MELS500 Test 1
1/159
Earn XP
Description and Tags
i'm cooked bismillah
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
Phases of testing
pre-analytical, analytical testing phase, post-analytical
pre-analytical testing phase
pre-testing, admin tasks
what does the pre-analytical phase consist of?
selecting appropriate test, obtaining and labelling specimen, providing timely transport to lab, registering receipt in lab, processing before testing
what does the analytical testing phase consist of?
testing the sample/running tests
what does the post-analytical testing phase consist of?
reporting of case to patients via clinicians
Types of fume hood
ducted, non-ducted, downflow/laminar, special
Ducted fume hood
wall or roof-controlled ducting to facilitate safe work environment
Non-ducted fume hood
filtration of air using activated charcoal
Downflow fume hood
working with fumes heavier than air
Laminar fume hood
has horizontal and vertical air flow for working with powders
Special fume hood
PCR work, genomics, molecular biology work, weight potent compounts and chemicals, radiation, highly corrosive material
Biohazard hood/cabinet
Enclosed, ventilated laboratory workspace for materials contaminated with pathogens requiring a defined biosafety level
Types of protection
Product protection, environmental protection, personnel protection
HEPA filter
protects environment by filtering air before it is exhausted
Class I biohazard hood
provides personnel and environmental protection, suitable for low to moderate risk, has hepa filter
Class II biohazard hood
provides personnel, environment and product protection, has 3 main features
Main features of class II biohazard hood
Front opening with maintained inward airflow, hepa filtered unidirectional airflow inside work area, hepa filtered exhaust air to the room
Class III biohazard hood
work with microbiological agents assigned to biosafety level 4, maximum protection ot user and environment
Class III applications
diseases that are emerging or near eradication, weighing and diluting chemical carcinogens
spectrometer use
measure wavelengths of light that has interacted with a sample
autoclaves
sterilisation at elevated temperature and pressure in relation to ambient
oven
drying, material testing, curing, heated storage
incubator
temperature-controlled environment to support growth of microbiological cultures
water baths
incubate samples at a constant temperature over a long period of time, heating flammable chemicals
light microscope
uses visible light and a system of lenses to generate magnified images
fluorescence filters
excitation filter, emission filter, dichroic beamsplitter
stereoscopic/dissecting microscope
low magnification using light reflected from surface of object
centrifuge
separate fluids/gases/liquids based on density for cell collection, organelle/virus/protein/nucleic acid purification
internal maintenance
housekeeping, validation, QC
external maintenance
service technician, service contracts
test tube

beaker

conical flask

volumetric flask

Chemical Hazard — Flammable

Chemical Hazard — Compressed Gas

Chemical Hazard — Corrosive

Chemical Hazard — Oxidising

Chemical Hazard — Harmful
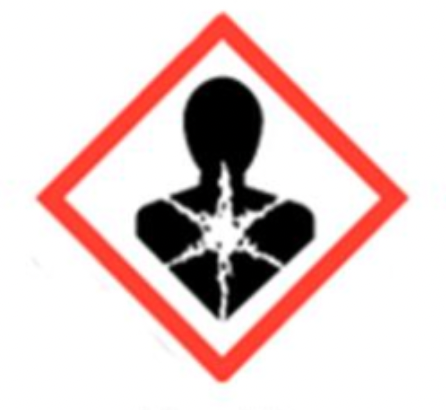

Chemical Hazard — Harmful
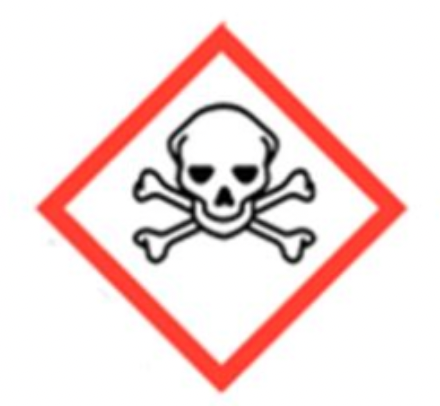

Chemical Hazard — Toxic
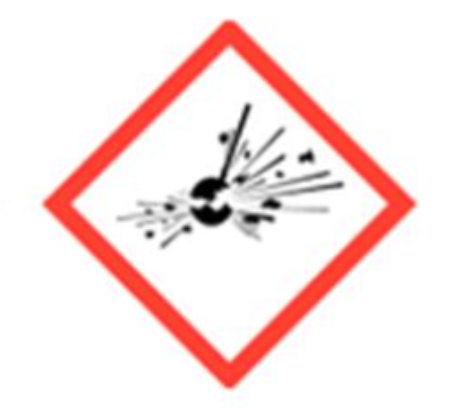

Chemical Hazard — Explosive
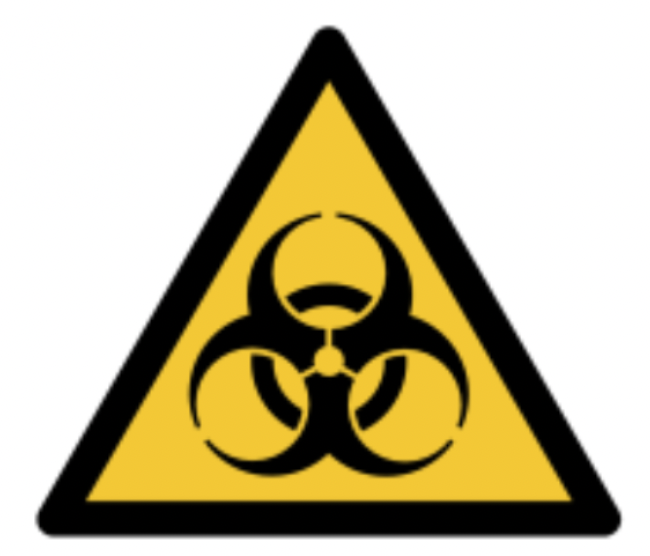

Biological Hazard
Formula for volumes for reagent preparation
C1V1=C2V2
Define Molarity
Number of moles of solute per one litre of solution; A measure of concentration
Define Normality
Number of equivalents of solute per litre of solution
Molarity of needed solution (M)
Mass of Solute (g) x 1/Molar Mass (g/mol) x 1/Final Volume of Solution (L)
Mass of Solute (g)
Molarity (M) x Final Volume of Solution (L) x Molar Mass (g/mol)
Final Volume of Solution (L)
Mass of Solute (g) x 1/Molar Mass (g/mol) x 1/Molarity (M)
Saturated Solution
Solution containing maximum amount of a particular solute that will dissolve at that temp
Supersaturated Solution
Solution containing more solute than equilibrium conditions allow
Solute
Substance which is dissolved or has gone into solution; typically a solid
Solution
Uniform homogenous mixture of two or more substances; Individual substance may be present in varying amounts
Solvent
Substance which does the dissolving; typically liquid
Standard solution
Very precise solution used in quantitative analysis; 3-4 s.f.
Lab Math
Using calculations to analyse lab results; Any math skill or technique used in laboratory science
Why do we need lab math?
To understand principles of lab tech and experiments, calculate correct amounts of reagents used in sample testing, analyse results and troubleshoot problems
When do we use lab math?
Dilutions of samples or reagents, calculating concentrations, unit conversions, calculating volumes for reagent preparation, calculating analyte amounts or rates, quality control and SD, specimen volume calculations
How much water will you add to 20 mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid to make a 20% (v/v) HCl solution?
80mL water
How much sodium chloride (NaCl) in grams is needed to make up 5% (w/v) sodium chloride solution in 100 mL of distilled water?
5g NaCl
True or false? Always add water to acid, and not vice versa.
False
What does pH stand for?
Potential of hydrogen
Acid pH range
1 to just under 7
Base pH range
7 to 14; over 7
Exponential component use in laboratory settings?
To model phenomena exhibiting growth or decay at a rate proportional to their current value; e.g. bacteria growth
hecto
10²
kilo
10³
mega
106
giga
109
tera
1012
peta
1015
deca
101
deci
10-1
centi
10-2
milli
10-3
micro
10-6
nano
10-9
pico
10-12
femto
10-15
Histology specimen
Body tissues
Microbiology specimen
Urine, faeces, bodily fluids
Haematology specimen
Blood
Transfusion science specimen
Blood
Immunology specimen
Blood, bodily fluids
Clinical chemistry specimen
Blood, bodily fluids
Specimen labelling
patient name, DOB, NHI#, date and time of collection, specimen type, test requested, clinical history and infectious status if known
Transport systems
lampson tubes, hand delivery, posting, sea, air, road
Specimen collection consideration
Aseptic precautions, anatomic sites/locations, timing, lab request form, transport media, correct specimen container, avoid contamination
Specimen criteria for rejection
Labelling errors, unsatisfactory specimens, insufficient quality, inappropriate container, contamination suspected, inappropriate transport or storage
Specimens must be…
good quality (adequate), sealed tightly and securely, not externally contaminated
Blood serum
liquid that remains after blood has clotted
Blood plasma
liquid that remains when clotting is prevented with addition of anticoagulant
Light blue top — Sodium citrate
coagulation tests
Red top — serum
therapeutic drug monitoring
Gold top — SST II
LFTs, iron, hormones
green top — heparin
lactate, ammonia, plasma K
Lavender top — EDTA
CBC, CD4
Pearlescent top — PPT
use as discard
Pink top — cross match
transfusion medicine
Grey top — fluoride oxalate
glucose, glucose tolerance