Module #6-Mendalian genetics, genes & chromosomes. Genes & alleles2.
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
P generation
the parental generation, true-breeding parents
multiple allele
The human ABO blood group.
Trait
A characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes.
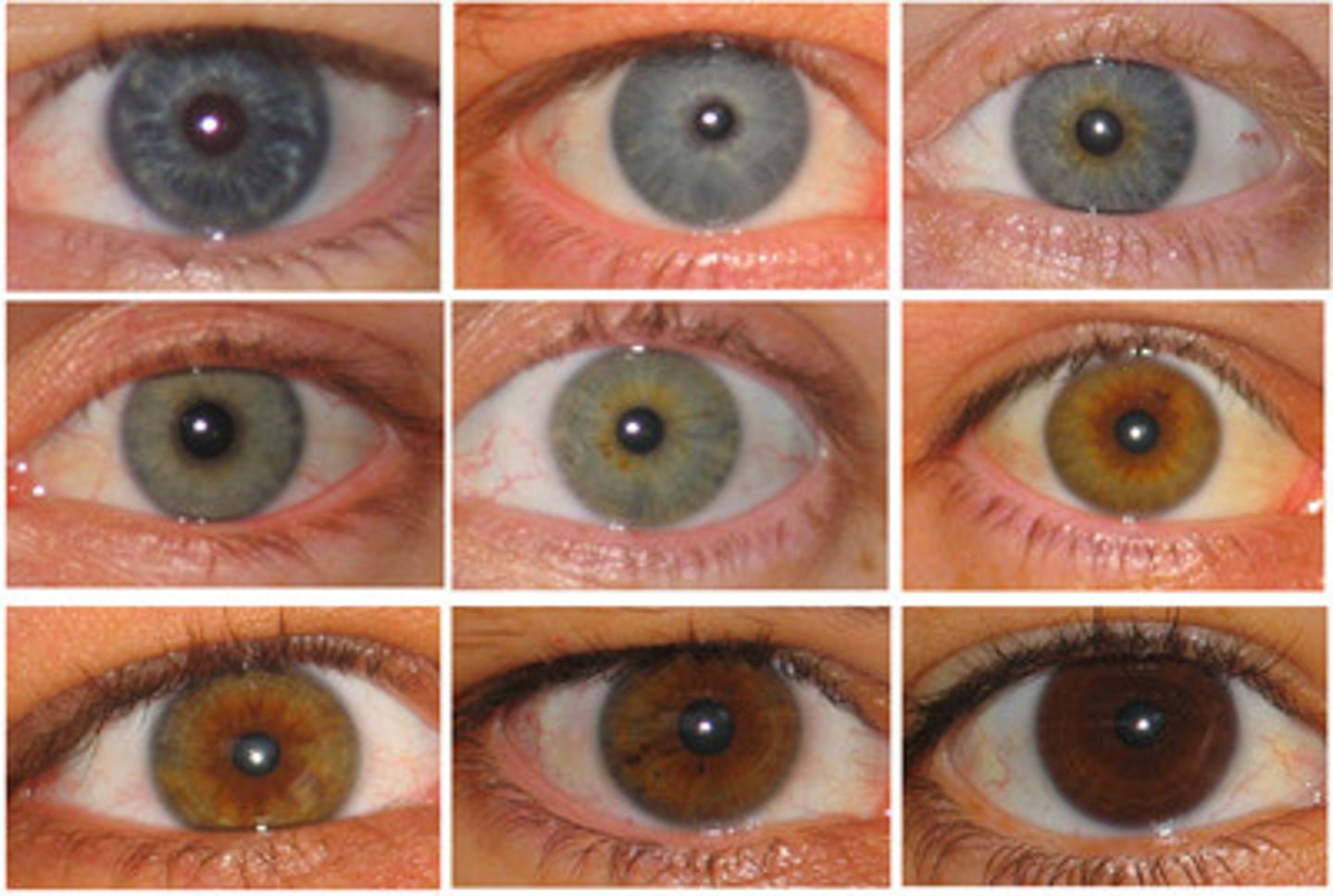
For instance: Eye color
gametes contain
one allele for every gene
Mendel studied
pea plants and experimented with clearly contrasting phenotypes.
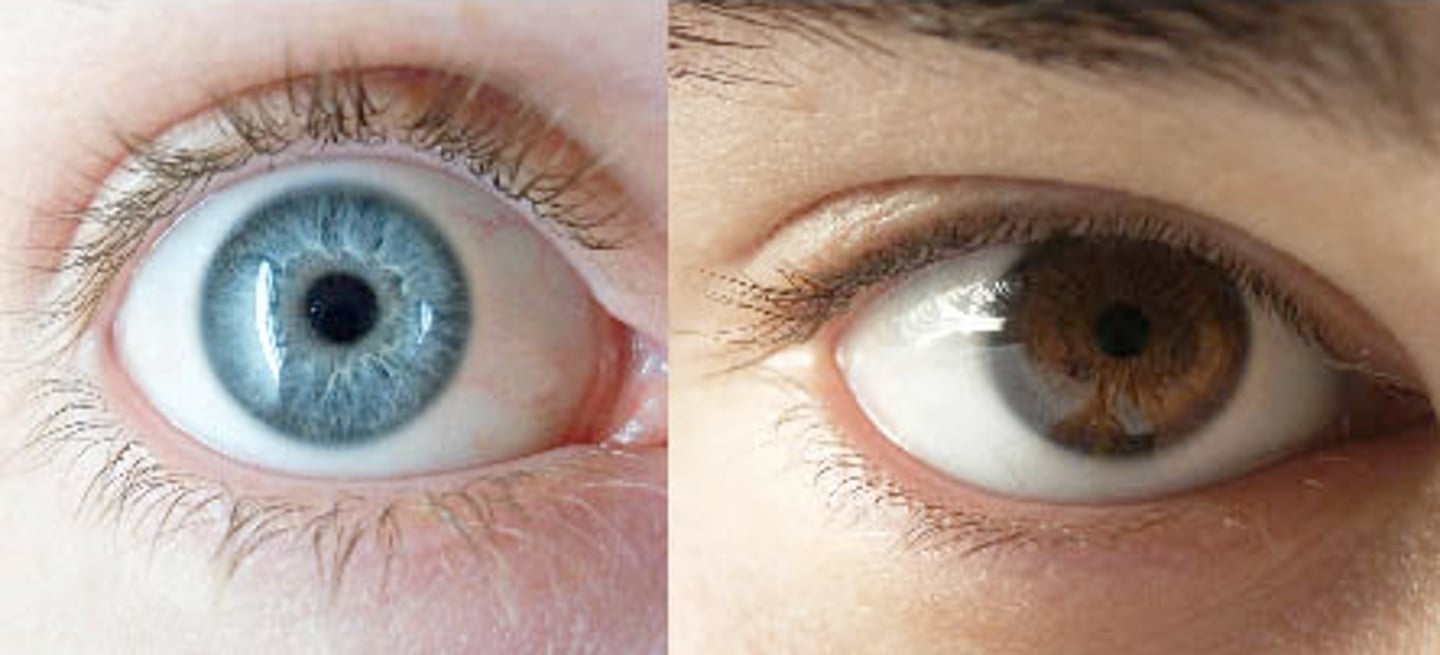
Phenotype
physical appearance.
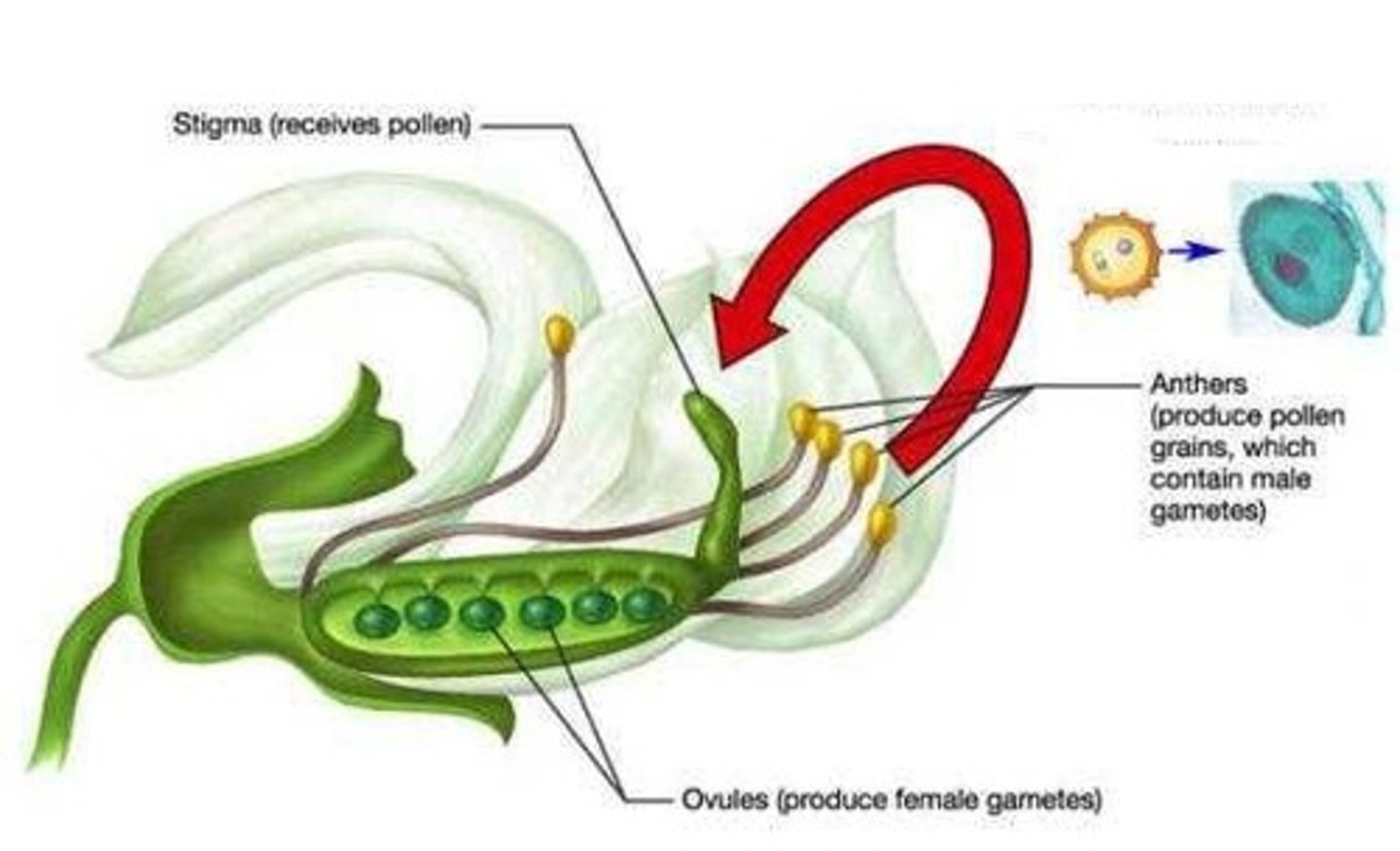
self-pollinate
male and female gametes fertilize within the same flower
Genotype
genetic structure; "letters"
F1 generation
offspring of the P generation.
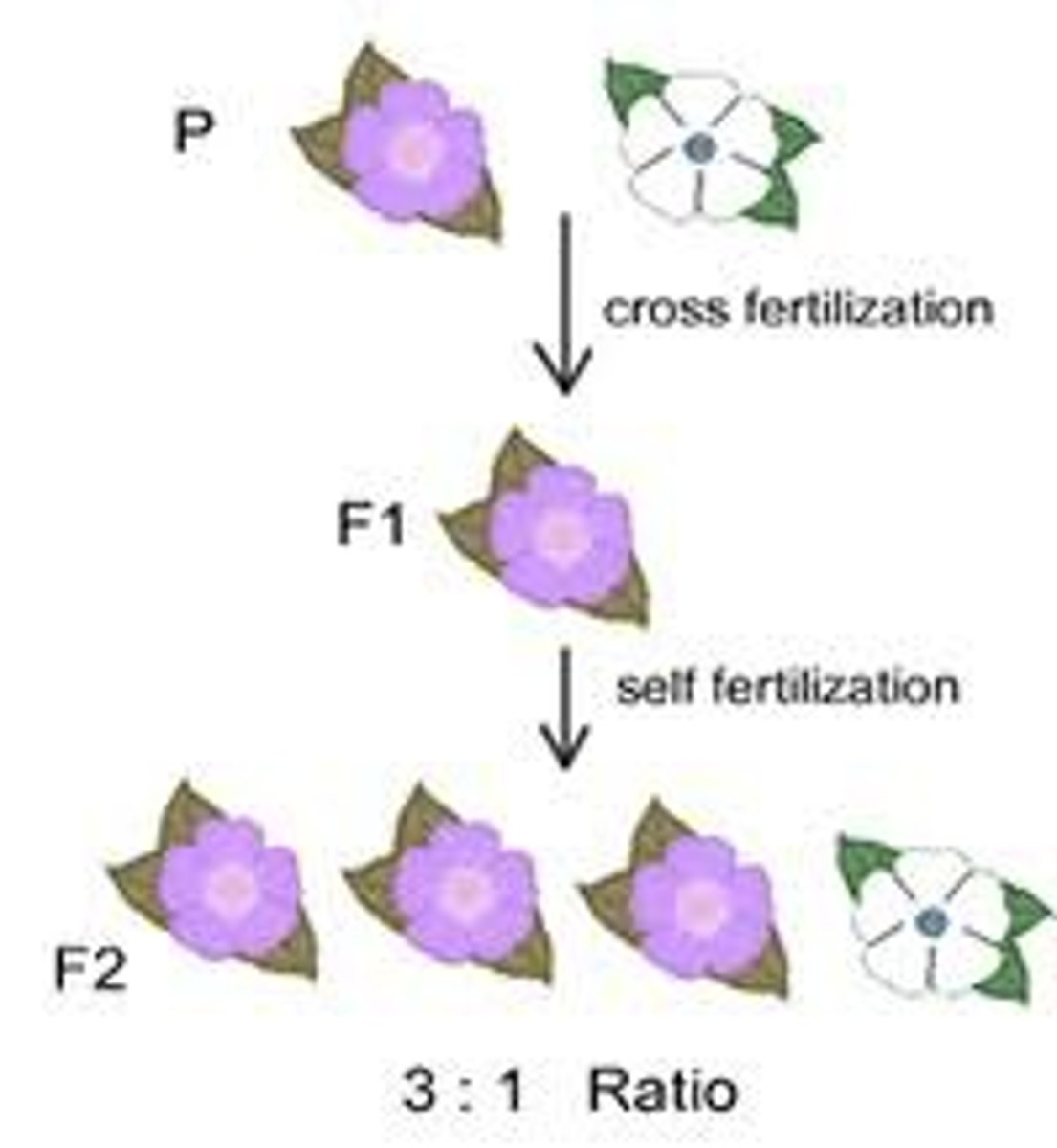
F2 generation
the second generation of offspring, obtained from an experimental cross between F1 individuals or by self-pollination of F1 individuals
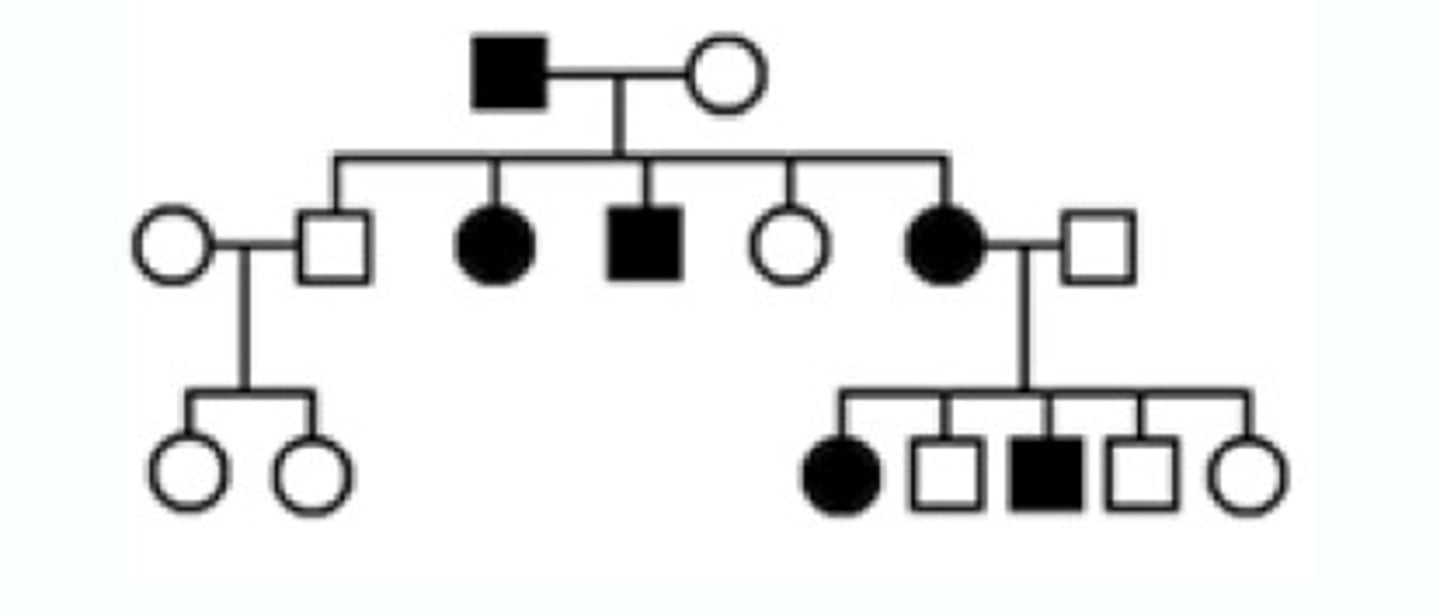
Pedigree
A diagram that shows the occurrence of a genetic trait in several generations of a family.
Alleles
Alternative forms of a gene.
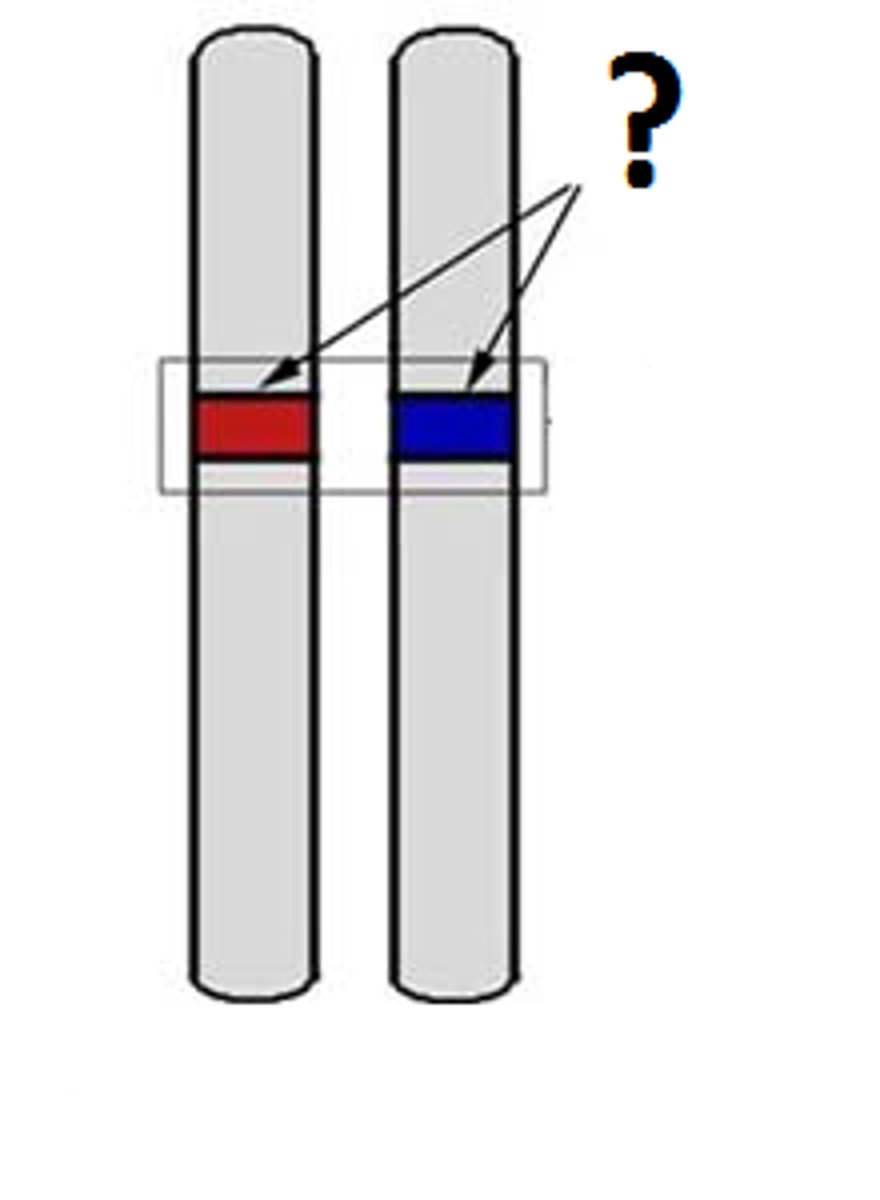
Dominent allele/trait
An allele whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present.
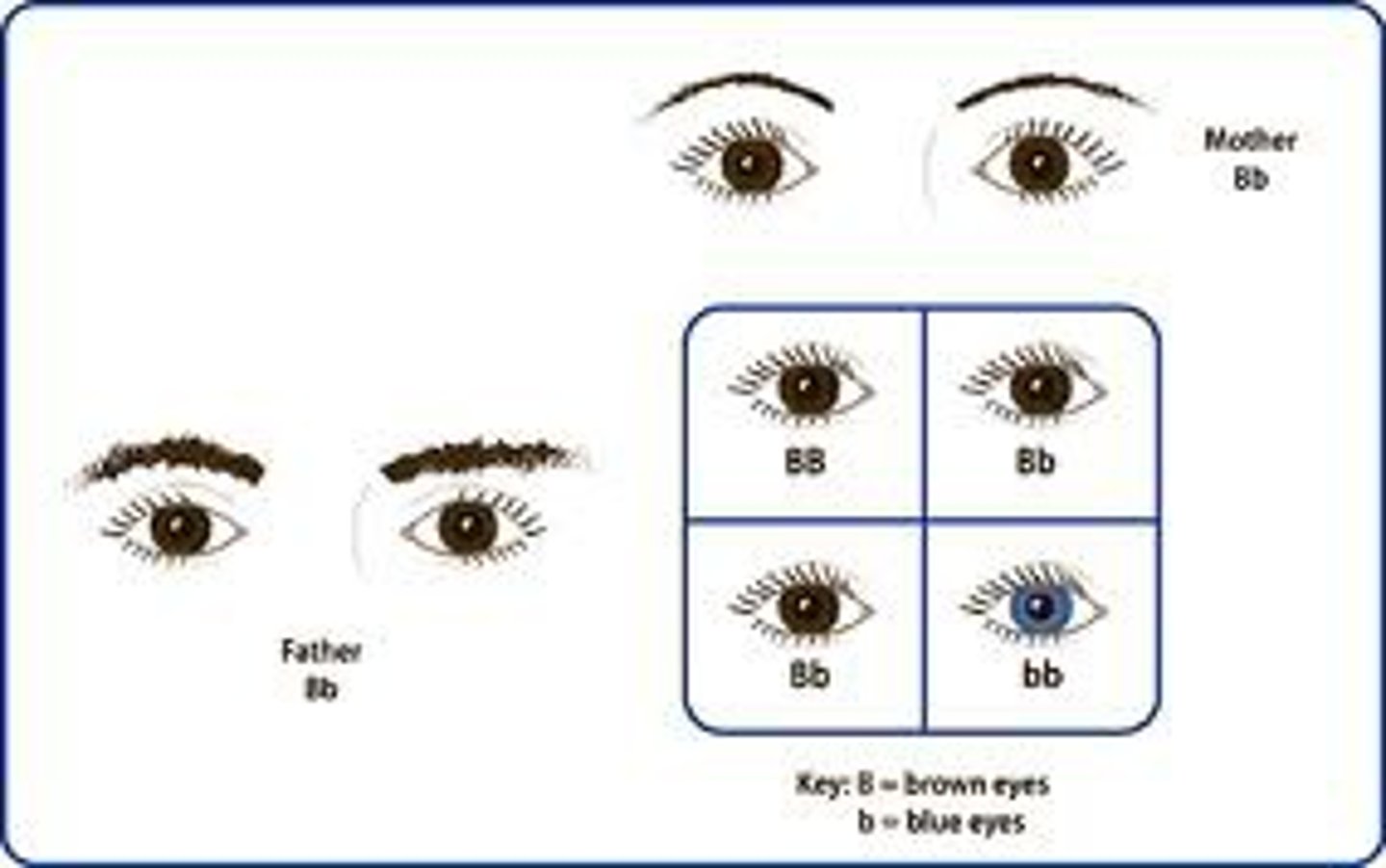
Recessive allele/trait
An allele that is masked when a dominant allele is present
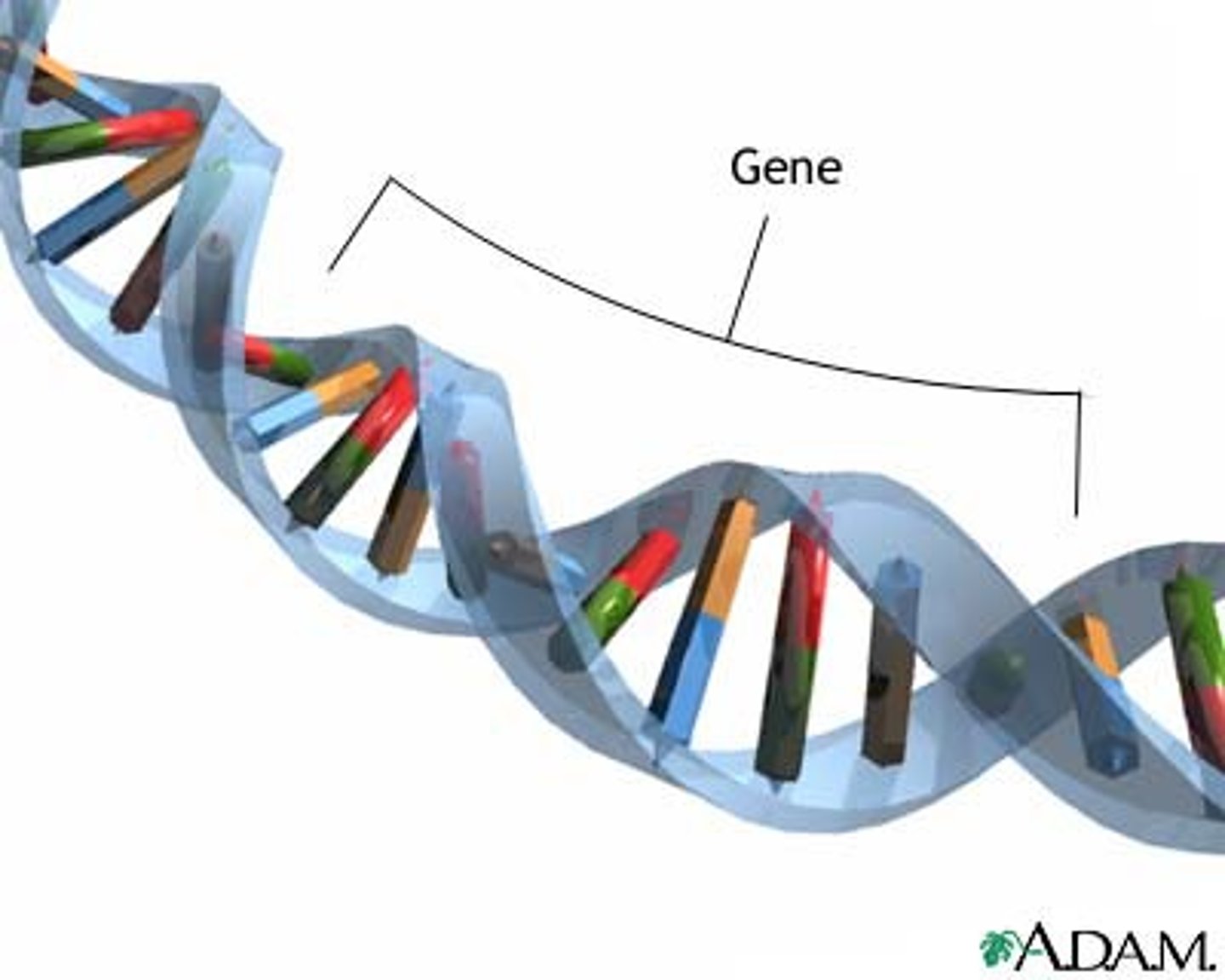
Gene
a DNA sequence that cotains the information to make an RNA or ptrotein product with a specific function.
Each gene is a segment of DNA molecule.
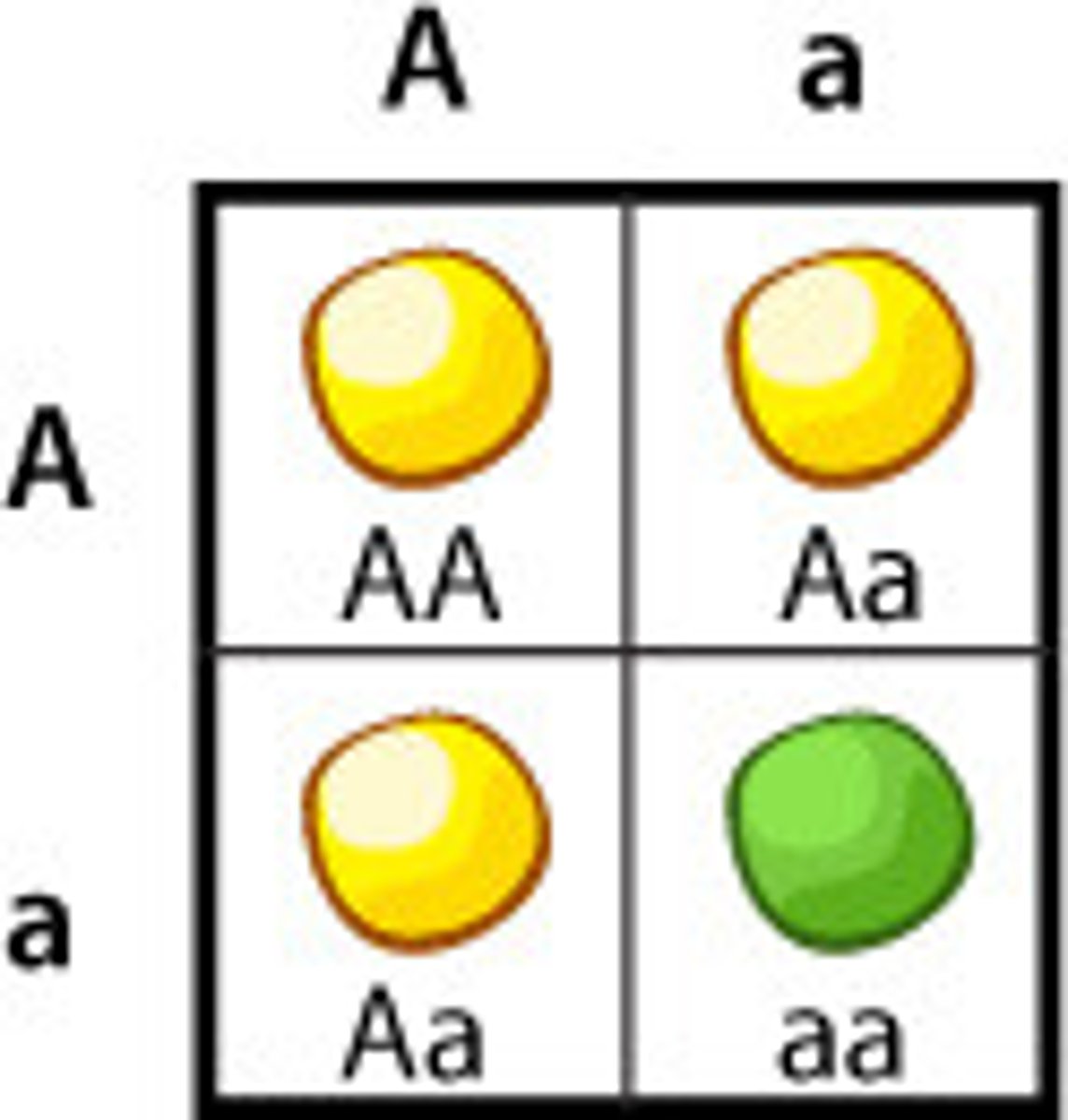
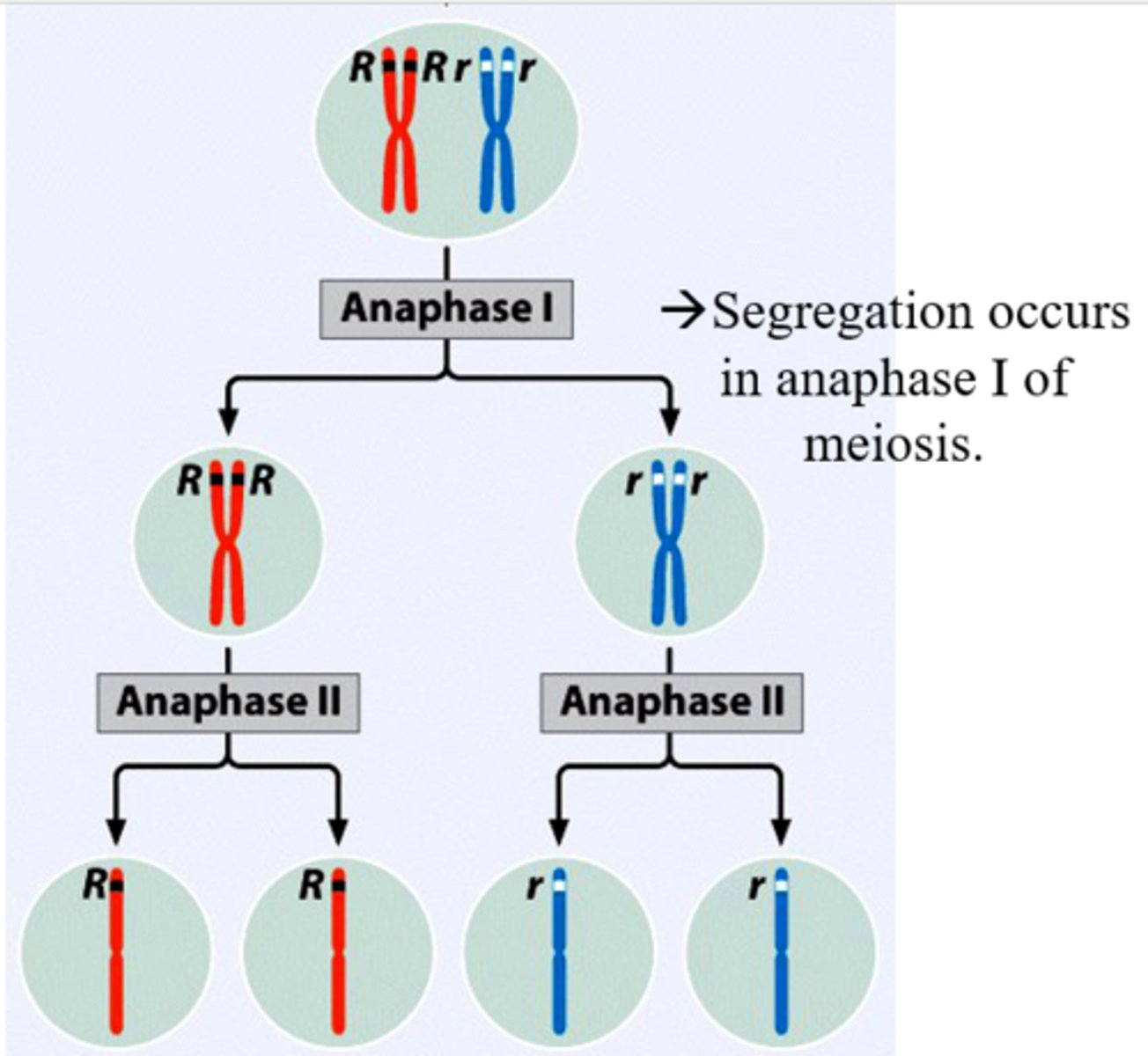
Principle of Segregation (Mendel's First Law)
states that before sexual production occcurs, the two alleles carried by an individual parent must become separarted.
Gametes
sex cells
homologous chromosomes
usually have the same genes, often with different alleles, that located in corresponding positions
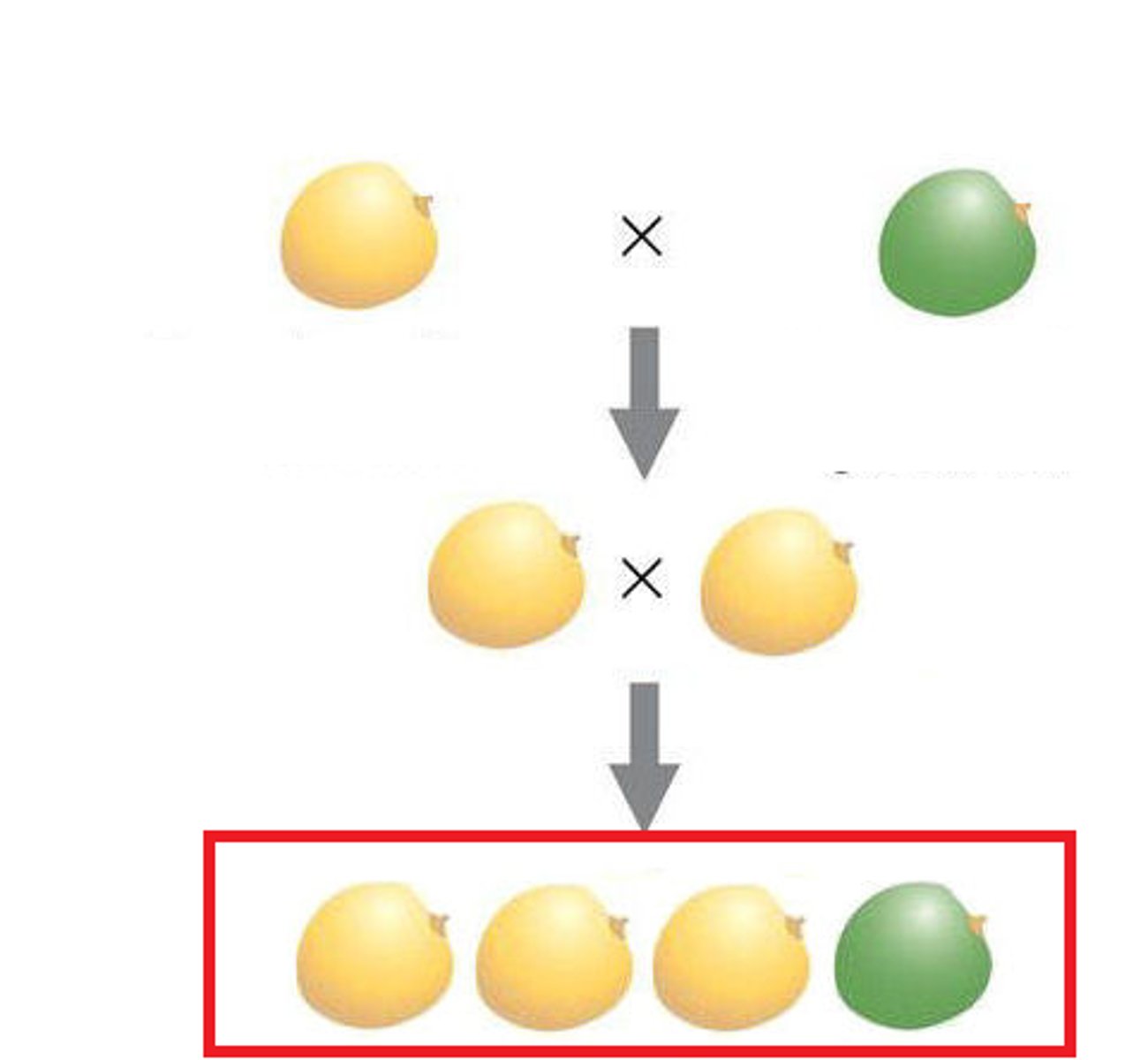
monohybrid cross
the inheritence of two different alleles of a single gene
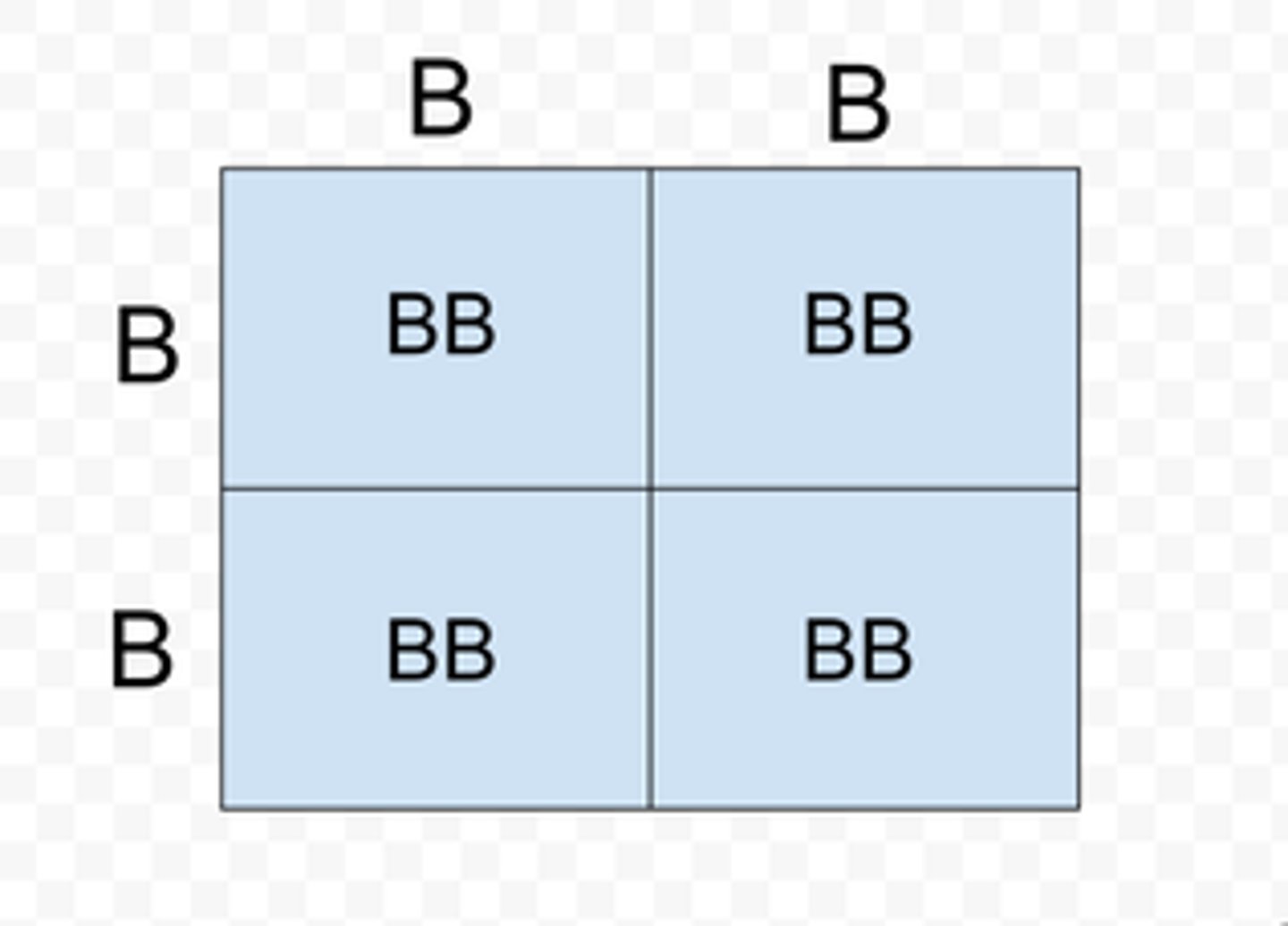
Homozygous
two identical alleles
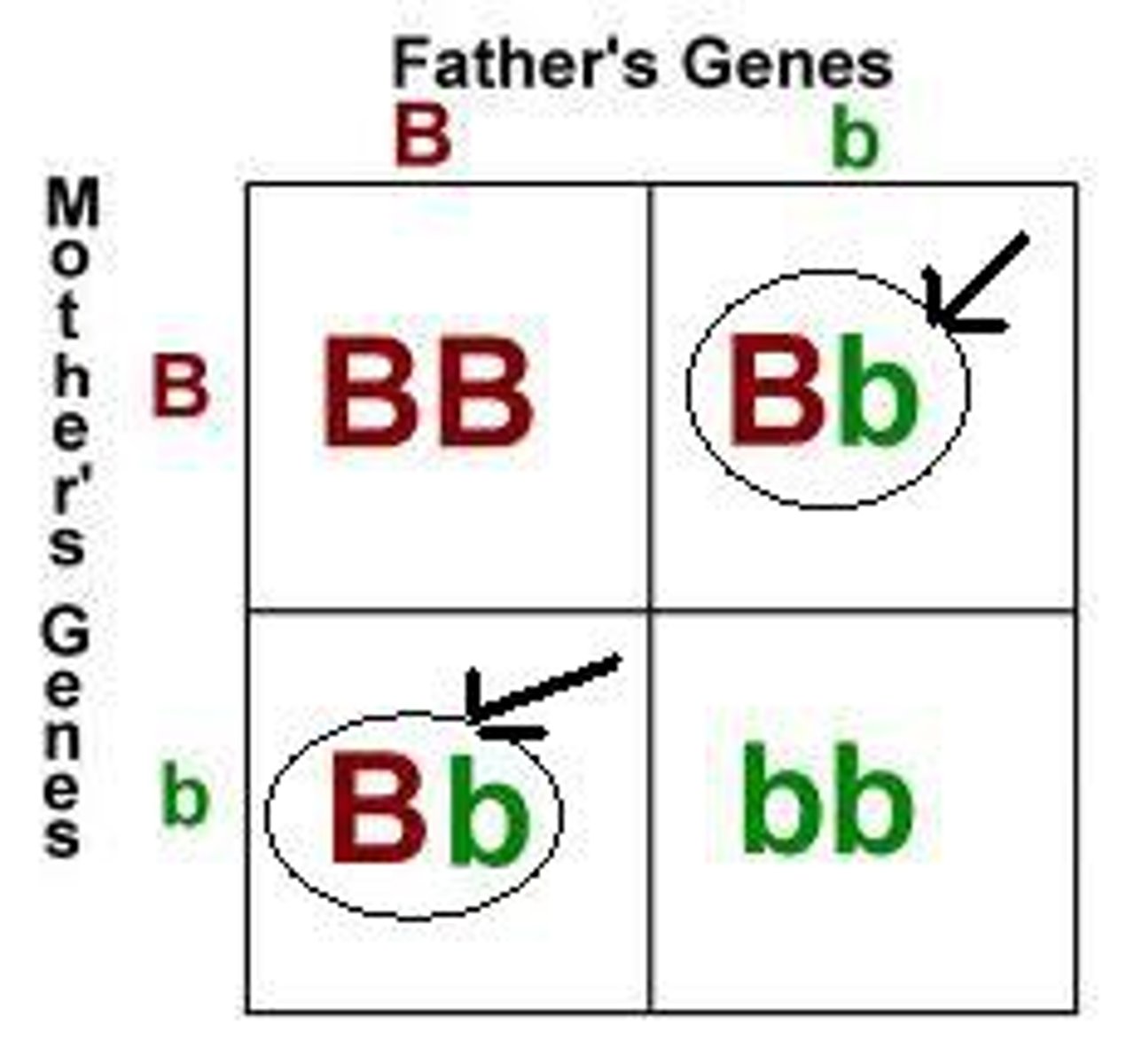
Heterozygous
two different alleles
Principle of Independent Assortment
stats that memebers of any gene pair segregate from one another independently of the memebers of the other gene pairs.
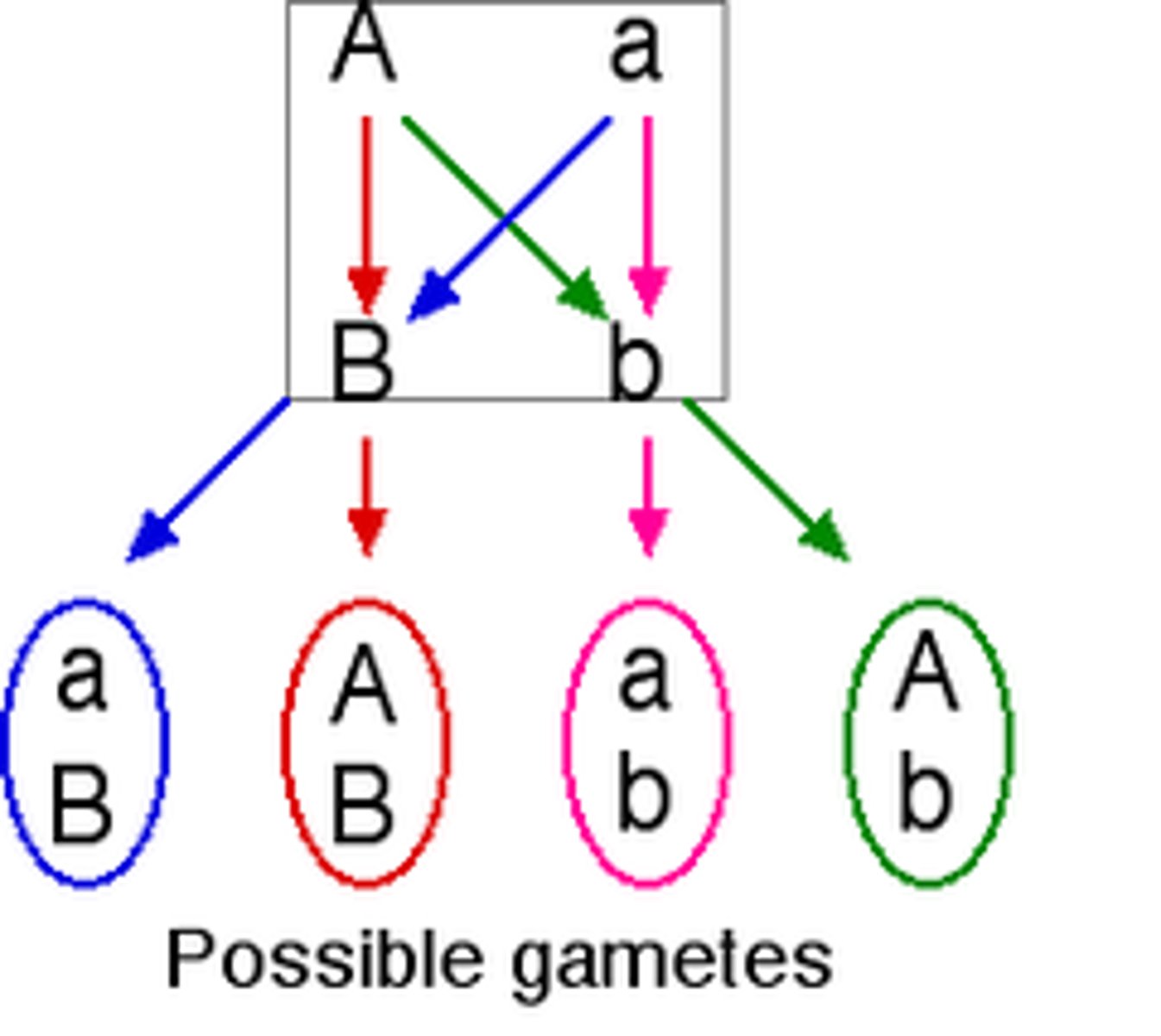
human females have
two X chromosomes
Y chromosome
found in human males
Autosomes
Chromosomes that are not directly involved in determining the sex of an individual.
sex chromosomes
carries the major sex-determining genes.
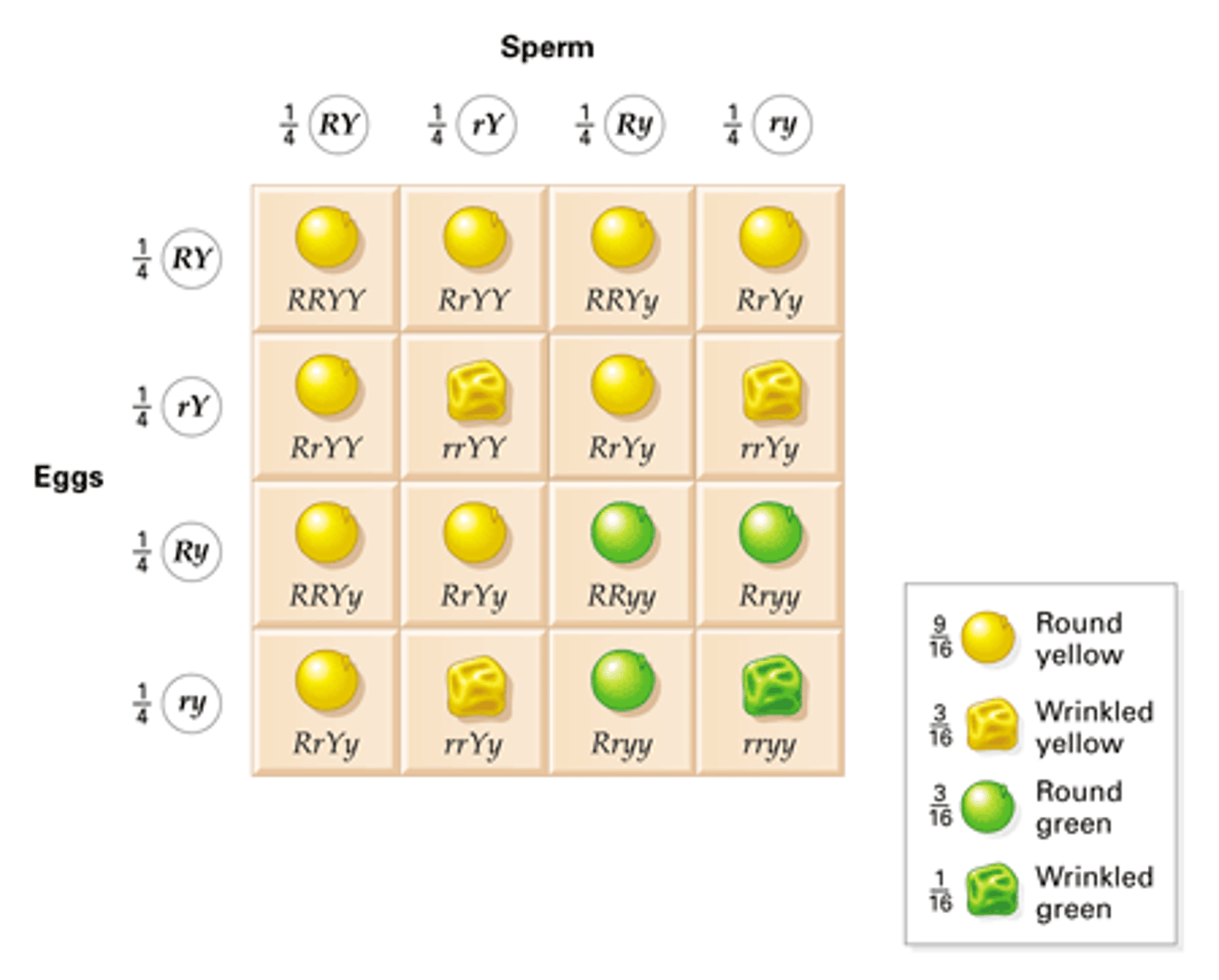
dihybrid cross
A cross between individuals that have different alleles for the same gene.
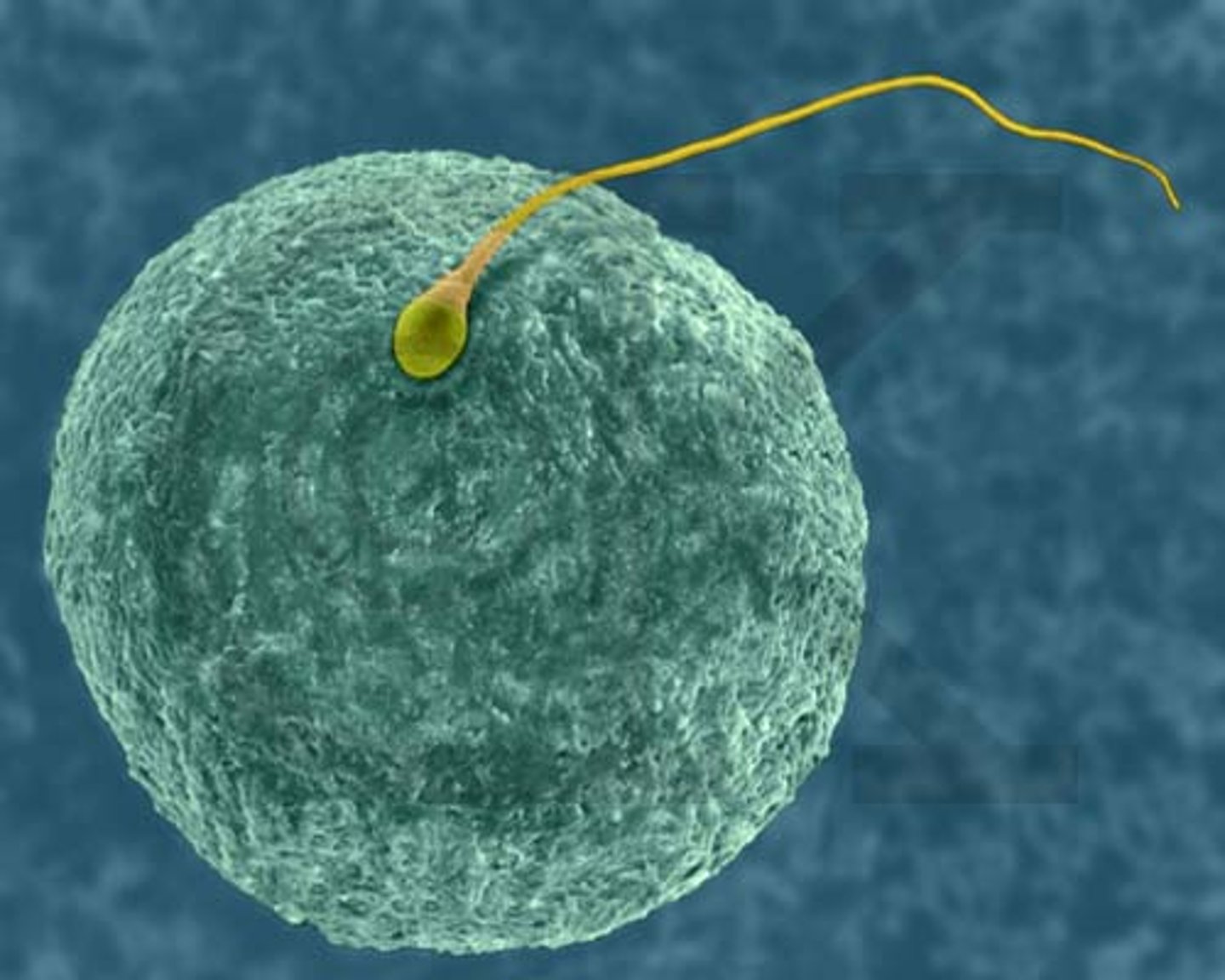
Fertilization
Fusion of an egg and sperm cell
X-linked
Genes located in the X chromosome.
X chromosome
contains many numerous genes required by both sexes, yet a normal female has two copies
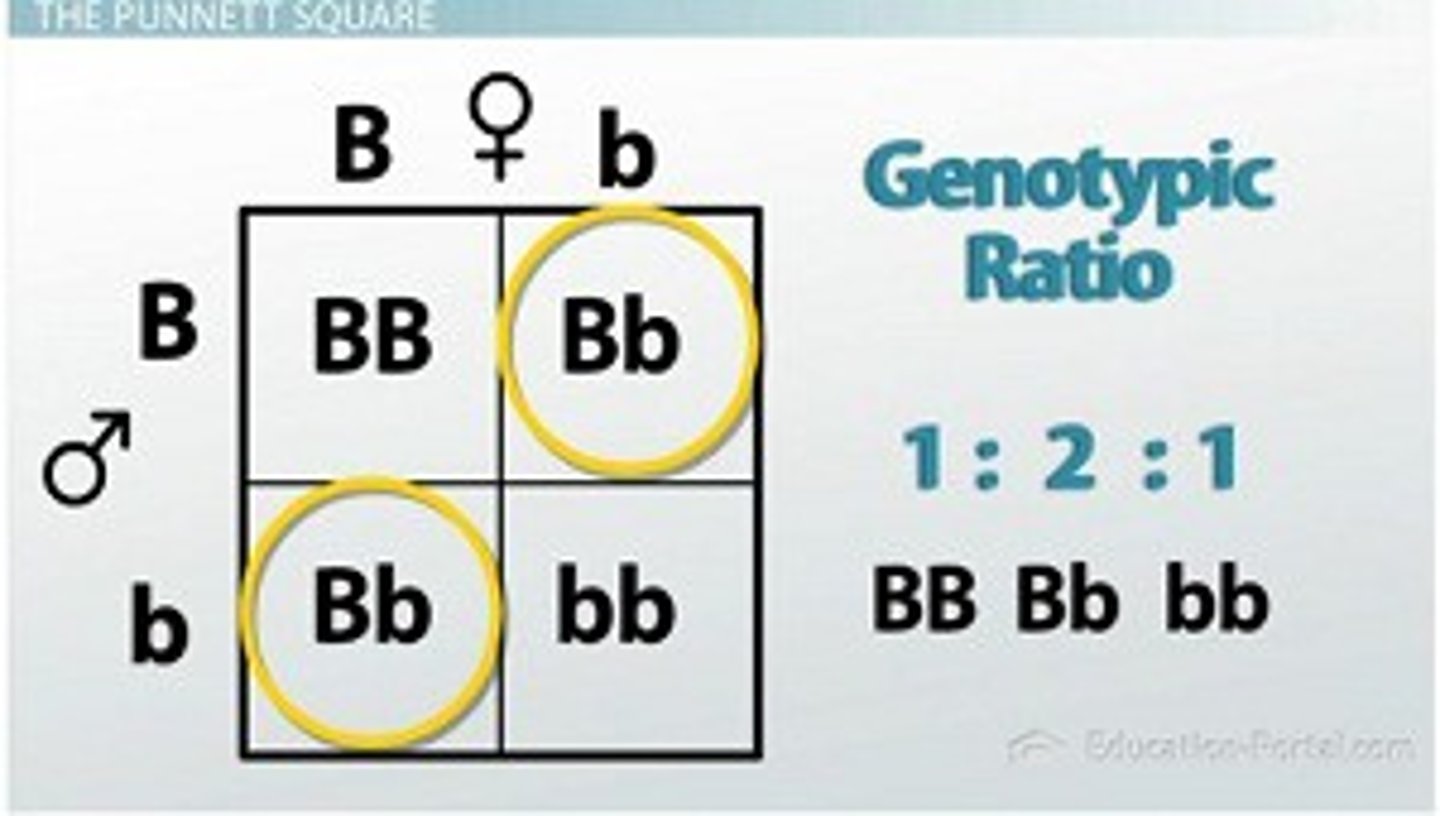
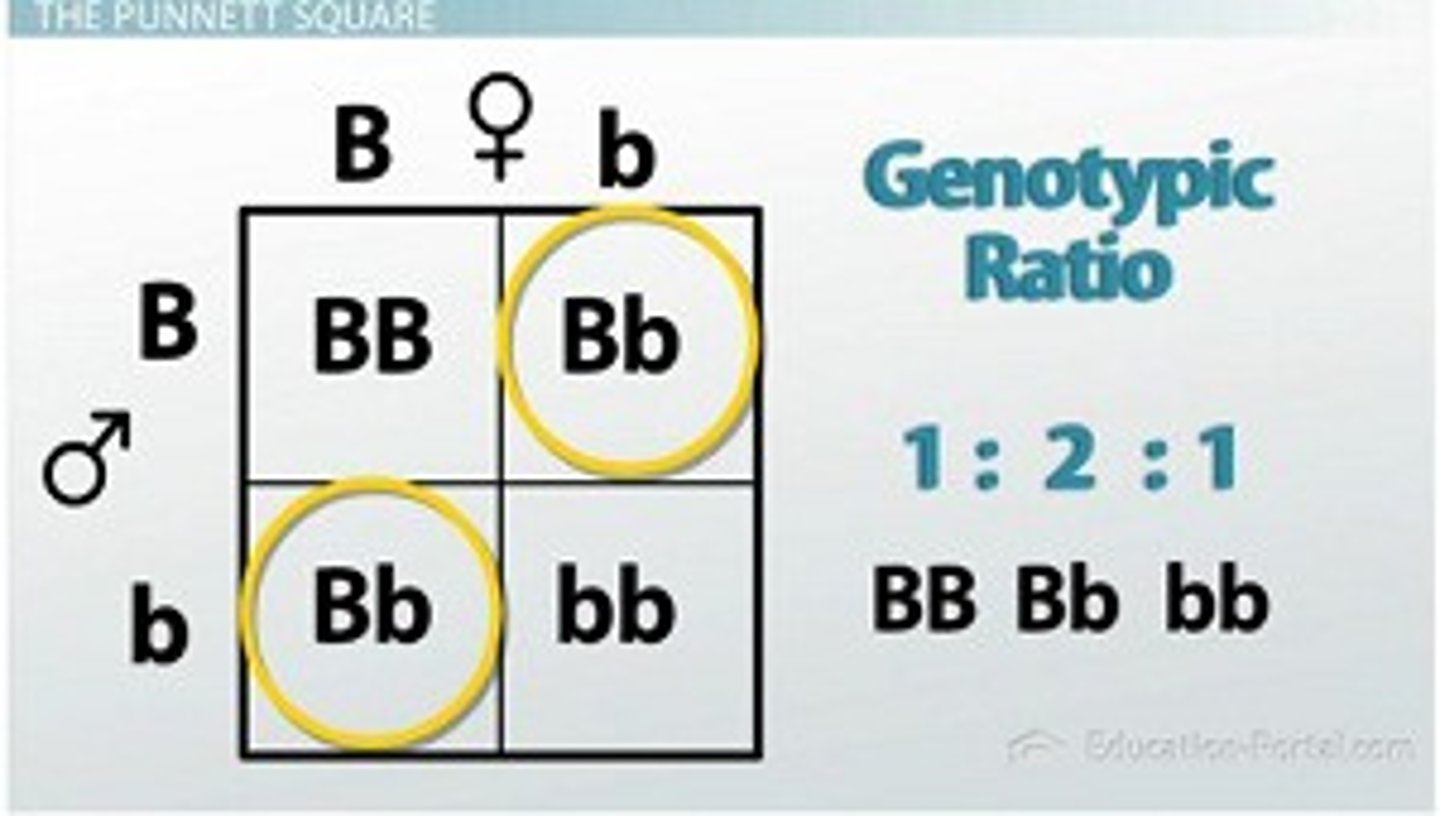
Punnett Square
form of a grid that represents the possible combinations of egg and sperm at fertilization.
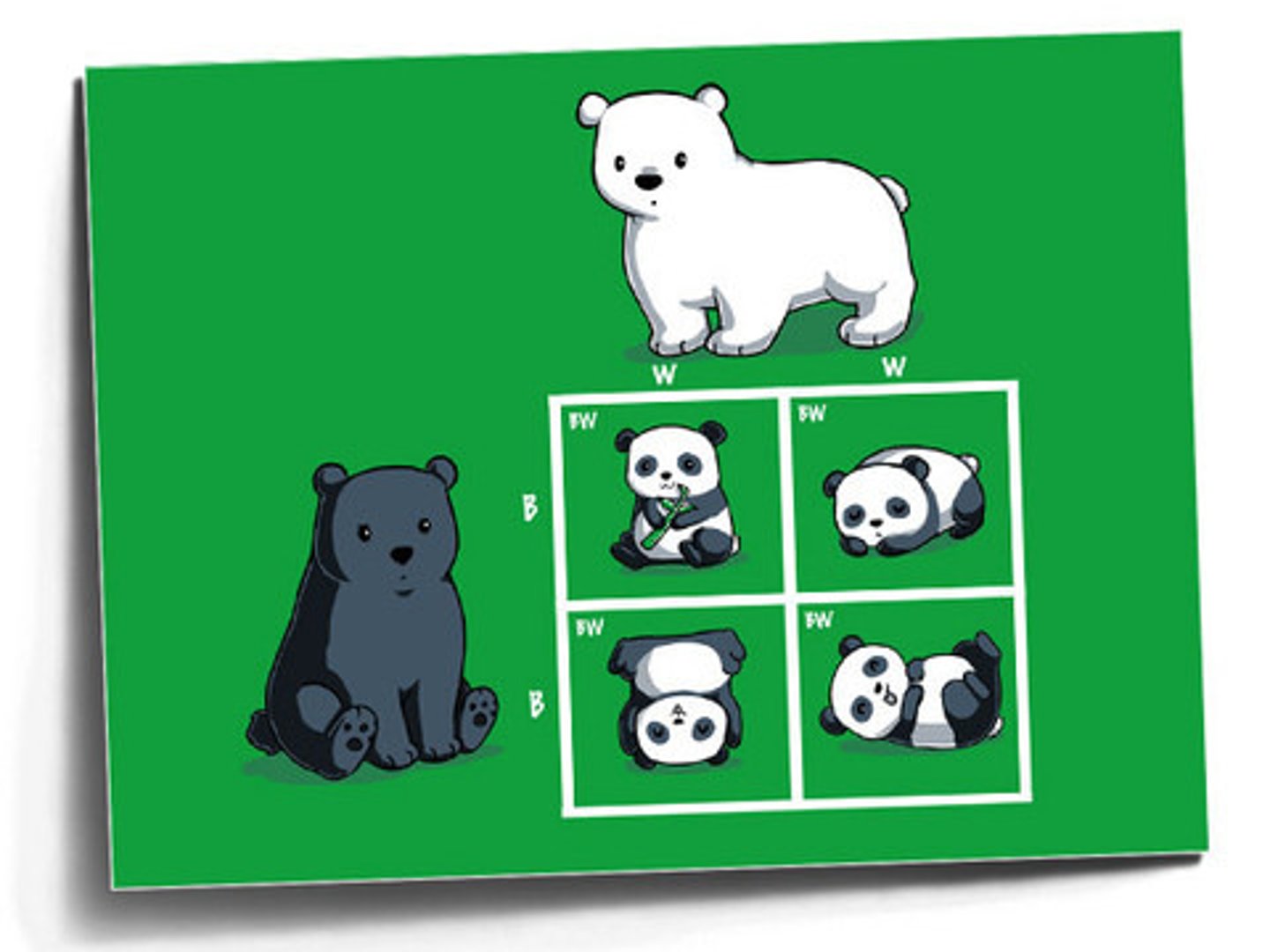
Codominance
The alleles do not dominent one over another,
they make combination, a mixture.
Both alleles in the genotype are seen in the phenotype.
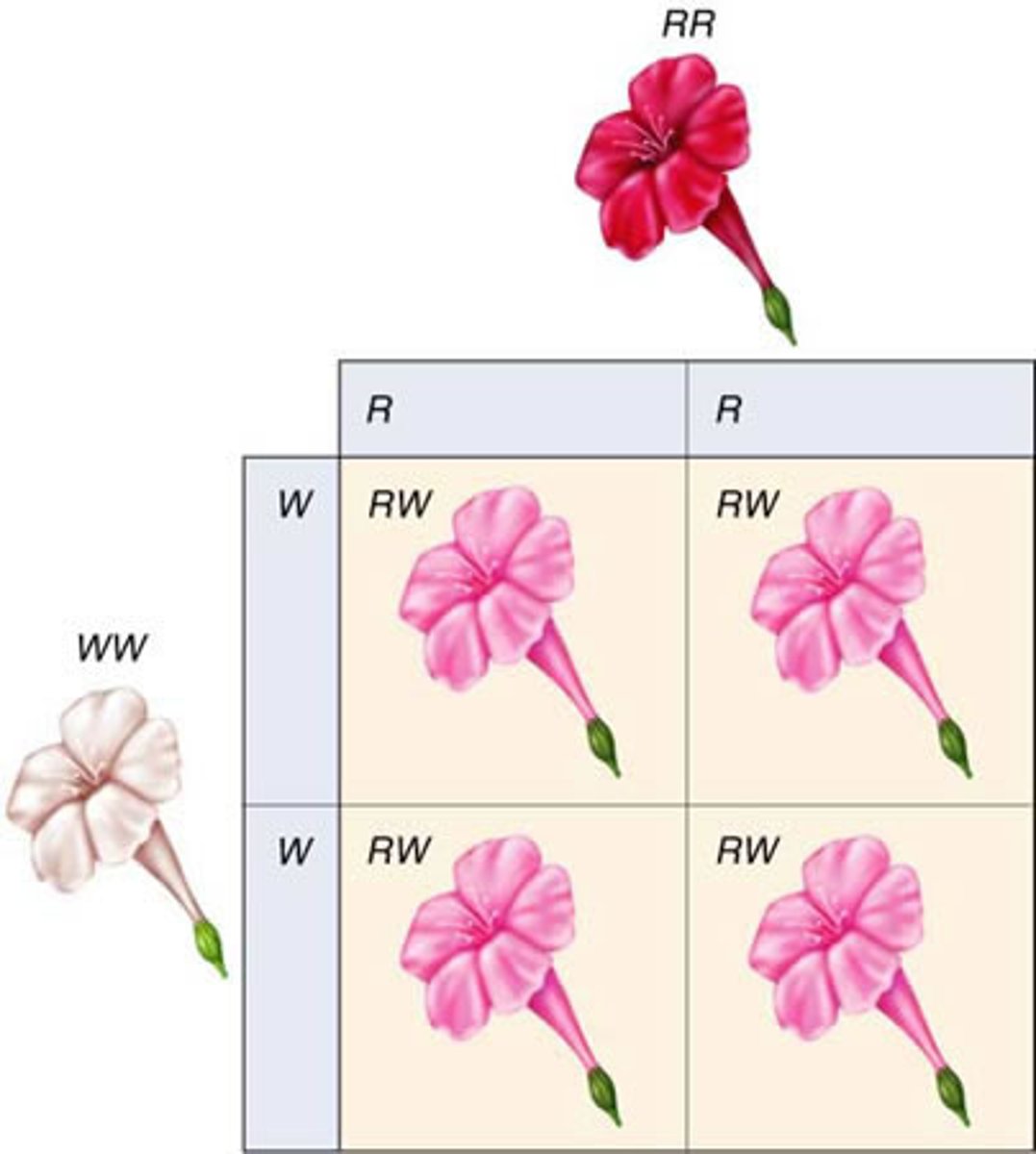
Incomplete dominance
Cases in which one allele is not completely dominant over another. "blended"
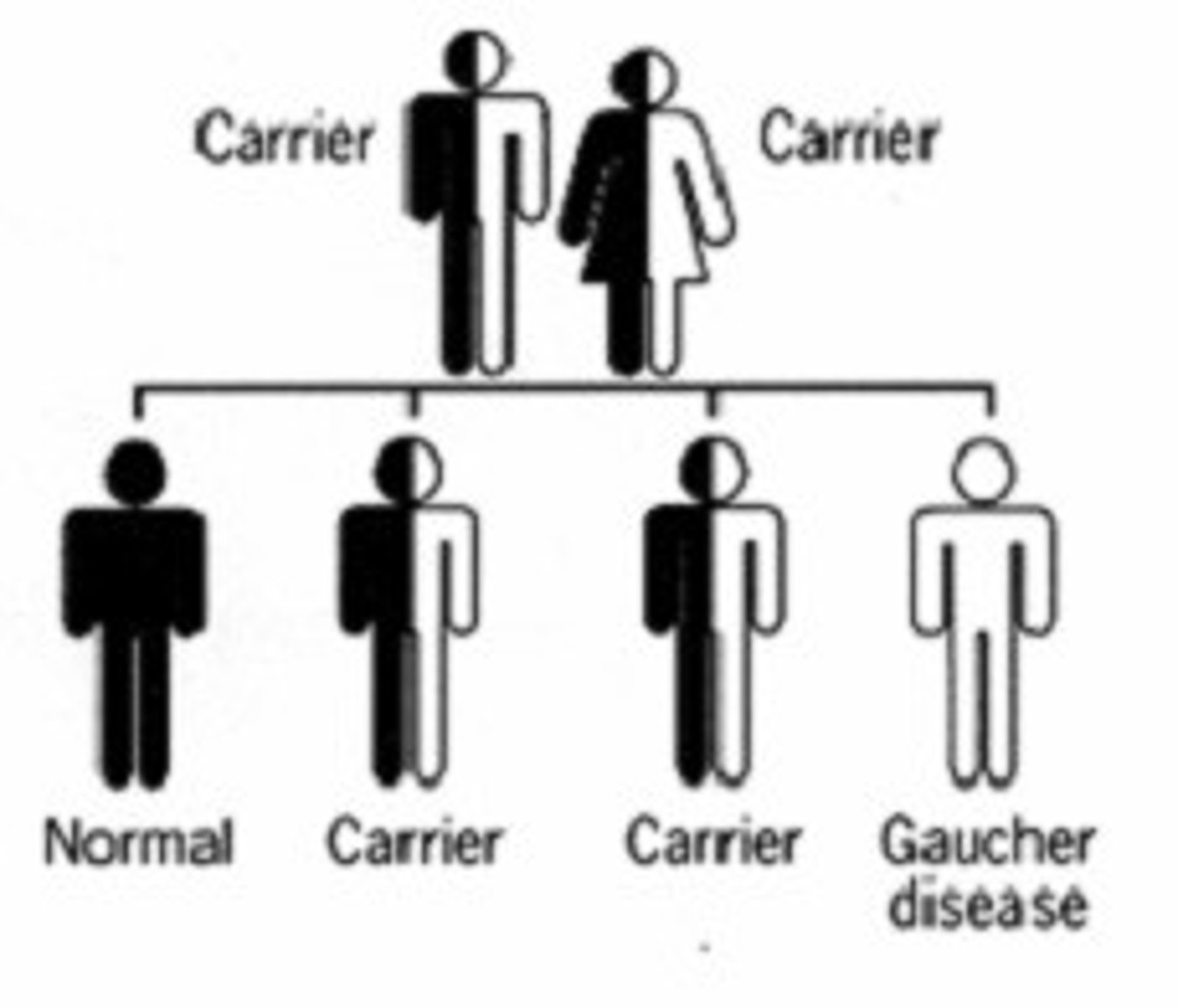
carrier
A person whose genotype includes a gene that is not expressed in the phenotype.
polygenic traits
traits controlled by two or more genes; example skin color
Hemophilia
An X-linked recessive disorder in which blood fails to clot properly, leading to excessive bleeding if injured.
Huntington's disease
A human genetic disease caused by a dominant allele; characterized by uncontrollable body movements and degeneration of the nervous system; usually fatal 10 to 20 years after the onset of symptoms.
Hybrid
Offspring of crosses between parents with different traits