Micro210 Biochemical Test
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What 3 sugars are present on TSI?
Glucose, Sucrose, Lactose
What does 6.5% NaCl test for? What does it differentiate?Appearance
If organism can grow in high salt concentration
Differentiates Enterococcus sp. from non-Enterococcus sp. and other NH streptococci
Cloudy = Growth
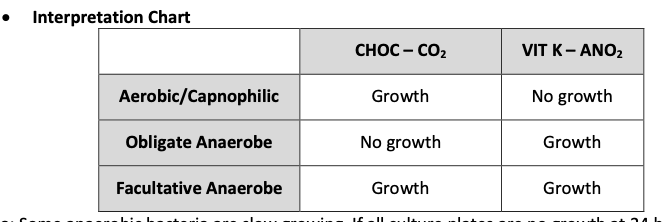
Purpose of Aerotolerance testing? What media is used and hot to interpret?
To determine is suspect colony is aerobe/capnophile, an obligate anaerobe or facultative

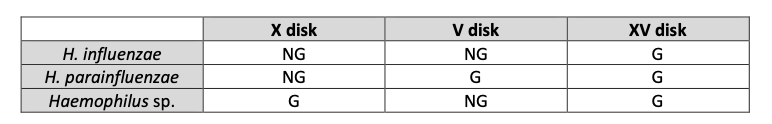
Purpose of KVC disks?
To help in identification of anaerobe Gram-negative bacteria
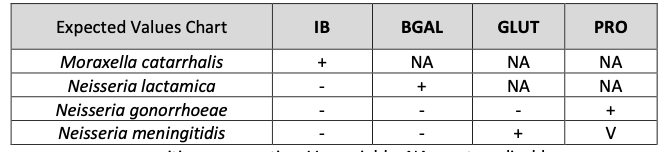
Expected Results in Bacticard
Purpose and Principle of Bile Esculin
if organism can grow in bile salts and hydrolize esculin to esculetin which reacts with ferric chloride to produce black brown precipitate
Differentiate Enterococcus sp. from other organism
Slant agar

Principle and Purpose of Bile solubility
Streptococcus pneumoniae has a natural autolytic process (lyse in presence of O2), bile salts speed up autolytic process.
Differentiates Streptococcus pneumoniae from other AH Strep
Principle and Purpose of BA with S. aureus streak?
Staphylococcus aureus lyse RBC to release X+V factors and releases its own V factor
If organism grows around BH zone (satellism) then organism depends on X+V factors to grow (Haemophillus sp.)
Principle and Purpose of Butyrate Esteras
If Butyrate esterase is present it will release the indoxyl butyrate to produce blue-green colour
Aids in identification of Moraxella catarrhalis (only perform on oxidase pos, GNC)

Principle and Purpose of CAMP test
Group B Strep produces CAMP factor and when combined with BH reaction of S. aureus it creates an arrow head zone of hemolysis
Confirmatory of Streptococcus agalactiae

Principle and Purpose of Catalase (What enzyme can cause false positive)
If bacteria posses catalase it converts hydrogen peroxide into water (bubbles)
Differentiates Micrococcus and Staphylococcus from Streptococcus

Principle and Purpose of Cefinase (Nitrocefin)
If beta-lactamase is present and can break beta lactam ring, a red colour will be visible indicating resistance to beta lactam drugs (penicillins or cephalosporin)
Determines presence of beta-lactamase in Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Haemophilus influenzae

Principle and Purpose of Citrate Utilization
If organism can use sodium citrate (carbon) and ammonium salt (nitrogen) for energy. If so breakdown of ammonium salt creates alkaline pH changing bromthymol blule indicator to green-blue
Differentiates members of Enterobacterales

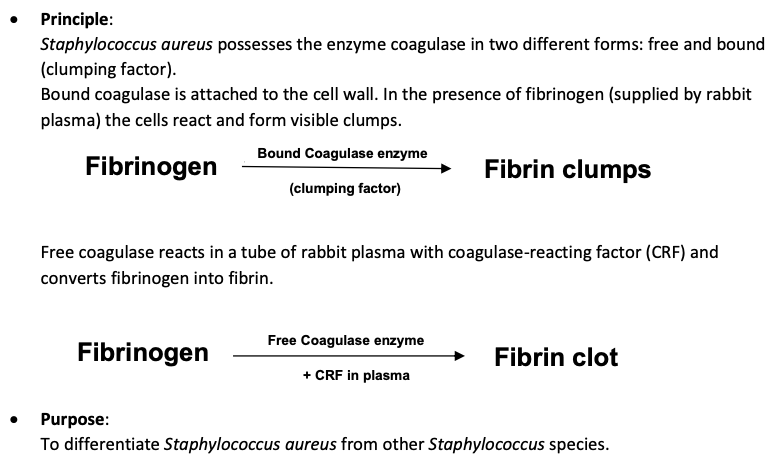
Principle and Purpose of Coagulase Test (What can cause false negative?)
The S. aureus enzyme coagulase exist free and bound form(clumping factor).

Principle and Purpose of Decarboxylase Test (Lysine or Ornithine)
If organism posses decarboxylase enzyme in anaerobic-acidic environment (fermentation of glucose) it removes a carboxyl group from an amino acid creating alkaline end product.
ph Indicator is bromcresol purple, which turn yellow in acid (fermentation of glucose), and back to purple in alkaline (if decarboxylase is present)
A control is present without amino acid
Differentiate Enterobacterales

Principle and Purpose of DNase
If organism has deoxyribonuclease (DNase) it hydrolizes DNA which unbind to methyl green resulting in clear halo
Positive for Moraxella catarrhalis, Serratia marcescens, Staphylococcus aureus

Principle and Purpose of Germ Tube
Candida albicans incubated in rabbit plasma or fetal calf serum it will produce germ tubes
Differentiates Candida albicans from other Candida
Principle and Purpose of Gram Stain
Gram Positive have thick peptidoglycan and teichoic/lipoteichoic acids
Gram Negative have thinner layer
Principle and Purpose of Indole Production
If bacteria posses tryptophanase they hyrolyze tryptophan to indole. If Kovacs reagent is added observe for pink color change
Differentiates Enterobacterales

Principle and Purpose of Spot Indole
If bacteria can grow in medium with trytophan (BA) then they posses tryptophanase. Indole is detected in pre-soaked filter paper if blue-green color is produced

Kirby-Bauer Susceptibility
Media?0.5 McFarland in CFU? CLSI modifacation?
MH
1.5×10^8 CFU
MH with 5% sheeps blood
Incubated in CO2
Principle and Purpose of Motility
If bacteria has flagella
differentiates Enterobacterales

Expected results of MIL

Principle and Purpose of Nagler Reaction (Lectinase)
Clostridium perfringens produces lectinase which breaks down lecithin (in egg yolk)
Egg yolk agar has one side streaked with antitoxin then suspect organism is streaked across
If precipitate on antitoxin free side then organism produced lectinase
If nothing on antitoxin side then antitoxin neutralized the lictinase
This aids in identification of Clostridium perfringes
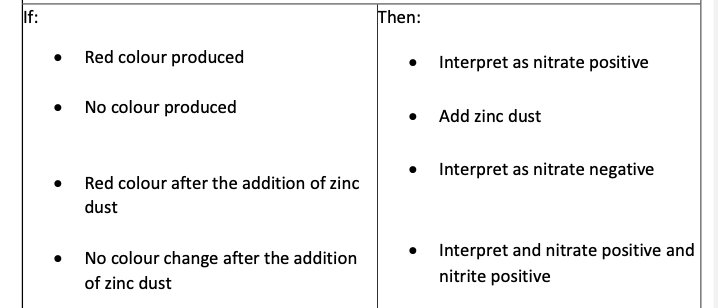
Principle and Purpose of Nitrate Reduction Test (What alternative tube can be used to detect gas production.
All Enterobacterales can reduce nitrates to nitrites but some can further reduce nitrite to nitrogenous compounds, some do not utilize nitrates
If organism has nitrate reductase it can reduce nitrate to nitrite
Durham tube (traps gas)
Principle and Purpose of Novobiocin
Staphylococcus saprophyticus is resistant to Novobiocin <16mm
Principle and Purpose of ONPG
LF have B-galactosidase + permease, LLF only have B-galactosidase
If they have B-galactosidase ONPG will be hydrolyzed and produce yellow colour
This test differentiate LF and LLF from NLF

Principle and Purpose of Optochin? What other screen can be performed at the same time?
This differentiate Streptococcus pnuemoniae from other AH Strep because S. pneumoniae is susceptible to Optochin >=14
An oxacillin screen can be performed to determine susceptibility of organism to penicilin >=20mm
Principle and Purpose of Oxidase Test
Organism with cytochrome oxidase will oxidize Kovacs reagent into indophenol to creat a dark purple color
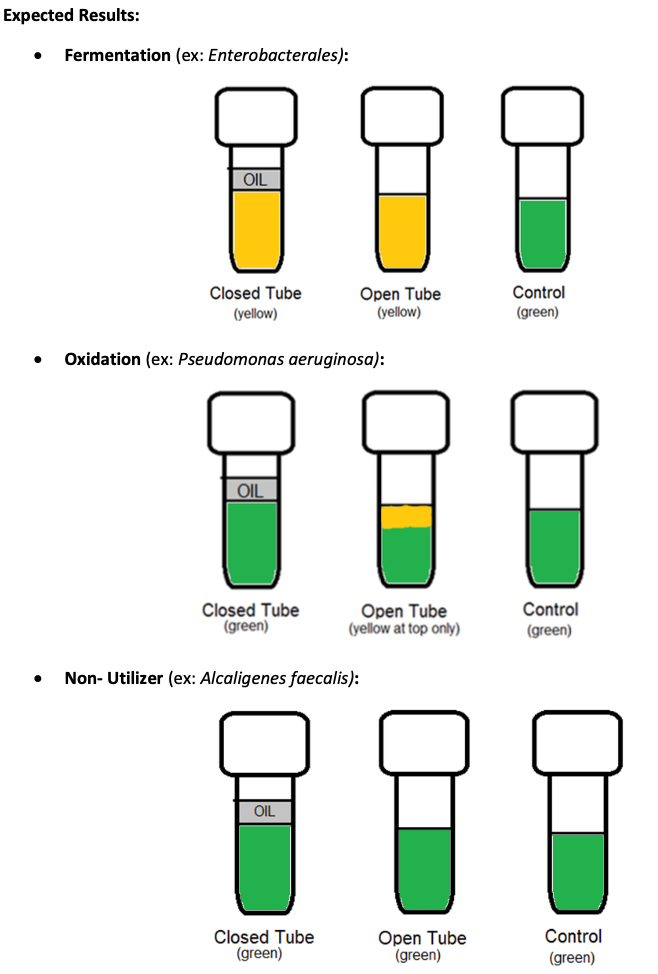
Principle and Purpose of Oxidation/Fermentation (O/F) Medium
Differentiates organism based on their ability to oxidize, ferment, or not utilize specific carbohydrates
Principle and Purpose of PathoDX
Identifies BH Streptococci based on which reagents agglutinates with the antigens
Principle and Purpose of Porphyrin Test
Haemophilus parainfluenzae produces porphobilinogen synthase making it capable of making its own X Factor
Differentiates Haemophilus influenzae and Haemophilus parainfluenzae

Principle and Purpose of PYR
Detects enzyme PYRase which is present on Enterococcus and Streptococcus pyogenes

Rhamnose Broth
Aids in identification of yersinia enterocolitica
Yersinia enterocolitica is incapable of fermenting rhamnose while most Enterobacterales can

Principle and Purpose of Reverse CAMP
Aids in identification of Clostridium perfringens
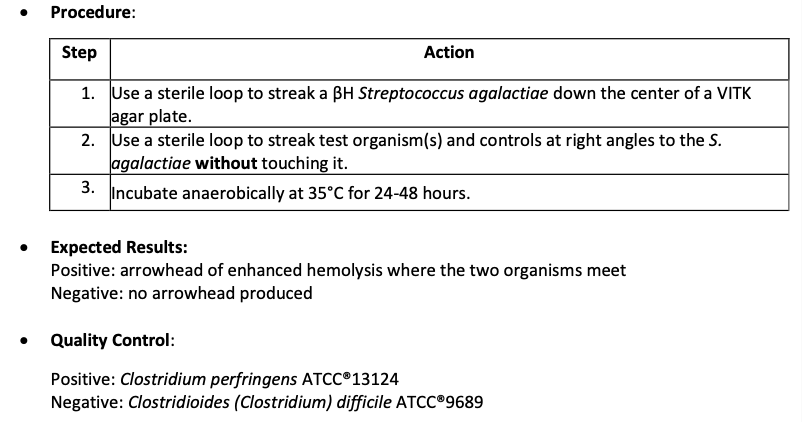
Principle and Purpose of Staphaurex
Latex particle with fibrinogen and IgG can react with clumping factor and Protein A of S. aureus to cause clumping

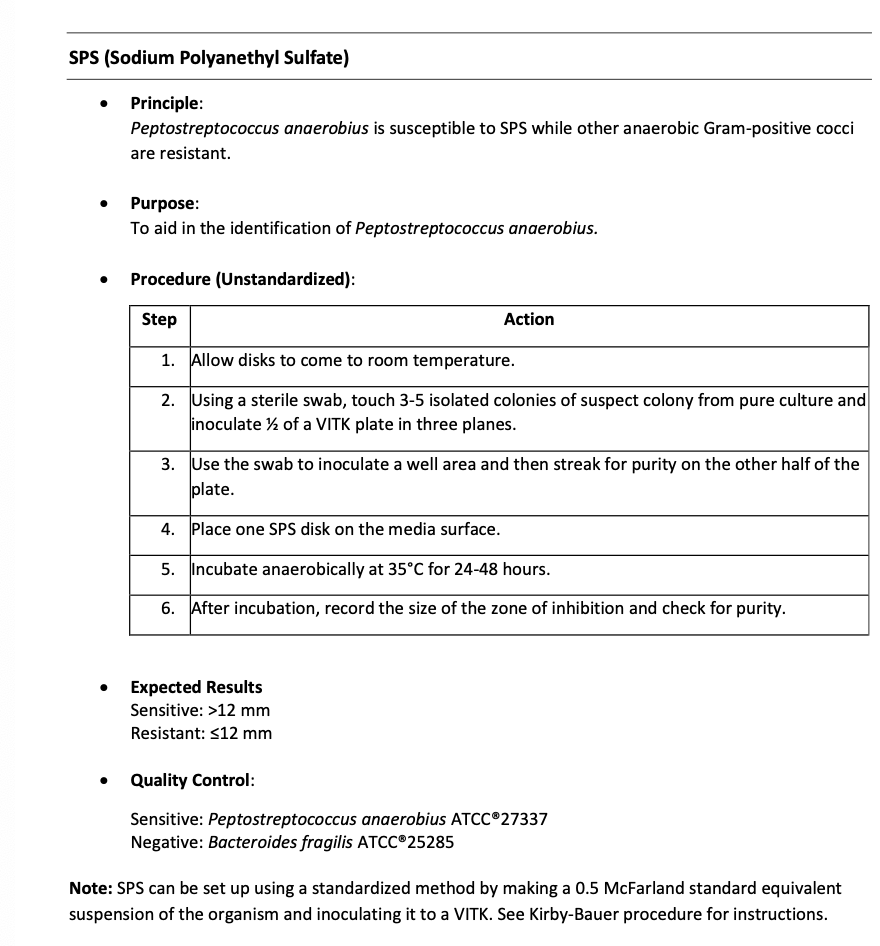
Principle and Purpose of SPS
Principle and Purpose of TSI
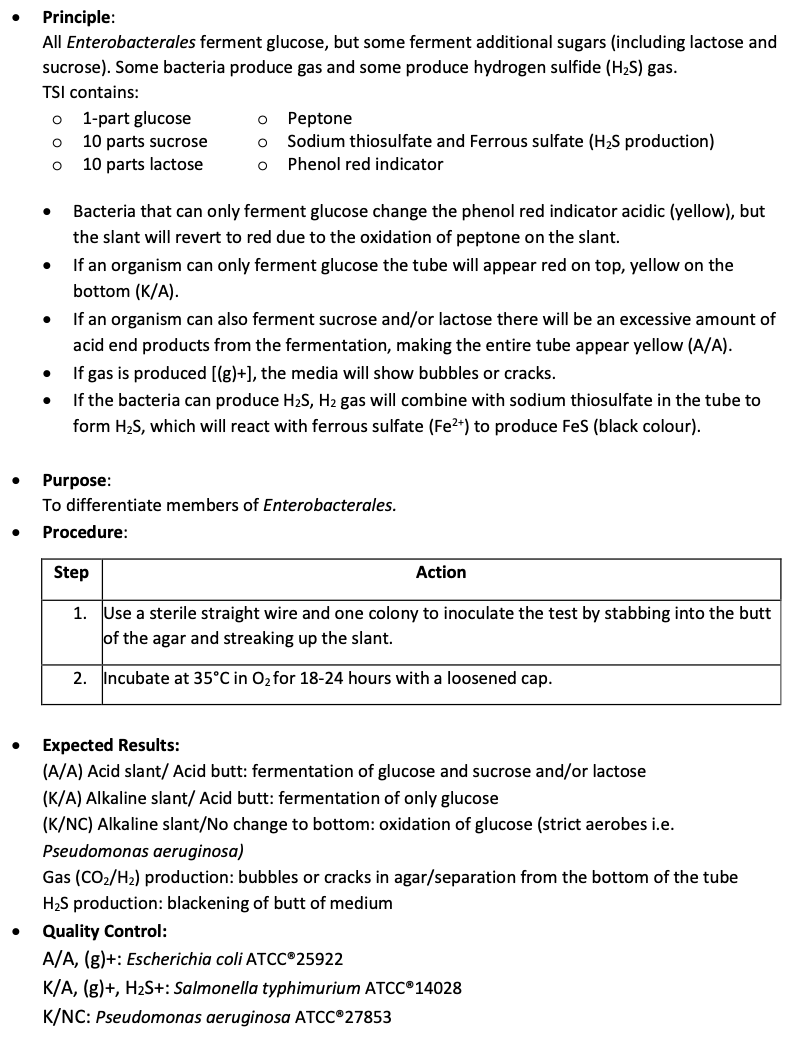
K = red
Growth Result of Haemophilus sp. on X,V, XV, Disk Test