3.5 Labour Market Demand
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What type of demand is demand for labour?
Derived demand
What does derived demand mean?
The demand for a FofP used to produce another g/s
If demand for goods/services increases then the demand for labour will increase - and vice versa
How would it look on a diagram and why?
Downwards sloping
Because the substitute for labour is capital
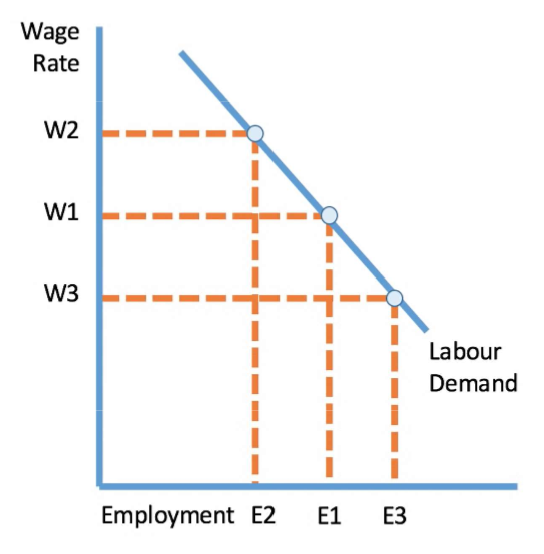
What does the demand for labour show?
Shows how many workers an employer is willing and able to hire at a given wage rate in a give time period
Why is there an inverse relationship between demand for labour and the wage rate?
If wage rate = high - more costly to hire extra employees
If wages = low - labour becomes relatively cheaper than capital
→ A fall in the wage rate might create a substitution effect + lead to an expansion in labour demand
A fall in the wage rate makes labour cheaper relative to capital, leading firms to substitute labour for capital and increase labour demand.
Why would the demand for labour likely fall during a recession?
When the economy is slowing down, many businesses will no longer be looking to hire extra workers as there is decreased output
How many factors impact the demand for labour?
6
How does the price of the good or service impact the demand for labour?
The higher the price of the g/s, the more profitable it is for firm to produce it
→ The more labour they will demand
How does the productivity of labour impact the demand for labour?
The more productive workers are, the more output they can produce per hour, and the more labour firms will demand
→ *Assuming they want to increase output - if firms have a fixed output, they will lay off the more productive workers
How does the cost of labour impact the demand for labour?
The higher the cost of labour, the less profitable it is for firms to hire workers - so they will demand less labour
→ e.g. national insurance contributions, pensions, holiday allowances
How does the cost and availability of substitutes impact the demand for labour?
If there are good substitutes for labour e.g. capital/automation, firms will be less likely to demand labour
How does the level of gov regulation impact the demand for labour?
The more regulations on businesses, the more costly it is for them to operate
→ So the less labour they will demand e.g. health + safety legislation
How does the level of economic activity impact the demand for labour?
The higher the level of economic activity, the more g+s are being produced - so firms will demand more labour