Understanding Management: Processes, Skills, and Approaches
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
Management
The process of working with and through other people to achieve business goals in a changing environment.
Planning
Establishing goals and deciding on methods to achieve them.
Organising
Structuring the organisation to translate plans and goals into action.
Leading
Motivating employees to work towards achieving the business's goals.
Controlling
Evaluating performance and taking corrective action to ensure goals are being achieved.
Interpersonal skills
Those skills needed to work and communicate with other people and to understand their needs.
Communication Skills
The exchange of information between people; the sending and receiving of the messages.
Strategic thinking skills
Allows a manager to see the business as a whole and to take the broad long term view.
Vision
The clear, shared sense of direction that allows people of a business to attain a common goal.
Problem-solving skills
A broad set of activities involved in searching for, identifying and then implementing a course of action to correct an unworkable situation.
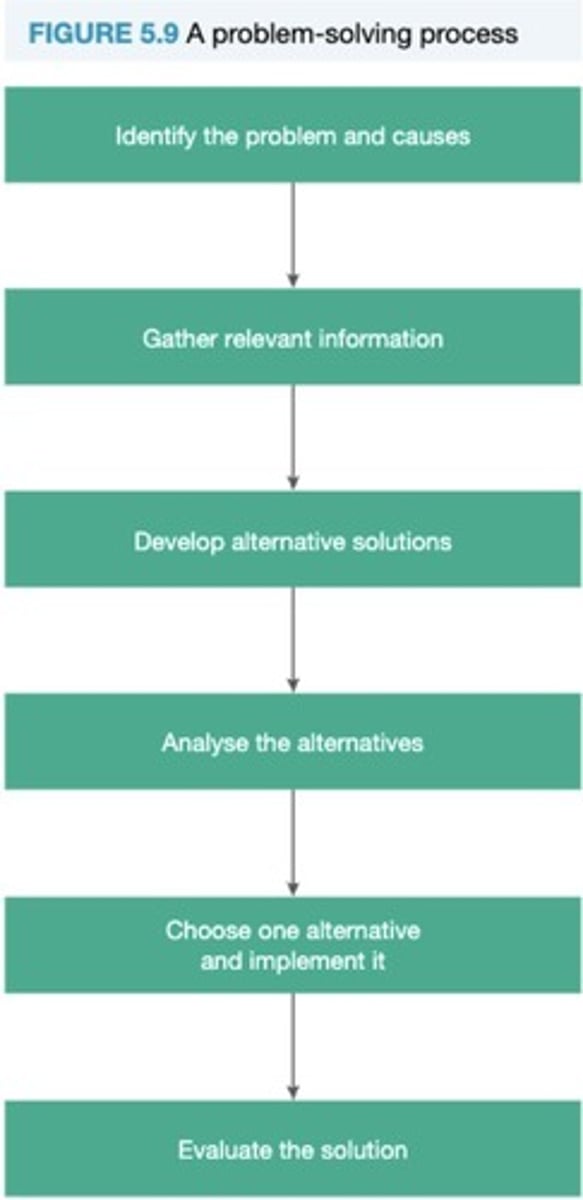
Decision-making skills
The process of identifying the options available and then choosing a specific course of action to solve a problem.
Flexibility
Being responsive to change and able to adjust to changing circumstances.
Proactive management style
Refers to a management style that incorporates dynamic action and forward planning to achieve particular objectives.
Reconciling the conflicting interests of stakeholders
Each stakeholder has a common interest in a business; sometimes the interests of each stakeholder is not always shared leading to conflict.
Achieving business goals
A goal is a desired outcome that a business intends to achieve within a certain time frame.
Importance of Interpersonal Skills
It is through people that managers achieve business objectives.
Importance of Communication Skills
Clear, articulate and concise communication helps build good relationships.
Importance of Strategic Thinking Skills
Involves thinking about a business's direction and what future goals the business wants to achieve.
Importance of Vision
No vision means there can be no sense of cooperation and commitment, which makes achieving business goals impossible.
Importance of Decision-making Skills
Incorrect decisions can be very costly for a business.
Importance of Flexibility and Adaptability Skills
Those who are passive will struggle to succeed in highly competitive, technologically driven and rapidly changing markets.
SMART Goals
Serves as target, benchmark, motivation, commitment; Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound.
Specific
A clear description of what needs to be achieved.
Measurable
Include a metric with a target that indicates success.
Achievable
Set a challenging target, but keeps it realistic.
Relevant
Keep the goals consistent with higher level goals.
Time-bound
Set a date for the goals to be achieved.
Common business goals
Profits, market share, growth, share price, social, environmental.
Profits
Profit = Revenue - Expenses.
Revenue
Total amount of money a company generates from sales.
Maximising profits
Increase revenue by increasing sales, and reduce expenses.
Market Share
The business' share of the total industry sales for a particular product.
Internal Growth
Employing more people, increasing sales, introducing innovative products, purchasing new equipment or establishing more outlets.
External Growth
Achieved by merging with or acquiring (buying) other businesses.
Share Price
A part ownership of a public company.
Shareholders
Owners of public companies.
Social responsibilities
Include community services, sponsoring a wide range of community events - educational, cultural, sporting and welfare.
Social Justice
Adopting a set of policies to ensure that employees or other community members are treated fairly and equally.
Sustainable development
Occurs when needs of the present population are met without endangering the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Labour Productivity
Measures how much an employee can produce in a set period of time.
Staff Involvement
Involving employees in the decision making process and giving them the necessary skills and rewards.
Innovation
Occurs when a new idea is applied to improving an existing product or idea.
Motivation
Refers to the individual, internal process that directs, energises and sustain a person's behaviour.
Mentoring
The process of developing another individual by offering tutoring and coaching, and modelling acceptable behaviour.
Training
Refers to the process of teaching staff how to perform their job more efficiently and effectively by boosting their knowledge and skills.
Classical approach
The Classical Approach is like building a LEGO set with instructions.
Scientific approach
An approach that focuses on improving productivity through time-and-motion studies and standardized tasks.
Ford Motors
In 1913, Henry Ford took Taylor's approach and applied it to the manufacturing of cars.
Assembly line
Invented by Henry Ford, it reduced the hours spent on the assembly of a car from 728 hours to just 1.5 hours.
Bureaucratic Approach
A set of rules and regulations that controls a business.
Features of Bureaucratic Approach
Strict hierarchical structure, clear lines of communication, jobs broken down to simple tasks, specialization, rules and procedure, impersonal evaluation of employee performance.
Advantages of Bureaucratic Approach
Shorter time to make decisions, could lead to improved efficiency, increased productivity, clear chain of command.
Disadvantages of Bureaucratic Approach
Specialization and repetitive tasks could lead to employee boredom, less job satisfaction which could lead to increased turnover, could discourage creativity and innovation, organization becomes inflexible and less able to adapt to changing conditions.
Management hierarchy
The arrangement that provides increasing authority at higher levels of the hierarchy.
Characteristics of Management hierarchy
Rigid lines of communication, numerous levels of management, clearly defined organisational positions, specialisation of labour, long chain of command, centralised control, narrow span of control.
Autocratic leadership style
A style where management makes all the decisions and dictates work methods.
Advantages of Autocratic leadership style
Clear directions and procedures reduce uncertainty, defined roles and expectations make performance monitoring easier, hierarchical structure ensures stability and alignment with management goals, centralized control enables quick decision making and efficiency.
Disadvantages of Autocratic leadership style
No employee input restrains creativity, low job satisfaction due to lack of responsibility, competition for managerial approval can create tension among employees, an 'us and them' mentality may arise.
Behavioural approach
An approach that stresses that people (employees) should be the main focus of the way in which the business is organised.
Design of Business in Behavioural Approach
The business should be designed around the needs of the people, not just rules or machines.
Hawthorne Effect
Belief that meeting people's social needs significantly impacts productivity.
Social Needs
Satisfaction is largely based on social respect rather than economic needs.
Employee Empowerment
Increased ownership of work leading to employees feeling trusted to make decisions.
Extrinsic Motivation
Motivation driven by external factors such as pay and working conditions.
Intrinsic Motivation
Motivation derived from self-worth, added responsibility, and enjoyment.
Participative Leadership Style
Management presents problems, asks for suggestions, and collaborates on decisions.
Two-way Communication
Improves employer-employee relations and reduces disputes.
Decision Making
Can be slower due to diverse opinions, potentially lowering quality.
Contingency Approach
Stresses the need for flexibility and adaptation of management practices to suit changing circumstances.
Interdependence
The mutual dependence that key business functions have on one another.
Management Process
Coordinating key business functions and resources.
Classical Management
Focuses on structure, rules, and control, asserting there is one best way to manage.
Behavioral Management
Focuses on the importance of people, motivation, and relationships.
Contingency Management
Suggests the best management approach depends on the situation, requiring flexibility.
Worker Recognition
Appreciation of workers should lead to increased motivation.
Team Inclusion
Feeling included in a team increases job satisfaction and output.
Management Trust
High levels of trust often result in improved employee performance.
Employee Skills Development
Employees gain more skills and work collaboratively in committed teams.
Management Authority
May weaken if employees gain excessive influence.
Organizational Structure
Importance may be minimized, leading to an informal system.
Employee Involvement
Not all employees want to contribute to decision-making.
Environmental Changes
Acknowledge the impact of changes and enable business flexibility.
Cost of Adaptation
Selecting alternative courses of action can be costly in terms of time and money.
Core goal
Maximise profits
Operations management
Consists of all the activities in which managers engage to produce a good or service.
Manufacturing Business
A manufacturer will transform inputs into goods.
Service Business
A service organisation will transform inputs into services.
Tangibles
Physical products that can be handled and stored before they are sold to the consumer, such as bread, clothing or a car.
Customer involvement in production (Manufacturing)
Little customer involvement in production - the consumer is usually not present when the good is produced.
Production process and consumption (Manufacturing)
Production process and consumption are not linked.
Manufactured goods
Tend to be homogenous or standardised.
Intangible
Services are intangible, which means that they cannot be touched.
Customer involvement in production (Service)
Customer is involved in production - the consumer typically has to be present when the service is produced.
Production process and consumption (Service)
Production process and consumption typically occur at the same time.
Services
Tend to be differentiated or tailored to individual customers.
Examples of services
Include haircut, transport and education.
Three key elements of the production process
Inputs, Processes and Output.

Inputs
The resources used in the transformation (production) process.
Transformed resources
Those inputs that are changed or converted in the operations process.
Transforming resources
Those inputs that carry out the transformation process.