Anatomy of Nervous System
1/136
Earn XP
Description and Tags
from ppt only
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
Three Major Plane Sections p
Coronal, Sagittal, Horizontal/Transverse
coronal
A plane that shows brain structures as seen from the front
sagittal
A plane that shows brain structures as seen from the side
Horizontal/Transverse
A plane that shows brain structures as seen from above
Anatomical Directions
dorsal, ventral, anterior, posterior, superior, inferior, lateral, medial, proximal, distal, ipsilateral, contralateral
dorsal
Toward the back, away from the ventral (stomach) side
Ventral
toward the stomach, away from dorsal (back) side
Protecting and Supplying of the Nervous System
•Meninges •Cerebrospinal Fluid •Blood Supply
Anterior
Toward the front end
Posterior
Toward the rear end
Superior
Above another part
inferior
Below another part
Lateral
Toward the side, away from the midline
Medial
Toward the midline, away from the side.
Proximal
Located close (approx.) to the point of origin or attachment
Distal
Located more distant from the point of origin or attachment
Contralateral
On the opposite side of the body.
Ipsilateral
on the same side of the bod
meninges
Layers of membranes that cover the CNS and PNS
1st Layer: Dura Mater (meninges)
Latin: "Tough Mother" • Composed of leather-like tissue
2nd Layer: Arachnoid Membrane (meninges)
Looks like spider's web in cross section
3rd Layer: Pia Mater (meninges)
latin: "Pious Mother • Transparent membrane sticking closely to the outside of the brain
meningitis Infection
(due to virus or bacteria) in meninges
meningiomas.
Tumors in the meninx's tissues
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Protective fluid around the brain and spinal cord
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
has similar composition as blood plasma
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
floats brain within the skull
subarachnoid space
between arachnoid membrane and pia mater
central canal
a small central channel that runs the length of spinal cord
cerebral ventricles
four large internal chambers of the brain. Ventricles are hollow spaces in the brain
CSF circulates through
subarachnoid space, central canal, cerebral ventricles
choroid plexus
where CSF is produced
networks of capillaries that protrude into the ventricles from the pia mater.
new CSF
made 3 times a day
old CSF
reabsorbed into blood supply at the top of the head
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Cushions the brain.
Prevents the neuron from giving maladaptive response due to pressure (ex: tumor that leads to seizure
Blood supply
flows through carotid arteries (sides of neck) and vertebral arteries (back of the skull).
Hemorrhagic
bleeding
Ischemia
lack of oxygen
brain
receives nutrients through blood supply.
brain
cannot store energy and interruptions of blood supply could lead to damages.
central nervous system
Tissues encased in bone
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and Spinal Cord
central nervous system
• Covered in 3 layers of membrane
central nervous system
Cells do not regenerate (Permanent damage)
central nervous system
With Cerebrospinal Fluid
peripheral nervous system
Tissues not encased in bone
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Covered in 2 layers
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
All nerves exiting the brain and spinal cord - carrying sensory and motor messages to and from other parts of the body
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Cells regenerate (With recovery)
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Without Cerebrospinal Fluid
NERVE
a set of actions in the periphery, either from the CNS to a muscle or gland or from a sensory organ to the CNS.
nucleus (pl. nuclei)
a cluster of neuron cell bodies with shared functions within the CNS
ganglion
a cluster of neuron cell bodies, usually outside the CNS (as in the sympathetic nervous system)
Spinal Cord
within the vertebral column. It extends from medulla to the first lumbar vertebra.
spinal cord
communicates with all the sense organs and muscles except those in the head.
spinal cord
cord is shorter than the vertebral column.
The central canal
runs down in the center of the spinal cord.
White matter
composed of myelinated axons
grey matter
H-shaped, densely packed with cell bodies and dendrites.
dorsal roots
Axons from sensory neurons are found here
The cell bodies are grouped together outside the cord and forms the dorsal root ganglia.
ventral horns
Axons from motor neurons are found here. They are responsible for movement.
ventral horns
The cell bodies are found here
dorsal horns
Most of the synaptic terminals are here
• 8 cervical nerves
serve the area of the head, neck, and arms
• 12 thoracic nerves
serve most of the torso
5 lumbar nerves
serve the lower back and legs
31 segments of spinal cord
8 cervical nerves, 12 thoracic nerves, 5 lumbar nerves, 5 sacral nerves, 1 coccygeal nerve
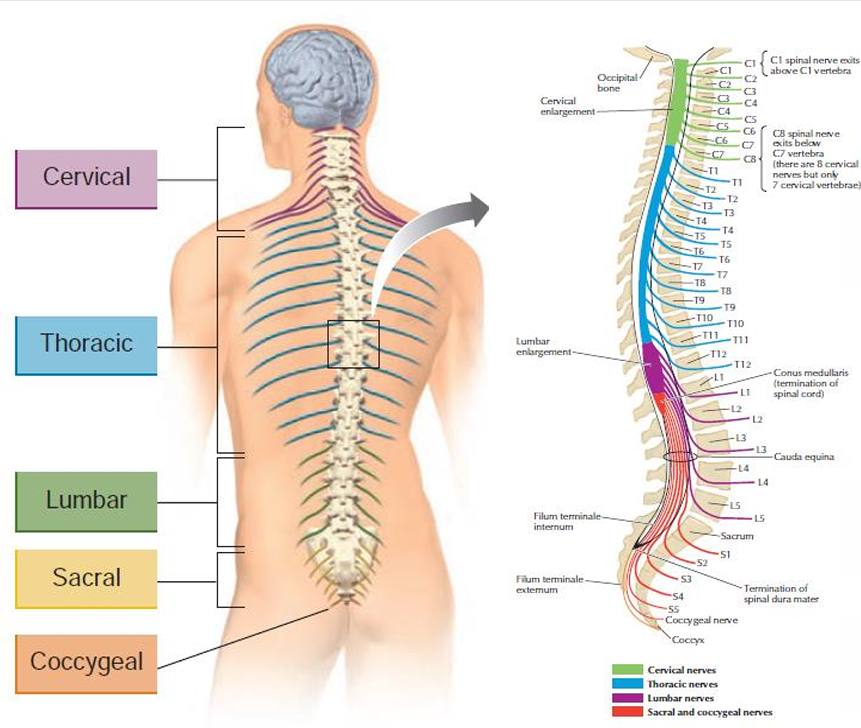
5 sacral nerves
serve the backs of the legs and the genitals
Paraplegic
Lumbar-level damage that leads to loss of sensation and inability to move the lower torso and legs. Arms and upper torso are retained.
Quadriplegic
(quad meaning four – loss of four limbs) – Cervical damage that leads loss of sensation and inability to move the arms, legs, and torso.
sensation and voluntary movement
Damage to the spinal cord results in loss of _ (of both the skin and internal organs) and loss of _in parts of the body served by nerves located below the damaged area.
developing brain
has three swellings which will eventually develop into adult forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain.
encephalon
Within the head”
5 divisions of the adult brain
Telencephalon, Diencephalon, Mesencephalon, Metencephalon, and Myelencephalon
Hindbrain
The posterior (likod) part of the brain, consists of the medulla, the pons, and the cerebellum.
Myelencephalon and Metencephalon
the two division of Hindbrain
Pons and Cerebellum
two major structures of Metencephalon
Myelencephalon or Medulla or Medulla Oblongata
The most posterior division of the brain
Reticular formation
a complex network of about 100 tiny nuclei that runs along the midline of brainstem from medulla up into the midbrain. Plays important role in regulation of sleep and arousal
Reticular formation and cranial nerves
important structure of myencephalon or medulla
cranial nerves
originating in the medulla control vital reflexes such as breathing, heart rate, vomiting, salivation, coughing, and sneezing .
pons
Means “bridge” in Latin.
• Anterior and ventral to the medulla
cochlear nucleus, vestibular nucleus, raphe nuclei, locus coeruleus
important structures of pons
Cochlear nucleus (pons)
receives information about sound
Vestibular nucleus (pons)
receives information about the position and movement of head. Helps in keeping our balance
Raphe nuclei (pons)
regulation of sleep and arousal
Locus Coeruleus (pons)
participates in arousal
Cerebellum
Means “little brain” in Latin.
• Large hindbrain structure with many deep folds
• An important sensorimotor structure coordinating and control of movements, maintaining muscle tone, and regulating balance.
• Damage in here affects skilled movements and speech production.
tectum and tegmentum
two division of midbrain (mesencephalon)
Tectum
Roof /dorsal/top half of the midbrain
• Tectum is the Latin word for “roof.”
- covers the tegmentum
Tegmentum
intermediate level/ventral/bottom half of the midbrain.
• Tegmentum is the Latin word for “covering”.the tegmentum covers several other midbrain structures.
Tectum
composed of two pairs of bumps or swellings called colliculi (little hills)
Inferior colliculi
Posterior pair
• Auditory function. Includes auditory reflex (turning of head on loud noise direction), and localization of sounds in an environment.
Superior colliculi
Anterior pair
• Visual-motor function, specifically visual guided movements -to direct the body’s orientation toward or away from particular visual stimuli. Also includes variety of visual reflex – changing of pupil size in response to light conditio
Periaqueductal Gray, Substantia Nigra, Red Nuclei
significant structures of tegmentum
Red Nuclei
• Located within the reticular formation
• Communicates motor information between spinal cord and the cerebellum
Substantia Nigra
Literally means “black stuff”
• Motor nuclei that is an important component of sensorimotor system
• Degeneration occurs in Parkinson’s disease
Periaqueductal Gray
• Gray matter situated around cerebral aqueduct.
• Has important role in perception of pain specifically mediating the analgesic (pain-reducing) effects of opioid drugs.