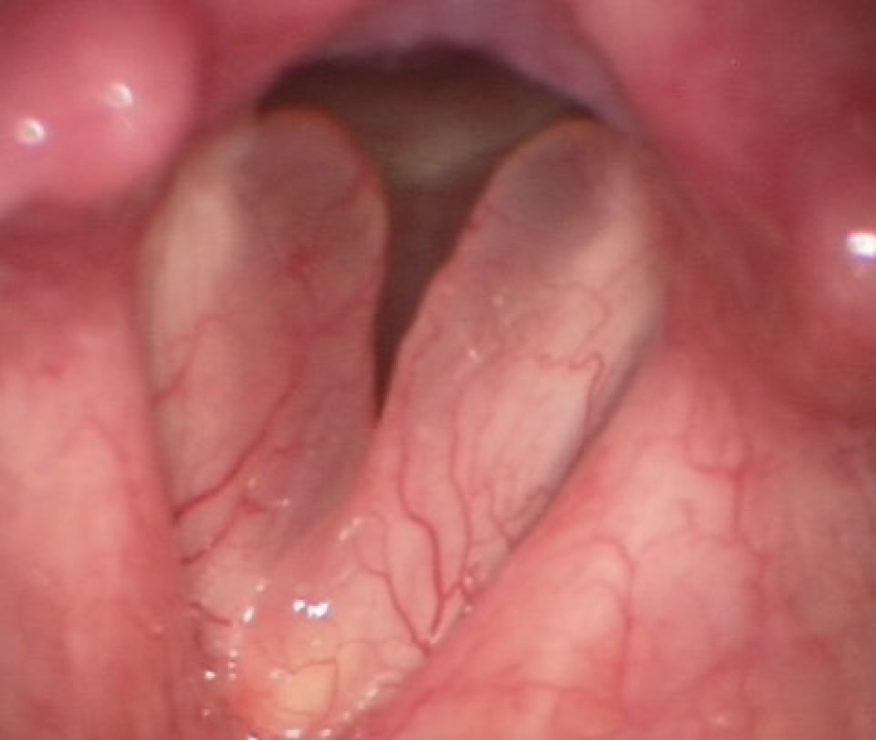
contact ulcers & what’s associated with it
aka laryngogranuloma; an open sore. leaves a bitter taste in mouth and causes odynophagia or sharp pain during coughing or throat clearing
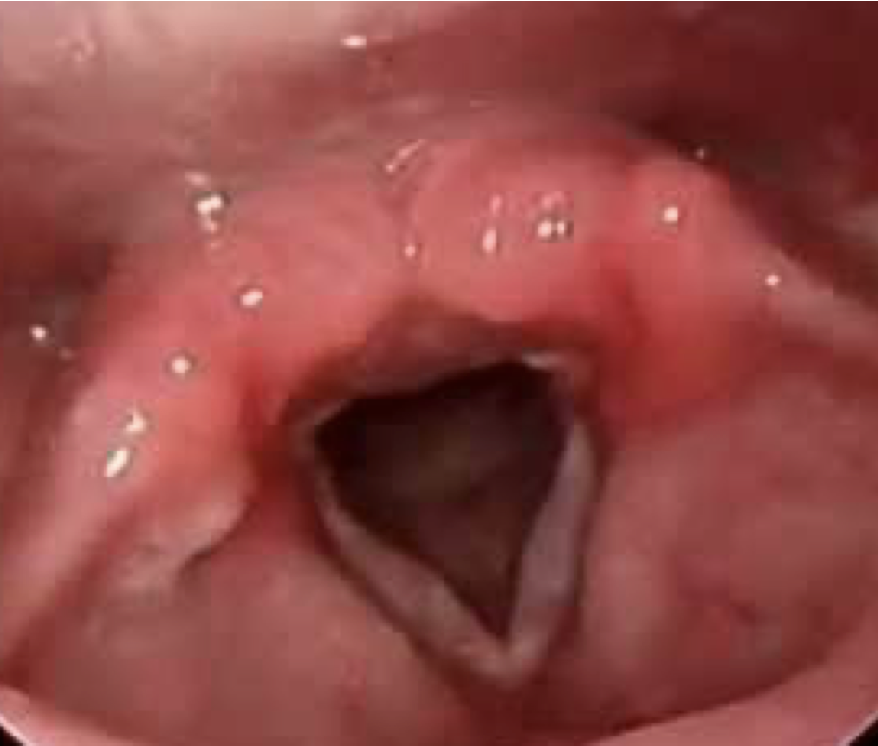
sulcus vocalis
groove in the development or a narrow cut in the vocal fold
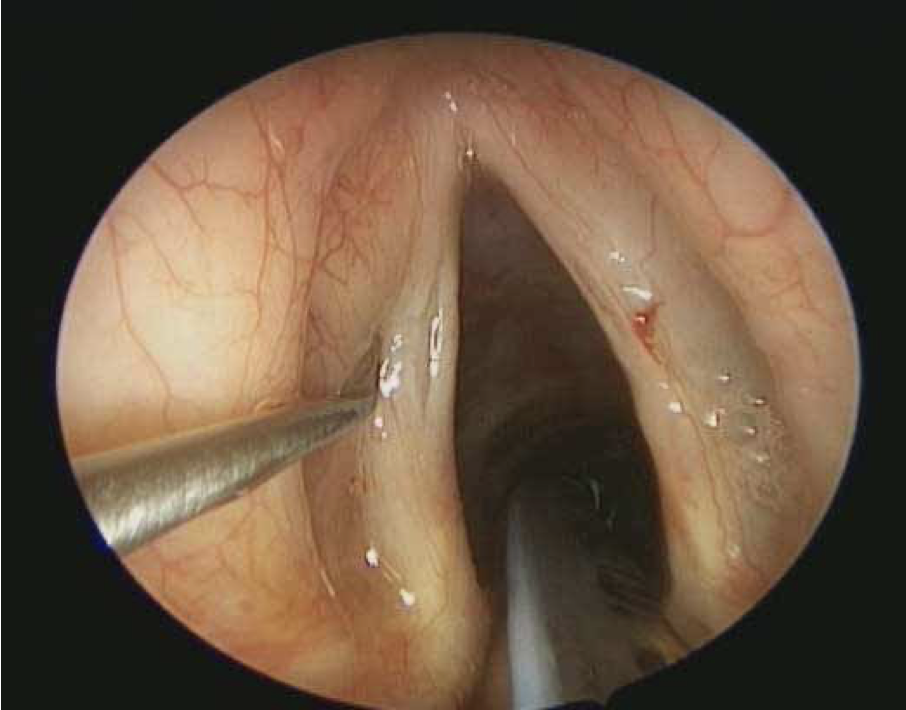
laryngeal leukoplakia
white plaque-like lesions and red patches; can be precancerous
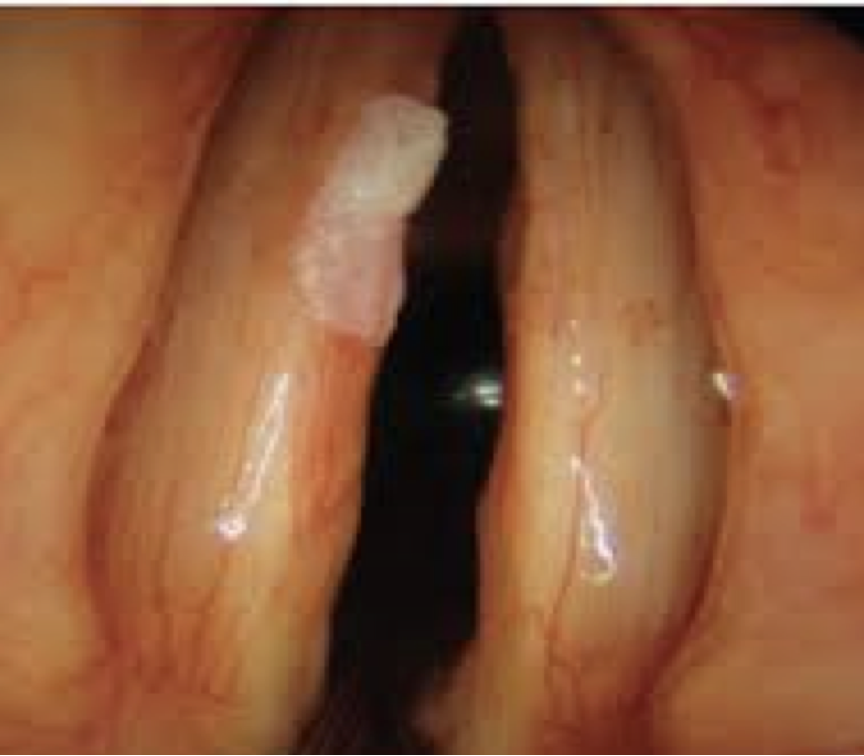
laryngeal cancer
aka carcinoma; it can metastasize
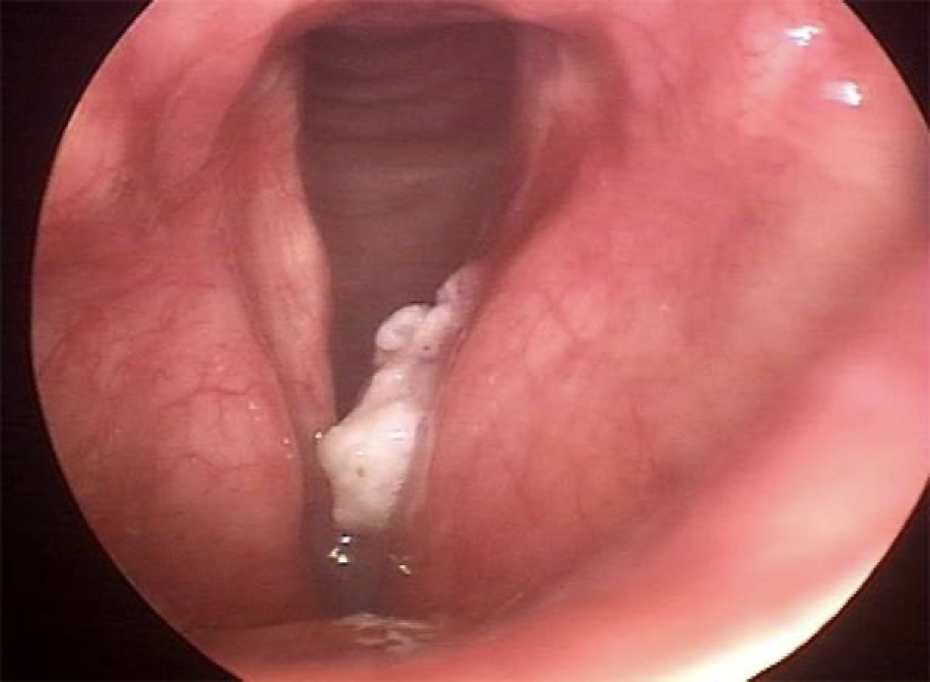
laryngeal papilloma & two ways it can be contracted
benign tumor with wart-like bumps. chronic so it can reoccur
HPV 6 and 11 through skin or STD; congenital through mother’s amniotic fluid or infected area that makes contact during the birth process
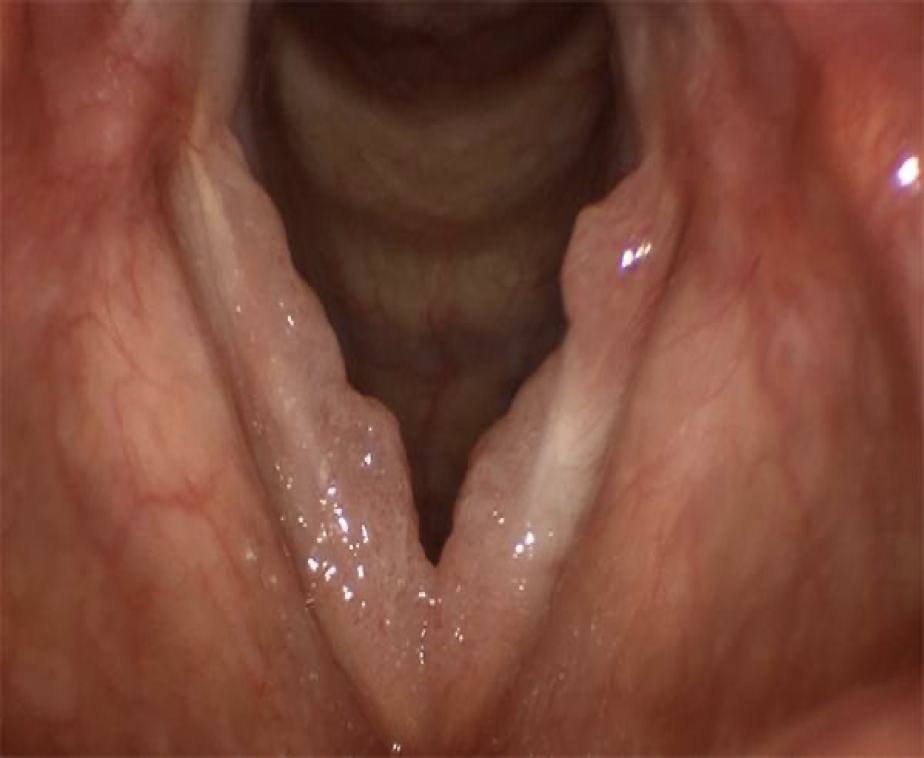
laryngeal web & symptoms
sheet of tissue over the vocal folds, that can grow back if removed
stridor, shortness of breath, difficulty swallowing, weak cry in infants, higher pitch
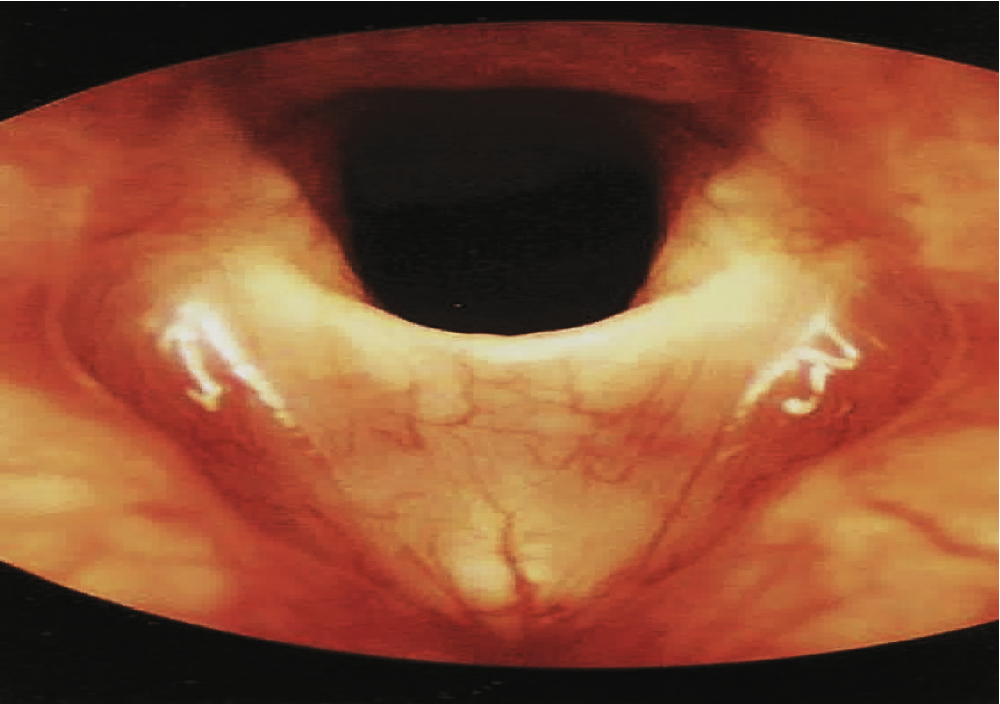
laryngeal ankylosis & 2 typical causes
abnormal stiffening and immobility of the cricoarytenoid jount, that can causes fixed addiction, fixed abduction, dyspnea & odynophagia
typically caused by:
arthritis/joint disease
intubation
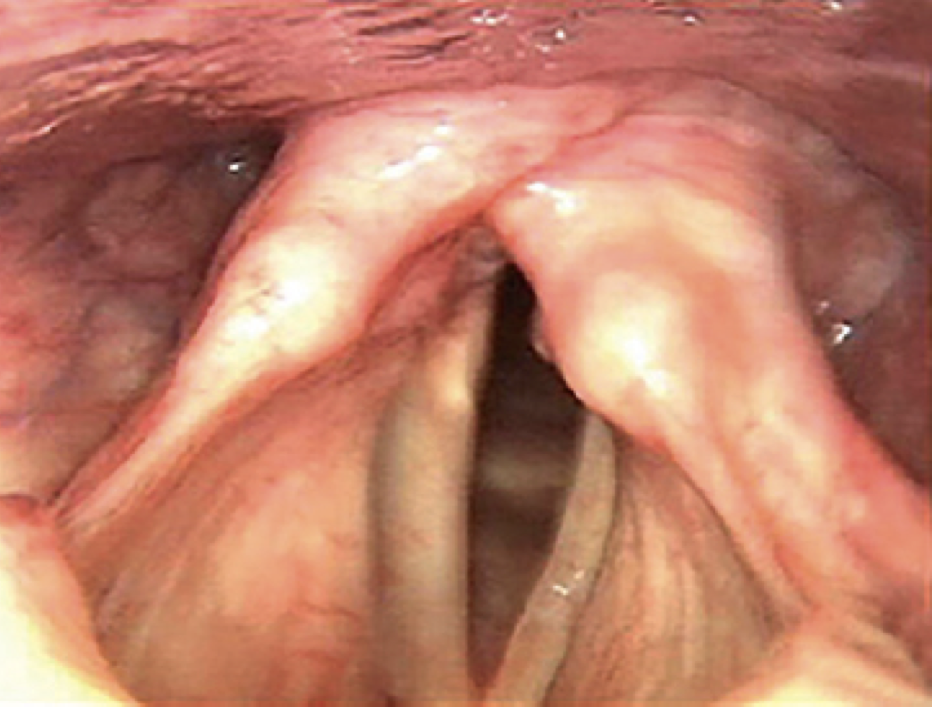
presbyphonia
voice issues that occur due to aging changes & anatomical changes. especially loss of muscle mass, muscle strength, and vocal folds becoming thinner, drier and less pliable (vocal atrophy)
puberphonia — organic & causes
remaining prepubescent voice after puberty
congenital laryngeal anomalies, underdevelopment, changes in hormonal development, debilitating disease during puberty
laryngomalacia
malformation of infraglottal tissue, where tissues fall over airway opening, partially blocking it
must resolve without surgery by 18-20 months
three kinds of organic neurogenic disorders, and what can cause them
essential tremor — caused by neurological disease or condition
spasmodic dysphonia — caused by neurological disease, condition, or acute event
unilateral/bilateral vocal fold paresis/paralysis — caused by neurological disease, condition, or acute event
essential tremor & what causes it
shake in the voice. due to involuntary movements of any muscles related to voicing — intrinsic laryngeal, extrinsic laryngeal, pharyngeal, chest wall, abdomen, diaphragm.
disorder is about movement
spasmodic dysphonia & 3 kinds
aka laryngeal dystonia; spasms or jerking movements due to muscle contractions or abnormal fixed postures. may see tremors in other parts of the body as well as in the voice
abductor
adductor
mixed (both)
the disorder is about movement
vocal cord paresis/paralysis & two types for both
weak or lack of movement of the vocal cords
may see vocal fold bowing, and there’s a unilateral type and a bilateral type. unilateral is more common
two kinds of functional use voice disorders
inappropriate use
psychogenic reasons
two kinds of inappropriate use functional disorders
muscle tension dysphonia
ventricular phonation
two kinds of psychogenic functional disorders
conversion aphonia
puberphonia
muscle tension dysphonia
habitual use of excessive muscle tension or constriction; aka functional dysphonia
ventricular phonation
habitual use of the false or ventricular folds during phonation
conversion aphonia
aphonia due to manifestation of stress, depression, or anxiety due to traumatic experience. aka psychogenic aphonia
this is a disorder of movement
puberphonia — functional & 3 possible causes
result of habitual use of a higher pitch or falsetto register. voice sounds the same as the type due to organic reasons
Possible causes:
resistance to pubertal changes
Difficulty accepting change of voice
voice does not match identity
4 specific voice qualities that often face misperception
glottal fry
upspeak
high pitched/nasal voice
monotone voice
glottal fry — definition and misperceptions
use of a low, gravely, crackly sounding voice
may be perceived as sexy, edgy or with the time; lazy or immature in the business world/a different generation
upspeak — definition and misperceptions
tendency to raise pitch of voice at the end of a sentence regardless of whether or not it’s a question
may be perceived as contemporary, immature, less confident & less intelligent
high pitched or nasal voice — definition and misperceptions
use of a higher pitch or a denasal/hypernasal voice
may be perceived as immature, less authoritative, less “manly”
monotone voice — definition and misperceptions
use of a vocal tone with no change in pitch or inflection
may be perceived as bored/disconnected, lacking enthusiasm, lacking concern
percentage of people affected by voice disorders and percentage that seek treatment
3-9% of the US population; however, less than 1% seek treatment
Populations that experience higher incidence
Female adults
Male children
Elderly adults
Professions who speak for long periods of time
Prevention — what three things to do
provide prevention information to individuals and groups; both those who are at a higher risk of them & those who work with those at risk
refer clients in need of medical or psychological intervention
Remain informed of best practices in vocal health
advocacy — what two things to do
support clients with voice disorders or clients who desire voice modification — give them a voice
remain informed of research in the area of voice — knowledge is power