Psych-Soc Class 4 - Personality, Motivation, Emotion, and Stress
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What are big five personality traits?
Openness to experience
Conscientiousness
Extraversion
Agreeableness
Neuroticism
OCEAN
What is personality?
Encompasses thoughts, feelings, ways of thinking, beliefs, and behaviors
What are people with low vs high openness to experience like?
Low: prefer familiarity, conservative, resistant to change
High: like unique experiences, values differences in people, embrace new ideas
What are people with low vs high conscientiousness like?
Low: disorganized, irresponsible
High: self disciplined, manages time well, strive to achieve
What are people with low vs high extraversion like?
Low: prefer solitary activities, need to recharge after social event
High: gregarious, outgoing, energized by social gatherings
What are those with low vs high agreeableness like?
Low: high maintenance, manipulative, strong opinions
High: think of others, go with flow, do not demand attention
What are those with low vs high neuroticism like?
Low: less easily upset, more secure, cope well with stress
High: high levels of negative emotions, impulsive
What is the life course perspective?
Multidisciplinary approach to understanding personality
Focuses on family structure, SES, demographics, disorder prevalence, age, health, major life events
What is Freud’s psychoanalytic perspective of personality?
Personality shaped by unconscious
Libido (life instinct) drives behaviors like pleasure, survival, avoidance of pain
Death instinct drives behaviors fueled by unconscious desire to die, hurt oneself, hurt others
Human psyche in three parts: id, ego, superego
Reality principle: ego is ruled by this, which uses logical thinking to control consciousness and id
What is the id?
Largely unconscious
Responsible for drives that avoid pain and seek pleasure
What is the ego?
Responsible for logical thinking/planning
What is the superego?
Responsible for moral judgement of right/wrong and strives for perfection
What are Freud’s five stages of psychosexual development?
Stage (age) → erogenous zone (not sexual, necessarily) → adult fixations (problems) if over/under stimulated
Oral (0-1) → mouth (sucking, eating, biting, vocalizing) → orally aggressive/passive (verbal abuse/smoking, overeating)
Anal (1-3) → anus (bowel and bladder) → anal retentive/expulsive (overly neat/disorganized)
Phallic (3-6) → genitals (masturbation) → Oedipus (male) vs Electra complex (female)
Latency (6-12) → sexual feelings are dormant → no fixations
Genital (12 +) → mature sexual interests → frigidity, impotence, difficulty in intimate relationships
What is Erikson’s psychoanalytic perspective?
Elaborated on Freud’s psychoanalytic perspective
Included social and interpersonal factors of personality
Extended stages through adulthood
What are Erikson’s stages of psychosexual development? TM, AS, IG, II, IR, II, GS, ID
Trust vs mistrust (infancy 0-1)
Autonomy vs shame
Initiative vs guilt (preschool 3-5)
Industry vs inferiority (school 5-12)
Identity vs role confusion (adolescence 12-18)
Intimacy vs isolation (young adulthood 18-40)
Generativity vs stagnation (middle age 40-65)
Integrity vs despair (later life 65+) → develop wisdom vs feel unaccomplished
What is Carl Roger’s humanist personality theory?
Humans driven by tendency to actualize highest potential, resulting in conflicts when thwarted
Goal is development of a self-concept
Those raised with unconditional positive regard can self-actualize
Those raised with conditional positive regard only feel worthy when certain conditions are met
Ideal self is impossible to achieve, formed by society’s expectations
When real self and ideal self are incongruent → psychopathology
What is BF Skinner’s behaviorist theory of personality?
Personality is learned from environment
Deterministic: people are blank slates forged by reinforcement/punishment entirely
Development occurs through: classical or operant conditioning
What is the Albert Bandura social cognitive perspective of personality?
Personality formed from reciprocal interactions among behavioral, cognitive, and environmental factors
Behavioral: classical and operant conditioning, observational learning
Cognitive: mental processes involved in learning, cognitive processes like self-efficacy beliefs
Environmental: situational influences (opportunity, reward, punishment)
How does the psychoanalytic perspective treat mental conditions?
Root of conflict: unconscious
How to treat: bring more psychic facts into conscious awareness
Therapy: psychodynamic, psychotherapy, talk therapy
How does the behavioral perspective treat mental conditions?
Root of conflict: reinforcement and punishment
How to treat: reinforce better behaviors
Therapy: behavioral therapy
How does the humanist perspective treat mental conditions?
Root of conflict: conditional positive regard
How to treat: let client guide process while providing unconditional positive regard
Therapy: client centered therapy
Never call the client a patient
How does the social cognitive perspective treat mental conditions?
Root of conflict: behaviorism + cognition and observation
How to treat: reinforce better thoughts, provide better models
Therapy: cognitive behavioral therapy
What is motivation?
Driving force that causes us to act
Influenced by instincts, drives, needs, and arousal
What are instincts?
Behaviors that are unlearned and present in fixed patterns in a species
What are drives?
Urges originating from physiological discomfort
What are needs?
Include biological needs (aka physiological needs) and higher-level needs
Ex: safety, love, achievement
What is arousal?
Internal level of stimulation
Even when all needs are met, restlessness, boredom, or curiosity may drive behaviors
What is drive reduction theory?
Physiological needs creates an aroused state that drives the organism to reduce that need by engaging in some behavior
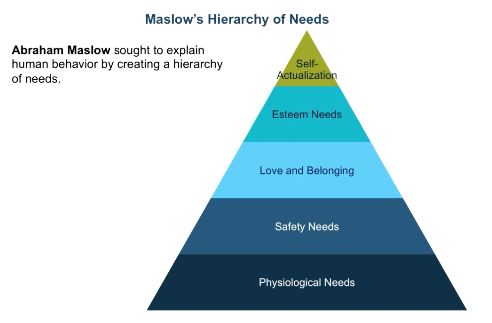
What is Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
Sought to explain human behavior
In order of most - least important: physiological needs, safety needs, love/belonging, esteem needs, and self-actualization
Once baser level is met → can move up
What are three components of emotion?
Physiological: body state
Behavioral: expressions of emotion
Cognitive: appraisal and interpretation of situation
What are universal emotions?
Expressed by humans across all cultures → strong genetic basis
Happiness, sadness, surprise, fear, disgust, anger
How are emotions adaptive?
Enhances survival by spurring quick decisions
Promotes group cohesion and solidarity
Helps with decision making
When do people perform best?
At the midpoint of emotional arousal
What is the James-Lange theory of emotion?
Stimulus → physiological response → emotion
Physiological arousal causes emotion
Largely discounted other than in terms of phobias
What is the Cannon-Bard theory of emotion?
Stimulus → simultaneous emotional response and physiological arousal
What is the Schachter-Singer theory of emotion?
Stimulus → physiological response → cognitive interpretation → emotion
Bodily sensations can be experienced differently based on context
How is emotion processed?
Limbic system: thalamus, hypothalamus, frontal lobe, olfactory bulb, amygdala, hippocampus

What is stress?
Anything that poses a threat to physical/mental well-being
What are responses to acute stress?
Increased blood pressure, heartrate, respiration rate, muscle tension
Decreased digestion
Sleep disturbances
What responses are caused by chronic stress?
Chronic high blood pressure (can lead to heart disease)
Damage to muscle tissue
Inhibition of growth
Suppression of immune and reproductive systems
Mental health issues
What are three types of stressors?
Catastrophe: unpredictable, large scale, affect many people
Significant life changes: positive or negative both cause stress
Daily hassles: everyday irritations (more frequent than others)
What is attitude?
Evaluation of other people, events, things, etc.
Formed from past/present experiences
Measurable and mutable
Important impact on behavior and emotions
What are three components of attitude?
Affect: feelings
Behavior: internal and external responses
Cognition: thoughts and beliefs
All influence one another
When is attitude a good predictor of behavior? Principle of Aggregation
Social influences are reduced
General patterns of behavior, not specific ones, are observed (principle of aggregation)
Specific attitudes, not general ones, are considered
When self-reflection occurs prior to action
When are behaviors more likely to influence attitude?
Role-playing
Public declarations
Justification of effort (assign greater value to outcomes more effort was put into)
What is cognitive dissonance?
Feel tension when thoughts/beliefs are incompatible with actions
When attitudes and behaviors do not match